Hepatopulmonary syndrome diagnostic study of choice: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
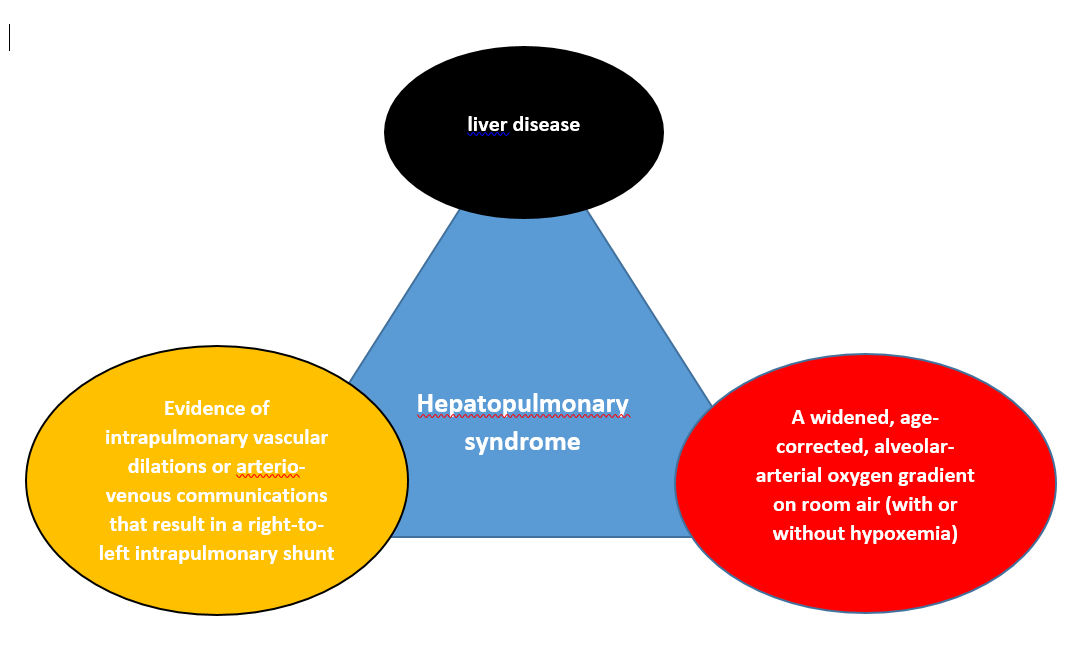
[[Image:HPS triad.png|thumb|right|500 px|'''Hepatopulmonary syndrome diagnostic triad.''' Diagram by Soroush Seifirad, MD.]] | |||
{{Hepatopulmonary syndrome}} | {{Hepatopulmonary syndrome}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Soroush}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Soroush}} | ||
== Overview == | |||
There is no single diagnostic study of choice for the diagnosis of hepatopulmonary syndrome, but hepatopulmonary syndrome can be diagnosed based on history of '''liver disease''', atrial blood gas analysis (widened '''alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient''' measurement); and evidences of '''intra-pulmonary vascular dilation''' or arterio-venous communications that result in a '''right-to-left intrapulmonary shunt.''' | |||
== Diagnostic Study of Choice == | |||
'''Study of choice:''' | |||
There is no single diagnostic study of choice for the diagnosis of hepatopulmonary syndrome, but hepatopulmonary syndrome can be diagnosed based on history of '''liver disease''', atrial blood gas analysis (widened '''alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient''' measurement); and evidences of '''intra-pulmonary vascular dilation''' or arterio-venous communications that result in a '''right-to-left intrapulmonary shunt.<ref name="pmid1642191">Hopkins WE, Waggoner AD, Barzilai B (1992) [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=1642191 Frequency and significance of intrapulmonary right-to-left shunting in end-stage hepatic disease.] ''Am J Cardiol'' 70 (4):516-9. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0002-9149(92)91200-n DOI:10.1016/0002-9149(92)91200-n] PMID: [https://pubmed.gov/1642191 1642191]</ref>'''<ref name="pmid27326810">Krowka MJ, Fallon MB, Kawut SM, Fuhrmann V, Heimbach JK, Ramsay MA et al. (2016) [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27326810 International Liver Transplant Society Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis and Management of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome and Portopulmonary Hypertension.] ''Transplantation'' 100 (7):1440-52. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000001229 DOI:10.1097/TP.0000000000001229] PMID: [https://pubmed.gov/27326810 27326810]</ref><ref name="pmid14708947">Lima BL, França AV, Pazin-Filho A, Araújo WM, Martinez JA, Maciel BC et al. (2004) [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14708947 Frequency, clinical characteristics, and respiratory parameters of hepatopulmonary syndrome.] ''Mayo Clin Proc'' 79 (1):42-8. [http://dx.doi.org/10.4065/79.1.42 DOI:10.4065/79.1.42] PMID: [https://pubmed.gov/14708947 14708947]</ref> | |||
'''Investigations:''' | |||
* Among the patients who present with clinical signs of hepatopulmonary syndrome, the [[Hepatopulmonary syndrome echocardiography and ultrasound|'''contrast-enhanced transthoracic echocardiography with agitated saline''']] is the most specific test for the diagnosis.<ref name="pmid12427789">Schenk P, Fuhrmann V, Madl C, Funk G, Lehr S, Kandel O et al. (2002) [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12427789 Hepatopulmonary syndrome: prevalence and predictive value of various cut offs for arterial oxygenation and their clinical consequences.] ''Gut'' 51 (6):853-9. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.51.6.853 DOI:10.1136/gut.51.6.853] PMID: [https://pubmed.gov/12427789 12427789]</ref> | |||
<ref name="pmid7557096">Abrams GA, Jaffe CC, Hoffer PB, Binder HJ, Fallon MB (1995) [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=7557096 Diagnostic utility of contrast echocardiography and lung perfusion scan in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome.] ''Gastroenterology'' 109 (4):1283-8. PMID: [https://pubmed.gov/7557096 7557096]</ref> | |||
