Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer pathophysiology
|
Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer pathophysiology |
|
FDA on Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer pathophysiology |
|
CDC on Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer pathophysiology |
|
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer pathophysiology in the news |
|
Blogs on Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer pathophysiology |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Maria Fernanda Villarreal, M.D. [2]
Overview
HNPCC is an autosomal dominant genetic disease characterized by the early onset of colon cancer, endometrial cancer, and other malignant tumors caused by genetic mutations, that lead to an accumulation of DNA mismatches in MMR gene.[1] Development of HNPCC is the result of multiple genetic mutations. Genes involved in the pathogenesis of HNPCC include; MSH-2, MLH-1, MSH-6, PMS-2 ,PMS-1, TGF-BR2, and MLH-3. This syndrome occurs mostly in the proximal colon (60% to 80%) and endometrial cancer is the most common sentinel cancer among female patients with HNPCC.[1]
Pathogenesis
- HNPCC defects in DNA mismatch repair leading to microsatellite instability, also known as MSI-H, which is a hallmark of HNPCC. Three major groups of MSI-H cancers can be recognized by histopathological criteria:
- Right-sided poorly differentiated cancers
- Right-sided mucinous cancers
- Adenocarcinomas in any location showing any measurable level of intraepithelial lymphocyte
- MSI is identifiable in cancer specimens in the pathology laboratory. In hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer, colon malignancies usually occur from a single or a few adenomas, and mostly occurs in the proximal colon.
Genetics
- The hallmark of HNPCC is defective DNA mismatch repair, which leads to microsatellite instability, also known as MSI-H. Most cases result in changes in the lengths of dinucleotide repeats of the nucleobases cytosine and adenine.[2]
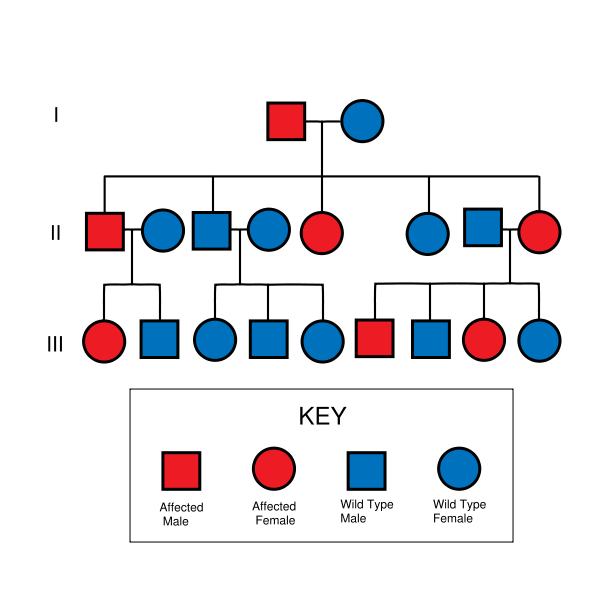
- HNPCC is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Therefore, most people with HNPCC inherit the condition from a parent. Families found to have a deleterious mutation in an HNPCC gene should be considered to have HNPCC regardless of the extent of the family history. However, due to incomplete penetrance, variable age of cancer diagnosis, cancer risk reduction, or early death, not all patients with an HNPCC gene mutation have a parent who had cancer.
- Some patients develop HNPCC de-novo in a new generation, without inheriting the gene. These patients are often only identified after developing an early-life colon cancer. Parents with HNPCC have a 50% chance to pass the gene on to each child. Most mutations (90%) that cause HNPCC are found in the MLH1 or MSH2 genes. The other genes, account for the other 10% of mutations.[3]
- MSH2 mutations have an increased risk of urothelial carcinoma relative to MLH1 and MSH6 mutations.[4]
- Development of HNPCC is the result of multiple genetic mutations.[1]
- Genes involved in the pathogenesis of HNPCC include:
| Genes implicated in HNPCC | Frequency of mutations in HNPCC families | Locus |
|---|---|---|
| MSH2 | approximately 60% | 2p22 |
| MLH1 | approximately 30% | 3p21 |
| MSH6 | 7-10% | 2p16 |
| PMS2 | relatively infrequent | 7p22 |
| PMS1 | case report | 2q31-q33 |
| TGFBR2 | case report | 3p22 |
| MLH3 | disputed | 14q24.3 |
Associated Conditions
- Colorectal carcinoma
- Endometrial carcinoma
- Non-endometrioid endometrial carcinoma[5][6]
- Endometrioid endometrial carcinoma[7]
- Stomach carcinoma,[8] intestinal-type.[9]
- Biliary tree carcinoma[8]
- Pancreatic carcinoma[8]
- Urinary system carcinoma[8]
Gross Pathology
- On gross pathology, there are no characteristic findings of HNPCC.[1]
Microscopic Pathology
- On microscopic histopathological analysis, HNPCC is more likely to be poorly differentiated, abundant in extracellular mucin, and distinguished by a lymphoid (peritumoral lymphocytes) host response to the tumor.[1]
Gallery
-
Micrograph of a sebaceous adenoma, as may be seen in Muir-Torre syndrome.
-
HNPCC is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Si JW, Wang L, Ba XJ, Zhang X, Dong Y, Zhang JX, Li WT, Li T (2015). "[Clinicopathological screening of Lynch syndrome: a report of 2 cases and literature review]". Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao (in Chinese). 47 (5): 858–64. PMID 26474631.
- ↑ Oki E, Oda S, Maehara Y, Sugimachi K (Mar 1999). "Mutated gene-specific phenotypes of dinucleotide repeat instability in human colorectal carcinoma cell lines deficient in DNA mismatch repair". Oncogene. 18 (12): 2143–7. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202583. PMID 10321739.
- ↑ Lynch Syndrome. Canadian Cancer Society http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-101/what-is-a-risk-factor/genetic-risk/lynch-syndrome/?region=ab#ixzz3t69IQ9M7 Accessed on December 01 2015
- ↑ van der Post, RS.; Kiemeney, LA.; Ligtenberg, MJ.; Witjes, JA.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, CA.; Bodmer, D.; Schaap, L.; Kets, CM.; van Krieken, JH. (2010). "Risk of urothelial bladder cancer in Lynch syndrome is increased, in particular among MSH2 mutation carriers". J Med Genet. 47 (7): 464–70. doi:10.1136/jmg.2010.076992. PMID 20591884. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Okuda T, Sekizawa A, Purwosunu Y; et al. (2010). "Genetics of endometrial cancers". Obstet Gynecol Int. 2010: 984013. doi:10.1155/2010/984013. PMC 2852605. PMID 20396392.
- ↑ Garg, K.; Soslow, RA. (2009). "Lynch syndrome (hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer) and endometrial carcinoma". J Clin Pathol. 62 (8): 679–84. doi:10.1136/jcp.2009.064949. PMID 19638537. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Lax, SF. (2002). "[Dualistic model of molecular pathogenesis in endometrial carcinoma]". Zentralbl Gynakol. 124 (1): 10–6. doi:10.1055/s-2002-20303. PMID 11873308. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 120435
- ↑ Cristofaro, G.; Lynch, HT.; Caruso, ML.; Attolini, A.; DiMatteo, G.; Giorgio, P.; Senatore, S.; Argentieri, A.; Sbano, E. (1987). "New phenotypic aspects in a family with Lynch syndrome II". Cancer. 60 (1): 51–8. PMID 3581033. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help)