Systemic lupus erythematosus CT: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Systemic lupus erythematosus}} | {{Systemic lupus erythematosus}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} {{AE}} {{MIR}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
On abdominal CT-scan, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) may be characterized by | On abdominal [[CT-scans|CT-scan]], systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) may be characterized by [[hepatosplenomegaly]], [[pancreatic]] parenchymal enlargement, and [[ascites]]. On cardiac [[CT-scans|CT-scan]], SLE may be characterized by enhancement of the thickened [[pericardium]]. On brain [[Computed tomography|CT-scan,]] SLE may be characterized by [[brain atrophy]], stroke patterns like [[Cortical area|cortical]] hypodensity, and increased [[attenuation]] of the [[Cerebral cortex|cortex]]. | ||
== Key CT Findings in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus == | == Key CT Findings in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus == | ||
On CT-scan, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) may be characterized by the following features, based on the organ system involvement: | On [[CT-scans|CT-scan]], systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) may be characterized by the following features, based on the organ system involvement:<ref name="pmid23812167">{{cite journal |vauthors=Appenzeller S |title=Magnetic resonance imaging in systemic lupus erythematosus: where do we stand? |journal=Cogn Behav Neurol |volume=26 |issue=2 |pages=53–4 |year=2013 |pmid=23812167 |doi=10.1097/WNN.0b013e31829d5b60 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26309728">{{cite journal |vauthors=Thurman JM, Serkova NJ |title=Non-invasive imaging to monitor lupus nephritis and neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=F1000Res |volume=4 |issue= |pages=153 |year=2015 |pmid=26309728 |pmc=4536614 |doi=10.12688/f1000research.6587.2 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26038342">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lin K, Lloyd-Jones DM, Li D, Liu Y, Yang J, Markl M, Carr JC |title=Imaging of cardiovascular complications in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Lupus |volume=24 |issue=11 |pages=1126–34 |year=2015 |pmid=26038342 |pmc=4567427 |doi=10.1177/0961203315588577 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26236469">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sarbu N, Bargalló N, Cervera R |title=Advanced and Conventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Neuropsychiatric Lupus |journal=F1000Res |volume=4 |issue= |pages=162 |year=2015 |pmid=26236469 |pmc=4505788 |doi=10.12688/f1000research.6522.2 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24696368">{{cite journal |vauthors=Qin H, Guo Q, Shen N, Huang X, Wu H, Zhang M, Bao C, Chen S |title=Chest imaging manifestations in lupus nephritis |journal=Clin. Rheumatol. |volume=33 |issue=6 |pages=817–23 |year=2014 |pmid=24696368 |doi=10.1007/s10067-014-2586-2 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22901453">{{cite journal |vauthors=Goh YP, Naidoo P, Ngian GS |title=Imaging of systemic lupus erythematosus. Part II: gastrointestinal, renal, and musculoskeletal manifestations |journal=Clin Radiol |volume=68 |issue=2 |pages=192–202 |year=2013 |pmid=22901453 |doi=10.1016/j.crad.2012.06.109 