Sorbitol: Difference between revisions
m Protected "Sorbitol": Protecting pages from unwanted edits ([edit=sysop] (indefinite) [move=sysop] (indefinite)) |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{chembox | ||
| ImageFile = | | Verifiedfields = changed | ||
| ImageSize = | | Watchedfields = changed | ||
| IUPACName = | | verifiedrevid = 477859013 | ||
| OtherNames = | | ImageFile = Sorbitol.png | ||
| ImageSize = 220px | |||
| ImageFile1 = 800px-Sorbitol-3D-balls.png | |||
| ImageSize1 = 220px | |||
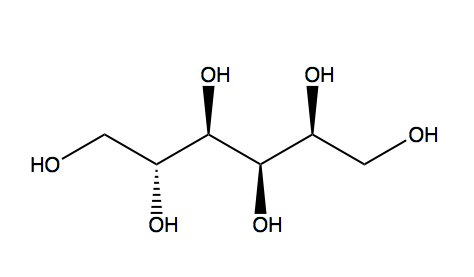
| IUPACName = (2''S'',3''R'',4''R'',5''R'')-Hexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol | |||
| OtherNames = <small>D</small>-glucitol; <small>D</small>-Sorbitol; Sorbogem; Sorbo | |||
| Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| CASNo = 50-70-4 | | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| PubChem = | | ChemSpiderID = 96680 | ||
| SMILES = | | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | ||
| ChEMBL = 1682 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = 506T60A25R | |||
| InChI = 1/C6H12O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h3,5-9,11-12H,1-2H2/t3-,5+,6+/m1/s1 | |||
| InChIKey = BJHIKXHVCXFQLS-PYWDMBMJBD | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h3,5-9,11-12H,1-2H2/t3-,5+,6+/m1/s1 | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey = BJHIKXHVCXFQLS-PYWDMBMJSA-N | |||
| CASNo = 50-70-4 | |||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | |||
| PubChem = 5780 | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank = DB01638 | |||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEBI = 17317 | |||
| SMILES = OC([C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO)CO | |||
| MeSHName = Sorbitol | | MeSHName = Sorbitol | ||
| ATCCode_prefix = A06 | |||
| ATCCode_suffix = AD18 | |||
| ATC_Supplemental = {{ATC|A06|AG07}} {{ATC|B05|CX02}} {{ATC|V04|CC01}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| | | C=6|H=14|O=6 | ||
| MolarMass = 182.17 g/mol | | MolarMass = 182.17 g/mol | ||
| Appearance = | | Appearance = white crystalline powder | ||
| Density = | | Density = 1.489 g/cm³ | ||
| | | MeltingPtC = 111 | ||
| | | Solubility = 2350 g/L | ||
| BoilingPtC = 290-295 | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Section3 = {{Chembox Hazards | | Section3 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| | | NFPA-H = 2 | ||
| NFPA-F = 1 | |||
| NFPA-R = 0 | |||
| MainHazards = | | MainHazards = | ||
| | | FlashPtC = 100 | ||
| | | AutoignitionC = 150 | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{SI}} | {{SI}} | ||
{{Details0|Sorbitol (irrigation)}} | |||
{{CMG}} | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
'''Sorbitol''', also known as '''glucitol''', is a [[sugar alcohol]] the body | '''Sorbitol''', also known as '''glucitol''', is a [[sugar alcohol]] with a [[sweet]] [[taste]] which the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by [[Redox|reduction]] of [[glucose]], changing the [[aldehyde]] group to a [[hydroxyl]] group. Most sorbitol is made from [[corn syrup]], but it is also found in apples, pears, peaches, and prunes.<ref name=Teo>{{cite journal | pmid = 17132742 | year = 2006 | last1 = Teo | first1 = G | last2 = Suzuki | first2 = Y | last3 = Uratsu | first3 = SL | last4 = Lampinen | first4 = B | last5 = Ormonde | first5 = N | last6 = Hu | first6 = WK | last7 = Dejong | first7 = TM | last8 = Dandekar | first8 = AM | title = Silencing leaf sorbitol synthesis alters long-distance partitioning and apple fruit quality | volume = 103 | issue = 49 | pages = 18842–7 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.0605873103 | pmc = 1693749 | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America}}</ref> It is converted to fructose by [[Sorbitol-6-phosphate 2-dehydrogenase]]. Sorbitol is an [[isomer]] of [[mannitol]], another sugar alcohol; the two differ only in the orientation of the [[hydroxyl]] group on carbon 2.<ref name="Kearsley, M. W. pp 249-249">Kearsley, M. W.; Deis, R. C. Sorbitol and Mannitol. In Sweeteners and Sugar Alternatives in Food Technology; Ames: Oxford, 2006; pp 249-249-261.</ref> While similar, the two sugar alcohols have very different sources in nature, melting points, and uses. | ||
