Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
[[File:Autosomal recessive gene.png|alt=autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance|thumb|Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. Picture courtesy by By en:User:Cburnett - Own work in Inkscape, CC BY-SA 3.0, <nowiki>https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1840082</nowiki>]] | |||
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome is a rare [[autosomal recessive]] condition that leads to [[Sensorineural hearing loss|sensorineural deafness]], abnormal [[ventricular]] [[myocardial]] [[repolarization]] with results in [[long QT syndrome]] ([[Long QT syndrome|LQTS]]) and other [[cardiac]] events. Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome is due to '''''[[KCNQ1]]''''' or '''''[[KCNE1]]''''' [[Gene mutation|gene mutations]]. The range of [[symptoms]] and severity of [[symptoms]] in Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome differs from [[patient]] to [[patient]]. | Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome is a rare [[autosomal recessive]] condition that leads to [[Sensorineural hearing loss|sensorineural deafness]], abnormal [[ventricular]] [[myocardial]] [[repolarization]] with results in [[long QT syndrome]] ([[Long QT syndrome|LQTS]]) and other [[cardiac]] events. Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome is due to '''''[[KCNQ1]]''''' or '''''[[KCNE1]]''''' [[Gene mutation|gene mutations]]. The range of [[symptoms]] and severity of [[symptoms]] in Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome differs from [[patient]] to [[patient]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 26 November 2019
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Synonyms and keywords: Autosomal recessive long QT syndrome (LQTS), cardioauditory syndrome, cardioauditory syndrome of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen, deafness, congenital, and functional heart disease, Jervell and Lange-Nielsen (JLNS), surdocardiac syndrome
Overview
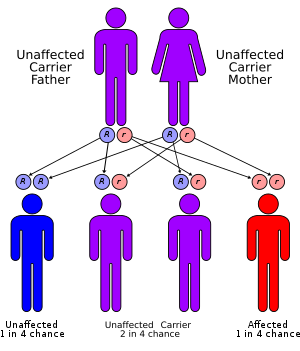
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive condition that leads to sensorineural deafness, abnormal ventricular myocardial repolarization with results in long QT syndrome (LQTS) and other cardiac events. Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome is due to KCNQ1 or KCNE1 gene mutations. The range of symptoms and severity of symptoms in Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome differs from patient to patient.
Historical Perspective
- Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) was first discovered by Anton Jervell a Norwegian physician and Fred Lange-Nielsen a Norwegian doctor and jazz musician, in 1957.[1][2]
Classification
- Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) may be classified according into two subtypes:[3][4][5][6]
| Type | Chromosome Locus | Gene Mutation | Protein Involved |
| Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome 1 | 11p15.5-p15.4 | KCNQ1 | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 |
| Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome 2 | 21q22.12 | KCNE1 | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 1 |
Pathophysiology
Physiology
The normal physiology of KCNQ1 and KCNE1 genes can be understood as follows:[7]
- Both KCNQ1 and KCNE1 genes encodes for the slow potassium channel currents of the cochlea and the heart.
- Normally the slow potassium channel currents were stimulated by the sound, when stimulated the potassium from the scala media passes the action potential through the apex of the hair cells.
- The potassium action potential then depolarises the hair cells.
- Once depolarised there is a release calcium-channel-induced release of neurotransmitter.
- The neurotransmitter then passes along with the auditory nerve and then depolarizes and the currents are sent centrally where they are received as sound.
Pathogenesis
- It is understood that Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is the result of mutations in the gene KCNQ1 and KCNE1.[8]
- KCNQ1 gene normally consists of 16 exons and have a general spanning of 400 kb.[9][10][11][12][13]
- The normal gene product of KCNQ1 gene is potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1.
- When KCNQ1 gene undergoes frameshift mutation it results in yielding truncated protein.
- Then the truncated protein either delete or duplicate the exons of the KCNQ1 gene and results in abnormal gene product which is known to result in long QT syndrome.
- KCNE1 gene normally consists of 3 exons and have a general spanning of 40 kb.[14][15][16][17][18]
- The normal gene product of KCNE1 gene is potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 1.
- Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E member 1 is also called as minK potassium channel protein beta subunit.[19]
- When KCNE1 gene undergoes missense mutation it results in yielding truncated protein.
- Then the truncated protein results in impairing potassium channel function, which is known to result in long QT syndrome.
Genetics
- Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is transmitted in a autosomal recessive pattern.[20]
- Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome appear to have low penetrance.[21]
- Genes involved in the pathogenesis of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) include:
Causes
Genetic Causes
Differentiating Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome from other Diseases
- Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) must be differentiated from Romano-Ward syndrome, Timothy syndrome, Andersen-Tawil syndrome, Brugada syndrome, and Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).[22][23][24][25][26][27][28]
Epidemiology and Demographics
Incidence
- The incidence of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is approximately 1 per 100,000 individuals in Norway.[29][30][31]
- The incidence of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is approximately 1 per 100,000 individuals in Sweden.
- It is estimated that Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) affects 166,000 to 625,000 children worldwide.
Prevalence
- The prevalence of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is approximately 1:200,000 individuals in Norway.[1][32]
Age
- The incidence of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) increases with age; the median age at diagnosis is 6.8 years.[33][34]
- The exact time of presentation in Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is highly variable.
Gender
- Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) affects men and women equally. But the severity of cardiac events is much more common in men.[35]
Risk Factors
- The most potent risk factor in the development of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is KCNQ1 and KCNE1 genes mutation.
- Other common risk factors in the development of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) symptoms include sudden sleep arousal, exercise and intense or sudden emotion which include the following:[36]
- Competitive sports
- Amusement park rides
- Frightening movies
- Jumping into cold water
Screening
- According to the American College of Medical Genetics, screening for Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) by hearing evaluation which is standard and electrocardiograms is recommended among patients with a family history.[37][38][39][40]
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Natural History
- The symptoms of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) usually develop in the first or second of life, and start with symptoms such as hearing loss and syncope.[41]
Complications
- Common complications of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) include:
Prognosis
- Depending on the severity of the genetic mutation at the time of diagnosis, the prognosis may vary. However, the prognosis is generally regarded as poor as most of the untreated patients die around the age of 15 years.[42]
- The prognosis varies with the gender, gene mutation and baseline QTc interval.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Study of Choice
- Molecular genetic testing is the gold standard test for the diagnosis of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) which includes single-gene testing, use of a multigene testing panel, and more comprehensive genomic testing
- The following result of molecular genetic testing is confirmatory of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS):
- KCNQ1 or KCNE1 pathogenic gene mutation variants identification
History and Symptoms
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) include:
- Congenital Deafness: Usually identified at the time of birth, most commonly sensorineural hearing loss and is due to disruption of endolymph homeostasis in the cochlea and vestibular system[43]
- Syncope: Due to abnormal heart rhythm and is typically precipitous and without warning
- Seizures: Most commonly grand mal seizures
- Palpitations
- Mild to moderate chest pain
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Sudden cardiac death
Physical Examination
HEENT
- All patients with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) are positive for profound bilateral congenital sensorineural deafness.[44][45]
| Hearing Loss Severity | Hearing Threshold |
|---|---|
| Mild hearing loss | 26-40 Decibels |
| Moderate hearing loss | 41-55 Decibels |
| Moderately severe hearing loss | 56-70 Decibels |
| Severe hearing loss | 71-90 Decibels |
| Profound hearing loss | 90 Decibels |
Heart
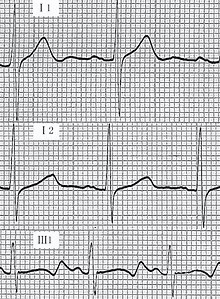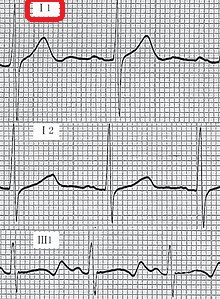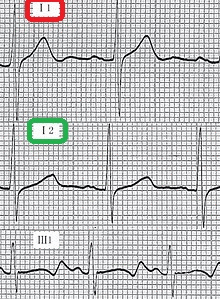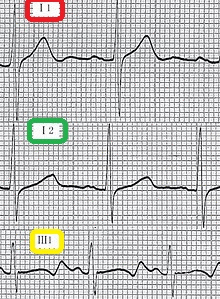
- Cardiovascular examination of patients with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) shows Long QTc.[47][48][49]
- Patients with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) shows QTc interval more than 500 mse.