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23943987">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gal Y, Twig G, Mozes O, Greenberg G, Hoffmann C, Shoenfeld Y |title=Central nervous system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: an imaging challenge |journal=Isr. Med. Assoc. J. |volume=15 |issue=7 |pages=382–6 |year=2013 |pmid=23943987 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid1448334">{{cite journal |vauthors=Shirato M, Hisa N, Fujikura Y, Ohkuma K, Kutsuki S, Hiramatsu K |title=[Imaging diagnosis of lupus enteritis--especially about sonographic findings] |language=Japanese |journal=Nihon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi |volume=52 |issue=10 |pages=1394–9 |year=1992 |pmid=1448334 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid25275093">{{cite journal |vauthors=Adachi JD, Lau A |title=Systemic lupus erythematosus, osteoporosis, and fractures |journal=J. Rheumatol. |volume=41 |issue=10 |pages=1913–5 |year=2014 |pmid=25275093 |doi=10.3899/jrheum.140919 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid21718325">{{cite journal |vauthors=Curiel R, Akin EA, Beaulieu G, DePalma L, Hashefi M |title=PET/CT imaging in systemic lupus erythematosus |journal=Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. |volume=1228 |issue= |pages=71–80 |year=2011 |pmid=21718325 |doi=10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06076.x |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22901452">{{cite journal |vauthors=Goh YP, Naidoo P, Ngian GS |title=Imaging of systemic lupus erythematosus. Part I: CNS, cardiovascular, and thoracic manifestations |journal=Clin Radiol |volume=68 |issue=2 |pages=181–91 |year=2013 |pmid=22901452 |doi=10.1016/j.crad.2012.06.110 |url=}}</ref> | ||
