C-reactive protein
| VALUE_ERROR (nil) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Aliases | |||||||
| External IDs | GeneCards: [1] | ||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||
| Entrez |
|
| |||||
| Ensembl |
|
| |||||
| UniProt |
|
| |||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) |
|
| |||||
| RefSeq (protein) |
|
| |||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||
| Wikidata | |||||||
| |||||||
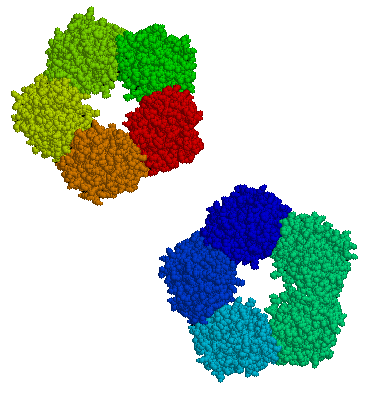
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped), pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose levels rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin-6 secretion by macrophages and T cells. Its physiological role is to bind to lysophosphatidylcholine expressed on the surface of dead or dying cells (and some types of bacteria) in order to activate the complement system via C1q.[1]
CRP is synthesized by the liver[2] in response to factors released by macrophages and fat cells (adipocytes).[3] It is a member of the pentraxin family of proteins.[2] It is not related to C-peptide (insulin) or protein C (blood coagulation). C-reactive protein was the first pattern recognition receptor (PRR) to be identified.[4]
History and nomenclature
Discovered by Tillett and Francis in 1930,[5] it was initially thought that CRP might be a pathogenic secretion since it was elevated in a variety of illnesses, including cancer.[2] The later discovery of hepatic synthesis (made in the liver) demonstrated that it is a native protein.[6][7][8] Initially, CRP was measured using Quellung reaction which gave a positive or a negative reaction. More precise methods nowadays is using dynamic light scattering on antibodies specific to CRP.[9]
CRP was so named because it was first identified as a substance in the serum of patients with acute inflammation that reacted with the antibody against the somatic capsular polysaccharide (C-polysaccharide) of pneumococcus.[10][11]
Genetics and structure
The CRP gene is located on chromosome 1 (1q23.2[12]). It is a member of the small pentraxins family. The monomer has 224 amino acids,[13] and molecular mass of 25,106 Da. In serum, it assembles into stable pentameric structure with a discoid shape.
Function
CRP binds to the phosphocholine expressed on the surface of dead or dying cells and some bacteria. This activates the complement system, promoting phagocytosis by macrophages, which clears necrotic and apoptotic cells and bacteria.[9]
This so-called acute phase response occurs as a result of a rise in the concentration of IL-6, which is produced by macrophages[2] as well as adipocytes[3] in response to a wide range of acute and chronic inflammatory conditions such as bacterial, viral, or fungal infections; rheumatic and other inflammatory diseases; malignancy; and tissue injury and necrosis. These conditions cause release of interleukin-6 and other cytokines that trigger the synthesis of CRP and fibrinogen by the liver.
CRP binds to phosphocholine on micro-organisms. It is thought to assist in complement binding to foreign and damaged cells and enhances phagocytosis by macrophages (opsonin-mediated phagocytosis), which express a receptor for CRP. It plays a role in innate immunity as an early defense system against infections.[9]
Serum levels
In healthy adults, the normal concentrations of CRP varies between 0.8 mg/L to 3.0 mg/L. However, some healthy adults show elevated CRP at 10 mg/L. When there is a stimulus, the CRP level can rise 10,000-fold from less than 50 μg/l to more than 500 mg/L. Such levels can rise to 5 mg/L by 6 hours and peaks at 48 hours. The plasma half-life of CRP is 19 hours. Such half-life is constant in all medical conditions. Therefore, the only factor that affects the level of CRP in blood is its rate of production. The rate of CRP production increases with inflammation, infection, trauma, necrosis, malignancy, and allergic reaction. The CRP level also increases with age, possibly due to increasing subclinical condition. There is also no seasonal variations of CRP levels. Gene polymorphism of interleukin-1 family, interleukin 6, and polymorphic GT repeat of the CRP gene do affects the usual CRP levels when a person does not have any medical illnesses.[2] Other inflammatory mediators that can cause a rise in CRP are TGF beta 1, and tumor necrosis factor alpha. In acute inflammation, CRP can raise as much as 50 to 100 mg/dL within 4 to 6 hours in mild to moderate inflammation or insult such as skin infection, cystitis, or bronchitis. It can double every 8 hours and reaches its peak at 36 to 50 hours following injury or inflammation. CRP between 100 to 500 mg/dL is considered as bacterial inflammation. CRP concentrations between 2 to 10 mg/dL are considered as metabolic inflammation (metabolic pathways that causes arteriosclerosis and type II diabetes mellitus). Once inflammation subsides, CRP level falls quickly because of its relatively short half-life.[9]
Clinical significance
Diagnostic use
CRP is used mainly as a marker of inflammation. Apart from liver failure, there are few known factors that interfere with CRP production.[2] Interferon alpha inhibits CRP production from liver cells which may explain the relatively low levels of CRP found during viral infections compared to bacterial infections [14]
Measuring and charting CRP values can prove useful in determining disease progress or the effectiveness of treatments. ELISA, immunoturbidimetry, nephelometry, rapid immunodiffusion, and visual agglutination are all methods used to measure CRP.