* Among the patients who present with clinical signs of hepatopulmonary syndrome, the [[Hepatopulmonary syndrome laboratory findings|'''atrial blood gas analysis''']] is the most sensitive test for diagnosis.<ref name="pmid8665789">Castro M, Krowka MJ (1996) [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8665789 Hepatopulmonary syndrome. A pulmonary vascular complication of liver disease.] ''Clin Chest Med'' 17 (1):35-48. PMID: [https://pubmed.gov/8665789 8665789]</ref> | |||
* Among the patients who present with clinical signs of hepatopulmonary syndrome, the [ | |||
===== Diagnostic results ===== | ===== Diagnostic results ===== | ||
The following | The following findings are confirmatory for hepatopulmonary syndrome: (discussed in details) | ||
* [ | * Presence of bubbles on the left heart in contrast-enhanced transthoracic echocardiography with agitated saline <ref name="pmid7557096">Abrams GA, Jaffe CC, Hoffer PB, Binder HJ, Fallon MB (1995) [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=7557096 Diagnostic utility of contrast echocardiography and lung perfusion scan in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome.] ''Gastroenterology'' 109 (4):1283-8. PMID: [https://pubmed.gov/7557096 7557096]</ref> | ||
* Presence of radioactivity on the left heart in Technetium 99m-labeled macroaggregated albumin scanning<ref name="pmid9453490">Abrams GA, Nanda NC, Dubovsky EV, Krowka MJ, Fallon MB (1998) [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9453490 Use of macroaggregated albumin lung perfusion scan to diagnose hepatopulmonary syndrome: a new approach.] ''Gastroenterology'' 114 (2):305-10. PMID: [https://pubmed.gov/9453490 9453490]</ref> | |||
*Diffusion defect in atrial blood gas analysis particularly studying <ref name="pmid17392034">Arguedas MR, Singh H, Faulk DK, Fallon MB (2007) [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=17392034 Utility of pulse oximetry screening for hepatopulmonary syndrome.] ''Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol'' 5 (6):749-54. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2006.12.003 DOI:10.1016/j.cgh.2006.12.003] PMID: [https://pubmed.gov/17392034 17392034]</ref> | |||
==== | *Abnormal liver function studies | ||
*Abnormal pulmonary function test | |||
* [ | |||
=== | |||
<br /> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 130: | Line 36: | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
[[Category:Surgery]] | |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Pulmonology]] | |||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | |||
[[Category:Gastroentrology]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:57, 6 September 2019
|
Hepatopulmonary syndrome Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Hepatopulmonary syndrome from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hepatopulmonary syndrome diagnostic study of choice On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hepatopulmonary syndrome diagnostic study of choice |
|
Hepatopulmonary syndrome diagnostic study of choice in the news |
|
Blogs on Hepatopulmonary syndrome diagnostic study of choice |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Hepatopulmonary syndrome diagnostic study of choice |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Soroush Seifirad, M.D.[2]
Overview
There is no single diagnostic study of choice for the diagnosis of hepatopulmonary syndrome, but hepatopulmonary syndrome can be diagnosed based on history of liver disease, atrial blood gas analysis (widened alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient measurement); and evidences of intra-pulmonary vascular dilation or arterio-venous communications that result in a right-to-left intrapulmonary shunt.