=== More common complications === | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Organ | ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; " |Organ | ||
!Disease | ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; " |Disease | ||
!CT | ! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; " |CT | ||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; " |Preview | |||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan=" | | rowspan="2" style="background: #DCDCDC; " align="center" |<small><small>[[Gastrointestinal]]</small></small> | ||
|[[Intestinal pseudo-obstruction]] | ![[Hepatitis]] | ||
| | |||
* Nonspecific, ranging from normal to [[hepatomegaly]] and [[cirrhosis]] | |||
* May present hepatic [[granulomas]] | |||
** Discrete, sharply defined [[nodular lesions]] within the [[liver]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (13).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |||
![[Mesenteric vascular occlusion|Mesenteric vasculitis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Ascites]] | |||
** Fluid in the [[abdomen]] | |||
* Dilated bowel | |||
* Mural thickening | |||
* Abnormal wall enhancement | |||
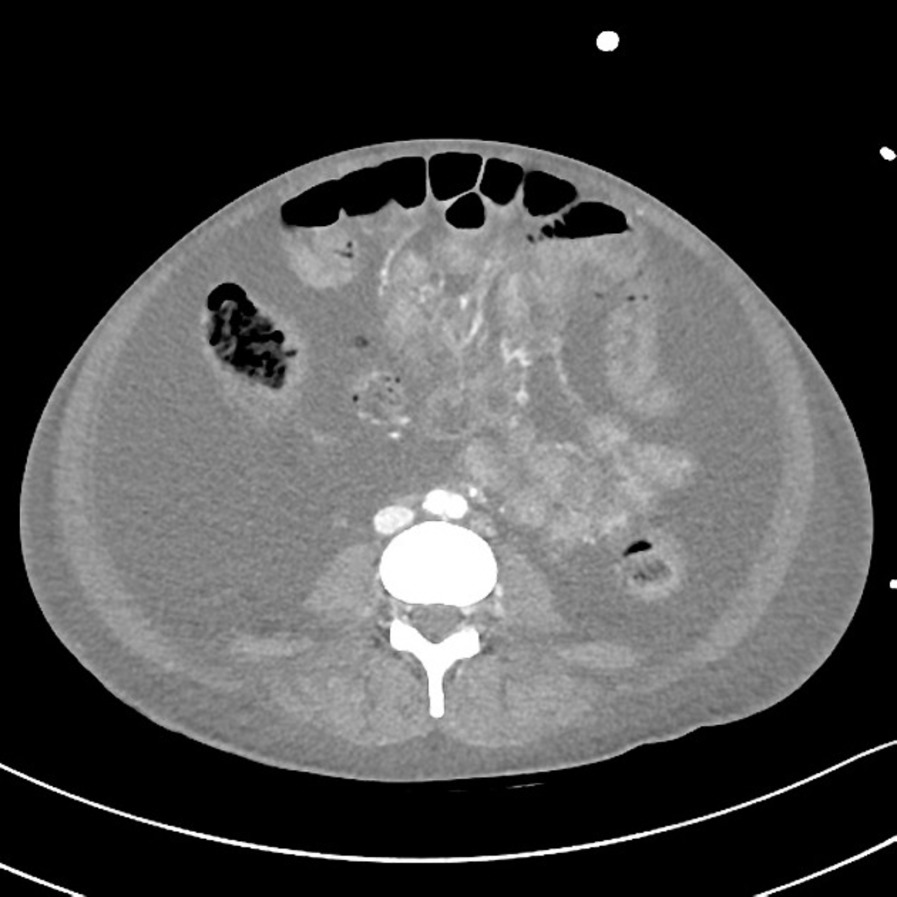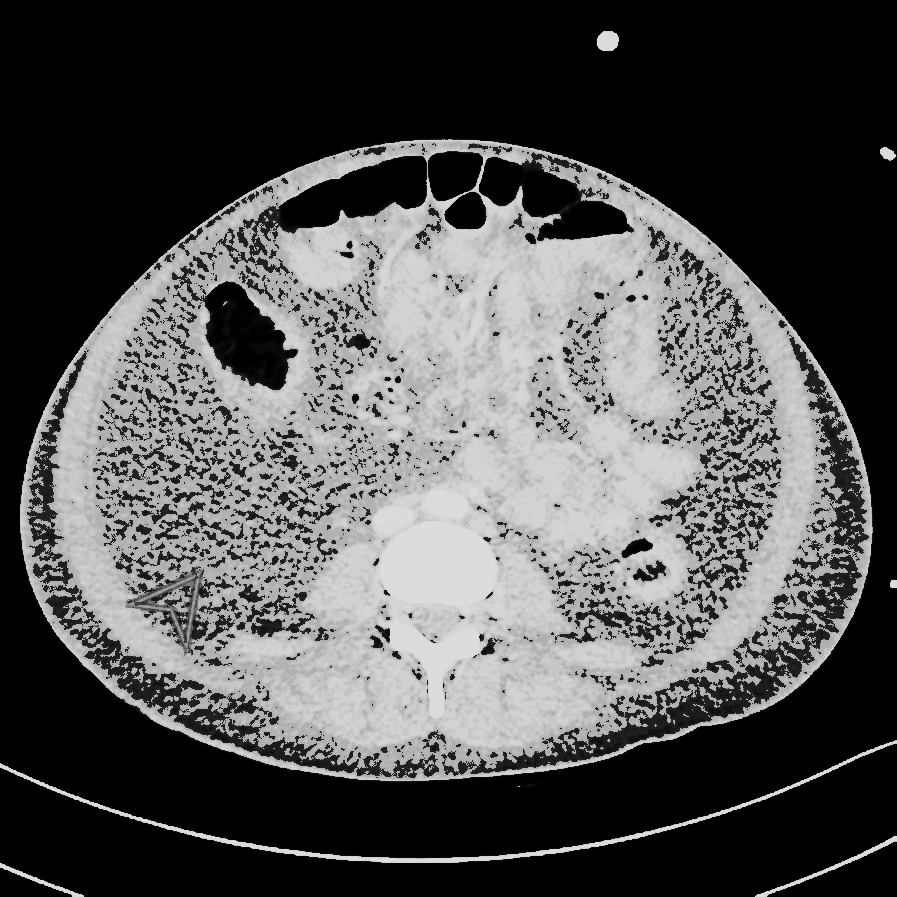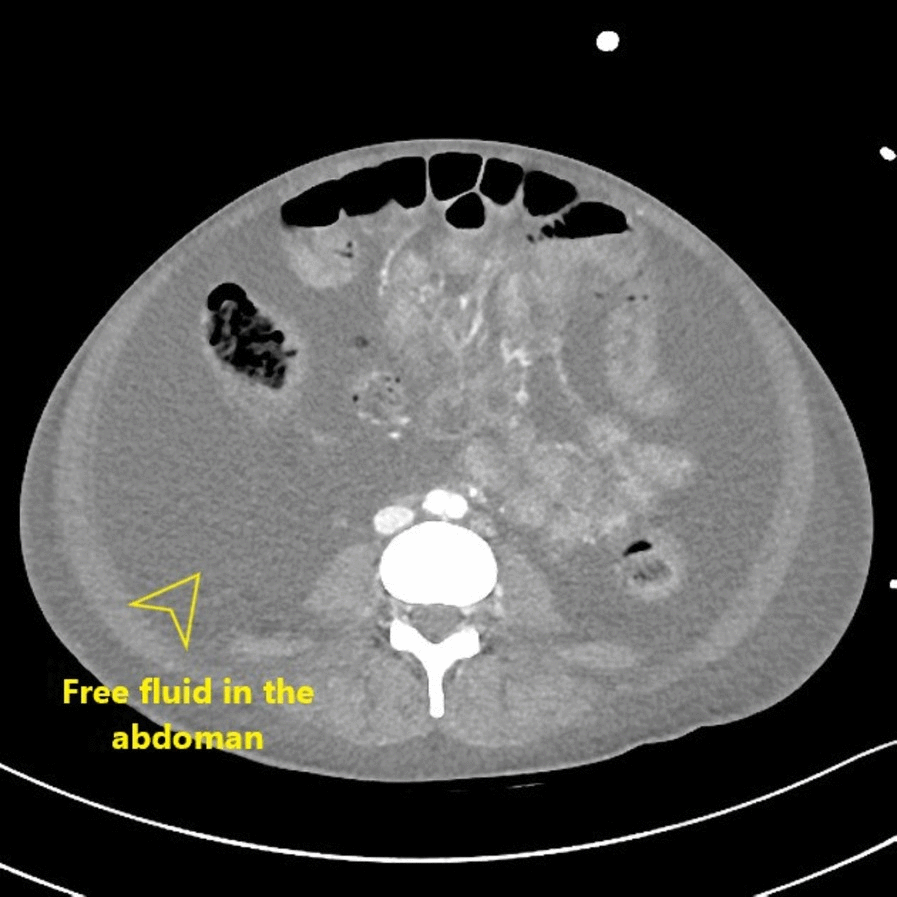
* [[Mesentery|Mesentric]] vessel engorgement | |||
* Comb sign: | |||
** Hypervascular appearance of the [[mesentery]] | |||
** Linear densities on the [[mesenteric]] side of the affected segments of [[small bowel]], which lead to the appearance of the teeth of a comb | |||
| | |||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (15).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; " align="center" |<small><small>[[Kidney]]</small></small> | |||
