Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Undo revision 1339906 by Mehrian.jafari (talk)) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" rowspan="2" colspan="2" |Disease | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" rowspan="2" colspan="2" |Disease | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |History and symptoms | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |History and symptoms | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" colspan=" | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" colspan="3" |Laboratory findings | ||
! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Defective gene | ! align="center" style="background:#DCDCDC;" |Defective gene | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Blood pressure | !Blood pressure | ||
!Genitalia | !Genitalia | ||
! | !Increased | ||
!Decreased | |||
! | |||
!Potassium levels | !Potassium levels | ||
! | ! | ||
| Line 43: | Line 40: | ||
* Male: normal or scrotal pigmentation and large phallus | * Male: normal or scrotal pigmentation and large phallus | ||
| | | | ||
* [[Deoxycorticosterone]] | * [[Deoxycorticosterone]] | ||
* 11-Deoxy-[[cortisol]] | * 11-Deoxy-[[cortisol]] | ||
* [[17-Hydroxyprogesterone|17-hydroxyprogesterone]], mild elevation | * [[17-Hydroxyprogesterone|17-hydroxyprogesterone]], mild elevation | ||
| | |||
* [[Cortisol]] | |||
* [[Corticosterone]] | |||
* [[Aldosterone]] | |||
| | | | ||
* High in salt-wasting type | * High in salt-wasting type | ||
| Line 57: | Line 54: | ||
* CYP21A1 and CYP21A2 gene | * CYP21A1 and CYP21A2 gene | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Non-classic type | |||
| | | | ||
* Normal | * Normal | ||
| Line 63: | Line 60: | ||
* Female: [[virilization]] after [[puberty]] | * Female: [[virilization]] after [[puberty]] | ||
* Male: normal appearance | * Male: normal appearance | ||
| | | | ||
* [[17-Hydroxyprogesterone|17-hydroxyprogesterone]] | * [[17-Hydroxyprogesterone|17-hydroxyprogesterone]] | ||
* Exaggerated [[Androstenedione]], [[DHEA]], and [[17-Hydroxyprogesterone|17-hydroxyprogesterone]] response to [[ACTH]] | * Exaggerated [[Androstenedione]], [[DHEA]], and [[17-Hydroxyprogesterone|17-hydroxyprogesterone]] | ||
response to [[ACTH]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Cortisol]] | |||
* [[Aldosterone]] | |||
| | | | ||
* Normal | * Normal | ||
| Line 81: | Line 79: | ||
* Female: normal | * Female: normal | ||
* Male: [[ambiguous genitalia]] | * Male: [[ambiguous genitalia]] | ||
| | | | ||
* [[Deoxycorticosterone]] | * [[Deoxycorticosterone]] | ||
* [[Corticosterone]] | |||
* [[Progesterone]] | * [[Progesterone]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | * [[Cortisol]] | ||
* [[Aldosterone]] | |||
| | |||
* Low | |||
| | |||
* [[CYP17A1]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |[[11β-hydroxylase deficiency|11-β hydroxylase deficiency]] | | align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |[[11β-hydroxylase deficiency|11-β hydroxylase deficiency]] | ||
| | | | ||
* [[Hypertension]] | * [[Hypertension]] | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 99: | Line 98: | ||
* Male: normal or scrotal pigmentation and large phallus | * Male: normal or scrotal pigmentation and large phallus | ||
| | |||
| | |||
* [[Deoxycorticosterone]] | * [[Deoxycorticosterone]] | ||
* 11-Deoxy-[[cortisol]] | * 11-Deoxy-[[cortisol]] | ||
* [[17-Hydroxyprogesterone|17-hydroxyprogesterone]], mild elevation | * [[17-Hydroxyprogesterone|17-hydroxyprogesterone]], mild elevation | ||
| | | | ||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | CYP11B1 | * [[Cortisol]] | ||
* [[Corticosterone]] | |||
* [[Aldosterone]] | |||
| | |||
* Low | |||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | | |||
* CYP11B1 | |||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |[[3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency]] | | align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |[[3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency]] | ||
| Line 115: | Line 116: | ||
| | | | ||
* Both male and female: [[ambiguous genitalia]] | * Both male and female: [[ambiguous genitalia]] | ||
| | |||
| | |||
* [[Dehydroepiandrosterone]] | * [[Dehydroepiandrosterone]] | ||
* [[17-hydroxypregnenolone]] | * [[17-hydroxypregnenolone]] | ||
* [[Pregnenolone]] | * [[Pregnenolone]] | ||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | High | | | ||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | HSD3B2 | * [[Cortisol]] | ||
* [[Aldosterone]] | |||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | | |||
* High | |||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | | |||
* HSD3B2 | |||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |Cytochrome P450-oxidoreductase (POR) deficiency (ORD) | | align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |Cytochrome P450-oxidoreductase (POR) deficiency (ORD) | ||
| Line 130: | Line 132: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 138: | Line 137: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia | | align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia | ||
| [[Hypotension]] | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme deficiency | | align="center" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" colspan="2" |Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme deficiency | ||
| Line 155: | Line 148: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
Revision as of 16:05, 11 August 2017
This page contains general information about Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. For more information on specific types, please visit the pages on 21-hydroxylase deficiency, 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency, 11β-hydroxylase deficiency, 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency, Cytochrome P450-oxidoreductase (POR) deficiency (ORD), congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia, cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme deficiency .