- Palpitations
Laboratory Findings
Laboratory findings consistent with the diagnosis of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) include:[50][51]
- Anemia: patients with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) are more prone to develop anemia especially iron deficiency anemia
- Hypergastrinemia is due to the potassium channels defect
- Increased gastrin levels due to gastric hyperplasia
Electrocardiogram
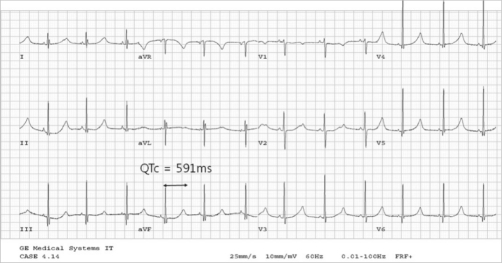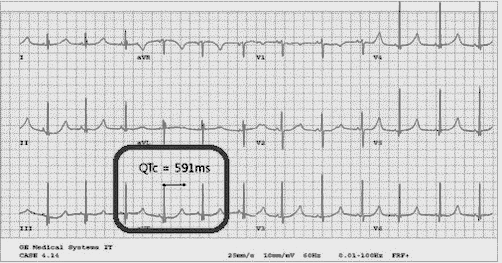
An ECG may be helpful in the diagnosis of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS). Findings on an ECG diagnostic of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) include the following:[4]
- Prolongation of the QTc interval greater than 500 msec
- Tachyarrhythmias: due to abnormal cardiac depolarization and cardiac repolarization
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Torsade de pointes ventricular tachycardia
- Ventricular fibrillation
Imaging Findings
There are no other imaging findings associated with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS).
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- Pharmacologic medical therapy is recommended among patients with [disease subclass 1], [disease subclass 2], and [disease subclass 3].
- Pharmacologic medical therapies for [disease name] include (either) [therapy 1], [therapy 2], and/or [therapy 3].
- Empiric therapy for [disease name] depends on [disease factor 1] and [disease factor 2].
- Patients with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) are treated with beta-adrenergic blockers as the first line in the management of the disease.
- In patients with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) despite treated with the beta-blockers risk of cardiac events still persists.
- Propranolol and nadolol are the beta-blockers of choice when treating a patient with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS).
Disease Name
- 1 Stage 1 - Name of stage
- 1.1 Specific Organ system involved 1
- 1.1.1 Adult
- Preferred regimen (1): drug name 100 mg PO q12h for 10-21 days (Contraindications/specific instructions)
- Preferred regimen (2): drug name 500 mg PO q8h for 14-21 days
- Preferred regimen (3): drug name 500 mg q12h for 14-21 days
- Alternative regimen (1): drug name 500 mg PO q6h for 7–10 days
- Alternative regimen (2): drug name 500 mg PO q12h for 14–21 days
- Alternative regimen (3): drug name 500 mg PO q6h for 14–21 days
- 1.1.2 Pediatric
- 1.1.2.1 (Specific population e.g. children < 8 years of age)
- Preferred regimen (1): drug name 50 mg/kg PO per day q8h (maximum, 500 mg per dose)
- Preferred regimen (2): drug name 30 mg/kg PO per day in 2 divided doses (maximum, 500 mg per dose)
- Alternative regimen (1): drug name10 mg/kg PO q6h (maximum, 500 mg per day)
- Alternative regimen (2): drug name 7.5 mg/kg PO q12h (maximum, 500 mg per dose)
- Alternative regimen (3): drug name 12.5 mg/kg PO q6h (maximum, 500 mg per dose)
- 1.1.2.2 (Specific population e.g. 'children < 8 years of age')
- Preferred regimen (1): drug name 4 mg/kg/day PO q12h(maximum, 100 mg per dose)
- Alternative regimen (1): drug name 10 mg/kg PO q6h (maximum, 500 mg per day)
- Alternative regimen (2): drug name 7.5 mg/kg PO q12h (maximum, 500 mg per dose)
- Alternative regimen (3): drug name 12.5 mg/kg PO q6h (maximum, 500 mg per dose)
- 1.1.2.1 (Specific population e.g. children < 8 years of age)