==Uses== | |||
===Sweetener=== | |||
Sorbitol is a [[sugar substitute]]. It may be listed under the inactive ingredients listed for some foods and products. Its [[List of food additives, Codex Alimentarius|INS number]] and [[E number]] is 420. Sorbitol has approximately 60% the sweetness of sucrose (table sugar).<ref>[[Sugar substitute]]</ref> | |||
Sorbitol is referred to as a nutritive sweetener because it provides dietary energy: 2.6 [[kilocalorie]]s (11 [[kilojoule]]s) per [[gram]] versus the average 4 kilocalories (17 kilojoules) for carbohydrates. It is often used in [[diet food]]s (including diet drinks and ice cream), mints, [[cough syrup]]s, and sugar-free [[chewing gum]].<ref>{{cite book |last=Campbell |first= |last2=Farrell |first2= |title=Biochemistry |location= |publisher=Brooks/Cole |edition=Seventh |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-111-42564-7 }}</ref> | |||
It also occurs naturally in many [[drupe|stone fruit]]s and berries from trees of the genus ''[[Sorbus]]''.<ref>{{cite book |last=Nelson |first= |last2=Cox |first2= |title=Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry |location=New York |publisher=W. H. Freeman |edition=Fourth |year=2005 |isbn=0-7167-4339-6 }}</ref> | |||
== | ===Laxative=== | ||
Sorbitol can be used as a non-stimulant [[laxative]] | Sorbitol can be used as a non-stimulant [[laxative]] via an oral suspension or [[enema]]. As with other [[sugar alcohol]]s, gastrointestinal distress may result when food products that contain sorbitol are consumed. Sorbitol exerts its laxative effect by drawing water into the [[large intestine]], thereby stimulating [[bowel movements]].<ref>[http://www.cancer.org/docroot/CDG/content/CDG_sorbitol.asp ACS :: Cancer Drug Guide: sorbitol<!--Bot generated title -->]</ref> Sorbitol has been determined safe for use by the elderly, although it is not recommended without consultation with a clinician.<ref>{{cite journal | pmid= 7663066 | year= 1995 | last1= Lederle | first1= FA | title= Epidemiology of constipation in elderly patients. Drug utilisation and cost-containment strategies | volume= 6 | issue= 6 | pages= 465–9 | journal= Drugs & aging | doi=10.2165/00002512-199506060-00006}}</ref> Sorbitol is found in some dried fruits and may contribute to the laxative effects of prunes.<ref>{{Cite journal | pmid = 11401245 | year = 2001 | last1 = Stacewicz-Sapuntzakis | first1 = M | last2 = Bowen | first2 = PE | last3 = Hussain | first3 = EA | last4 = Damayanti-Wood | first4 = BI | last5 = Farnsworth | first5 = NR | title = Chemical composition and potential health effects of prunes: a functional food? | volume = 41 | issue = 4 | pages = 251–86 | doi = 10.1080/20014091091814 | journal = Critical reviews in food science and nutrition}}</ref> Sorbitol was discovered initially in the fresh juice of mountain ash berries in 1872.<ref>{{cite book|last=Panda|first=H.|title=The Complete Book on Sugarcane Processing and By-Products of Molasses (with Analysis of Sugar, Syrup and Molasses)|year=2011|publisher=ASIA PACIFIC BUSINESS PRESS Inc|isbn=8178331446|page=416|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=2UM4AQAAQBAJ&dq=sorbitol+in+molasses&source=gbs_navlinks_s}}</ref> It is found in the fruits of apples, plums, pears, cherries, dates, peaches, and apricots. | ||
== | ===Medical applications=== | ||
Sorbitol is used in bacterial culture media to distinguish the pathogenic [[Escherichia coli O157:H7|''Escherichia coli'' O157:H7]] from most other strains of ''[[Escherichia coli|E. coli]]'', as it is usually incapable of fermenting sorbitol, but 93% of known ''E. coli'' strains are capable of doing so.<ref name=wells_1983_101>{{cite journal|author=Wells JG, Davis BR, Wachsmuth IK, et al.|title=Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype|journal=Journal of clinical microbiology|volume=18|issue=3|pages=512–20| date=September 1983 |pmid=6355145|pmc=270845|doi=|url=http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=6355145|quote=The organism does not ferment sorbitol; whereas 93% of E. coli of human origin are sorbitol positive}}</ref> | |||
A treatment using sorbitol and [[ion-exchange]] resin [[sodium polystyrene sulfonate]] (tradename Kayexalate), helps remove excess [[potassium]] ions when in a [[hyperkalaemia|hyperkalaemic]] state.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Rugolotto S, Gruber M, Solano PD, Chini L, Gobbo S, Pecori S |title=Necrotizing enterocolitis in a 850 gram infant receiving sorbitol-free sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate): clinical and histopathologic findings |journal=J Perinatol |volume=27 |issue=4 |pages=247–9 | date=April 2007 |pmid=17377608 |doi=10.1038/sj.jp.7211677 |url=}}</ref> The resin exchanges sodium ions for potassium ions in the bowel, while sorbitol helps to eliminate it. In 2010 the U.S. [[FDA]] issued a warning of increased risk for GI necrosis with this combination.<ref>http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/ucm186845.htm</ref> | |||
== | ===Health care, food, and cosmetic uses=== | ||
Sorbitol is | Sorbitol often is used in modern [[cosmetics]] as a [[humectant]] and [[thickener]].<ref>http://www.bttcogroup.in/sorbitol-70.html</ref> Sorbitol often is used in [[mouthwash]] and [[toothpaste]]. Some transparent [[gel]]s can be made only with sorbitol, as it has a [[refractive index]] sufficiently high for transparent formulations. It is also used frequently in "sugar free" chewing gum. | ||
Sorbitol is used as a [[cryoprotectant]] additive (mixed with [[sucrose]] and sodium poly[[phosphate]]s) in the manufacture of surimi, a highly refined | Sorbitol is used as a [[cryoprotectant]] additive (mixed with [[sucrose]] and sodium poly[[phosphate]]s) in the manufacture of [[surimi]], a highly refined fish paste most commonly produced from [[Alaska pollock]] (''Theragra chalcogramma''). {{Citation needed|date=October 2007}} It is also used as a humectant in some [[cigarette]]s.<ref>[http://www.gallaher-group.com/products/table3_display.asp?brand_name=Benson+%26+Hedges+Gold&brand_family=Benson+%26+Hedges&product_type=CIGARETTE&country=UNITED+KINGDOM Gallaher Group Plc - Ingredients<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> | ||
Sorbitol sometimes is used as a sweetener and humectant in cookies and other foods that are not identified as "dietary" items. | |||
===Miscellaneous uses=== | |||
A mixture of sorbitol and [[potassium nitrate]] has found some success as an amateur solid [[rocket fuel]].<ref>[http://www.nakka-rocketry.net/sorb.html Richard Nakka's Experimental Rocketry Web Site]</ref> | |||
Sorbitol is identified as a potential key chemical intermediate <ref> | Sorbitol is identified as a potential key chemical intermediate<ref>{{Cite journal | ||
| last1 = Metzger | first1 = Jürgen O. | |||
| title = Production of Liquid Hydrocarbons from Biomass | |||
| doi = 10.1002/anie.200502895 | |||
| journal = [[Angewandte Chemie]] International Edition | |||
| volume = 45 | |||
| issue = 5 | |||
| pages = 696–698 | |||
| year = 2006 | |||
