Bacterial pneumonia chest x ray
|
Bacterial pneumonia Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Bacterial pneumonia chest x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Bacterial pneumonia chest x ray |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Bacterial pneumonia chest x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Arooj Naz, M.B.B.S
Overview
Imaging with chest x-rays remains as the gold standard of diagnosis when supported with other laboratory findings. Although x-rays provide reliable findings, it is recommended that the entire clinical picture along with supporting laboratory findings be taken into consideration before treatment is started. Patterns commonly found on imaging include lobar or focal nonsegmental pneumonia, lobular or multifocal bronchopneumonia, and diffuse or interstitial (atypical) pneumonia. Radiological findings may take 6-12 weeks to clear.
Chest X-Ray
| Type of Pneumonia[1] | Common Organisms[2] | Chest X-Ray | Typical Findings[3] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lobar/ Focal non-segmental | Klebsiella pneumoniae | 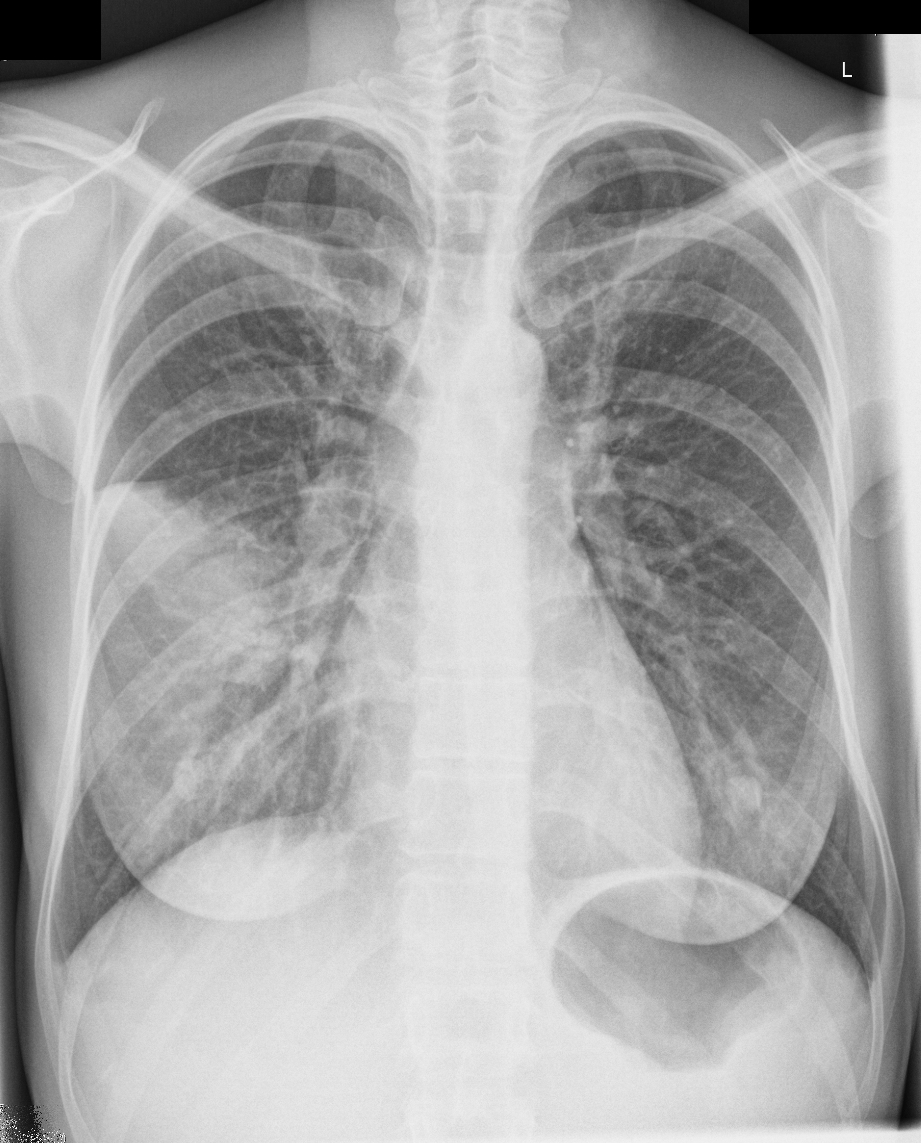 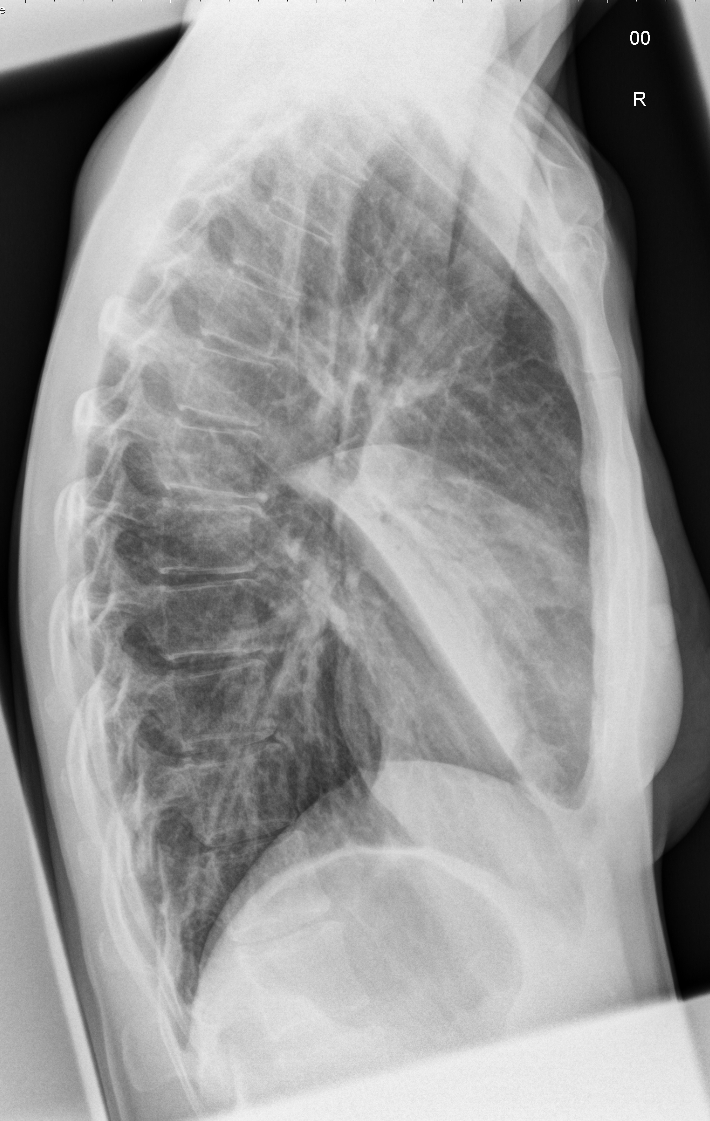 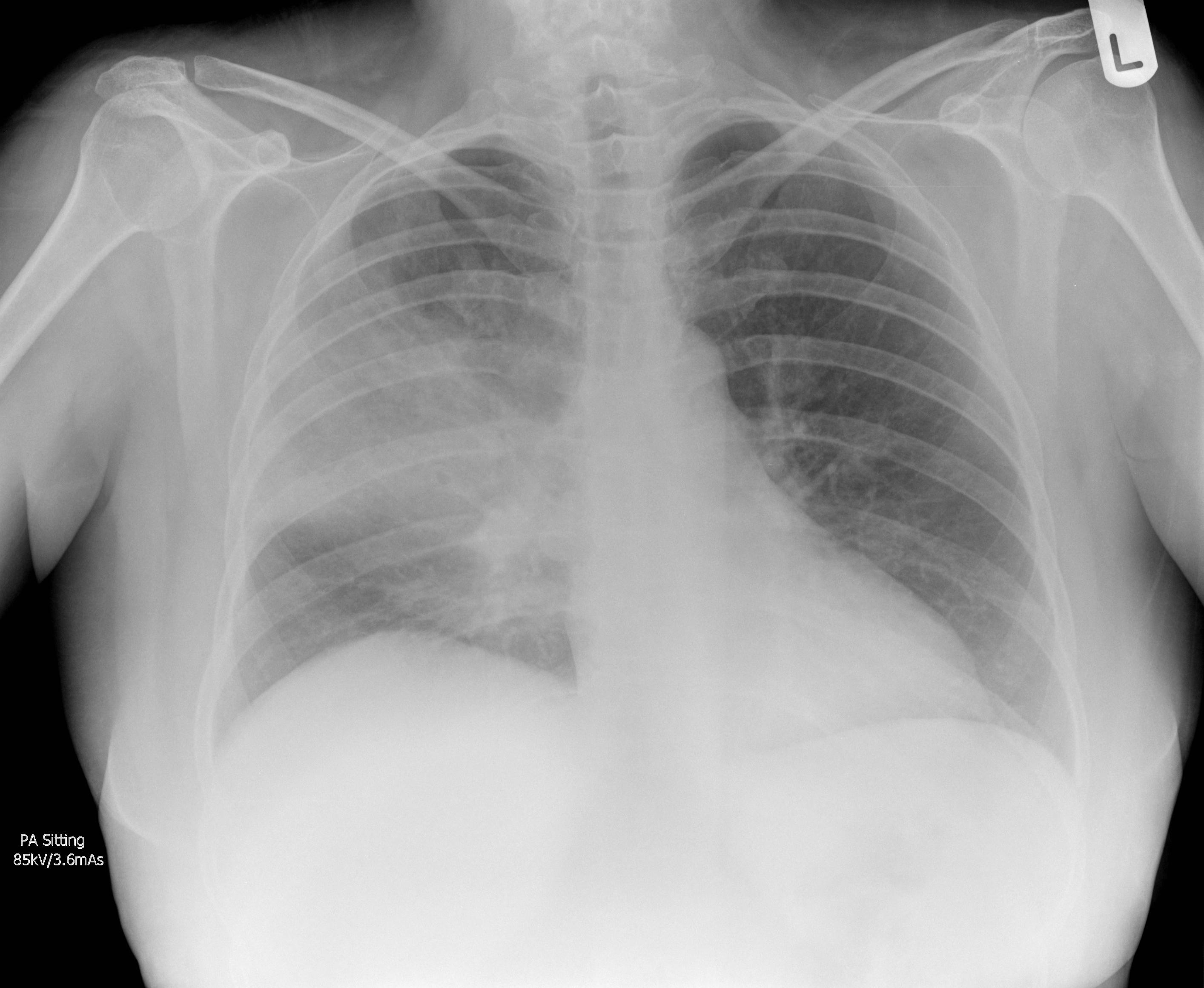 |
|
| Lobular/ Multifocal Bronchopneumonia | Staphylococcus aureus | 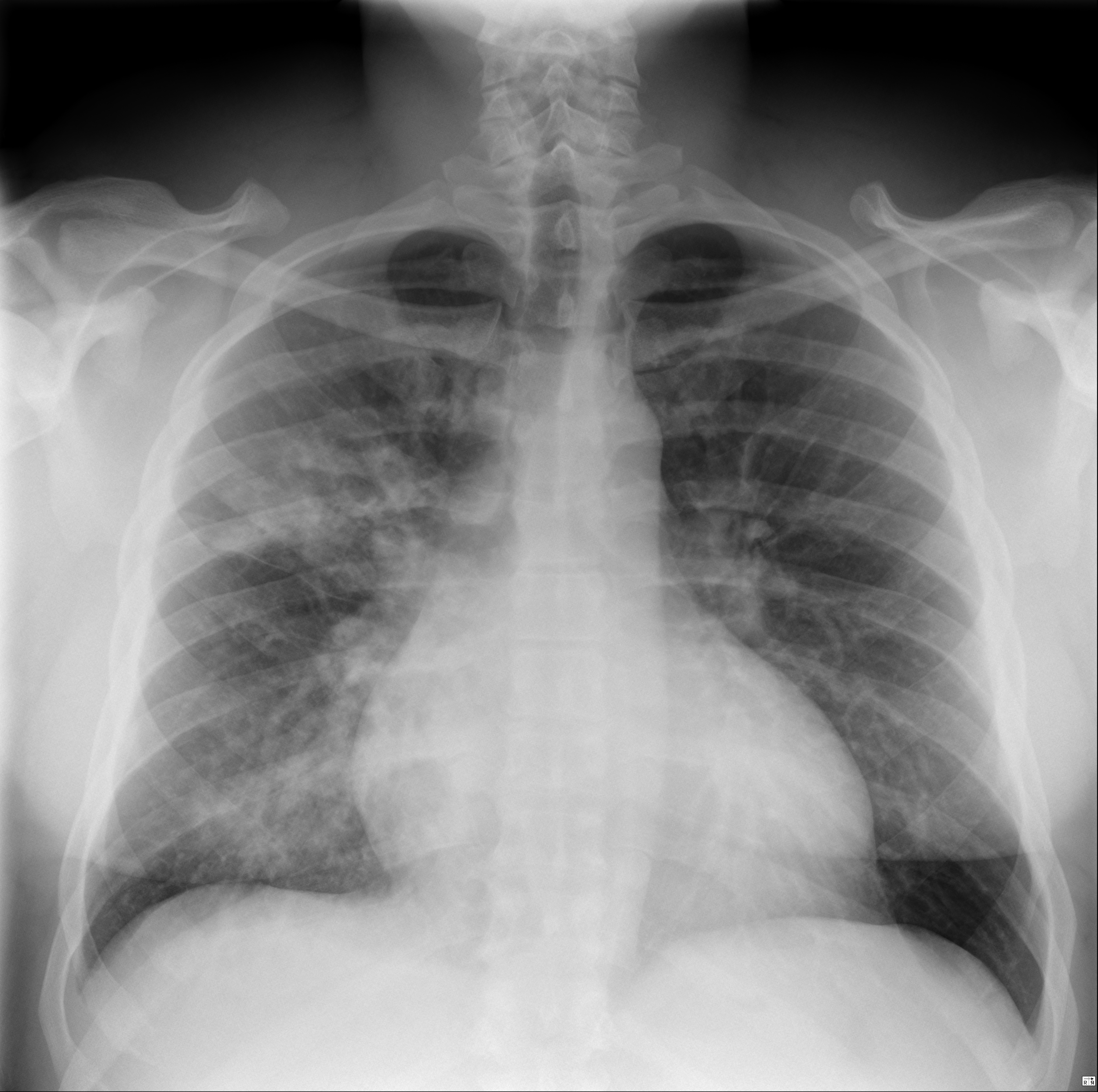 