Uveitis
| Uveitis | |
 | |
|---|---|
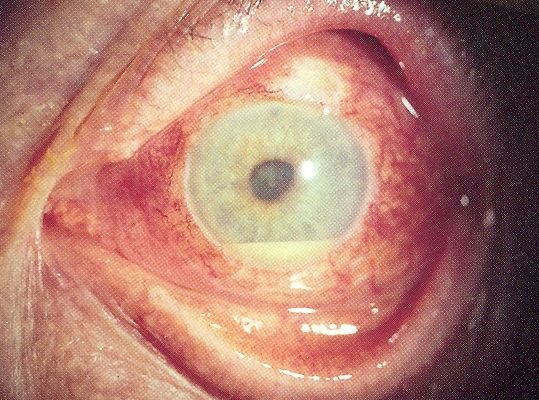
| Hypopyon in anterior uveitis, seen as yellowish exudate in lower part of anterior chamber of eye | |
| ICD-10 | H20 |
| ICD-9 | 364 |
| DiseasesDB | 13676 |
| eMedicine | oph/580 emerg/284 |
For patient information click here'
|
WikiDoc Resources for Uveitis |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Uveitis |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Uveitis at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Uveitis at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Uveitis
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Uveitis Risk calculators and risk factors for Uveitis
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Uveitis |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Join in Editing This Page and Apply to be an Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Uveitis specifically refers to inflammation of the middle layer of the eye, termed the "uvea" but in common usage may refer to any inflammatory process involving the interior of the eye.
Uveitis is estimated to be responsible for approximately 10% of the blindness in the United States.
Uveitis requires an urgent referral and thorough examination by an ophthalmologist, along with urgent treatment to control the inflammation.
Types
Uveitis is usually categorized anatomically into anterior, intermediate, posterior and panuveitic forms.
- Anywhere from two-thirds to 90% of uveitis cases are anterior in location (anterior uveitis), frequently termed iritis - or inflammation of the iris and anterior chamber. This condition can occur as a single episode and subside with proper treatment or may take on a recurrent or chronic nature. Symptoms include red eye, injected conjunctiva, pain and decreased vision. Signs include dilated ciliary vessels, presence of cells and flare in the anterior chamber, and keratic precipitates ("KP") on the posterior surface of the cornea.
- Intermediate uveitis consists of vitritis - inflammatory cells in the vitreous cavity, sometimes with snowbanking, or deposition of inflammatory material on the pars plana.
- Posterior uveitis is the inflammation of the retina and choroid.
- Pan-uveitis is the inflammation of all the layers of the uvea.
Causes
A myriad of conditions can lead to the development of uveitis, including systemic diseases as well as syndromes confined to the eye. In anterior uveitis, no specific diagnosis is made in approximately one-half of cases. However, anterior uveitis is often one of the syndromes associated with HLA-B27.
Systemic disorders causing uveitis
Systemic disorders that can cause uveitis include: White G. "Uveitis." AllAboutVision.com. Retrieved August 20, 2006.</ref>
- Acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Behçet's disease
- Birdshot retinochoroidopathy
- Brucellosis
- Herpes simplex
- Herpes zoster
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Kawasaki disease
- Leptospirosis
- Lyme disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reiter's syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Syphilis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Toxocariasis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tuberculosis
- Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome
- Whipple disease
Masquerade syndromes
Masquerade syndromes are ophthalmic disorders that clinically present as either an anterior or posterior uveitis, but are not primarily inflammatory. The following are some of the most common:
- Anterior segment
- Intraocular foreign body
- Juvenile xanthogranuloma
- Leukemia
- Malignant melanoma
- Retinoblastoma
- Retinal detachment
- Posterior segment
- Lymphoma
- Malignant melanoma
- Multiple sclerosis
- Reticulum cell sarcoma
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Retinoblastoma
Symptoms
- Redness of the eye
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Dark, floating spots along the visual field
- Eye pain
Treatment
The prognosis is generally good for those who receive prompt diagnosis and treatment, but serious complication (including cataracts, glaucoma, band keratopathy, retinal edema and permanent vision loss) may result if left untreated. The type of uveitis, as well as its severity, duration, and responsiveness to treatment or any associated illnesses, all factor in to the outlook.[3]
Uveitis is typically treated with glucocorticoid steroids, either as topical eye drops (such as betamethasone, dexamethasone or prednisolone) or oral therapy with prednisolone tablets. In addition topical cycloplegics, such as atropine or homatropine, may be used. In some cases an injection of PSTTA can also be given to reduce the swelling of the eye. [1]
Antimetabolite medications, such as methotrexate are often used for recalcitrant or more aggressive cases of uveitis. Experimental treatment with Infliximab infusions may prove helpful.
See also
- List of eye diseases and disorders
- List of systemic diseases with ocular manifestations
- Intermediate uveitis
References
External links
- The Heidelberg DiagnoseFinder - a web application to find common uveitis diseases in their typical manifestation (english/german)
- http://www.uveitissociety.org
- http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001005.htm
- Interdisciplinary Uveitis Center Heidelberg, Germany
- http://www.uveitis.org
- http://www.preventblindness.org/uveitis
de:Uveitis ca:uveïtis hr:Uveitis nl:Uveïtis sv:Druvhinneinflammation