|
|
| (34 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| __NOTOC__ | | __NOTOC__ |
| '''For patient information click [[{{PAGENAME}} (patient information)|here]]''' | | |
| | '''For patient information, click [[{{PAGENAME}} (patient information)|here]]''' |
|
| |
|
| {{Infobox_Disease | | | {{Infobox_Disease | |
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |
| Image = Glaucoma,optic_nerve.jpg | | | Image = Glaucoma,optic_nerve.jpg | |
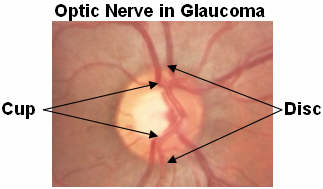
| Caption = The '''pink rim''' of disc contains nerve fibers. The '''white cup''' is a pit with no nerve fibers. As glaucoma advances, the cup enlarges until it occupies most of the disc area. Courtesy [http://www.agingeye.net/glaucoma/glaucomainformation.php AgingEye Times] | | | Caption = The ''pink rim'' of [[optic disc|disc]] contains [[nerve fiber]]s. The ''white cup'' is a pit with no [[nerve fiber]]s. As glaucoma advances, the cup enlarges until it occupies most of the [[optic disc|disc]] area.| |
| DiseasesDB = 5226 |
| |
| ICD10 = {{ICD10|H|40||h|40}}-{{ICD10|H|42||h|40}}|
| |
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|365}} |
| |
| ICPC2 = F93|
| |
| OMIM = |
| |
| MedlinePlus = |
| |
| MeshID = D005901 |
| |
| }} | | }} |
| {{Glaucoma}} | | {{Glaucoma}} |
| {{CMG}} | | {{CMG}} {{AE}}{{RBS}} |
| | |
| ==Diagnosis==
| |
| | |
| ===Surgery===
| |
| [[Image:Conventional surgery to treat glaucoma EDA11.JPG|thumb|Conventional surgery to treat glaucoma makes a new opening in the meshwork. This new opening helps fluid to leave the eye and lowers intraocular pressure.]]
| |
| {{main|Glaucoma surgery}} | |
| | |
| Surgery is the primary therapy for those with congenital glaucoma.<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=231300 "Glaucoma, Congenital: GLC3 Buphthalmos."] OMIM - Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Accessed October 17, 2006.</ref> Both [[laser]] and conventional surgeries are performed. Generally, these operations are a temporary solution, as there is no cure for glaucoma as of yet.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==== Canaloplasty ==== | | == [[Glaucoma overview|Overview]] == |
| Canaloplasty is an advanced, nonpenetrating procedure designed to enhance and restore the eye’s natural drainage system to provide sustained reduction of IOP. Canaloplasty utilizes breakthrough microcatheter technology in a simple and minimally invasive procedure.
| | == [[Glaucoma historical perspective|Historical Perspective]] == |
| To perform a canaloplasty, a doctor will create a tiny incision to gain access to a canal in the eye. A microcatheter will circumnavigate the canal around the iris, enlarging the main drainage channel and its smaller collector channels through the injection of a sterile, gel-like material called viscoelastic. The catheter is then removed and a suture is placed within the canal and tightened. By opening the canal, the pressure inside the eye will be relieved.
| | == [[Glaucoma classification | Classification]] == |
| | == [[Glaucoma pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]] == |
| | == [[Glaucoma causes| Causes]]== |
| | == [[Glaucoma epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]] == |
| | == [[Glaucoma risk factors | Risk Factors]]== |
| | == [[Glaucoma screening|Screening]] == |
| | == [[Glaucoma natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]] == |
|
| |
|
| ====Laser surgery==== | | == Diagnosis == |
| '''Laser trabeculoplasty''' may be used to treat open angle glaucoma. It is a temporary solution, not a cure. A 50 μm argon laser spot is aimed at the trabecular meshwork to stimulate opening of the mesh to allow more outflow of aqueous fluid. Usually, half of the angle is treated at a time. Traditional laser trabeculoplasty utilizes a thermal argon laser. The procedure is called argon laser trabeculoplasty or ALT. A newer type of laser trabeculoplasty uses a "cold" (non-thermal) laser to stimulate drainage in the trabecular meshwork. This newer procedure is call selective laser trabeculoplasty or SLT. Studies show that SLT is as effective as ALT at lowering eye pressure. In addition, SLT may be repeated three to four times, whereas ALT can usually be repeated only once.