}}</ref> for production of fuels from [[biomass]] resources. [[Carbohydrate]] fractions in biomass such as [[cellulose]] undergo sequential [[hydrolysis]] and [[hydrogenation]] in the presence of metal catalysts to produce sorbitol.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Shrotri|first=Abhijit|author2=Tanksale, Akshat |author3=Beltramini, Jorge Norberto |author4=Gurav, Hanmant |author5= Chilukuri, Satyanarayana V. |title=Conversion of cellulose to polyols over promoted nickel catalysts|journal=Catalysis Science & Technology|year=2012|volume=2|issue=9|pages=1852–1858|doi=10.1039/C2CY20119D}}</ref> Complete reduction of sorbitol opens the way to [[alkane]]s, such as [[hexane]], which can be used as a [[biofuel]]. Hydrogen required for this reaction can be produced by aqueous phase reforming of sorbitol.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Tanksale|first=Akshat|author2=Beltramini, Jorge Norberto |author3=Lu, GaoQing Max |title=A review of catalytic hydrogen production processes from biomass|journal=Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews|year=2010|volume=14|issue=1|pages=166–182|doi=10.1016/j.rser.2009.08.010}}</ref> | |||
:19 C<sub>6</sub> | :19 C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>14</sub>O<sub>6</sub> → 13 C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>14</sub> + 36 CO<sub>2</sub> + 42 H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
The above [[chemical reaction]] is [[exothermic reaction|exothermic]] | The above [[chemical reaction]] is [[exothermic reaction|exothermic]]; 1.5 [[mole (unit)|mole]]s of sorbitol generate approximately 1 mole of [[hexane]]. When hydrogen is co-fed, no [[carbon dioxide]] is produced. | ||
It is also added after [[electroporation]] of yeasts in transformation protocols, allowing the cells to recover by raising the osmolarity of the medium. | |||
== | ==Medical importance== | ||
[[Aldose reductase]] is the first enzyme in the [[Polyol pathway|sorbitol-aldose reductase pathway]]<ref>{{cite journal | pmid = 10783895 | year = 2000 | last1 = Nishikawa | first1 = T | last2 = Edelstein | first2 = D | last3 = Du | first3 = XL | last4 = Yamagishi | first4 = S | last5 = Matsumura | first5 = T | last6 = Kaneda | first6 = Y | last7 = Yorek | first7 = MA | last8 = Beebe | first8 = D | last9 = Oates | first9 = PJ | last10 = Oates | first10 = Peter J. | last11 = Hammes | first11 = Hans-Peter | last12 = Giardino | first12 = Ida | title = Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage | volume = 404 | issue = 6779 | pages = 787–90 | doi = 10.1038/35008121 | journal = Nature | display-authors = 8 }}</ref> responsible for the reduction of glucose to sorbitol, as well as the reduction of [[galactose]] to [[galactitol]]. Too much sorbitol trapped in retinal cells, the cells of the lens, and the [[Schwann cells]] that [[myelin]]ate peripheral nerves can damage these cells, leading to [[retinopathy]], [[cataract]]s and peripheral [[neuropathy]], respectively. Aldose reductase inhibitors, which are substances that prevent or slow the action of aldose reductase, are currently being investigated as a way to prevent or delay these complications, which frequently occur in the setting of long-term hyperglycemia that accompanies poorly controlled [[diabetes]]. It is thought that these agents may help to prevent the accumulation of intracellular sorbitol that leads to cellular damage in diabetics.<ref>[http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0876/is_n67/ai_14676055 Sorbitol: a hazard for diabetics? Nutrition Health Review]</ref> | |||
< | |||
==Adverse medical effects== | |||
Sorbitol may aggravate [[irritable bowel syndrome]]<ref>[http://www.ahealthyme.com/topic/ibs#s15 Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Causes and Treatment - What can aggravate my symptoms?]</ref> and similar [[gastrointestinal tract|gastrointestinal]] conditions, resulting in severe abdominal pain for those affected, even from small amounts ingested. | |||
It has been noted that the sorbitol added to SPS (sodium polystyrene sulfonate, used in the treatment of [[hyperkalemia]]) can cause complications in the GI tract, including bleeding, perforated colonic ulcers, ischemic colitis and colonic necrosis, particularly in patients with uremia. The authors of the paper in question cite a study on rats (both non-uremic and uremic) in which all uremic rats died on a sorbitol enema regimen, whilst uremic rats on non-sorbitol regimens - even with SPS included - showed no signs of colonic damage. In humans, it is suggested that the risk factors for sorbitol-induced damage include "... immunosuppression, hypovolemia, postoperative setting, hypotension after hemodialysis, and peripheral vascular disease." They conclude that SPS-sorbitol should be used with caution, and that "Physicians need to be aware of SPS-sorbitol GI side effects while managing hyperkalemia." <ref>http://www.practicalgastro.com/pdf/November10/ErfaniArticle.pdf</ref> | |||
