Retroperitoneal hematoma: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Infobox_Disease | | {{Infobox_Disease | | ||
Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | ||
Image = Retroperitoneal_hematoma_MRI_001.jpg| | Image = Retroperitoneal_hematoma_MRI_001.jpg| | ||
Caption = Retroperitoneal hematoma. <br> ([http://www.radswiki.net Image courtesy of RadsWiki])| | Caption = Retroperitoneal hematoma. <br> ([http://www.radswiki.net Image courtesy of RadsWiki])| | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{SI}} | {{SI}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{CZ}} | ||
{{ | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Retroperitoneal hemorrhage and retroperitoneal hematoma are potentially life-threatening conditions. Common causes of retroperitoneal hemorrhage are [[cardiac catheterization]] and [[trauma]]. | |||
== Symptoms== | == Symptoms== | ||
The patient may complain of intense [[flank pain]] or back pain. | The patient may complain of intense [[flank pain]] or back pain. | ||
==Signs== | ==Signs== | ||
The patient may develop [[tachycardia]] and [[hypotension]] if the rate of hemorrhage is rapid. | The patient may develop [[tachycardia]] and [[hypotension]] if the rate of hemorrhage is rapid. | ||
Rarely, later in the course, the patient may develop a [[Grey-Turner's sign]] with bulging flanks, and a bluish discoloration in the region of the flank. Again, it should be emphasized that this sign appears 24 to 48 hours after a severe retroperitoneal bleed and should not be used to gauge whether a retroperitoneal bleed is present acutely. | Rarely, later in the course, the patient may develop a [[Grey-Turner's sign]] with bulging flanks, and a bluish discoloration in the region of the flank. Again, it should be emphasized that this sign appears 24 to 48 hours after a severe retroperitoneal bleed and should not be used to gauge whether a retroperitoneal bleed is present acutely. | ||
==Differentiating retroperitoneal heamatoma from other diseases== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; width: 100px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Disease}} | |||
! colspan="3" style="background: #4479BA; width: 100px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Clinical feature}} | |||
! rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; width: 100px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Laboratory findings}} | |||
! rowspan="2" style="background: #4479BA; width: 100px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Imaging findings}} | |||
|- | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 100px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Fever}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 100px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Weight loss}} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 100px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Abdominal pain}} | |||
|- | |||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Retroperitoneal hematoma]] | |||
|_ | |||
|_ | |||
|✔ | |||
|[[Anemia]] | |||
| rowspan="4" |[[MRI]] is the best radiologic tool to differentiate between retroperitoneal masses. | |||
|- | |||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Retroperitoneal abscess]] | |||
|✔ | |||
|_ | |||
|✔ | |||
|[[Leukocytosis]], positive inflammatory markers | |||
|- | |||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |Retroperitoneal tumors (.e.g. [[liposarcoma]]) | |||
|✔ | |||
|✔ | |||
|✔ | |||
|positive [[tumor marker]] | |||
|- | |||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |[[Chronic pancreatitis]] | |||
|_ | |||
|✔ | |||
|✔ | |||
|[[Diabetes mellitus|DM type II]], [[amylase]] and [[lipase]] levels may be slightly elevated | |||
|} | |||
{| align="center" | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
{| style="border: 0px; font-size: 90%; margin: 3px;" align="center" | |||
! colspan="2" rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" | Classification of acute abdomen based | |||
on etiology | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" |Presentation | |||
! colspan="8" rowspan="1" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" | Clinical findings | |||
