Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | |
 | |
|---|---|
| ICD-10 | C91.0 |
| ICD-9 | 204.0 |
| ICD-O: | 9821/3 |
| DiseasesDB | 195 |
| MeSH | D015447 |
For patient information click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Raviteja Guddeti, M.B.B.S. [2]
Synonyms and keywords: Acute lymphocytic leukaemia; ALL
Overview
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a form of leukemia, or cancer of the white blood cells. 'Acute' refers to the undifferentiated, immature state of the circulating lymphocytes ("blasts"), and to the rapid progression of disease, which can be fatal in weeks to months if left untreated.
Classification
Subtyping of the various forms of ALL used to be done according to the French-American-British (FAB) classification, which was used for all acute leukemias (including acute myelogenous leukemia, AML). As ALL is not a solid tumour, the TxNxMx notation as used in solid cancers is of little use.
The FAB classification was:
- ALL-L1: small uniform cells
- ALL-L2: large varied cells
- ALL-L3: large varied cells with vacuoles (bubble-like features)
Note: The recent WHO International panel on ALL recommends that this classification be abandoned, since the morphological classification has no clinical or prognostic relevance. It instead advocates the use of the immunophenotypic classification mentioned below.
Each subtype is then further classified by determining the surface markers of the abnormal lymphocytes, called immunophenotyping. There are 2 main immunologic types: pre-B cell and pre-T cell. The mature B-cell ALL (L3) is now classified as Burkitt leukemia/lymphoma. Subtyping helps determine the prognosis and most appropriate treatment in treating ALL.
Some cytogenetic subtypes have a worse prognosis than others. These include:
- A translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, known as the Philadelphia chromosome, occurs in about 20% of adult and 5% in pediatric cases of ALL.
- A translocation between chromosomes 4 and 11 occurs in about 4% of cases and is most common in infants under 12 months.
- Not all translocations of chromosomes carry a poorer prognosis. Some translocations are relatively favorable. For example, Hyperdiploidy (>50 chromosomes) is a good prognostic factor.
(Images shown below are courtesy of Melih Aktan MD, Istanbul Medical Faculty - Turkey, and Kyoto University - Japan)
Pathophysiology
The cause of most ALL is not known. In general, cancer is caused by damage to DNA that leads to uncontrolled cellular growth and spread throughout the body, either by increasing chemical signals that cause growth, or interrupting chemical signals that control growth. This damage may be caused by environmental factors such as chemicals, drugs or radiation.
In leukemias, including ALL, chromosomal translocations occur regularly. It is thought that most translocations occur before birth during fetal development. These translocations may trigger oncogenes to "turn on", causing unregulated mitosis where cells divide too quickly and abnormally, resulting in leukemia.
Some families have a hereditary predisposition to ALL.[1]
ALL is associated with exposure to radiation and chemicals in animals and humans. The association of radiation and leukemia in humans has been clearly established in studies of victims of the Chernobyl nuclear reactor and atom bombs in Hiroshima and Nagasaki. In animals, exposure to benzene and other chemicals can cause leukemia. Epidemiological studies have associated leukemia with workplace exposure to chemicals, but these studies are not as conclusive. Patients who are treated for other cancers with radiation and chemotherapy often develop leukemias as a result of that treatment.
Malignant, immature white blood cells continuously multiply and are overproduced in the bone marrow. ALL causes damage and death by crowding out normal cells in the bone marrow, and by spreading (metastasizing) to other organs.
Genetics
Cytogenetics, the study of characteristic large changes in the chromosomes of cancer cells, has been increasingly recognized as an important predictor of outcome in ALL.[2]
| Cytogenetic change | Risk category |
|---|---|
| Philadelphia chromosome | Poor prognosis |
| t(4;11)(q21;q23) | Poor prognosis |
| t(8;14)(q24.1;q32) | Poor prognosis |
| Complex karyotype (more than four abnormalities) | Poor prognosis |
| Low hypodiploidy or near triploidy | Poor prognosis |
| High hypodiploidy | Good prognosis |
| del(9p) | Good prognosis |
Epidemiology and Demographics
Incidence
- The number of annual ALL cases in the US is roughly 4000, 3000 of which inflict children.
- There is an increased incidence in people with Down's Syndrome, Fanconi's anemia, Bloom's syndrome, ataxia-telangiectasia, X-linked agammaglobulinemia and severe combined immunodeficiency.
Age
- ALL accounts for approximately 80 percent of all childhood leukemia cases, making it the most common type of childhood cancer.