==Overdose effects== | |||
Ingesting large amounts of sorbitol can lead to abdominal pain, [[flatulence]], and mild to severe [[diarrhea]].<ref>{{Cite journal | pmid = 17171792 | year = 2006 | last1 = Islam | first1 = MS | last2 = Sakaguchi | first2 = E | title = Sorbitol-based osmotic diarrhea: possible causes and mechanism of prevention investigated in rats | volume = 12 | issue = 47 | pages = 7635–41 | journal = World journal of gastroenterology : WJG}}</ref> Sorbitol ingestion of 20 grams (0.7 oz) per day as sugar-free gum has led to severe diarrhea leading to unintended weight loss of 11 kilograms (24 lb) in eight months, in a woman originally weighing 52 kilograms (115 lb); another patient required hospitalization after habitually consuming 30 grams (1 oz) per day.<ref name="titleSweetener Side Effects: Case Histories">{{cite web |url=http://www.webmd.com/diet/news/20080110/sweetener-side-effects-case-histories |title=Sweetener Side Effects: Case Histories |date=2008-01-10 | |||
|author=Kathleen Doheny|publisher=WebMD Medical News| | |||
accessdate=2008-01-10 |format= |work=}}</ref> | |||
==Compendial status== | |||
* [[European Pharmacopoeia]]<ref name=dsbtl>{{cite web | |||
| last = [[Sigma Aldrich]] | |||
| first = | |||
| authorlink = | |||
| title = D-Sorbitol | |||
| work = | |||
| publisher = | |||
| url = http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/ProductDetail.do?lang=en&N4=97336 | |||
| format = | |||
| doi = | |||
| accessdate = 6 July 2009 | |||
}}</ref> 6.1<ref name=ipe>{{cite web | |||
| last = [[European Pharmacopoeia]] | |||
| first = | |||
| authorlink = | |||
| title = Index, Ph Eur | |||
| work = | |||
| publisher = | |||
| url = https://www.edqm.eu/store/images/majbdd/200709201618250.6_1%20IndexE.pdf | |||
| format = | |||
| doi = | |||
| accessdate = 6 July 2009 }}</ref> | |||
* [[British Pharmacopoeia]] 2009<ref name=ib29>{{cite web | |||
| last = British Pharmacopoeia | |||
| first = | |||
| authorlink = | |||
| title = Index, BP 2009 | |||
| work = | |||
| publisher = | |||
| year = 2009 | |||
| url = http://www.pharmacopoeia.co.uk/pdf/2009_index.pdf | |||
| format = | |||
| doi = | |||
| accessdate = 6 July 2009 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Isosorbide dinitrate]] | |||
==References== | |||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
==External links== | |||
* [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe-srv/PDBeXplore/ligand/?ligand=SOR Sorbitol bound to proteins] in the [[Protein Data Bank|PDB]] | |||
{{Diagnostic agents}} | |||
{{Laxatives}} | |||
{{Fructose and galactose metabolism enzymes}} | |||
[[Category:Excipients]] | |||
[[Category:Laxatives]] | |||
[[Category:Osmotic diuretics]] | [[Category:Osmotic diuretics]] | ||
[[Category:Sugar alcohols]] | [[Category:Sugar alcohols]] | ||
[[Category:Sweeteners]] | [[Category:Sweeteners]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:01, 7 May 2015
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4R,5R)-Hexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol
| |
| Other names
D-glucitol; D-Sorbitol; Sorbogem; Sorbo
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | Lua error in Module:Wikidata at line 879: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). Lua error in Module:Wikidata at line 879: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| MeSH | Sorbitol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14O6 | |