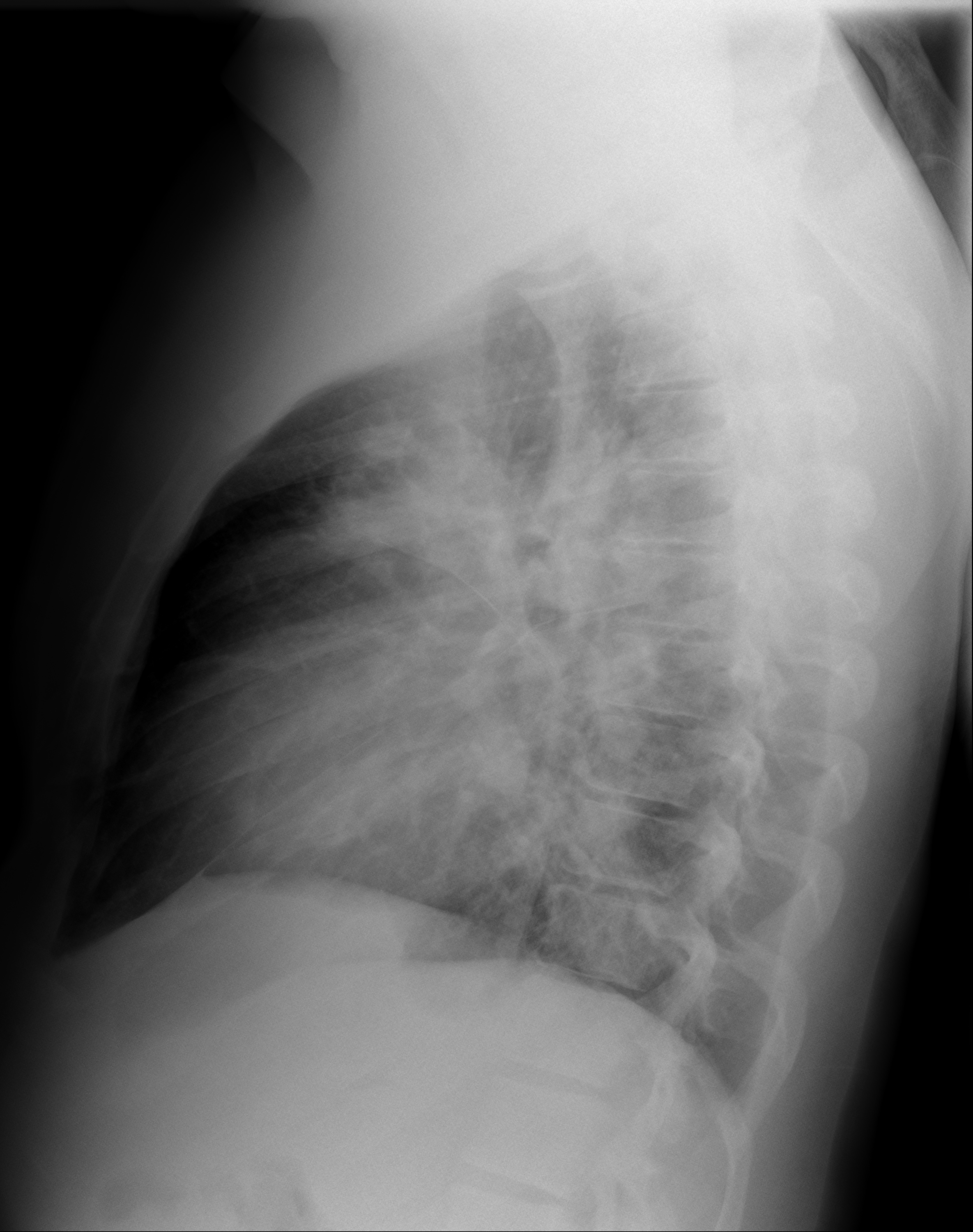 |
|
| Diffuse/ Interstitial (Atypical) | Mycoplasma | 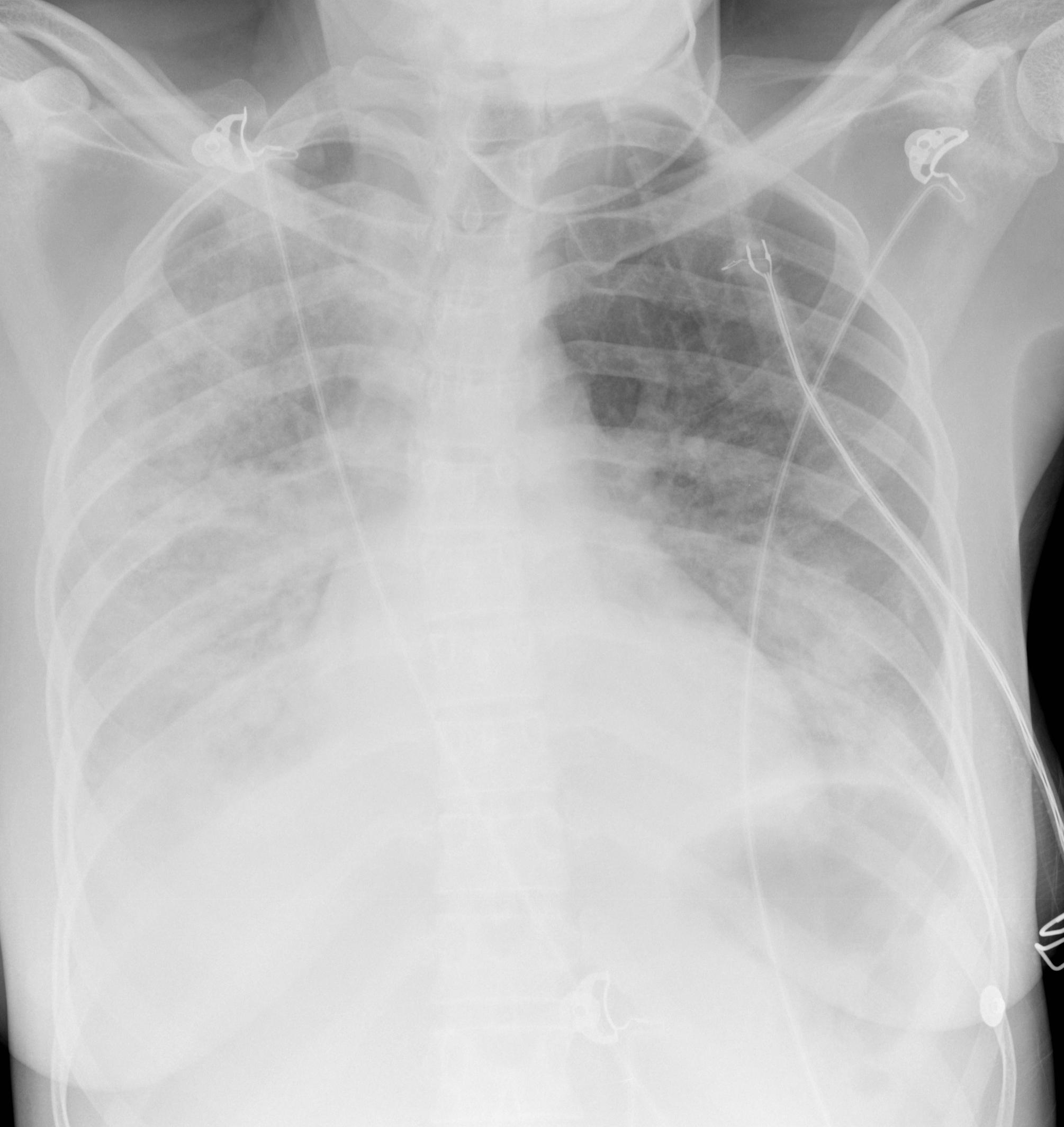 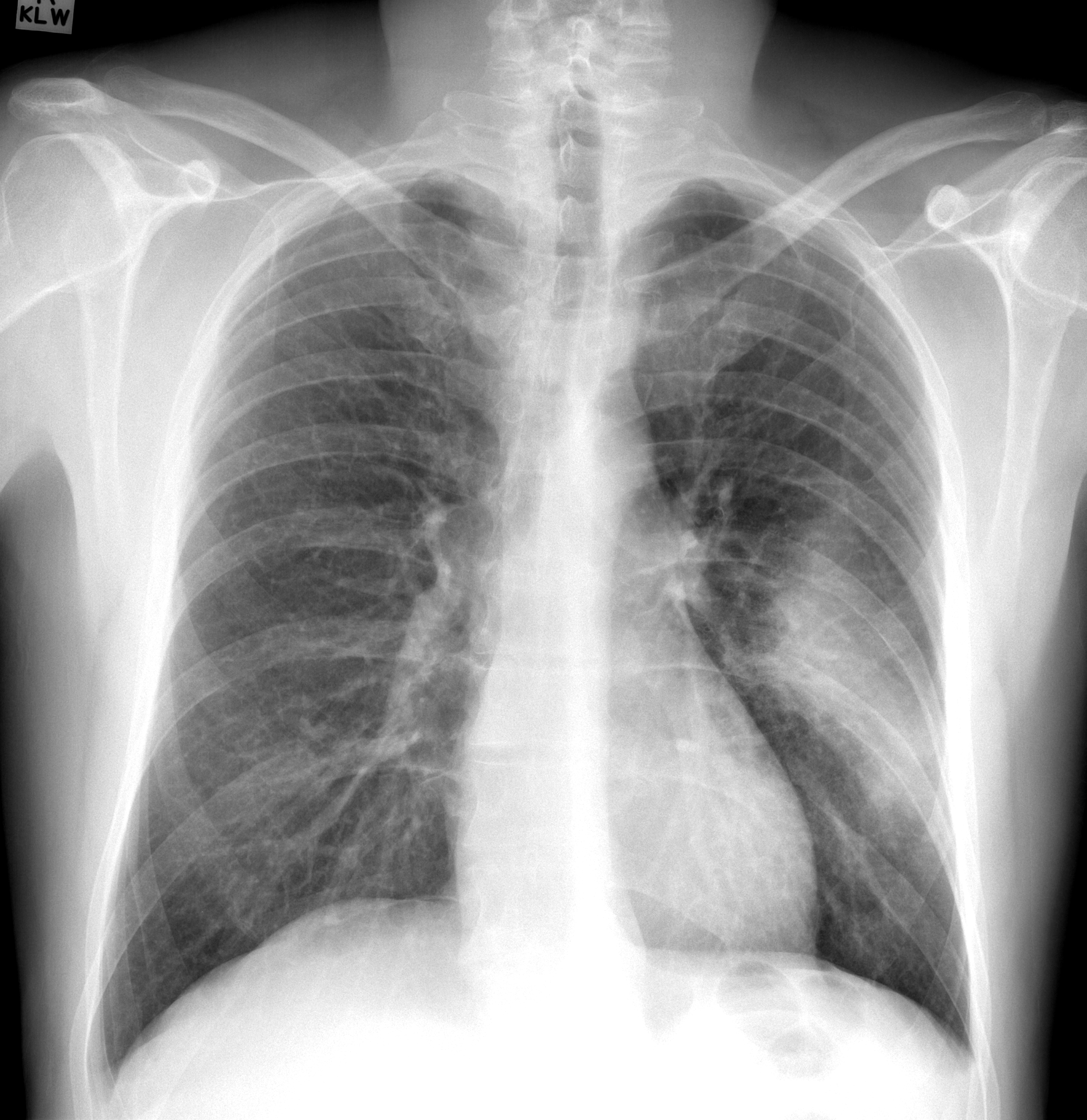 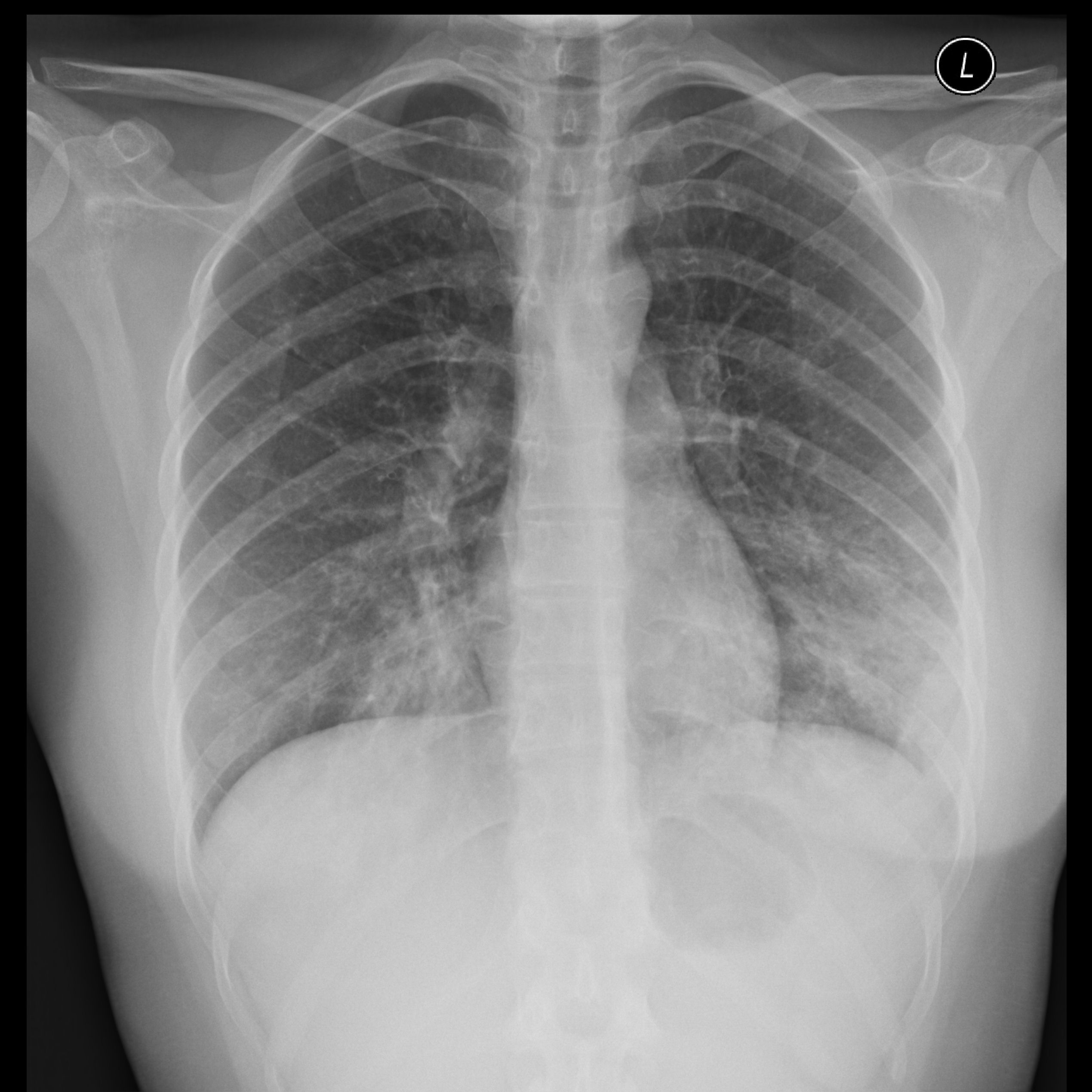 |
|