! colspan="2" rowspan="1" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" | Diagnosis | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" | Comments | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" | Fever | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" |Rigors and Chills | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" |Abdominal Pain | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" |Jaundice | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" |Hypotension | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" | Guarding | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" |Rebound Tenderness | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" |Bowel sounds | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="1" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" | Lab Findings | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" |Imaging | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2" rowspan="8" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | Common causes of | |||
Peritonitis | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | [[Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
|− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hypoactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Ascitic fluid [[PMN]]>250 cells/mm<small>³</small> | |||
* Culture: Positive for single organism | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Ultrasound for evaluation of liver cirrhosis | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | Perforated [[Gastric ulcer|gastric]] and [[duodenal ulcer]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* Ascitic fluid | |||
**[[LDH]] > serum [[LDH]] | |||
** Glucose < 50mg/dl | |||
** Total protein > 1g/dl | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Air under [[diaphragm]] in upright [[CXR]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Upper GI [[endoscopy]] for diagnosis | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | Acute suppurative cholangitis | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[RUQ]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | Acute cholangitis | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
|− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | [[RUQ]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
|− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Abnormal [[LFT]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Ultrasound shows [[biliary]] dilatation | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Biliary drainage ([[Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography|ERCP]]) + IV antibiotics | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | [[Acute Cholecystitis|Acute cholecystitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | [[RUQ]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hypoactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* [[Hyperbilirubinemia]] | |||
* [[Leukocytosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Ultrasound shows gallstone and evidence of inflammation | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Murphy's sign|Murphy’s sign]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | [[Acute pancreatitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | [[Epigastric]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Increased [[amylase]] / [[lipase]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Ultrasound shows evidence of [[inflammation]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Pain radiation to back | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | [[Acute appendicitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | RLQ | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hypoactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Leukocytosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Ultrasound shows evidence of [[inflammation]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Nausea and vomiting|Nausea & vomiting]], [[decreased appetite]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | [[Diverticulitis|Acute diverticulitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | LLQ | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hypoactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Leukocytosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |CT scan and ultrasound shows evidence of inflammation | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2" rowspan="5" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | Hollow Viscous Obstruction | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Small intestine obstruction | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hyperactive then absent | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Leukocytosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Abdominal X-ray|Abdominal X ray]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Nausea and vomiting|Nausea & vomiting]] associated with [[constipation]], [[Abdominal distension|abdominal distention]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Gall stone disease|Gall stone '''disease''']]/'''Cholelithiasis''' | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Volvulus]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hypoactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Leukocytosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |CT scan and [[Abdominal x-ray|abdominal X ray]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Nausea and vomiting|Nausea & vomiting]] associated with [[constipation]], [[Abdominal distension|abdominal distention]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Biliary colic]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |RUQ | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Increased [[bilirubin]] and [[alkaline phosphatase]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Ultrasound | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Nausea and vomiting|Nausea & vomiting]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Renal colic]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Flank pain]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Hematuria]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |CT scan and ultrasound | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Colicky [[abdominal pain]] associated with [[Nausea and vomiting|nausea & vomiting]] | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="4" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Vascular Disorders | |||
| rowspan="2" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Ischemic causes | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Mesenteric ischemia]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Periumbilical | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hyperactive | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Leukocytosis]] and [[lactic acidosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |CT scan | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Nausea and vomiting|Nausea & vomiting]], normal physical examination | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Ischemic colitis|Acute ischemic colitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Hyperactive then absent | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Leukocytosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |CT scan | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Nausea and vomiting|Nausea & vomiting]] | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="2" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Hemorrhagic causes | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Normal | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |CT scan | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Unstable hemodynamics | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Intra-abdominal or [[retroperitoneal hemorrhage]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Anemia]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |CT scan | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |History of [[trauma]] | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="5" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Gynaecological Causes | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Fallopian tube | |||