![[Nephritis]] | |||
| | |||
* Heterogeneous enlarged kidneys | |||
* Mostly illustrate the rim of normal density tissue | |||
* Wedge shaped areas of low density | |||
| | |||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (16).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="3" style="background: #DCDCDC; " align="center" |<small><small>[[Pulmonary]]</small></small> | |||
![[Pleural effusion]] | |||
| | |||
* May be associated with [[Pleural Fibrosis|thickening of the pleura]] | |||
* Fluid density | |||
| | |||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (17).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |||
![[Pulmonary hypertension]] | |||
| | |||
* ECG-gated CT [[pulmonary angiography]] | |||
** [[Right ventricular hypertrophy]]: defined as wall thickness of >4 mm | |||
** Straightening or bowing (towards the [[left ventricle]]) of the [[interventricular septum]] | |||
** [[Right ventricle|Right ventricular]] dilatation (a [[right ventricle]] to [[left ventricle]] diameter ratio of more than 1:1 at the midventricular level on axial images) | |||
** Decreased [[right ventricular]] [[ejection fraction]] | |||
** Ancillary features | |||
*** Dilatation of the [[inferior vena cava]] and [[hepatic veins]] | |||
*** [[Pericardial effusion]] | |||
* Enlarged [[pulmonary trunk]] (measured at [[Pulmonary artery|pulmonary artery bifurcation]] on an axial slice vertical to its long axis) | |||
* Enlarged [[pulmonary arteries]] | |||
* Mural calcification in central [[pulmonary arteries]] | |||
* Centrilobular ground-glass [[nodules]] | |||
* [[Neovascularization]] | |||