| Molar mass | 182.17 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Sorbitol |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Sorbitol |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Sorbitol at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Sorbitol at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Sorbitol
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Sorbitol Risk calculators and risk factors for Sorbitol
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Sorbitol |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Sorbitol, also known as glucitol, is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste which the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by reduction of glucose, changing the aldehyde group to a hydroxyl group. Most sorbitol is made from corn syrup, but it is also found in apples, pears, peaches, and prunes.[1] It is converted to fructose by Sorbitol-6-phosphate 2-dehydrogenase. Sorbitol is an isomer of mannitol, another sugar alcohol; the two differ only in the orientation of the hydroxyl group on carbon 2.[2] While similar, the two sugar alcohols have very different sources in nature, melting points, and uses.
Uses
Sweetener
Sorbitol is a sugar substitute. It may be listed under the inactive ingredients listed for some foods and products. Its INS number and E number is 420. Sorbitol has approximately 60% the sweetness of sucrose (table sugar).[3]
Sorbitol is referred to as a nutritive sweetener because it provides dietary energy: 2.6 kilocalories (11 kilojoules) per gram versus the average 4 kilocalories (17 kilojoules) for carbohydrates. It is often used in diet foods (including diet drinks and ice cream), mints, cough syrups, and sugar-free chewing gum.[4]
It also occurs naturally in many stone fruits and berries from trees of the genus Sorbus.[5]
Laxative
Sorbitol can be used as a non-stimulant laxative via an oral suspension or enema. As with other sugar alcohols, gastrointestinal distress may result when food products that contain sorbitol are consumed. Sorbitol exerts its laxative effect by drawing water into the large intestine, thereby stimulating bowel movements.[6] Sorbitol has been determined safe for use by the elderly, although it is not recommended without consultation with a clinician.[7] Sorbitol is found in some dried fruits and may contribute to the laxative effects of prunes.[8] Sorbitol was discovered initially in the fresh juice of mountain ash berries in 1872.[9] It is found in the fruits of apples, plums, pears, cherries, dates, peaches, and apricots.
Medical applications
Sorbitol is used in bacterial culture media to distinguish the pathogenic Escherichia coli O157:H7 from most other strains of E. coli, as it is usually incapable of fermenting sorbitol, but 93% of known E. coli strains are capable of doing so.[10]
A treatment using sorbitol and ion-exchange resin sodium polystyrene sulfonate (tradename Kayexalate), helps remove excess potassium ions when in a hyperkalaemic state.[11] The resin exchanges sodium ions for potassium ions in the bowel, while sorbitol helps to eliminate it. In 2010 the U.S. FDA issued a warning of increased risk for GI necrosis with this combination.[12]
Health care, food, and cosmetic uses
Sorbitol often is used in modern cosmetics as a humectant and thickener.[13] Sorbitol often is used in mouthwash and toothpaste. Some transparent gels can be made only with sorbitol, as it has a refractive index sufficiently high for transparent formulations. It is also used frequently in "sugar free" chewing gum.
Sorbitol is used as a cryoprotectant additive (mixed with sucrose and sodium polyphosphates) in the manufacture of surimi, a highly refined fish paste most commonly produced from Alaska pollock (Theragra chalcogramma). [citation needed] It is also used as a humectant in some cigarettes.[14]
Sorbitol sometimes is used as a sweetener and humectant in cookies and other foods that are not identified as "dietary" items.