- It has a peak incident rate of 2-5 years old, decreasing in incidence with increasing age before increasing again at around 50 years old.
Gender
- ALL is slightly more common in males than females.
Risk Factors
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia risk factors may include the following:
- Down syndrome
- Ataxia telangiectasia
- Bloom syndrome
- X-linked agammaglobulinemia
- Fanconi's anemia
- Severe combined immunodeficiency
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
The overall cure rate in children is 85%, and about 50% of adults have long-term disease-free survival.[3]
Advancements in medical technology and research over the past four decades in the treatment of ALL has improved the overall prognosis significantly from a zero to 20-75 percent survival rate, largely due to the continuous development of clinical trials and improvements in bone marrow transplantation (BMT) and stem cell transplantation (SCT) technology.
It is worth noting that medical advances in recent years, both through matching the best treatment to the genetic characteristics of the blast cells and through the availability of new drugs, are not fully reflected in statistics that usually refer to five-year survival rates. The prognosis for ALL differs between individuals depending on a wide variety of factors:
- Gender: Females tend to fare better than males.
- Ethnicity: Caucasians are more likely to develop acute leukemia than African-Americans, Asians and Hispanics and tend to have a better prognosis than non-Caucasians.
- Age at diagnosis: children between 1-10 years of age are most likely to be cured.
- White blood cell count at diagnosis of less than 50,000/µl
- Whether the cancer has spread to the brain or spinal cord
- Morphological, immunological, and genetic subtypes
- Response of patient to initial treatment
- Genetic disorders such as Down's Syndrome
Diagnosis
Symptoms
Initial symptoms are not specific to ALL, but worsen to the point that medical help is sought. The signs and symptoms of ALL are variable but follow from bone marrow replacement and / or organ infiltration.
- Generalised weakness and fatigue
- Anemia
- Frequent or unexplained fever and infections
- Weight loss and/or loss of appetite
- Excessive bruising or bleeding from wounds, nosebleeds, petechiae (red pinpoints on the skin)
- Bone pain, joint pains (caused by the spread of "blast" cells to the surface of the bone or into the joint from the marrow cavity)
- Breathlessness
- Enlarged lymph nodes, liver and/or spleen
The signs and symptoms of ALL result from the lack of normal and healthy blood cells because they are crowded out by malignant and immature leukocytes (white blood cells). Therefore, people with ALL experience symptoms from malfunctioning of their erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes, and platelets not functioning properly. Laboratory tests which might show abnormalities include blood count tests, renal function tests, electrolyte tests and liver enzyme tests.
Physical Examination
Diagnosing ALL begins with a medical history and physical examination, Because the symptoms are so general, many other diseases with similar symptoms must be excluded. Blast cells are seen on blood films in 90% of cases. A bone marrow biopsy is conclusive proof of ALL.[4] A spinal tap will tell if the spinal column and brain has been invaded.
Pathological examination, cytogenetics (particularly the presence of Philadelphia chromosome) and immunophenotyping, establish whether the "blast" cells began from the B lymphocytes or T lymphocytes. DNA testing can establish how aggressive the disease is; different mutations have been associated with shorter or longer survival.
Medical imaging (such as ultrasound or CT scanning) can find invasion of other organs commonly the lung, liver, spleen, lymph nodes, brain kidneys and reproductive organs.[5]
Laboratory Findings
- complete blood count shows the following abnormalities:
- Ferritin levels raised (serum)
- Peripheral smear
Treatment
The earlier acute lymphocytic leukemia is detected, the more effective the treatment. The aim is to induce a lasting remission, defined as the absence of detectable cancer cells in the body (usually less than 5% blast cells on the bone marrow).
Treatment for acute leukemia can include chemotherapy, steroids, radiation therapy, intensive combined treatments (including bone marrow or stem cell transplants), and growth factors.
Proper management of ALL focuses on control of bone marrow and systemic (whole-body) disease as well as prevention of cancer at other sites, particularly the central nervous system (CNS). In general, ALL treatment is divided into several phases:
Induction chemotherapy to bring about remission - that is, leukemic cells are no longer found in bone marrow samples. For adult ALL, standard induction plans include prednisone, vincristine, and an anthracycline drug; other drug plans may include L-asparaginase or cyclophosphamide. For children with low-risk ALL, standard therapy usually consists of three drugs (prednisone, L-asparaginase, and vincristine) for the first month of treatment. High-risk children may receive these drugs plus an anthracycline such as daunorubicin.