** Tiny serpiginous intrapulmonary vessels that often emerge from centrilobular [[arterioles]] but do not conform to usual [[Pulmonary artery|pulmonary arterial anatomy]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:Pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-7.jpg|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |||
![[Pneumonitis]] | |||
| | |||
* Unilateral or bilateral patchy and focal [[Consolidation (medicine)|consolidation]] typically in the lung bases | |||
* May accompany [[pleural effusion]] | |||
| | |||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (19).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; " align="center" |<small><small>[[Neurological]]</small></small> | |||
!Genreral | |||
| | |||
* [[Brain atrophy]] | |||
* May be due to [[steroid therapy]] or age | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
=== Less common complications === | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; " |Organ | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; " |Disease | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; " |CT | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; " |Preview | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="4" style="background: #DCDCDC; " align="center" |<small><small>[[Gastrointestinal]]</small></small> | |||
![[Intestinal pseudo-obstruction]] | |||
| | | | ||
* Dilated bowel loops with or without the presence of fluid levels | * Dilated bowel loops with or without the presence of fluid levels | ||
** A distinct transition point where bowel calibre changes from normal to abnormal | ** A distinct transition point where bowel calibre changes from normal to abnormal | ||
** Dilated bowel loops proximal to the transition point | ** Dilated bowel loops [[proximal]] to the transition point: | ||
*** Small bowel >3.5 cm | *** [[Small bowel]] >3.5 cm | ||
*** Large bowel >5 cm | *** [[Large bowel]] >5 cm | ||
** Collapsed or normal calibre bowel distal to the transitional point | ** Collapsed or normal calibre [[bowel]] distal to the transitional point | ||
** Bowel wall thickening | ** Bowel wall thickening | ||
** Obstruction: | ** [[Intestinal obstruction|Obstruction]]: | ||
*** [[Pneumoperitoneum]] indicating perforation | *** [[Pneumoperitoneum]] indicating [[perforation]] | ||
*** [[Bowel ischaemia]] | *** [[Bowel ischaemia]] | ||
| | | | ||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (20).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
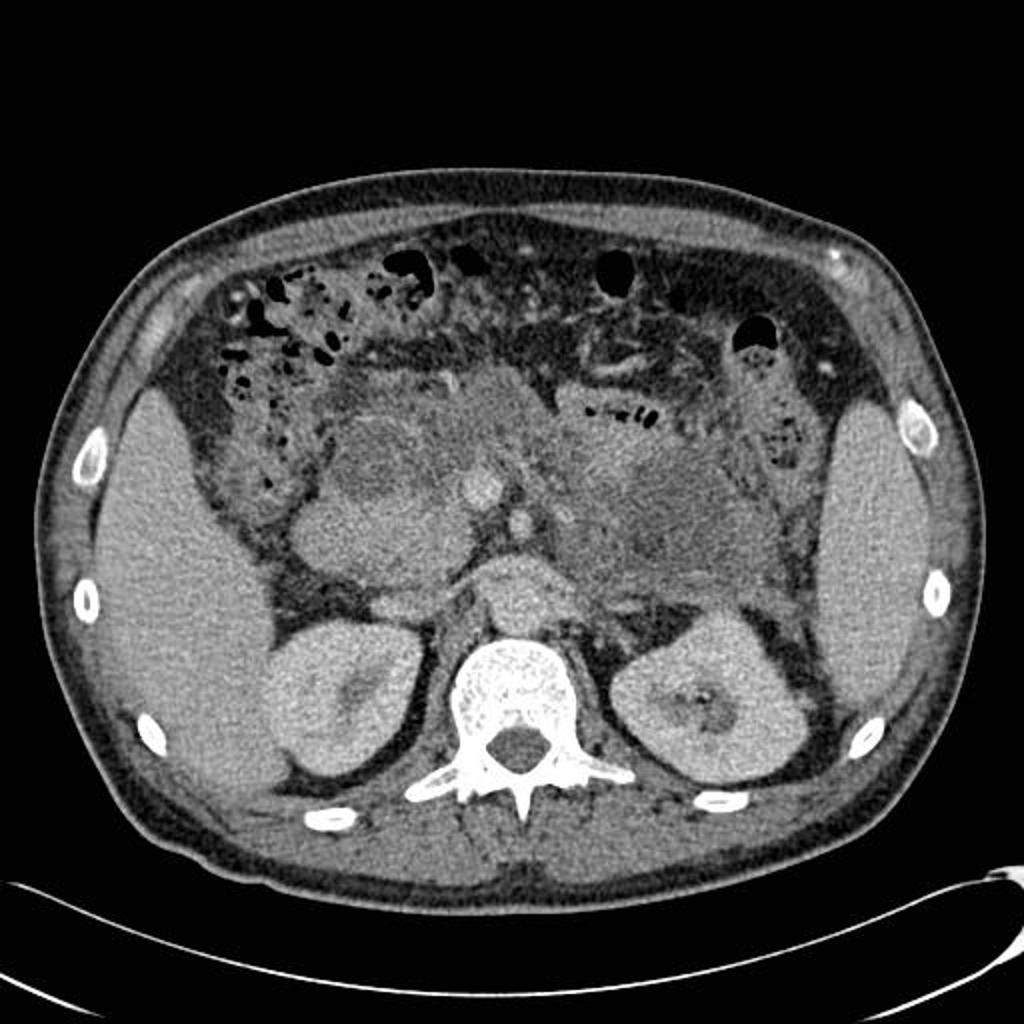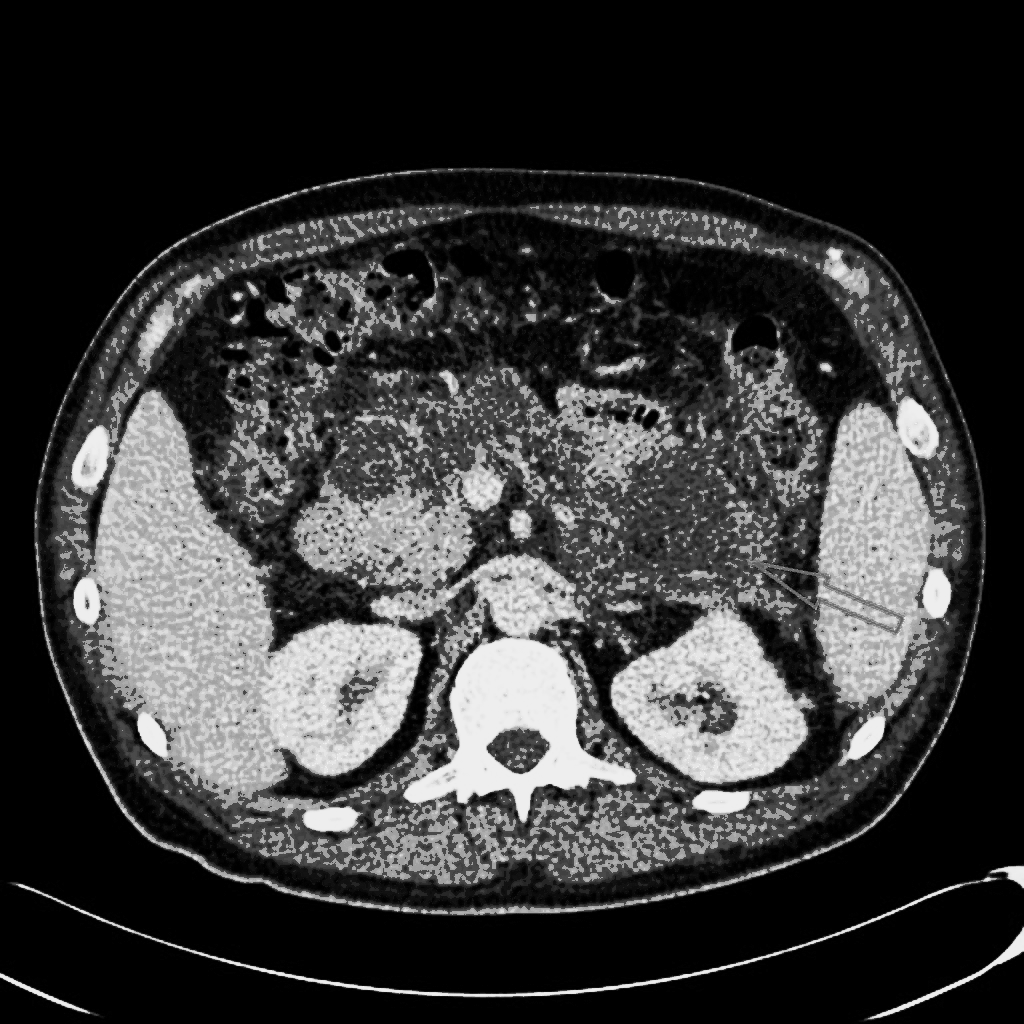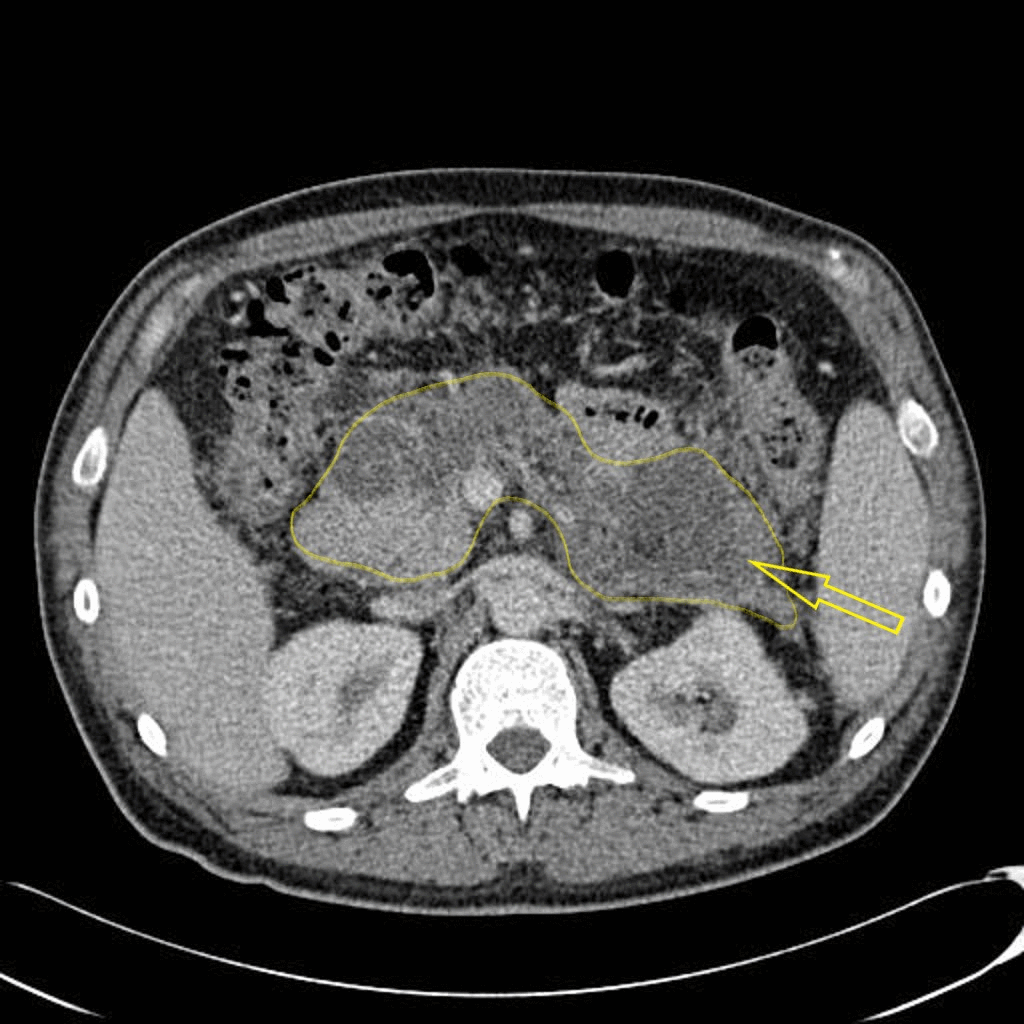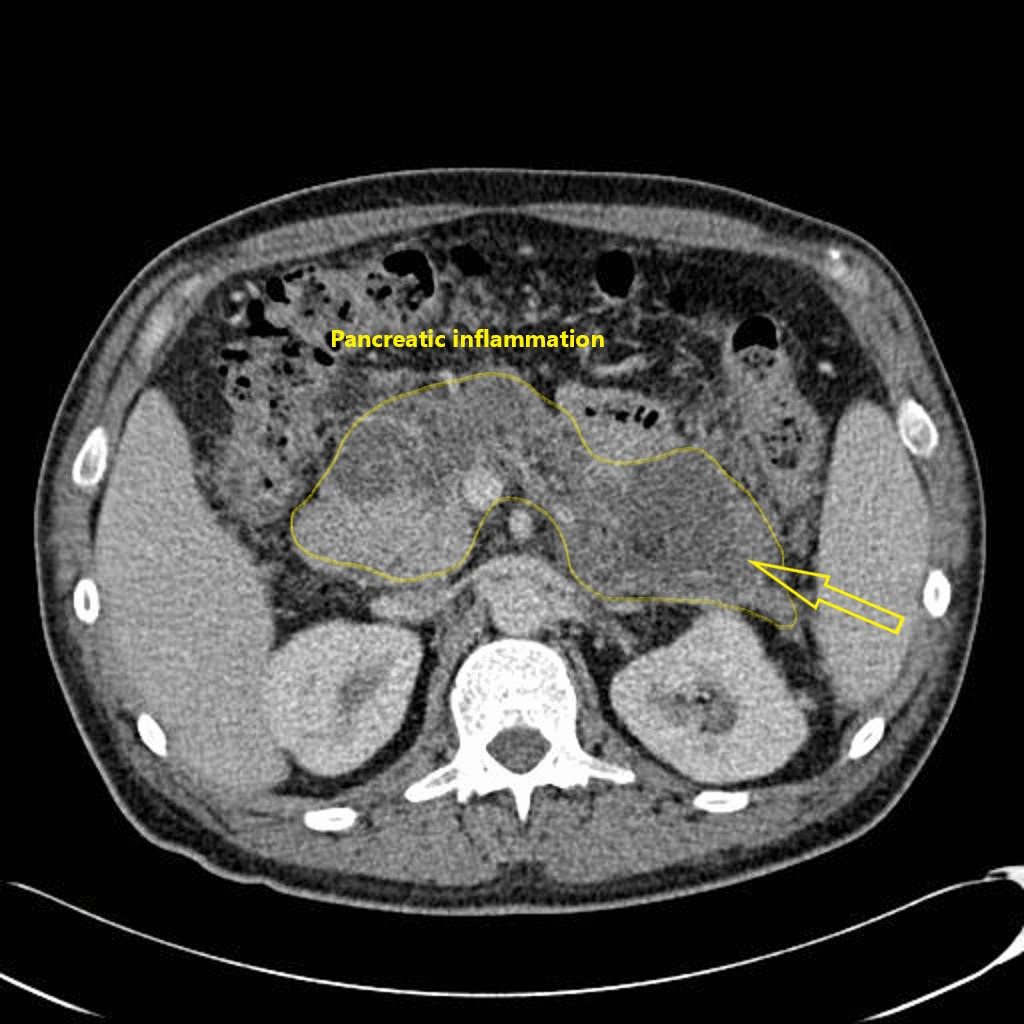
![[Acute pancreatitis]] | |||
|Abnormalities that may be seen in the pancreas include: | |Abnormalities that may be seen in the [[pancreas]] include: | ||
* Typical findings | * Typical findings | ||
** Focal or diffuse parenchymal enlargement | ** Focal or diffuse parenchymal enlargement | ||
** Changes in density because of [[edema]] | ** Changes in density because of [[edema]] | ||
** Indistinct pancreatic margins owing to inflammation | ** Indistinct [[Pancreas|pancreatic]] margins owing to inflammation | ||
** Mesenteric fatty infiltration around the pancreas | ** [[Mesentery|Mesenteric]] fatty infiltration around the [[pancreas]] | ||
* [[Liquefactive necrosis]] of pancreatic parenchyma | * [[Liquefactive necrosis]] of pancreatic parenchyma | ||
** Lack of parenchymal enhancement | ** Lack of parenchymal enhancement | ||
** Often multifocal | ** Often multifocal | ||
* Abscess formation | * [[Abscess of pancreas|Abscess]] formation | ||