Miscellaneous uses
A mixture of sorbitol and potassium nitrate has found some success as an amateur solid rocket fuel.[15]
Sorbitol is identified as a potential key chemical intermediate[16] for production of fuels from biomass resources. Carbohydrate fractions in biomass such as cellulose undergo sequential hydrolysis and hydrogenation in the presence of metal catalysts to produce sorbitol.[17] Complete reduction of sorbitol opens the way to alkanes, such as hexane, which can be used as a biofuel. Hydrogen required for this reaction can be produced by aqueous phase reforming of sorbitol.[18]
- 19 C6H14O6 → 13 C6H14 + 36 CO2 + 42 H2O
The above chemical reaction is exothermic; 1.5 moles of sorbitol generate approximately 1 mole of hexane. When hydrogen is co-fed, no carbon dioxide is produced.
It is also added after electroporation of yeasts in transformation protocols, allowing the cells to recover by raising the osmolarity of the medium.
Medical importance
Aldose reductase is the first enzyme in the sorbitol-aldose reductase pathway[19] responsible for the reduction of glucose to sorbitol, as well as the reduction of galactose to galactitol. Too much sorbitol trapped in retinal cells, the cells of the lens, and the Schwann cells that myelinate peripheral nerves can damage these cells, leading to retinopathy, cataracts and peripheral neuropathy, respectively. Aldose reductase inhibitors, which are substances that prevent or slow the action of aldose reductase, are currently being investigated as a way to prevent or delay these complications, which frequently occur in the setting of long-term hyperglycemia that accompanies poorly controlled diabetes. It is thought that these agents may help to prevent the accumulation of intracellular sorbitol that leads to cellular damage in diabetics.[20]
Adverse medical effects
Sorbitol may aggravate irritable bowel syndrome[21] and similar gastrointestinal conditions, resulting in severe abdominal pain for those affected, even from small amounts ingested.
It has been noted that the sorbitol added to SPS (sodium polystyrene sulfonate, used in the treatment of hyperkalemia) can cause complications in the GI tract, including bleeding, perforated colonic ulcers, ischemic colitis and colonic necrosis, particularly in patients with uremia. The authors of the paper in question cite a study on rats (both non-uremic and uremic) in which all uremic rats died on a sorbitol enema regimen, whilst uremic rats on non-sorbitol regimens - even with SPS included - showed no signs of colonic damage. In humans, it is suggested that the risk factors for sorbitol-induced damage include "... immunosuppression, hypovolemia, postoperative setting, hypotension after hemodialysis, and peripheral vascular disease." They conclude that SPS-sorbitol should be used with caution, and that "Physicians need to be aware of SPS-sorbitol GI side effects while managing hyperkalemia." [22]
Overdose effects
Ingesting large amounts of sorbitol can lead to abdominal pain, flatulence, and mild to severe diarrhea.[23] Sorbitol ingestion of 20 grams (0.7 oz) per day as sugar-free gum has led to severe diarrhea leading to unintended weight loss of 11 kilograms (24 lb) in eight months, in a woman originally weighing 52 kilograms (115 lb); another patient required hospitalization after habitually consuming 30 grams (1 oz) per day.[24]
Compendial status
See also
References
- ↑ Teo, G; Suzuki, Y; Uratsu, SL; Lampinen, B; Ormonde, N; Hu, WK; Dejong, TM; Dandekar, AM (2006). "Silencing leaf sorbitol synthesis alters long-distance partitioning and apple fruit quality". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 103 (49): 18842–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605873103. PMC 1693749. PMID 17132742.
- ↑ Kearsley, M. W.; Deis, R. C. Sorbitol and Mannitol. In Sweeteners and Sugar Alternatives in Food Technology; Ames: Oxford, 2006; pp 249-249-261.
- ↑ Sugar substitute
- ↑ Campbell; Farrell (2011). Biochemistry (Seventh ed.). Brooks/Cole. ISBN 978-1-111-42564-7.
- ↑ Nelson; Cox (2005). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (Fourth ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-4339-6.