| colspan="1" rowspan="1" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" | [[Salpingitis|Acute salpingitis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | + | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | LLQ/ RLQ | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |− | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Leukocytosis]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Pelvic ultrasound]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |[[Vaginal discharge]] | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="3" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Ovarian cyst]] complications and endometrial disease | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Torsion of the cyst | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |RLQ / LLQ | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |± | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Increased [[ESR]] and [[CRP]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Ultrasound | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Sudden onset severe pain with [[nausea and vomiting]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Endometriosis | |||
| - | |||
| | |||
|RLQ/LLQ | |||
| - | |||
| | |||
| +/- | |||
| +/- | |||
|N | |||
|Normal | |||
|Laproscopy | |||
|Menstrual-associated symptoms, pelvic | |||
symptoms | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Cyst rupture | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |RLQ / LLQ | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Increased [[ESR]] and [[CRP]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Ultrasound | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Sudden onset severe pain with [[nausea and vomiting]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Pregnancy | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Ruptured [[ectopic pregnancy]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |RLQ / LLQ | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Positive [[pregnancy test]] | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Ultrasound | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |History of missed period and [[vaginal bleeding]] | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="4" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Functional | |||
| colspan="2" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC;" align="center" |Irritable Bowel Syndrome | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Diffuse | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| align="left" style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |N | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
[[Diagnosis|Clinical diagnosis]] | |||
* ROME III/IV criteria | |||
* [[Pharmacological|Pharmacologic]] studies based criteria | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | - | |||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | | |||
* High [[dietary fiber]] | |||
* [[Osmotic]] [[laxatives]] | |||
* [[Antispasmodic]]<nowiki/>drugs | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==Diagnostic Findings== | ==Diagnostic Findings== | ||
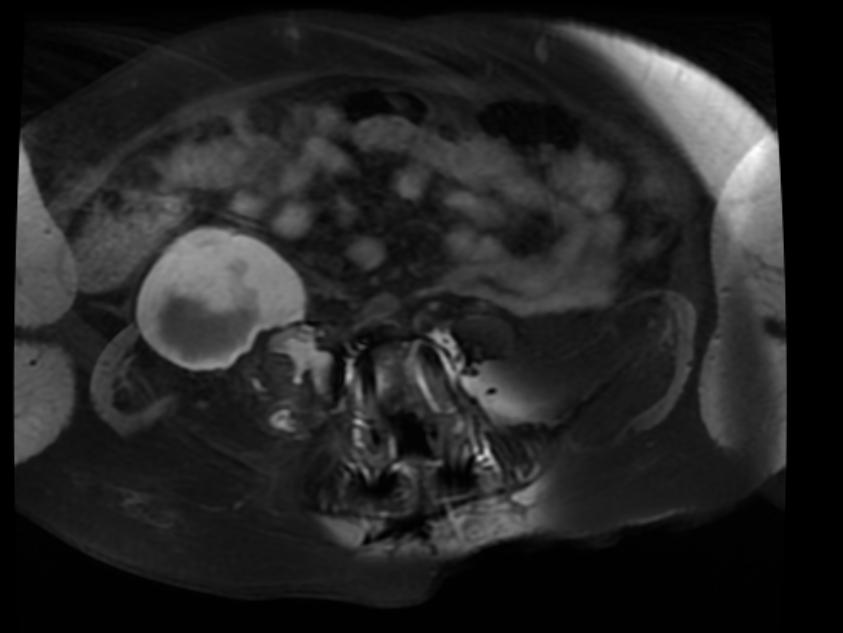
[http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki] | |||
===Patient #1=== | |||
[[Image:Psoas-hematoma-001.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Hematoma in Psoas muscles]] | |||
<br clear="left"/> | |||
[[Image:Psoas-hematoma-002.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Hematoma in Psoas muscles]] | |||
<br clear="left"/> | |||
===Patient #2=== | |||
[[Image:Retroperitoneal_hematoma_MRI_001.jpg|thumb|350px|left|MRI demonstrates a right sided retroperitoneal hematoma ]] | |||
<br clear="left"/> | |||
[[Image:Retroperitoneal_hematoma_MRI_002.jpg|thumb|350px|left|MRI demonstrates a right sided retroperitoneal hematoma ]] | |||
<br clear="left"/> | |||
[[Image:Retroperitoneal_hematoma_MRI_003.jpg|thumb|350px|left|MRI demonstrates a right sided retroperitoneal hematoma ]] | |||
<br clear="left"/> | |||
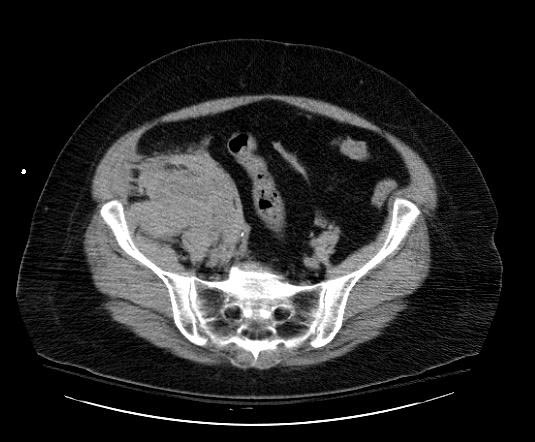
=== | ===Patient #3=== | ||
[[Image:Retroperitoneal-hematoma-001.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Retroperitoneal hematoma: The first sign was hypotension after cardiac catheterization]] | |||