A high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) test measures low levels of CRP using laser nephelometry. The test gives results in 25 minutes with a sensitivity down to 0.04 mg/L.
The risk of developing cardiovascular disease is quantified as follows:[15]
- low: hs-CRP level under 1.0 mg/L
- average: between 1.0 and 3.0 mg/L
- high: above 3.0 mg/L
Normal levels increase with aging.[16] Higher levels are found in late pregnant women, mild inflammation and viral infections (10–40 mg/L), active inflammation, bacterial infection (40–200 mg/L), severe bacterial infections and burns (>200 mg/L).[17]
CRP is a more sensitive and accurate reflection of the acute phase response than the ESR[18] (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate). ESR may be normal while CRP is elevated. CRP returns to normal more quickly than ESR in response to therapy.
The utility of CRP in differentiating inflammatory diseases (including inflammatory bowel disease, intestinal lymphoma, intestinal tuberculosis, and Behcet's syndrome) has been investigated and compared to other inflammatory biomarkers, such as ESR and WBC.[18]
Cardiovascular disease
Recent research suggests that patients with elevated basal levels of CRP are at an increased risk of diabetes,[19][20] hypertension and cardiovascular disease. A study of over 700 nurses showed that those in the highest quartile of trans fat consumption had blood levels of CRP that were 73% higher than those in the lowest quartile.[21] Although one group of researchers indicated that CRP may be only a moderate risk factor for cardiovascular disease,[22] this study (known as the Reykjavik Study) was found to have some problems for this type of analysis related to the characteristics of the population studied, and there was an extremely long follow-up time, which may have attenuated the association between CRP and future outcomes.[23] Others have shown that CRP can exacerbate ischemic necrosis in a complement-dependent fashion and that CRP inhibition can be a safe and effective therapy for myocardial and cerebral infarcts; so far, this has been demonstrated in animal models only.[24]
It has been hypothesized that patients with high CRP levels might benefit from use of statins. This is based on the JUPITER trial that found that elevated CRP levels without hyperlipidemia benefited. Statins were selected because they have been proven to reduce levels of CRP.[2][25] Studies comparing effect of various statins in hs-CRP revealed similar effects of different statins.[26][27] A subsequent trial however failed to find that CRP was useful for determining statin benefit.[28]
In a meta-analysis of 20 studies involving 1,466 patients with coronary artery disease, CRP levels were found to be reduced after exercise interventions. Among those studies, higher CRP concentrations or poorer lipid profiles before beginning exercise were associated with greater reductions in CRP.[29]
To clarify whether CRP is a bystander or active participant in atherogenesis, a 2008 study compared people with various genetic CRP variants. Those with a high CRP due to genetic variation had no increased risk of cardiovascular disease compared to those with a normal or low CRP.[30] A study published in 2011 shows that CRP is associated with lipid responses to low-fat and high-polyunsaturated fat diets.[31]
Coronary heart disease risk
Arterial damage results from white blood cell invasion and inflammation within the wall. CRP is a general marker for inflammation and infection, so it can be used as a very rough proxy for heart disease risk. Since many things can cause elevated CRP, this is not a very specific prognostic indicator.[32][33] Nevertheless, a level above 2.4 mg/L has been associated with a doubled risk of a coronary event compared to levels below 1 mg/L;[2] however, the study group in this case consisted of patients who had been diagnosed with unstable angina pectoris; whether elevated CRP has any predictive value of acute coronary events in the general population of all age ranges remains unclear. Currently, C-reactive protein is not recommended as a cardiovascular disease screening test for average-risk adults without symptoms.[34]
The American Heart Association and U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have defined risk groups as follows:[35]
- Low Risk: less than 1.0 mg/L
- Average risk: 1.0 to 3.0 mg/L
- High risk: above 3.0 mg/L
But hs-CRP is not to be used alone and should be combined with elevated levels of cholesterol, LDL-C, triglycerides, and glucose level. Smoking, hypertension and diabetes also increase the risk level of cardiovascular disease.