- 1.1.1 Adult
- 1.2 Specific Organ system involved 2
- 1.2.1 Adult
- Preferred regimen (1): drug name 500 mg PO q8h
- 1.2.2 Pediatric
- Preferred regimen (1): drug name 50 mg/kg/day PO q8h (maximum, 500 mg per dose)
- 1.2.1 Adult
- 1.1 Specific Organ system involved 1
- 2 Stage 2 - Name of stage
- 2.1 Specific Organ system involved 1
- Note (1):
- Note (2):
- Note (3):
- 2.1.1 Adult
- Parenteral regimen
- Preferred regimen (1): drug name 2 g IV q24h for 14 (14–21) days
- Alternative regimen (1): drug name 2 g IV q8h for 14 (14–21) days
- Alternative regimen (2): drug name 18–24 MU/day IV q4h for 14 (14–21) days
- Oral regimen
- Preferred regimen (1): drug name 500 mg PO q8h for 14 (14–21) days
- Preferred regimen (2): drug name 100 mg PO q12h for 14 (14–21) days
- Preferred regimen (3): drug name 500 mg PO q12h for 14 (14–21) days
- Alternative regimen (1): drug name 500 mg PO q6h for 7–10 days
- Alternative regimen (2): drug name 500 mg PO q12h for 14–21 days
- Alternative regimen (3):drug name 500 mg PO q6h for 14–21 days
- Parenteral regimen
- 2.1 Specific Organ system involved 1
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tranebjaerg L, Bathen J, Tyson J, Bitner-Glindzicz M (1999). "Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: a Norwegian perspective". Am J Med Genet. 89 (3): 137–46. PMID 10704188.
- ↑ Schwartz, Peter J.; Spazzolini, Carla; Crotti, Lia; Bathen, Jørn; Amlie, Jan P.; Timothy, Katherine; Shkolnikova, Maria; Berul, Charles I.; Bitner-Glindzicz, Maria; Toivonen, Lauri; Horie, Minoru; Schulze-Bahr, Eric; Denjoy, Isabelle (2006). "The Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome". Circulation. 113 (6): 783–790. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.592899. ISSN 0009-7322.
- ↑ Tyson J, Tranebjaerg L, McEntagart M, Larsen LA, Christiansen M, Whiteford ML; et al. (2000). "Mutational spectrum in the cardioauditory syndrome of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen". Hum Genet. 107 (5): 499–503. doi:10.1007/s004390000402. PMID 11140949.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Schwartz PJ, Spazzolini C, Crotti L, Bathen J, Amlie JP, Timothy K; et al. (2006). "The Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: natural history, molecular basis, and clinical outcome". Circulation. 113 (6): 783–90. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.592899. PMID 16461811.
- ↑ Tranebjaerg L, Bathen J, Tyson J, Bitner-Glindzicz M (1999). "Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: a Norwegian perspective". Am J Med Genet. 89 (3): 137–46. PMID 10704188.
- ↑ ACMG (2002) Genetics Evaluation Guidelines for the Etiologic Diagnosis of Congenital Hearing Loss. Genetic Evaluation of Congenital Hearing Loss Expert Panel. ACMG statement. Genet Med 4 (3):162-71. DOI:10.1097/00125817-200205000-00011 PMID: 12180152
- ↑ Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K; et al. (1993). "GeneReviews®". PMID 20301579.
- ↑ Tranebjaerg L, Bathen J, Tyson J, Bitner-Glindzicz M (1999). "Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: a Norwegian perspective". Am J Med Genet. 89 (3): 137–46. PMID 10704188.
- ↑ Wang Z, Li H, Moss AJ, Robinson J, Zareba W, Knilans T; et al. (2002). "Compound heterozygous mutations in KvLQT1 cause Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome". Mol Genet Metab. 75 (4): 308–16. doi:10.1016/S1096-7192(02)00007-0. PMID 12051962.