<br clear="left"/> | |||
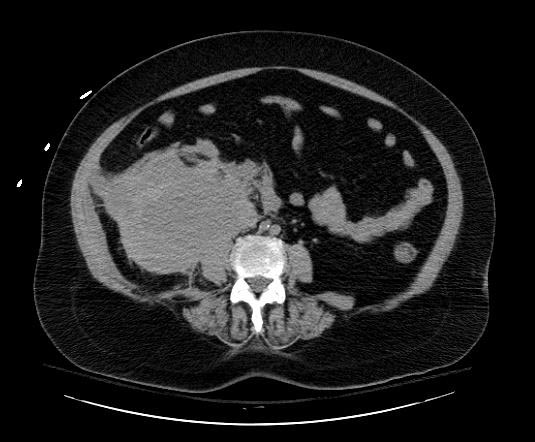
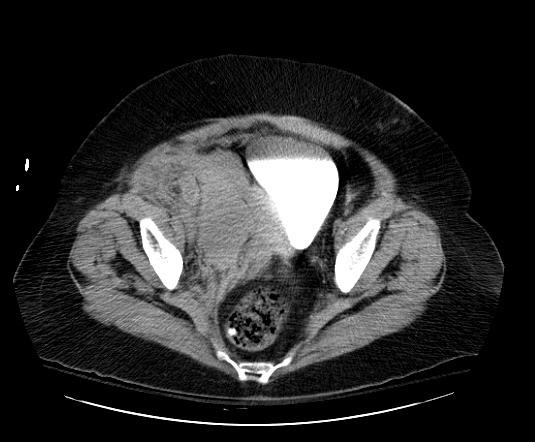
< | [[Image:Retroperitoneal-hematoma-002.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Retroperitoneal hematoma: The first sign was hypotension after cardiac catheterization]] | ||
Image: | <br clear="left"/> | ||
Image: | |||
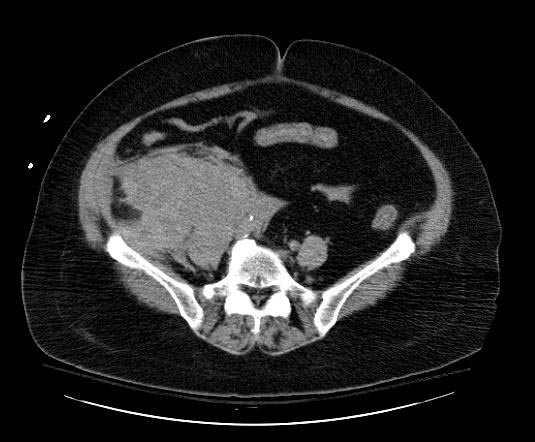
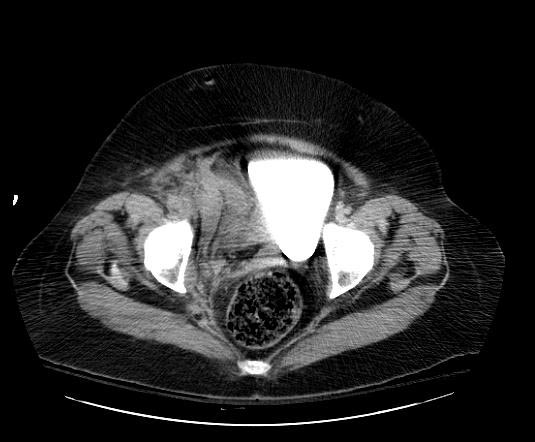
Image: | [[Image:Retroperitoneal-hematoma-003.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Retroperitoneal hematoma: The first sign was hypotension after cardiac catheterization]] | ||
</ | <br clear="left"/> | ||
[[Image:Retroperitoneal-hematoma-004.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Retroperitoneal hematoma: The first sign was hypotension after cardiac catheterization]] | |||
<br clear="left"/> | |||
[[Image:Retroperitoneal-hematoma-005.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Retroperitoneal hematoma: The first sign was hypotension after cardiac catheterization]] | |||
<br clear="left"/> | |||
[[Image:Retroperitoneal-hematoma-006.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Retroperitoneal hematoma: The first sign was hypotension after cardiac catheterization]] | |||
<br clear="left"/> | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
===Medical Therapy=== | |||
===Pharmacologic=== | ===Pharmacologic=== | ||
====Discontinuation of anti-coagulation==== | ====Discontinuation of anti-coagulation==== | ||
If possible, anticoagulation therapy including both anti-thrombins and anti-platelet agents should be discontinued. One exception is if the patient has had a coronary stent placed, in which case dual anti-platelet therapy should be continued if at all possible. If [[Clopidogrel]] must be discontinued, then low dose [[aspirin]] should be continued in a patient with a fresh stent. | |||
If possible anticoagulation therapy including both | |||
====Reversal of anti-coagulation==== | ====Reversal of anti-coagulation==== | ||
===== Antithrombins===== | ===== Antithrombins===== | ||
If the patient has received unfractionated [[heparin]], [[protamine]] can be used to reverse the [[heparin]]. [[Protamine]] does partially reverse [[enoxaparin]] as well. [[Bivalirudin]] has a fairly short half-life, and does not require reversal. | If the patient has received unfractionated [[heparin]], [[protamine]] can be used to reverse the [[heparin]]. [[Protamine]] does partially reverse [[enoxaparin]] as well. [[Bivalirudin]] has a fairly short half-life, and does not require reversal. | ||
===== Antiplatelets===== | ===== Antiplatelets===== | ||
If the antiplatelet effects must be overcome acutely, then a platelet transfusion can be administered. However, if the antiplatelet agents on board do not bind avidly to the platelets, then these agents can then bind to the new platelets that have just been transfused. Small molecule 2b3a inhibitors such as [[eptifibatide]] and [[Aggrastat]] are examples of these types of agents. Agents that permanently inhibit the platelet such as [[aspirin]] and [[Clopidogrel]] can take up to five days to reverse (the time that it takes for new platelets to form). | If the antiplatelet effects must be overcome acutely, then a platelet transfusion can be administered. However, if the antiplatelet agents on board do not bind avidly to the platelets, then these agents can then bind to the new platelets that have just been transfused. Small molecule 2b3a inhibitors such as [[eptifibatide]] and [[Aggrastat]] are examples of these types of agents. Agents that permanently inhibit the platelet such as [[aspirin]] and [[Clopidogrel]] can take up to five days to reverse (the time that it takes for new platelets to form). | ||
=== Surgery=== | === Surgery=== | ||