Consolidation therapy (1-3 months in adults; 4-8 months in children) to eliminate any leukemia cells that are still "hiding" within the body. A combination of chemotherapeutic drugs is used to keep the remaining leukemia cells from developing resistance. Patients with low- to average-risk ALL receive therapy with antimetabolite drugs such as methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP). High-risk patients receive higher drug doses plus treatment with extra chemotherapeutic agents.
CNS prophylaxis (preventive therapy) to stop the cancer from spreading to the brain and nervous system. Standard prophylaxis may consist of:
- Cranial (head) irradiation plus spinal tap or intrathecal (IT) delivery (into the space around the spinal cord and brain) of the drug methotrexate.
- High-dose systemic and IT methotrexate, without cranial irradiation
- IT chemotherapy.
Only children with T-cell leukemia, a high white blood cell count, or leukemia cells in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) need to receive cranial irradiation as well as IT therapy.
Maintenance treatments with chemotherapeutic drugs (e.g., prednisone + vincristine + cyclophosphamide + doxorubicin; methotrexate + 6-MP) to prevent disease recurrence once remission has been achieved. Maintenance therapy usually involves drug doses that are lower than those administered during the induction phase. In children, an intensive 6-month treatment program is needed after induction, followed by 2 years of maintenance chemotherapy.
Follow-up therapy for ALL patients usually consists of:
- supportive care, such as intravenous nutrition and treatment with oral antibiotics (e.g., ofloxacin, rifampin), especially in patients with prolonged granulocytopenia; that is, too few mature granulocytes (neutrophils), the bacteria-destroying white blood cells that contain small particles, or granules (< 100 granulocytes per cubic millimeter for 2 weeks)
- transfusions with red blood cells and platelets
A laboratory test known as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is advisable for ALL patients, since it may help to identify specific genetic abnormalities. Such abnormalities have a large impact upon prognosis and, consequently, treatment plans. PCR testing is especially important for patients whose disease is B-cell in type. B-cell ALL usually is not cured by standard ALL therapy. Instead, higher response rates are achieved with the aggressive, cyclophosphamide-based regimens that are used for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Among ALL patients, 3-5% children and 25-50% of adults are positive for the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph1). Because these patients have a worse prognosis than other individuals with ALL, many oncologists recommend allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (alloBMT), since remission may be brief following conventional ALL chemotherapy.
People who receive bone marrow transplantation will require protective isolation in the hospital, including filtered air, sterile food, and sterilization of the microorganisms in the gut, until their total white blood cell (WBC) count is above 500.
Recurrent ALL patients usually do not benefit from additional chemotherapy alone. If possible, they should receive re-induction chemotherapy, followed by allogeneic bone marrow transplant (alloBMT).
Alternatively, patients with recurrent ALL may benefit from participation in new clinical trials of alloBMT, immune system agents, and chemotherapeutic agents, or low-dose radiotherapy, if the cancer recurs throughout the body or CNS.
Chemotherapy is the initial treatment of choice. Most ALL patients end up receiving a combination of different treatments. There are no surgical options, due to the body-wide distribution of the malignant cells.
As the chemotherapy regimens can be intensive and protracted (often about 2 years in case of the GMALL UKALL, HyperCVAD or CALGB protocols; about 3 years for males on COG protocols), many patients have an intravenous catheter inserted into a large vein (termed a central venous catheter or a Hickman line), or a Portacath (a cone-shaped port with a silicone nose that is surgically planted under the skin, usually near the collar bone, and the most effective product available, due to low infection risks and the long-term viability of a portacath). Since ALL cells sometimes penetrate the Central Nervous System CNS, most protocols include delivery of chemotherapy into the CNS fluid. More advanced centers deliver the drug through Ommaya reservoir (a device surgically placed under the scalp and used to deliver drugs to the CNS fluid and to extract CNS fluid for various tests). More traditional centers would perform multiple lumbar punctures as needed for testing and treatment delivery.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is used on painful bony areas, in high disease burdens, or as part of the preparations for a bone marrow transplant (total body irradiation). Radiation in the form of whole brain radiation is also used for central nervous system prophylaxis, to prevent recurrence of leukemia in the brain. Whole brain prophylaxis radiation used to be a common method in treatment of children’s ALL. Recent studies showed that CNS chemotherapy provided results as favorable but with less developmental side effects. As a result, the use of whole brain radiation has been more limited.