- ↑ ACS :: Cancer Drug Guide: sorbitol
- ↑ Lederle, FA (1995). "Epidemiology of constipation in elderly patients. Drug utilisation and cost-containment strategies". Drugs & aging. 6 (6): 465–9. doi:10.2165/00002512-199506060-00006. PMID 7663066.
- ↑ Stacewicz-Sapuntzakis, M; Bowen, PE; Hussain, EA; Damayanti-Wood, BI; Farnsworth, NR (2001). "Chemical composition and potential health effects of prunes: a functional food?". Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. 41 (4): 251–86. doi:10.1080/20014091091814. PMID 11401245.
- ↑ Panda, H. (2011). The Complete Book on Sugarcane Processing and By-Products of Molasses (with Analysis of Sugar, Syrup and Molasses). ASIA PACIFIC BUSINESS PRESS Inc. p. 416. ISBN 8178331446.
- ↑ Wells JG, Davis BR, Wachsmuth IK; et al. (September 1983). "Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype". Journal of clinical microbiology. 18 (3): 512–20. PMC 270845. PMID 6355145.
The organism does not ferment sorbitol; whereas 93% of E. coli of human origin are sorbitol positive
- ↑ Rugolotto S, Gruber M, Solano PD, Chini L, Gobbo S, Pecori S (April 2007). "Necrotizing enterocolitis in a 850 gram infant receiving sorbitol-free sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate): clinical and histopathologic findings". J Perinatol. 27 (4): 247–9. doi:10.1038/sj.jp.7211677. PMID 17377608.
- ↑ http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/ucm186845.htm
- ↑ http://www.bttcogroup.in/sorbitol-70.html
- ↑ Gallaher Group Plc - Ingredients
- ↑ Richard Nakka's Experimental Rocketry Web Site
- ↑ Metzger, Jürgen O. (2006). "Production of Liquid Hydrocarbons from Biomass". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 45 (5): 696–698. doi:10.1002/anie.200502895.
- ↑ Shrotri, Abhijit; Tanksale, Akshat; Beltramini, Jorge Norberto; Gurav, Hanmant; Chilukuri, Satyanarayana V. (2012). "Conversion of cellulose to polyols over promoted nickel catalysts". Catalysis Science & Technology. 2 (9): 1852–1858. doi:10.1039/C2CY20119D.
- ↑ Tanksale, Akshat; Beltramini, Jorge Norberto; Lu, GaoQing Max (2010). "A review of catalytic hydrogen production processes from biomass". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 14 (1): 166–182. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2009.08.010.
- ↑ Nishikawa, T; Edelstein, D; Du, XL; Yamagishi, S; Matsumura, T; Kaneda, Y; Yorek, MA; Beebe, D; et al. (2000). "Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage". Nature. 404 (6779): 787–90. doi:10.1038/35008121. PMID 10783895.
- ↑ Sorbitol: a hazard for diabetics? Nutrition Health Review
- ↑ Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Causes and Treatment - What can aggravate my symptoms?
- ↑ http://www.practicalgastro.com/pdf/November10/ErfaniArticle.pdf
- ↑ Islam, MS; Sakaguchi, E (2006). "Sorbitol-based osmotic diarrhea: possible causes and mechanism of prevention investigated in rats". World journal of gastroenterology : WJG. 12 (47): 7635–41. PMID 17171792.
- ↑ Kathleen Doheny (2008-01-10). "Sweetener Side Effects: Case Histories". WebMD Medical News. Retrieved 2008-01-10.
- ↑ Sigma Aldrich. "D-Sorbitol". Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- ↑ European Pharmacopoeia. "Index, Ph Eur" (PDF). Retrieved 6 July 2009.
- ↑ British Pharmacopoeia (2009). "Index, BP 2009" (PDF). Retrieved 6 July 2009.
External links
- Sorbitol bound to proteins in the PDB
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al.
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- Articles without KEGG source
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Chembox
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from October 2007
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Excipients
- Laxatives
- Osmotic diuretics
- Sugar alcohols
- Sweeteners