Fibrosis and inflammation
Scleroderma, polymyositis, and dermatomyositis elicit little or no CRP response. CRP levels also tend not to be elevated in SLE unless serositis or synovitis is present. Elevations of CRP in the absence of clinically significant inflammation can occur in renal failure. CRP level is an independent risk factor for atherosclerotic disease. Patients with high CRP concentrations are more likely to develop stroke, myocardial infarction, and severe peripheral vascular disease.[36] Elevated level of CRP can also be observed in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.[18]
High levels of CRP has been associated to point mutation Cys130Arg in APOE gene, coding for apolipoprotein E, establishing a link between lipid values and inflammatory markers modulation.[37]
Cancer
The role of inflammation in cancer is not well understood. Some organs of the body show greater risk of cancer when they are chronically inflamed.[38] While there is an association between increased levels of C-reactive protein and risk of developing cancer, there is no association between genetic polymorphisms influencing circulating levels of CRP and cancer risk.[39]
In a 2004 prospective cohort study on colon cancer risk associated with CRP levels, people with colon cancer had higher average CRP concentrations than people without colon cancer.[40] It can be noted that the average CRP levels in both groups were well within the range of CRP levels usually found in healthy people. However, these findings may suggest that low inflammation level can be associated with a lower risk of colon cancer, concurring with previous studies that indicate anti-inflammatory drugs could lower colon cancer risk.[41]
Obstructive sleep apnea
C-reactive protein (CRP), a marker of systemic inflammation, is also increased in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). CRP and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels were significantly higher in patients with OSA compared to obese control subjects.[42] Patients with OSA have higher plasma CRP concentrations that increased corresponding to the severity of their apnea-hypopnea index score. Treatment of OSA with CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) significantly alleviated the effect of OSA on CRP and IL-6 levels.[42]
Rheumatoid arthritis
It has previously been speculated that single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the CRP gene may affect clinical decision-making based on CRP in rheumatoid arthritis, e.g. DAS28 (Disease Activity Score 28 joints). A recent study showed that CRP genotype and haplotype were only marginally associated with serum CRP levels and without any association to the DAS28 score.[43] Thus, that DAS28, which is the core parameter for inflammatory activity in RA, can be used for clinical decision-making without adjustment for CRP gene variants.
See also
Additional images
-
C-reactive protein
-
C-reactive protein
References
- ↑ Thompson D, Pepys MB, Wood SP (February 1999). "The physiological structure of human C-reactive protein and its complex with phosphocholine". Structure. 7 (2): 169–77. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(99)80023-9. PMID 10368284.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM (June 2003). "C-reactive protein: a critical update". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 111 (12): 1805–12. doi:10.1172/JCI18921. PMC 161431. PMID 12813013.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Lau DC, Dhillon B, Yan H, Szmitko PE, Verma S (May 2005). "Adipokines: molecular links between obesity and atheroslcerosis". American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 288 (5): H2031–41. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01058.2004. PMID 15653761.
- ↑ Mantovani A, Garlanda C, Doni A, Bottazzi B (January 2008). "Pentraxins in innate immunity: from C-reactive protein to the long pentraxin PTX3". Journal of Clinical Immunology. 28 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1007/s10875-007-9126-7. PMID 17828584.
- ↑ Tillett WS, Francis T (September 1930). "Serological reactions in pneumonia with a nonprotein somatic fraction of pneumococcus". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 52 (4): 561–71. doi:10.1084/jem.52.4.561. PMC 2131884. PMID 19869788.
- ↑ Kennelly PJ, Murray RF, Rodwell VW, Botham KM (2009). Harper's illustrated biochemistry. McGraw-Hill Medical. ISBN 0-07-162591-7.
- ↑ Pincus MR, McPherson RA, Henry JB (2007). Henry's clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 1-4160-0287-1.
- ↑ Ratey JJ, Noskin GA, Braun R, Hanley EN Jr, McInnes IB, Ruddy S (2008). Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology: 2-Volume Set, Expert Consult: Online and Print (Textbook of Rheumatology (Kelley's)(2 Vol)). Philadelphia: Saunders. ISBN 1-4160-3285-1.
- ↑ Jump up to: 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Bray C, Bell LN, Liang H, Haykal R, Kaiksow F, Mazza JJ, Yale SH (December 2016). "Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and C-reactive Protein Measurements and Their Relevance in Clinical Medicine" (PDF). Wisconsin Medical Journal (WMJ). 115 (6): 317–21. PMID 29094869.