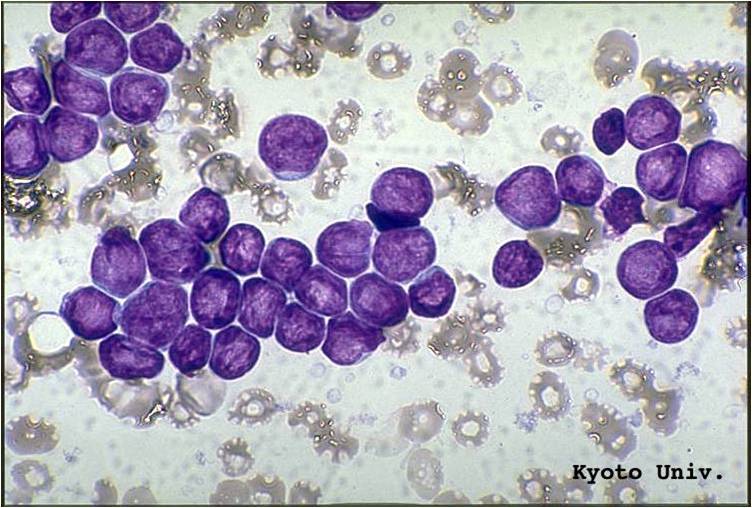
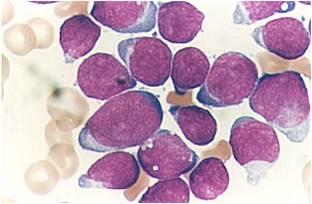
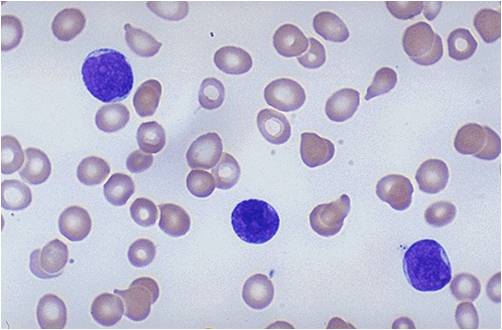
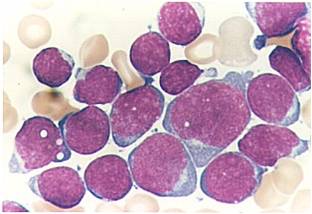
Additional images
-
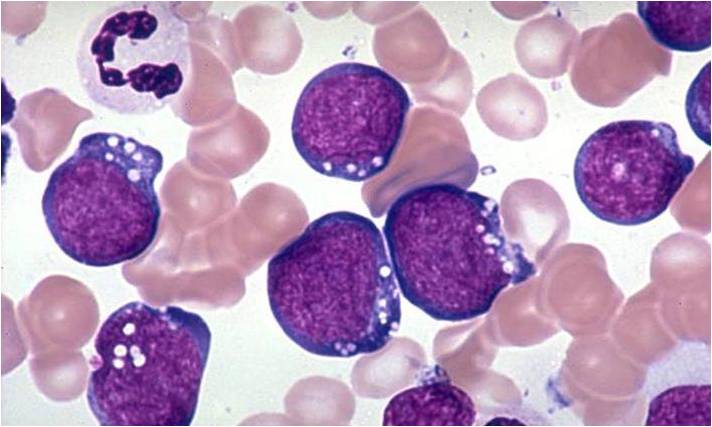
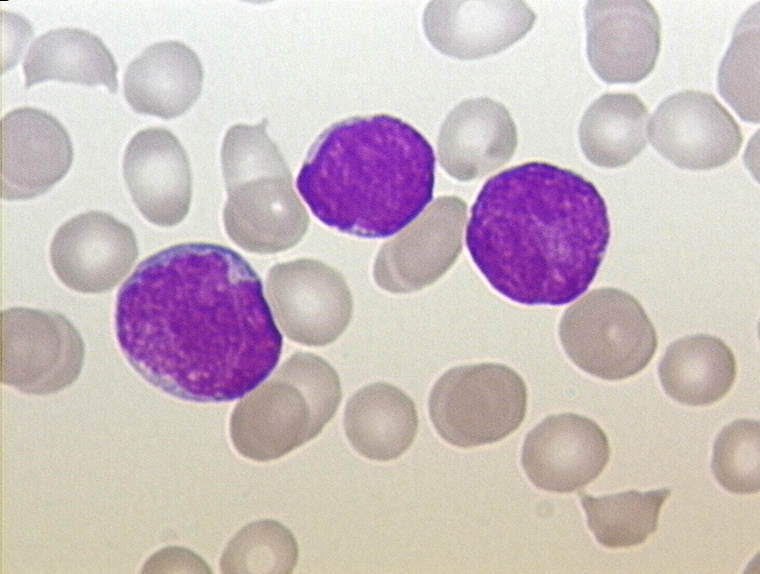
acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), peripheral blood of a child, Pappenheim stain, magnification x100
-
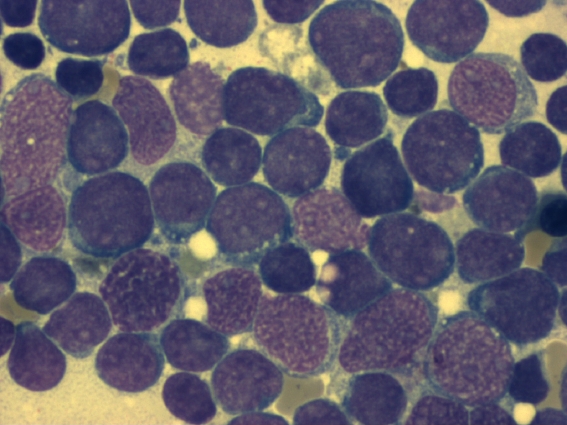
bone marrow smear (large magnification) from a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
-
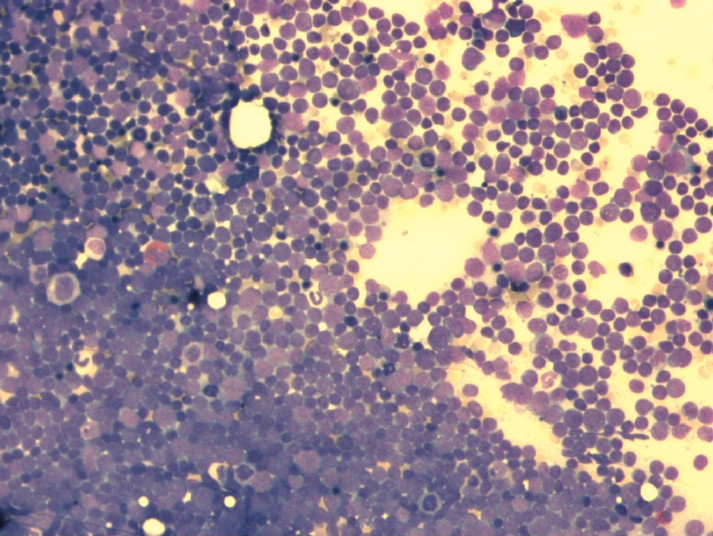
bone marrow smear from a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
References
- ↑ New Engl J Med somewhere
- ↑ Moorman A, Harrison C, Buck G, Richards S, Secker-Walker L, Martineau M, Vance G, Cherry A, Higgins R, Fielding A, Foroni L, Paietta E, Tallman M, Litzow M, Wiernik P, Rowe J, Goldstone A, Dewald G (2007). "Karyotype is an independent prognostic factor in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): analysis of cytogenetic data from patients treated on the Medical Research Council (MRC) UKALLXII/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 2993 trial". Blood. 109 (8): 3189–97. PMID 17170120.
- ↑ Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 16th Edition, Chapter 97. Malignancies of Lymphoid Cells. Clinical Features, Treatment, and Prognosis of Specific Lymphoid Malignancies.
- ↑ Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 16th EditioN, Chapter 97. Malignancies of Lymphoid Cells. Clinical Features, Treatment, and Prognosis of Specific Lymphoid Malignancies.
- ↑ Merck Manual
External links
- The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society - provides information about leukemia and related diseases, updates on current clinical trials, and discussion forums.
- Cancer Research UK - trains and supports scientists for cancer research, offers regional news about current research, and provides ways that individuals can become involved.
- Children's Cancer Web - a directory of children's cancer-related resources.
- The Centre for Cancer and Blood Disorders at Sydney Children’s Hospital provides information on cancers in children and adolescents, including Acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
- Children's Leukemia and Cancer Research Foundation (INC) (Australia) - provides funding for children's leukemia, especially to the Princess Margaret Hospital for Children [3].
- European LeukemiaNet
- Ped-Onc Resource Center - provides information on childhood ALL, including disease details (MRD, phenotypes, molecular characterization), a layman's list of current and past clinical trials, a collection of articles on the possible causes of ALL, a bibliography of journal articles, and links to sources of support for parents of children with ALL.
- Association of Cancer Online Resource (ACOR) Leukemia Links - provides links to information on leukemia, including ALL, primarily in adults.
de:Akute lymphatische Leukämie
nn:Akutt lymfatisk leukemi
sr:Акутна лимфоцитна леукемија
fi:Akuutti lymfaattinen leukemia
sv:Akut lymfatisk leukemi