| |
|
| |
|
| '''Laser peripheral iridotomy''' may be used in patients susceptible to or affected by angle closure glaucoma. During laser iridotomy, laser energy is used to make a small full-thickness opening in the iris. This opening equalizes the pressure between the front and back of the iris, causing the iris to move backward. This uncovers the trabecular meshwork. In some cases of intermittent or short-term angle closure this may lower the eye pressure. Laser iridotomy reduces the risk of developing an attack of acute angle closure. In most cases it also reduces the risk of developing chronic angle closure or gradual adhesion of the iris to the trabecular meshwork.
| | [[Glaucoma history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Glaucoma physical examination| Ocular Examination]] |
|
| |
|
| ====Trabeculectomy==== | | ==Treatment== |
| The most common conventional surgery performed for glaucoma is the [[trabeculectomy]]. Here, a partial thickness flap is made in the scleral wall of the eye, and a window opening made under the flap to remove a portion of the trabecular meshwork. The scleral flap is then sutured loosely back in place. This allows fluid to flow out of the eye through this opening, resulting in lowered intraocular pressure and the formation of a bleb or fluid bubble on the surface of the eye. Scarring can occur around or over the flap opening, causing it to become less effective or lose effectiveness altogether. One person can have multiple surgical procedures of the same or different types.
| | [[Glaucoma medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Glaucoma surgery|Surgery]] |
|
| |
|
| ====Glaucoma drainage implants==== | | ==Case Studies== |
| There are also several different glaucoma drainage implants. These include the original Molteno implant (1966), the Baerveldt tube shunt, or the valved implants, such as the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant and the later generation pressure ridge Molteno implants. These are indicated for glaucoma patients not responding to maximal medical therapy, with previous failed guarded filtering surgery (trabeculectomy). The flow tube is inserted into the anterior chamber of the eye and the plate is implanted underneath the conjunctiva to allow flow of aqueous fluid out of the eye into a chamber called a bleb. The Express mini-implant is currently being used as a modification of the standard trabeculectomy technique, and is a non-valved conduit between the anterior chamber and the space under the scleral flap<ref name="express"> Maris PJ, Jr., Ishida K, Netland PA. Comparison of trabeculectomy with Ex-PRESS miniature glaucoma device implanted under scleral flap. J Glaucoma 2007 January;16(1):14-9 </ref>.
| | [[Glaucoma case study one|Case #1]] |
|
| |
|
| * The first-generation Molteno and other non-valved implants sometimes require the ligation of the tube until the bleb formed is mildly fibrosed and water-tight<ref name="VicrylTie">
| | ==Related Chapters== |
| Molteno AC, Polkinghorne PJ, Bowbyes JA. The vicryl tie technique for inserting a draining implant in the treatment of secondary glaucoma. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol. 1986 Nov;14(4):343-54
| | *[[List of eye diseases and disorders|List of Eye Diseases and Disorders]] |
| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=3814422&dopt=Citation.]
| | *[[Ocular hypertension|Ocular Hypertension]] |
| </ref>This is done to reduce postoperative hypotony -- sudden drops in postoperative intraocular pressure (IOP).
| | *[[Glaucoma valves|Glaucoma Valves]] |
| * Valved implants such as the Ahmed glaucoma valve attempt to control postoperative hypotony by using a mechanical valve. Studies show that in severe cases of glaucoma, double plate Molteno implants are associated with lower mean IOP in the long term compared to the Ahmed glaucoma valve <ref name="AhmedCompare"> | | *[[eye surgery|Eye Surgery]] |
| Ayyala RS, Zurakowski D et al. Comparison of double-plate Molteno and Ahmed glaucoma valve in patients with advanced uncontrolled glaucoma.
| |
| Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 2002 Mar-Apr;33(2):94-101.[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=11942556&dopt=Citation].
| |
| </ref>
| |
| * Second and third generation Molteno implants incorporate a biological valve and studies show considerable improvement in postoperative outcome over the older style Ahmed and Molteno implants.
| |
| | |
| The ongoing scarring over the conjunctival dissipation segment of the shunt may become too thick for the [[aqueous humor]] to filter through. This may require preventive measures using anti-fibrotic medication like [[5-fluorouracil]] ([[5-FU]]) or [[mitomycin-C]] (during the procedure), or additional surgery.
| |
| | |
| == Major studies ==
| |
| *[http://www.nei.nih.gov/neitrials/static/study49.asp Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS)] - large American National Eye Institute (NEI) sponsored study designed "to assess the long-range outcomes of sequences of interventions involving trabeculectomy and argon laser trabeculoplasty in eyes that have failed initial medical treatment for glaucoma." It recommends different treatments based on race.