- ↑ Ananthanarayan R, Paniker CJ (1978). Ananthanarayan and Paniker's Textbook of Microbiology (7th ed.). Himayatnagar, Hyderabad: Orient Longman. p. 218. ISBN 9788125028086.
- ↑ Levine M (2011). "Chapter 13: Chronic Periodontitis". Topics in Dental Biochemistry. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-88115-5.
C-reactive protein (CRP) was originally identified as binding to the phosphocholine attachment site of capsular polysaccharide (C-polysaccharide) from Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- ↑ "CRP C-reactive protein [Homo sapiens]". Entrez Gene. National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "#CAA39671". NCBI Entrez Protein.
- ↑ Enocsson H, Sjöwall C, Skogh T, Eloranta ML, Rönnblom L, Wetterö J (December 2009). "Interferon-alpha mediates suppression of C-reactive protein: explanation for muted C-reactive protein response in lupus flares?". Arthritis and Rheumatism. 60 (12): 3755–60. doi:10.1002/art.25042. PMID 19950271.
- ↑ "Normal results". C-reactive protein. MedlinePlus. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ↑ Thomas, Lothar, Labor und Diagnose. TH-Books, Frankfurt, 2008, p. 1010
- ↑ Chew KS (April 2012). "What's new in Emergencies Trauma and Shock? C-reactive protein as a potential clinical biomarker for influenza infection: More questions than answers". Journal of Emergencies, Trauma, and Shock. 5 (2): 115–7. doi:10.4103/0974-2700.96477. PMC 3391832. PMID 22787338.
- ↑ Jump up to: 18.0 18.1 18.2 Liu S, Ren J, Xia Q, Wu X, Han G, Ren H, Yan D, Wang G, Gu G, Li J (December 2013). "Preliminary case-control study to evaluate diagnostic values of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in differentiating active Crohn's disease from intestinal lymphoma, intestinal tuberculosis and Behcet's syndrome". The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 346 (6): 467–72. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3182959a18. PMID 23689052.[unreliable medical source]
- ↑ Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE, Ridker PM (July 2001). "C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus". JAMA. 286 (3): 327–34. doi:10.1001/jama.286.3.327. PMID 11466099.
- ↑ Dehghan A, Kardys I, de Maat MP, Uitterlinden AG, Sijbrands EJ, Bootsma AH, et al. (March 2007). "Genetic variation, C-reactive protein levels, and incidence of diabetes". Diabetes. 56 (3): 872–8. doi:10.2337/db06-0922. PMID 17327459.
- ↑ Lopez-Garcia E, Schulze MB, Meigs JB, Manson JE, Rifai N, Stampfer MJ, et al. (March 2005). "Consumption of trans fatty acids is related to plasma biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction". The Journal of Nutrition. 135 (3): 562–6. doi:10.1093/jn/135.3.562. PMID 15735094.
- ↑ Danesh J, Wheeler JG, Hirschfield GM, Eda S, Eiriksdottir G, Rumley A, et al. (April 2004). "C-reactive protein and other circulating markers of inflammation in the prediction of coronary heart disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 350 (14): 1387–97. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa032804. PMID 15070788.
- ↑ Koenig, Wolfgang (2006). "C-reactive protein - a critical cardiovascular risk marker". CRPhealth.com.
- ↑ Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM, Tennent GA, Gallimore JR, Kahan MC, Bellotti V, et al. (April 2006). "Targeting C-reactive protein for the treatment of cardiovascular disease". Nature. 440 (7088): 1217–21. doi:10.1038/nature04672. PMID 16642000.
- ↑ Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM, Kastelein JJ, et al. (November 2008). "Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein". The New England Journal of Medicine. 359 (21): 2195–207. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0807646. PMID 18997196.
- ↑ Sindhu S, Singh HK, Salman MT, Fatima J, Verma VK (October 2011). "Effects of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and lipid profile in obese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients". Journal of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics. 2 (4): 261–5. doi:10.4103/0976-500X.85954. PMC 3198521. PMID 22025854.
- ↑ Jialal I, Stein D, Balis D, Grundy SM, Adams-Huet B, Devaraj S (April 2001). "Effect of hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitor therapy on high sensitive C-reactive protein levels". Circulation. 103 (15): 1933–5. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.103.15.1933. PMID 11306519.
- ↑ Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group, Emberson J, Bennett D, Link E, Parish S, Danesh J, Armitage J, Collins R (February 2011). "C-reactive protein concentration and the vascular benefits of statin therapy: an analysis of 20,536 patients in the Heart Protection Study". Lancet. 377 (9764): 469–76. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62174-5. PMC 3042687. PMID 21277016.