- ↑ Abbott GW, Xu X, Roepke TK (2007). "Impact of ancillary subunits on ventricular repolarization". J Electrocardiol. 40 (6 Suppl): S42–6. doi:10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2007.05.021. PMC 2128763. PMID 17993327.
- ↑ Abbott GW, Goldstein SA (2002). "Disease-associated mutations in KCNE potassium channel subunits (MiRPs) reveal promiscuous disruption of multiple currents and conservation of mechanism". FASEB J. 16 (3): 390–400. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0520hyp. PMID 11874988.
- ↑ Nishimura M, Ueda M, Ebata R, Utsuno E, Ishii T, Matsushita K; et al. (2017). "A novel KCNQ1 nonsense variant in the isoform-specific first exon causes both jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome 1 and long QT syndrome 1: a case report". BMC Med Genet. 18 (1): 66. doi:10.1186/s12881-017-0430-7. PMC 5465588. PMID 28595573.
- ↑ Neyroud N, Tesson F, Denjoy I, Leibovici M, Donger C, Barhanin J; et al. (1997). "A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome". Nat Genet. 15 (2): 186–9. doi:10.1038/ng0297-186. PMID 9020846.
- ↑ Lewis A, McCrossan ZA, Abbott GW (2004). "MinK, MiRP1, and MiRP2 diversify Kv3.1 and Kv3.2 potassium channel gating". J Biol Chem. 279 (9): 7884–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.M310501200. PMID 14679187.
- ↑ Lu Y, Mahaut-Smith MP, Huang CL, Vandenberg JI (2003). "Mutant MiRP1 subunits modulate HERG K+ channel gating: a mechanism for pro-arrhythmia in long QT syndrome type 6". J Physiol. 551 (Pt 1): 253–62. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2003.046045. PMC 2343156. PMID 12923204.
- ↑ Anantharam A, Abbott GW (2005). "Does hERG coassemble with a beta subunit? Evidence for roles of MinK and MiRP1". Novartis Found Symp. 266: 100–12, discussion 112-7, 155–8. PMID 16050264.
- ↑ Abbott GW, Goldstein SA (2002). "Disease-associated mutations in KCNE potassium channel subunits (MiRPs) reveal promiscuous disruption of multiple currents and conservation of mechanism". FASEB J. 16 (3): 390–400. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0520hyp. PMID 11874988.
- ↑ Abbott GW, Xu X, Roepke TK (2007). "Impact of ancillary subunits on ventricular repolarization". J Electrocardiol. 40 (6 Suppl): S42–6. doi:10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2007.05.021. PMC 2128763. PMID 17993327.
- ↑ McCrossan ZA, Roepke TK, Lewis A, Panaghie G, Abbott GW (2009). "Regulation of the Kv2.1 potassium channel by MinK and MiRP1". J Membr Biol. 228 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1007/s00232-009-9154-8. PMC 2849987. PMID 19219384.
- ↑ Priori SG, Napolitano C, Schwartz PJ (1999). "Low penetrance in the long-QT syndrome: clinical impact". Circulation. 99 (4): 529–33. doi:10.1161/01.cir.99.4.529. PMID 9927399.
- ↑ Berge KE, Haugaa KH, Früh A, Anfinsen OG, Gjesdal K, Siem G; et al. (2008). "Molecular genetic analysis of long QT syndrome in Norway indicating a high prevalence of heterozygous mutation carriers". Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 68 (5): 362–8. doi:10.1080/00365510701765643. PMID 18752142.
- ↑ Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K; et al. (1993). "GeneReviews®". PMID 20301308.
- ↑ Ackerman MJ, Siu BL, Sturner WQ, Tester DJ, Valdivia CR, Makielski JC; et al. (2001). "Postmortem molecular analysis of SCN5A defects in sudden infant death syndrome". JAMA. 286 (18): 2264–9. doi:10.1001/jama.286.18.2264. PMID 11710892.
- ↑ Arnestad M, Crotti L, Rognum TO, Insolia R, Pedrazzini M, Ferrandi C; et al. (2007). "Prevalence of long-QT syndrome gene variants in sudden infant death syndrome". Circulation. 115 (3): 361–7. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.658021. PMID 17210839.