| |
| *[http://www.nei.nih.gov/earlyglaucoma/index.asp Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial (EMGT)] -Another NEI study found that immediately treating people who have early stage glaucoma can delay progression of the disease.
| |
| *[http://www.nei.nih.gov/neitrials/viewStudyWeb.aspx?id=24 Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS)] -NEI study findings: "...Topical ocular hypotensive medication was effective in delaying or preventing onset of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma (POAG) in individuals with elevated Intraocular Pressure (IOP). Although this does not imply that all patients with borderline or elevated IOP should receive medication, clinicians should consider initiating treatment for individuals with ocular hypertension who are at moderate or high risk for developing POAG."
| |
| *[http://www.cvr.org.au/bmes.htm Blue Mountains Eye Study] "The Blue Mountains Eye Study was the first large population-based assessment of visual impairment and common eye diseases of a representative older Australian community sample." Risk factors for glaucoma and other eye disease were determined.
| |
| | |
| ==See also==
| |
| *[[List of eye diseases and disorders]]
| |
| *[[Ocular hypertension]] | |
| *[[Glaucoma valves]] | |
| *[[Mansour F. Armaly]] | | *[[Mansour F. Armaly]] |
| *[[Laszlo Z. Bito]] | | *[[Laszlo Z. Bito]] |
| Line 67: |
Line 41: |
| *[[American Glaucoma Society]] | | *[[American Glaucoma Society]] |
|
| |
|
| ==References==
| | ==External Links== |
| {{Reflist|2}}
| |
| | |
| ==External links== | |
| *[http://www.glaucoma-association.com/ International Glaucoma Association] A charity for people with glaucoma.
| |
| *[http://www.nei.nih.gov/health/glaucoma/glaucoma_facts.asp Glaucoma] Resource Guide from the National Eye Institute (NEI). | | *[http://www.nei.nih.gov/health/glaucoma/glaucoma_facts.asp Glaucoma] Resource Guide from the National Eye Institute (NEI). |
| * [http://www.globalaigs.org/ Global Association of International Glaucoma Societies] - featuring a hymn about the successful treatment of glaucoma
| |
| * [http://www.glaucoma.org Glaucoma Research Foundation]
| |
| * {{cite web | title= Glaucoma - What is Glaucoma? | url=http://health-net-now.blogspot.com/2007/04/glaucoma-what-is-glaucoma.html | publisher=NLM | accessdate=2007-04-21}} video
| |
| * [http://www.glaucomafoundation.org/ Nonprofit Foundation for Glaucoma]
| |
| * [http://www.ahaf.org/glaucoma/about/glabout.htm National Glaucoma Research]
| |
| * [http://www.djo.harvard.edu/ DJO | Digital Journal of Ophthalmology]
| |
| * [http://www.lei.org.au/ Lions Eye Institute, Perth, Australia]
| |
| * [http://www.glaucomavitamins.com Improving Glaucoma Naturally]
| |
|
| |
|
| {{Eye pathology}} | | {{Eye pathology}} |
| [[ca:Glaucoma]]
| | {{WH}} |
| [[da:Grøn stær]]
| | {{WS}} |
| [[de:Glaukom]]
| |
| [[es:Glaucoma]]
| |
| [[eo:Glaŭkomo]]
| |
| [[fr:Glaucome chronique]]
| |
| [[hr:Glaukom]]
| |
| [[it:Glaucoma (medicina)]]
| |
| [[he:גלאוקומה]]
| |
| [[ms:Glaukoma]]
| |
| [[nl:Glaucoom]]
| |
| [[ja:緑内障]]
| |
| [[no:Glaukom]]
| |
| [[pl:Jaskra]]
| |
| [[pt:Glaucoma]]
| |
| [[ru:Глаукома]]
| |
| [[sr:Глауком]]
| |
| [[fi:Glaukooma]]
| |
| [[sv:Glaukom]]
| |
| [[tr:Glokom]]
| |
| [[zh:青光眼]]
| |
| | |
| {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | |
| {{WikiDoc Sources}} | |
|
| |
|
| [[Category:Aging-associated diseases]] | | [[Category:Aging-associated diseases]] |
| [[Category:Blindness]] | | [[Category:Blindness]] |
| [[Category:Disease]]
| |
| [[Category:Ophthalmology]] | | [[Category:Ophthalmology]] |
| [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] |
| [[Category:Mature chapter]] | | [[Category:Mature chapter]] |
| | [[Category:Disease]] |