- ↑ Swardfager W, Herrmann N, Cornish S, Mazereeuw G, Marzolini S, Sham L, Lanctôt KL (April 2012). "Exercise intervention and inflammatory markers in coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis". American Heart Journal. 163 (4): 666–76.e1-3. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2011.12.017. PMID 22520533.
- ↑ Zacho J, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Jensen JS, Grande P, Sillesen H, Nordestgaard BG (October 2008). "Genetically elevated C-reactive protein and ischemic vascular disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 359 (18): 1897–908. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0707402. PMID 18971492.
- ↑ St-Onge MP, Zhang S, Darnell B, Allison DB (April 2009). "Baseline serum C-reactive protein is associated with lipid responses to low-fat and high-polyunsaturated fat diets". The Journal of Nutrition. 139 (4): 680–3. doi:10.3945/jn.108.098251. PMC 2666362. PMID 19297430.
- ↑ Lloyd-Jones DM, Liu K, Tian L, Greenland P (July 2006). "Narrative review: Assessment of C-reactive protein in risk prediction for cardiovascular disease". Annals of Internal Medicine. 145 (1): 35–42. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-145-1-200607040-00129. PMID 16818927. Archived from the original on 2008-04-17. Retrieved 2008-05-01.
- ↑ Bower JK, Lazo M, Juraschek SP, Selvin E (October 2012). "Within-person variability in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein". Archives of Internal Medicine. 172 (19): 1519–21. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2012.3712. PMC 3613132. PMID 22945505.
- ↑ Goldman L (2011). Goldman's Cecil Medicine (24th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. p. 54. ISBN 1437727883.
- ↑ "hs-CRP". Retrieved June 3, 2013.
- ↑ Clearfield MB (September 2005). "C-reactive protein: a new risk assessment tool for cardiovascular disease". The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association. 105 (9): 409–16. PMID 16239491. Archived from the original on 2012-01-10. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- ↑ Sidore C, Busonero F, Maschio A, Porcu E, Naitza S, Zoledziewska M, et al. (November 2015). "Genome sequencing elucidates Sardinian genetic architecture and augments association analyses for lipid and blood inflammatory markers". Nature Genetics. 47 (11): 1272–1281. doi:10.1038/ng.3368. PMC 4627508. PMID 26366554.
- ↑ Lu H, Ouyang W, Huang C (April 2006). "Inflammation, a key event in cancer development". Molecular Cancer Research. 4 (4): 221–33. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-05-0261. PMID 16603636.
- ↑ Allin KH, Nordestgaard BG (2011). "Elevated C-reactive protein in the diagnosis, prognosis, and cause of cancer". Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences. 48 (4): 155–70. doi:10.3109/10408363.2011.599831. PMID 22035340.
- ↑ Erlinger TP, Platz EA, Rifai N, Helzlsouer KJ (February 2004). "C-reactive protein and the risk of incident colorectal cancer" (PDF). JAMA. 291 (5): 585–90. doi:10.1001/jama.291.5.585. PMID 14762037.
- ↑ Baron JA, Cole BF, Sandler RS, Haile RW, Ahnen D, Bresalier R, et al. (March 2003). "A randomized trial of aspirin to prevent colorectal adenomas". The New England Journal of Medicine. 348 (10): 891–9. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa021735. PMID 12621133.
- ↑ Jump up to: 42.0 42.1 Latina JM, Estes NA, Garlitski AC (2013). "The Relationship between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Atrial Fibrillation: A Complex Interplay". Pulmonary Medicine. 2013: 621736. doi:10.1155/2013/621736. PMC 3600315. PMID 23533751.
- ↑ Ammitzbøll CG, Steffensen R, Bøgsted M, Hørslev-Petersen K, Hetland ML, Junker P, et al. (October 2014). "CRP genotype and haplotype associations with serum C-reactive protein level and DAS28 in untreated early rheumatoid arthritis patients". Arthritis Research & Therapy. 16 (5): 475. doi:10.1186/s13075-014-0475-3. PMC 4247621. PMID 25359432.
External links
- MedlinePlus Encyclopedia C-reactive protein
- Inflammation, Heart Disease and Stroke: The Role of C-Reactive Protein (American Heart Association)
- C-Reactive+Protein at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- CRP at Lab Tests Online
- CRP: analyte monograph - The Association for Clinical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
- George Vrousgos, N.D. - Southern Cross University
- Human CRP genome location and CRP gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.