After blunt trauma, selected retroperitoneal hematomas in the lateral perirenal and pelvic areas do not require operation and should not be opened if discovered at operation. Midline, lateral paraduodenal, lateral pericolonic not associated with pelvic, and portal hematomas are opened after proximal vascular control has been obtained, if appropriate. | After blunt trauma, selected retroperitoneal hematomas in the lateral perirenal and pelvic areas do not require operation and should not be opened if discovered at operation. Midline, lateral paraduodenal, lateral pericolonic not associated with pelvic, and portal hematomas are opened after proximal vascular control has been obtained, if appropriate. | ||
Retrohepatic hematomas without obvious active hemorrhage are not opened. After penetrating trauma, most retroperitoneal hematomas are still opened. Exceptions include isolated lateral perirenal hematomas that have been carefully staged by CT and some lateral pericolonic hematomas. As with blunt trauma, retrohepatic hematomas without obvious active hemorrhage are not opened. | Retrohepatic hematomas without obvious active hemorrhage are not opened. After penetrating trauma, most retroperitoneal hematomas are still opened. Exceptions include isolated lateral perirenal hematomas that have been carefully staged by CT and some lateral pericolonic hematomas. As with blunt trauma, retrohepatic hematomas without obvious active hemorrhage are not opened. | ||
==References== | |||
{{refbegin|2}} | |||
* Petersen JL, Mahaffey KW, Hasselblad V, Antman EM, Cohen M, Goodman SG, et al. Efficacy and Bleeding Complications Among Patients Randomized to Enoxaparin or Unfractionated Heparin for Antithrombin Therapy in Non–ST-Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Systematic Overview. JAMA 2004 Jul 7; 292(1): 89-96. | |||
* Jeong TK, Jeong GH, Park BS, Ma SK, Kim SW, Kim NH, et al. Dalteparin-sodium associated retroperitoneal hematoma in a patient with diabetic nephropathy. Korean J Med 2003 64: 322-7. | |||
* Collet JP, Montalescot G, Fine E, Golmard JL, Dalby M, Choussat R, et al. Enoxaparin in unstable angina patients who would have been excluded from randomized pivotal trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003 Jan 1; 41(1): 8-14. | |||
* Spinler SA, Inverso SM, Cohen M, Goodman SG, Stringer KA, Antman EM. Safety and efficacy of unfractionated heparin vs. enoxaparin in patients who are obese and patients with severe renal impairment: Analysis from the ESSENCE and TIMI 11B studies. Am Heart J 2003 Jul;146(1):33-41. | |||
* A Vayá, Y Mira, J Aznar. Enoxaparin-related fatal spontaneous retroperitoneal hematoma in the elderly. Thromb Res 2003 Apr 15; 110(1): 69-71. | |||
* The SYNERGY Trial Investigators. Enoxaparin vs unfractionated heparin in high-risk patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes managed with an intended early invasive strategy: Primary results of the SYNERGY randomized trial. JAMA 2004 Jul 7; 292(1): 45-54. | |||
* Lemos JA, Blazing MA, Wiviott SD, Brady WE, White HD, Fox KA, et al. Enoxaparin versus unfractionated heparin in patients treated with tirofiban, aspirin and an early conservative initial management strategy: Results from the A phase of the A-to-Z trial. Eur Heart J 2004 Oct 25(19): 1688-94. | |||
* Cadroy Y, Pourrat J, Baladre MF, Saivin S, Houin G, Montastruc JL, et al. Delayed elimination of enoxaparin in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. Thromb Res 1991 Aug 1;63(3):385-90. | |||
* Antman EM, Morrow DA, McCabe CH, Murphy SA, Ruda M, Sadowski Z, et al. Enoxaparin versus Unfractionated Heparin with Fibrinolysis for ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. N Engl J Med 2006 Apr 6;354(14): 1477-88. | |||
{{ | * Gonzalez C, Penado S, Llata L, Valero C, Riancho JA. The clinical spectrum of retroperitoneal hematoma in anticoagulated patients. Medicine 2003 Jul 82(4):257-62. | ||
{{refend}} | |||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
{{ | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
{{ | |||
{{WH}} | |||
{{WS}} | |||
Latest revision as of 19:32, 29 October 2019
| Retroperitoneal hematoma | |
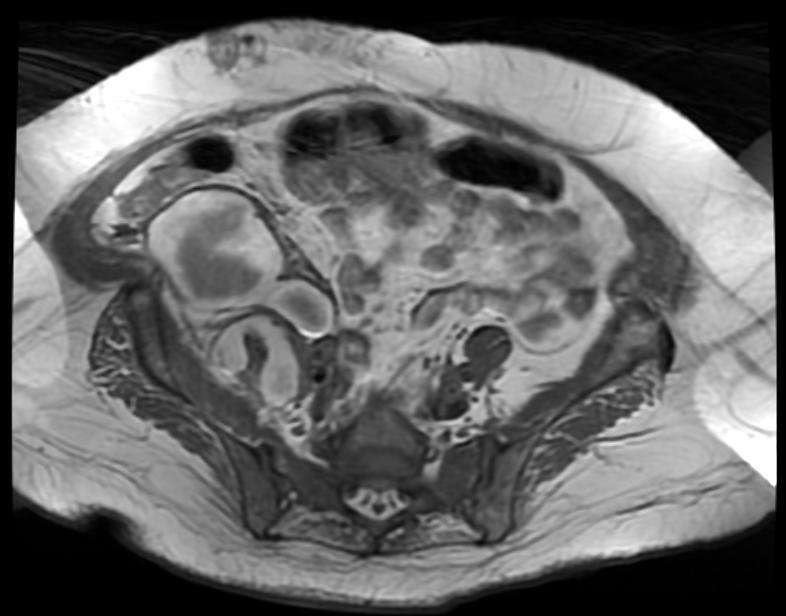 | |
|---|---|
| Retroperitoneal hematoma. (Image courtesy of RadsWiki) |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
Retroperitoneal hemorrhage and retroperitoneal hematoma are potentially life-threatening conditions. Common causes of retroperitoneal hemorrhage are cardiac catheterization and trauma.