|
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia main page |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mehrian Jafarizade, M.D [2]
Synonyms and keywords: Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, CAH, Adrenal hyperplasia
Overview
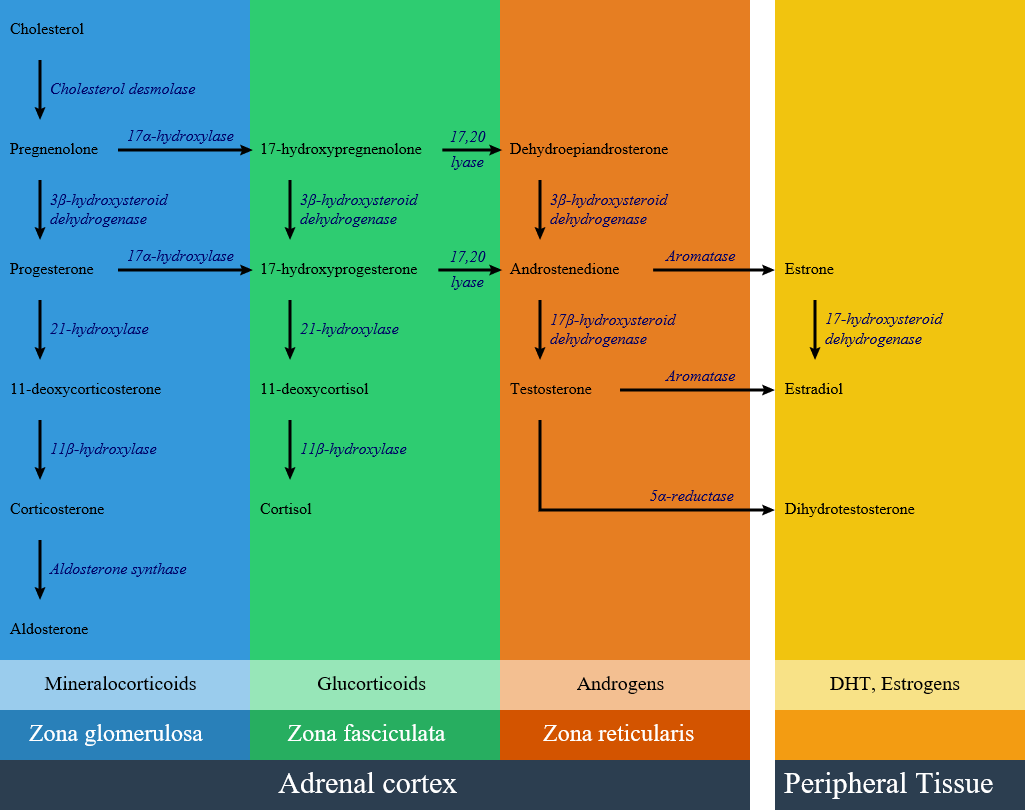
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia consists of several disorders result from defective enzymes and proteins involving in steroid and cortisol biosynthesis. Defects in steroid biosynthesis is caused by several genetic mutations. Decreasing cortisol levels leads to releasing the inhibitory feedback on corticotropin (ACTH) production. High ACTH level causes cortisol precursor accumulation and overproduction of other steroids. The most common cause of congenital adrenal hyperplasia is 21-hydroxylase deficiency, which accounts for more than 95% of cases. Other causes are 21-hydroxylase deficiency, 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency, 11β-hydroxylase deficiency, 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency, Cytochrome P450-oxidoreductase (POR) deficiency (ORD), congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia, cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme deficiency.