Diagnostic Study of Choice
Study of choice:
There is no single diagnostic study of choice for the diagnosis of hepatopulmonary syndrome, but hepatopulmonary syndrome can be diagnosed based on history of liver disease, atrial blood gas analysis (widened alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient measurement); and evidences of intra-pulmonary vascular dilation or arterio-venous communications that result in a right-to-left intrapulmonary shunt.[1][2][3]
Investigations:
- Among the patients who present with clinical signs of hepatopulmonary syndrome, the contrast-enhanced transthoracic echocardiography with agitated saline is the most specific test for the diagnosis.[4]
- Among the patients who present with clinical signs of hepatopulmonary syndrome, the atrial blood gas analysis is the most sensitive test for diagnosis.[6]
Diagnostic results
The following findings are confirmatory for hepatopulmonary syndrome: (discussed in details)
- Presence of bubbles on the left heart in contrast-enhanced transthoracic echocardiography with agitated saline [5]
- Presence of radioactivity on the left heart in Technetium 99m-labeled macroaggregated albumin scanning[7]
- Diffusion defect in atrial blood gas analysis particularly studying [8]
- Abnormal liver function studies
- Abnormal pulmonary function test
References
- ↑ Hopkins WE, Waggoner AD, Barzilai B (1992) Frequency and significance of intrapulmonary right-to-left shunting in end-stage hepatic disease. Am J Cardiol 70 (4):516-9. DOI:10.1016/0002-9149(92)91200-n PMID: 1642191
- ↑ Krowka MJ, Fallon MB, Kawut SM, Fuhrmann V, Heimbach JK, Ramsay MA et al. (2016) International Liver Transplant Society Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis and Management of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome and Portopulmonary Hypertension. Transplantation 100 (7):1440-52. DOI:10.1097/TP.0000000000001229 PMID: 27326810
- ↑ Lima BL, França AV, Pazin-Filho A, Araújo WM, Martinez JA, Maciel BC et al. (2004) Frequency, clinical characteristics, and respiratory parameters of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc 79 (1):42-8. DOI:10.4065/79.1.42 PMID: 14708947
- ↑ Schenk P, Fuhrmann V, Madl C, Funk G, Lehr S, Kandel O et al. (2002) Hepatopulmonary syndrome: prevalence and predictive value of various cut offs for arterial oxygenation and their clinical consequences. Gut 51 (6):853-9. DOI:10.1136/gut.51.6.853 PMID: 12427789
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Abrams GA, Jaffe CC, Hoffer PB, Binder HJ, Fallon MB (1995) Diagnostic utility of contrast echocardiography and lung perfusion scan in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 109 (4):1283-8. PMID: 7557096
- ↑ Castro M, Krowka MJ (1996) Hepatopulmonary syndrome. A pulmonary vascular complication of liver disease. Clin Chest Med 17 (1):35-48. PMID: 8665789
- ↑ Abrams GA, Nanda NC, Dubovsky EV, Krowka MJ, Fallon MB (1998) Use of macroaggregated albumin lung perfusion scan to diagnose hepatopulmonary syndrome: a new approach. Gastroenterology 114 (2):305-10. PMID: 9453490
- ↑ Arguedas MR, Singh H, Faulk DK, Fallon MB (2007) Utility of pulse oximetry screening for hepatopulmonary syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5 (6):749-54. DOI:10.1016/j.cgh.2006.12.003 PMID: 17392034