Symptoms
The patient may complain of intense flank pain or back pain.
Signs
The patient may develop tachycardia and hypotension if the rate of hemorrhage is rapid.
Rarely, later in the course, the patient may develop a Grey-Turner's sign with bulging flanks, and a bluish discoloration in the region of the flank. Again, it should be emphasized that this sign appears 24 to 48 hours after a severe retroperitoneal bleed and should not be used to gauge whether a retroperitoneal bleed is present acutely.
Differentiating retroperitoneal heamatoma from other diseases
| Disease | Clinical feature | Laboratory findings | Imaging findings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | Weight loss | Abdominal pain | |||
| Retroperitoneal hematoma | _ | _ | ✔ | Anemia | MRI is the best radiologic tool to differentiate between retroperitoneal masses. |
| Retroperitoneal abscess | ✔ | _ | ✔ | Leukocytosis, positive inflammatory markers | |
| Retroperitoneal tumors (.e.g. liposarcoma) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | positive tumor marker | |
| Chronic pancreatitis | _ | ✔ | ✔ | DM type II, amylase and lipase levels may be slightly elevated | |
Diagnostic FindingsPatient #1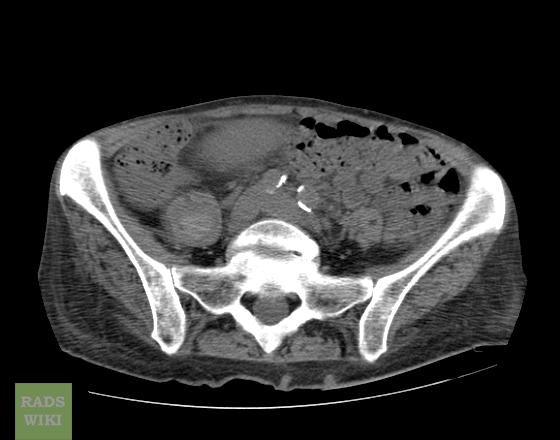
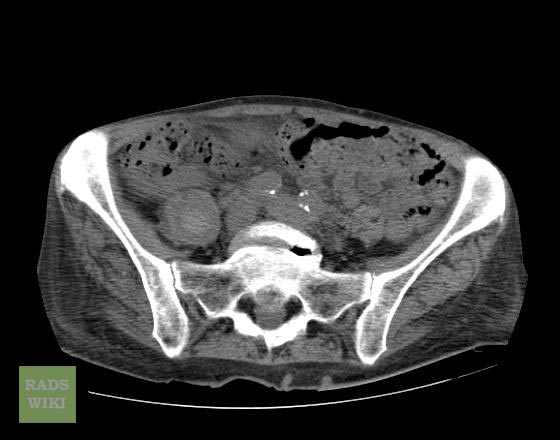
Patient #2
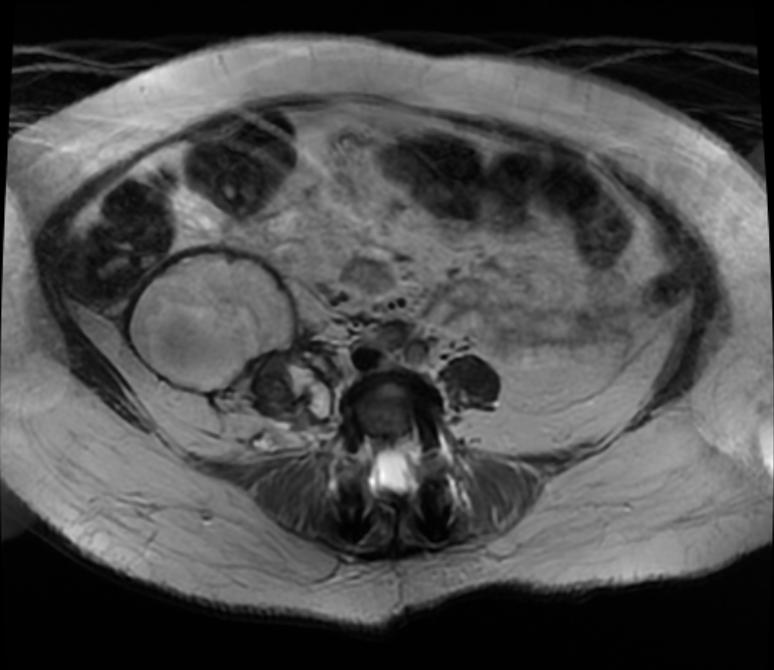
Patient #3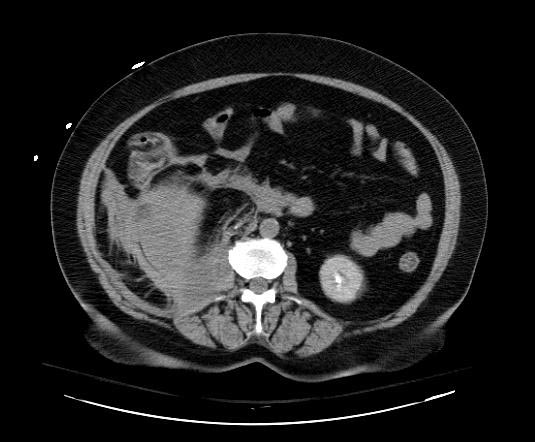
TreatmentMedical TherapyPharmacologicDiscontinuation of anti-coagulationIf possible, anticoagulation therapy including both anti-thrombins and anti-platelet agents should be discontinued. One exception is if the patient has had a coronary stent placed, in which case dual anti-platelet therapy should be continued if at all possible. If