- ↑ Schwartz PJ, Priori SG, Spazzolini C, Moss AJ, Vincent GM, Napolitano C; et al. (2001). "Genotype-phenotype correlation in the long-QT syndrome: gene-specific triggers for life-threatening arrhythmias". Circulation. 103 (1): 89–95. doi:10.1161/01.cir.103.1.89. PMID 11136691.
- ↑ Wedekind H, Bajanowski T, Friederich P, Breithardt G, Wülfing T, Siebrands C; et al. (2006). "Sudden infant death syndrome and long QT syndrome: an epidemiological and genetic study". Int J Legal Med. 120 (3): 129–37. doi:10.1007/s00414-005-0019-0. PMID 16012827.
- ↑ Juang JJ, Horie M (2016). "Genetics of Brugada syndrome". J Arrhythm. 32 (5): 418–425. doi:10.1016/j.joa.2016.07.012. PMC 5063259. PMID 27761167.
- ↑ Thomas D, Wimmer AB, Karle CA, Licka M, Alter M, Khalil M; et al. (2005). "Dominant-negative I(Ks) suppression by KCNQ1-deltaF339 potassium channels linked to Romano-Ward syndrome". Cardiovasc Res. 67 (3): 487–97. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.05.003. PMID 15950200.
- ↑ Siem G, Früh A, Leren TP, Heimdal K, Teig E, Harris S (2008). "Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome in Norwegian children: aspects around cochlear implantation, hearing, and balance". Ear Hear. 29 (2): 261–9. doi:10.1097/aud.0b013e3181645393. PMID 18595190.
- ↑ Berge KE, Haugaa KH, Früh A, Anfinsen OG, Gjesdal K, Siem G; et al. (2008). "Molecular genetic analysis of long QT syndrome in Norway indicating a high prevalence of heterozygous mutation carriers". Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 68 (5): 362–8. doi:10.1080/00365510701765643. PMID 18752142.
- ↑ Winbo A, Stattin EL, Nordin C, Diamant UB, Persson J, Jensen SM; et al. (2014). "Phenotype, origin and estimated prevalence of a common long QT syndrome mutation: a clinical, genealogical and molecular genetics study including Swedish R518X/KCNQ1 families". BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 14: 22. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-14-22. PMC 3942207. PMID 24552659.
- ↑ Winbo A, Stattin EL, Diamant UB, Persson J, Jensen SM, Rydberg A (2012). "Prevalence, mutation spectrum, and cardiac phenotype of the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome in Sweden". Europace. 14 (12): 1799–806. doi:10.1093/europace/eus111. PMID 22539601.
- ↑ Rohatgi RK, Sugrue A, Bos JM, Cannon BC, Asirvatham SJ, Moir C; et al. (2017). "Contemporary Outcomes in Patients With Long QT Syndrome". J Am Coll Cardiol. 70 (4): 453–462. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.05.046. PMID 28728690.
- ↑ Garson A, Dick M, Fournier A, Gillette PC, Hamilton R, Kugler JD; et al. (1993). "The long QT syndrome in children. An international study of 287 patients". Circulation. 87 (6): 1866–72. doi:10.1161/01.cir.87.6.1866. PMID 8099317.
- ↑ Schwartz PJ, Spazzolini C, Crotti L, Bathen J, Amlie JP, Timothy K; et al. (2006). "The Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: natural history, molecular basis, and clinical outcome". Circulation. 113 (6): 783–90. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.592899. PMID 16461811.
- ↑ Schwartz, Peter J.; Spazzolini, Carla; Crotti, Lia; Bathen, Jørn; Amlie, Jan P.; Timothy, Katherine; Shkolnikova, Maria; Berul, Charles I.; Bitner-Glindzicz, Maria; Toivonen, Lauri; Horie, Minoru; Schulze-Bahr, Eric; Denjoy, Isabelle (2006). "The Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome". Circulation. 113 (6): 783–790. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.592899. ISSN 0009-7322.
- ↑ Chang RK, Lan YT, Silka MJ, Morrow H, Kwong A, Smith-Lang J; et al. (2014). "Genetic variants for long QT syndrome among infants and children from a statewide newborn hearing screening program cohort". J Pediatr. 164 (3): 590-5.e1-3. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.11.011. PMC 3943925. PMID 24388587.