Classification
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is classified into seven types based on the genetic causes that lead to hyperplasia and hormonal imbalance. There are three zones of hormonal synthesis in adrenal cortex that are shown below, and impairment of each pathway may lead to a specific subtype of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
| Disease | History and symptoms | Laboratory findings | Defective gene | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood pressure | Genitalia | Increased | Decreased | Potassium levels | |||
| 21-hydroxylase deficiency | Classic type |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Non-classic type |
|
|
response to ACTH |
|
| ||
| 17-α hydroxylase deficiency |
|
|
|||||
| 11-β hydroxylase deficiency |
|
|
|
| |||
| 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency |
|
|
| ||||
| Cytochrome P450-oxidoreductase (POR) deficiency (ORD) | |||||||
| Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia | Hypotension | ||||||
| Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme deficiency | |||||||
Differential Diagnosis
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia must be differentiated from diseases that cause ambiguous genitalia:[1][2]
| Disease name | Laboratory tests | Important clinical findings | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased | Decreased | ||
| Classic type of 21-hydroxylase deficiency |
|
| |
| 11-β hydroxylase deficiency |
|
| |
| 17-α hydroxylase deficiency |
| ||
| 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency |
| ||
| Gestational hyperandrogenism |
|
| |
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia must be differentiated from diseases that cause virilization and hirsutism in female:[3][2][4]
| Disease name | Steroid status | Other laboratory | Important clinical findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-classic type of 21-hydroxylase deficiency | Increased:
response to ACTH |
|
|
| 11-β hydroxylase deficiency | Increased:
Decreased: |
|
|
| 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency | Increased:
Decreased: |
|
|
| Polycystic ovary syndrome |
|
|
|
| Adrenal tumors |
|
|
|
| Ovarian virilizing tumor |
|
|
|
| Cushing's syndrome |
|
||
| Hyperprolactinemia |
|
|
Some types of congenital adrenal hyperplasia must be differentiated from diseases with primary amenorrhea and female external genitalia.[5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12]
| Disease name | Cause | Differentiating | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Findings | Uterus | Breast development | Testosterone | LH | FSH | Karyotyping | ||
| Pregnancy | HCG positive | |||||||
| 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 deficiency |
|
Yes in female |
Yes in female |
Low |
Normal |
Normal |
XY and XX | |
| 17-alpha-hydroxylase deficiency |
|
No |
No |
Low |
Normal |
Normal |
||
| Gonadal dysgenesis |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Low |
High |
High |
|
| Testicular regression syndrome |
|
|
No |
No |
Low |
High |
High |
|
| LH receptor defects |
|
No |
No |
Low |
High |
High |
||
| 5-alpha-reductase type 2 deficiency |
|
No |
No |
Normal male range |
High to normal |
High to normal |
||
| Androgen insensitivity syndrome |
|
|
No |
Yes |
Normal male range |
Normal |
Normal |
XY |
| Mullerian agenesis |
|
No |
Yes |
Normal female range |
Normal |
Normal |
||
| Primary ovarian insufficiency |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Normal female range |
High |
High |
|
| Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism |
|
|
Yes |
No |
Normal female range |
Low |
Normal |
|
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Normal female range |
High |
High |
45 XO | |
References
- ↑ Hughes IA, Nihoul-Fékété C, Thomas B, Cohen-Kettenis PT (2007). "Consequences of the ESPE/LWPES guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of disorders of sex development". Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 21 (3): 351–65. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2007.06.003. PMID 17875484.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 White PC, Speiser PW (2000). "Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency". Endocr. Rev. 21 (3): 245–91. doi:10.1210/edrv.21.3.0398. PMID 10857554.
- ↑ Hohl A, Ronsoni MF, Oliveira M (2014). "Hirsutism: diagnosis and treatment". Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 58 (2): 97–107. PMID 24830586. Vancouver style error: initials (help)
- ↑ Melmed, Shlomo (2016). Williams textbook of endocrinology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0323297387.=
- ↑ Maimoun L, Philibert P, Cammas B, Audran F, Bouchard P, Fenichel P, Cartigny M, Pienkowski C, Polak M, Skordis N, Mazen I, Ocal G, Berberoglu M, Reynaud R, Baumann C, Cabrol S, Simon D, Kayemba-Kay's K, De Kerdanet M, Kurtz F, Leheup B, Heinrichs C, Tenoutasse S, Van Vliet G, Grüters A, Eunice M, Ammini AC, Hafez M, Hochberg Z, Einaudi S, Al Mawlawi H, Nuñez CJ, Servant N, Lumbroso S, Paris F, Sultan C (2011). "Phenotypical, biological, and molecular heterogeneity of 5α-reductase deficiency: an extensive international experience of 55 patients". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96 (2): 296–307. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-1024. PMID 21147889.
- ↑ Moreira AC, Leal AM, Castro M (1990). "Characterization of adrenocorticotropin secretion in a patient with 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 71 (1): 86–91. doi:10.1210/jcem-71-1-86. PMID 2164530.
- ↑ Heremans GF, Moolenaar AJ, van Gelderen HH (1976). "Female phenotype in a male child due to 17-alpha-hydroxylase deficiency". Arch. Dis. Child. 51 (9): 721–3. PMC 1546244. PMID 999330.
- ↑ Biglieri EG (1979). "Mechanisms establishing the mineralocorticoid hormone patterns in the 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency syndrome". J. Steroid Biochem. 11 (1B): 653–7. PMID 226795.
- ↑ Saenger P (1996). "Turner's syndrome". N. Engl. J. Med. 335 (23): 1749–54. doi:10.1056/NEJM199612053352307. PMID 8929268.
- ↑ Bastian C, Muller JB, Lortat-Jacob S, Nihoul-Fékété C, Bignon-Topalovic J, McElreavey K, Bashamboo A, Brauner R (2015). "Genetic mutations and somatic anomalies in association with 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis". Fertil. Steril. 103 (5): 1297–304. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.043. PMID 25813279.
- ↑ Imperato-McGinley J, Guerrero L, Gautier T, Peterson RE (1974). "Steroid 5alpha-reductase deficiency in man: an inherited form of male pseudohermaphroditism". Science. 186 (4170): 1213–5. PMID 4432067.
- ↑ Schnitzer JJ, Donahoe PK (2001). "Surgical treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia". Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 30 (1): 137–54. PMID 11344932.