Clopidogrel must be discontinued, then low dose aspirin should be continued in a patient with a fresh stent. Reversal of anti-coagulationAntithrombinsIf the patient has received unfractionated heparin, protamine can be used to reverse the heparin. Protamine does partially reverse enoxaparin as well. Bivalirudin has a fairly short half-life, and does not require reversal. AntiplateletsIf the antiplatelet effects must be overcome acutely, then a platelet transfusion can be administered. However, if the antiplatelet agents on board do not bind avidly to the platelets, then these agents can then bind to the new platelets that have just been transfused. Small molecule 2b3a inhibitors such as eptifibatide and Aggrastat are examples of these types of agents. Agents that permanently inhibit the platelet such as aspirin and Clopidogrel can take up to five days to reverse (the time that it takes for new platelets to form). SurgeryAfter blunt trauma, selected retroperitoneal hematomas in the lateral perirenal and pelvic areas do not require operation and should not be opened if discovered at operation. Midline, lateral paraduodenal, lateral pericolonic not associated with pelvic, and portal hematomas are opened after proximal vascular control has been obtained, if appropriate. Retrohepatic hematomas without obvious active hemorrhage are not opened. After penetrating trauma, most retroperitoneal hematomas are still opened. Exceptions include isolated lateral perirenal hematomas that have been carefully staged by CT and some lateral pericolonic hematomas. As with blunt trauma, retrohepatic hematomas without obvious active hemorrhage are not opened. References
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||