- ↑ Berge KE, Haugaa KH, Früh A, Anfinsen OG, Gjesdal K, Siem G; et al. (2008). "Molecular genetic analysis of long QT syndrome in Norway indicating a high prevalence of heterozygous mutation carriers". Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 68 (5): 362–8. doi:10.1080/00365510701765643. PMID 18752142.
- ↑ Uysal F, Turkgenc B, Toksoy G, Bostan OM, Evke E, Uyguner O; et al. (2017). ""Homozygous, and compound heterozygous mutation in 3 Turkish family with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: case reports"". BMC Med Genet. 18 (1): 114. doi:10.1186/s12881-017-0474-8. PMC 5644177. PMID 29037160.
- ↑ Olsson KS, Wålinder O, Jansson U, Wilbe M, Bondeson ML, Stattin EL; et al. (2017). "Common founder effects of hereditary hemochromatosis, Wilson´s disease, the long QT syndrome and autosomal recessive deafness caused by two novel mutations in the WHRN and TMC1 genes". Hereditas. 154: 16. doi:10.1186/s41065-017-0052-2. PMC 5735936. PMID 29270100.
- ↑ Neyroud N, Tesson F, Denjoy I, Leibovici M, Donger C, Barhanin J; et al. (1997). "A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome". Nat Genet. 15 (2): 186–9. doi:10.1038/ng0297-186. PMID 9020846.
- ↑ Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K; et al. (1993). "GeneReviews®". PMID 20301579.
- ↑ Winbo A, Rydberg A (2015). "Vestibular dysfunction is a clinical feature of the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome". Scand Cardiovasc J. 49 (1): 7–13. doi:10.3109/14017431.2014.988172. PMID 25471708.
- ↑ Yamasoba T, Lin FR, Someya S, Kashio A, Sakamoto T, Kondo K (2013). "Current concepts in age-related hearing loss: epidemiology and mechanistic pathways". Hear Res. 303: 30–8. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2013.01.021. PMC 3723756. PMID 23422312.
- ↑ Neyroud N, Tesson F, Denjoy I, Leibovici M, Donger C, Barhanin J; et al. (1997). "A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome". Nat Genet. 15 (2): 186–9. doi:10.1038/ng0297-186. PMID 9020846.
- ↑ "Identification of a novel KCNQ1 mutation associated with both Jervell and Lange-Nielsen and Romano-Ward forms of long QT syndrome in a Chinese family".
- ↑ Winbo A, Stattin EL, Diamant UB, Persson J, Jensen SM, Rydberg A (2012). "Prevalence, mutation spectrum, and cardiac phenotype of the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome in Sweden". Europace. 14 (12): 1799–806. doi:10.1093/europace/eus111. PMID 22539601.
- ↑ Winbo A, Stattin EL, Nordin C, Diamant UB, Persson J, Jensen SM; et al. (2014). "Phenotype, origin and estimated prevalence of a common long QT syndrome mutation: a clinical, genealogical and molecular genetics study including Swedish R518X/KCNQ1 families". BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 14: 22. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-14-22. PMC 3942207. PMID 24552659.
- ↑ Neyroud N, Tesson F, Denjoy I, Leibovici M, Donger C, Barhanin J; et al. (1997). "A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome". Nat Genet. 15 (2): 186–9. doi:10.1038/ng0297-186. PMID 9020846.
- ↑ Winbo A, Sandström O, Palmqvist R, Rydberg A (2013). "Iron-deficiency anaemia, gastric hyperplasia, and elevated gastrin levels due to potassium channel dysfunction in the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome". Cardiol Young. 23 (3): 325–34. doi:10.1017/S1047951112001060. PMID 22805636.
- ↑ Rice KS, Dickson G, Lane M, Crawford J, Chung SK, Rees MI; et al. (2011). "Elevated serum gastrin levels in Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: a marker of severe KCNQ1 dysfunction?". Heart Rhythm. 8 (4): 551–4. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.11.039. PMID 21118729.
- ↑ "Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome: Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutations in the KCNQ1 in a Korean Family".