Leukotriene B4
|
WikiDoc Resources for Leukotriene B4 |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Leukotriene B4 Most cited articles on Leukotriene B4 |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Leukotriene B4 |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Leukotriene B4 at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Leukotriene B4 Clinical Trials on Leukotriene B4 at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Leukotriene B4 NICE Guidance on Leukotriene B4
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Leukotriene B4 Discussion groups on Leukotriene B4 Patient Handouts on Leukotriene B4 Directions to Hospitals Treating Leukotriene B4 Risk calculators and risk factors for Leukotriene B4
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Leukotriene B4 |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
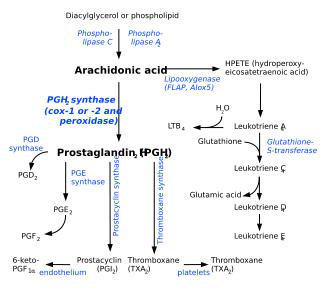
Leukotriene B4 is a leukotriene involved in inflammation. It is produced from leukocytes in response to inflammatory mediators and is able to induce the adhesion and activation of leukocytes on the endothelium, allowing them to bind to and cross it into the tissue[1]. In neutrophils, it is also a potent chemoattractant, and is able to induce the formation of reactive oxygen species and the release of lysosome enzymes by these cells[1].
References