** Circumscribed fluid collection | ** Circumscribed fluid collection | ||
** Little or no necrotic tissues (thus distinguishing it from infected necrosis) | ** Little or no [[Necrotic tissue|necrotic tissues]] (thus distinguishing it from infected necrosis) | ||
** Phlegmon formation | ** [[Phlegmon]] formation | ||
* [[Haemorrhage]] | * [[Haemorrhage]] | ||
** High-attenuation fluid in the [[retroperitoneum]] or peripancreatic tissues | ** High-attenuation fluid in the [[retroperitoneum]] or peripancreatic tissues | ||
| | |||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (21).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
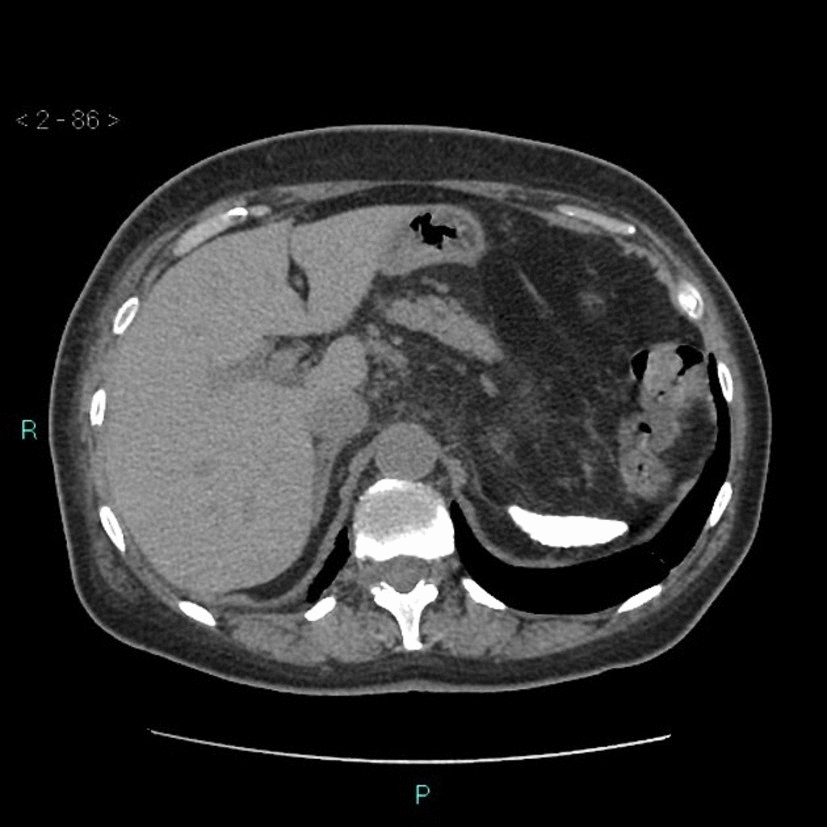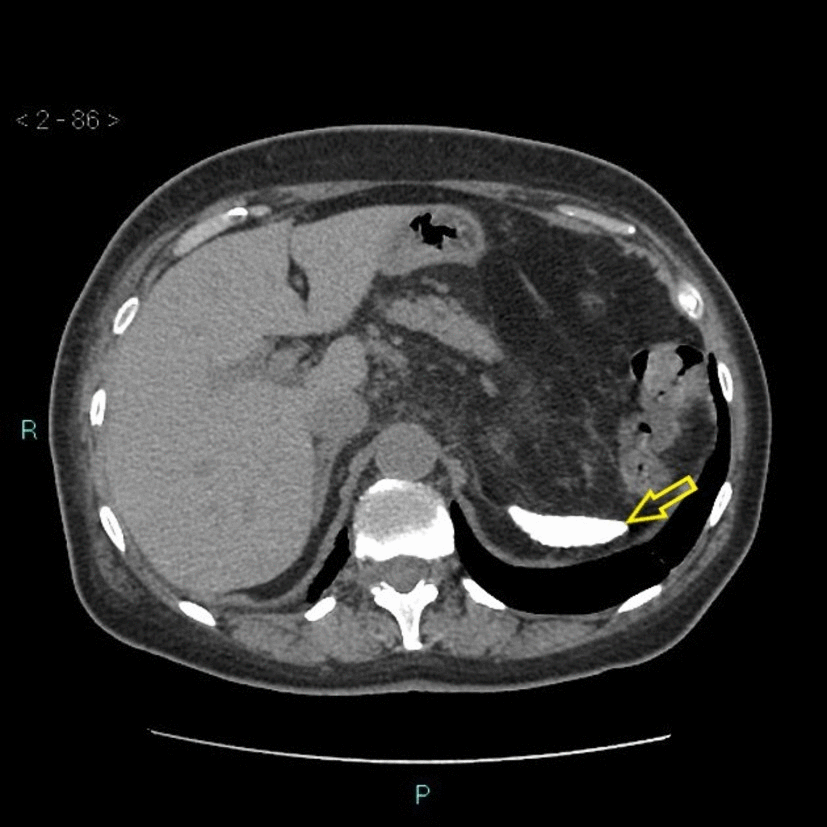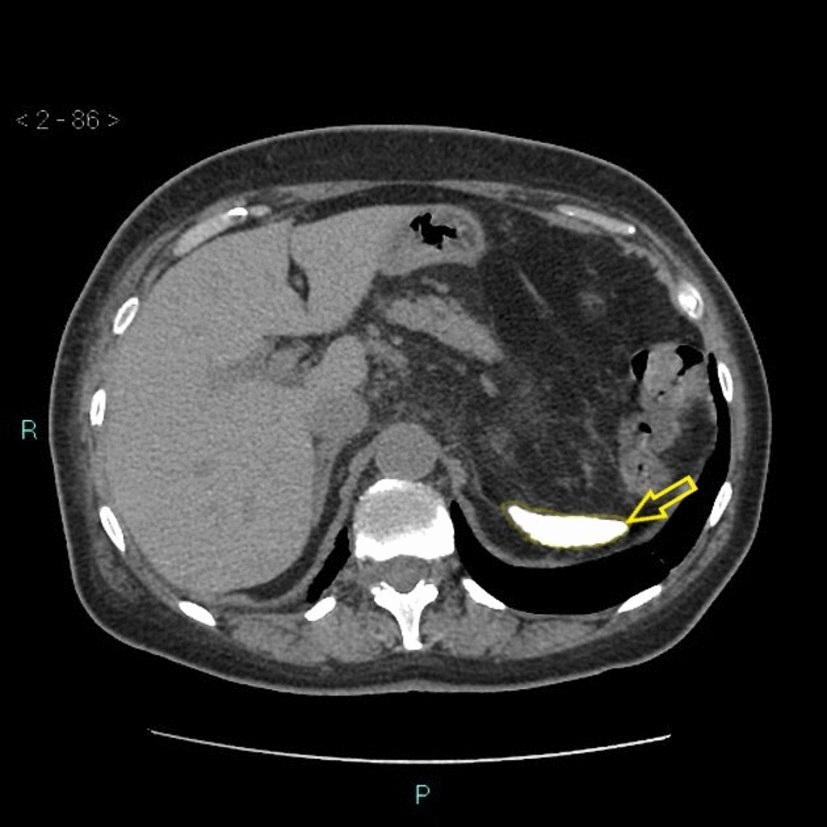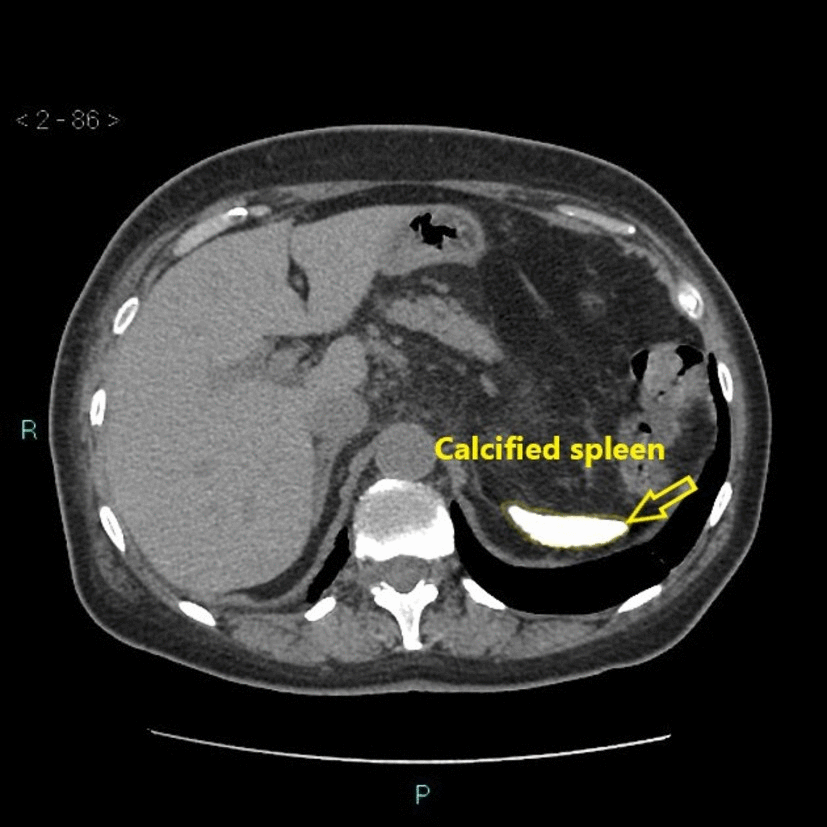
![[Autosplenectomy]] | |||
| | | | ||
* Abnormally small and irregular splenic remnant | * Abnormally small and irregular [[Spleen|splenic]] remnant | ||
* May show calcified | * May show [[Calcification|calcified]] [[spleen]] | ||
| | | | ||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (22).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
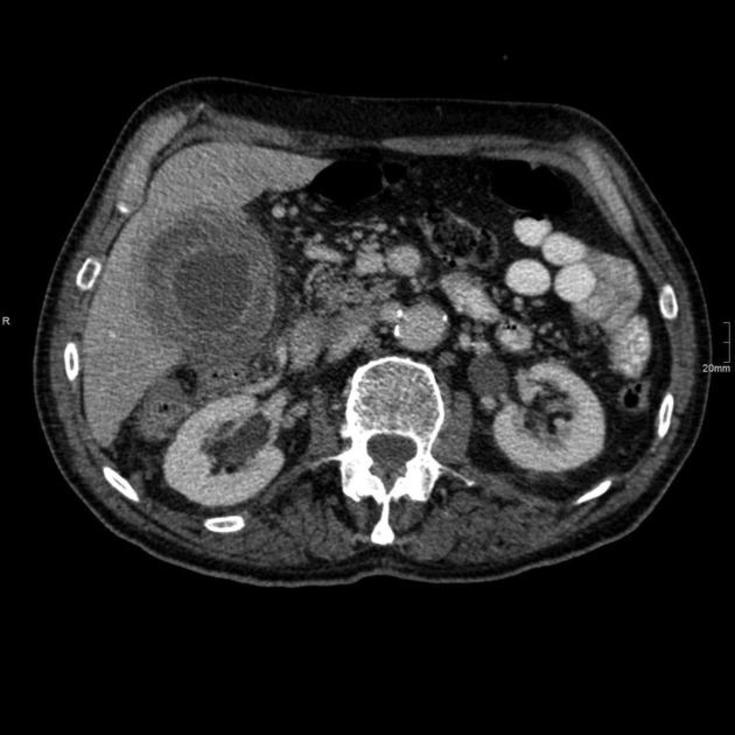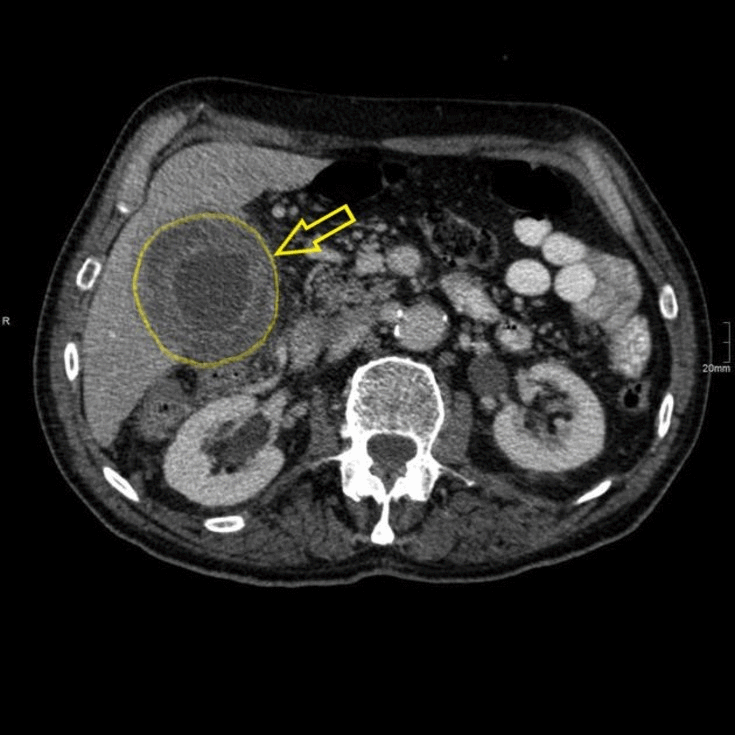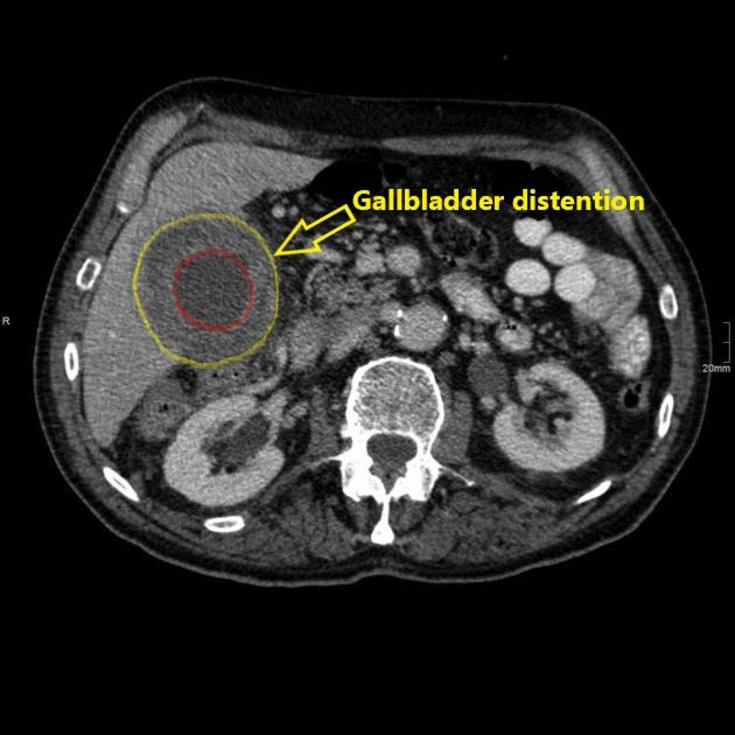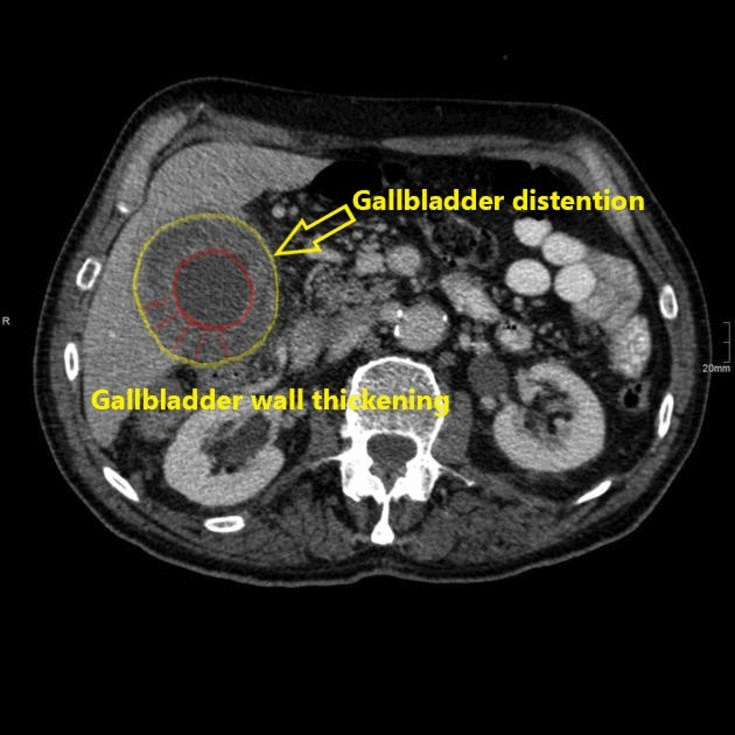
![[Acute cholecystitis]] | |||
| | | | ||
* [[Gallbladder]] distension | * [[Gallbladder]] distension | ||
* [[Gallbladder]] wall thickening | * [[Gallbladder]] wall thickening | ||
* Mural or mucosal hyperenhancement | * [[Mural thrombus|Mural]] or mucosal hyperenhancement | ||
* Pericholecystic fluid and inflammatory fat stranding | * Pericholecystic fluid and inflammatory fat stranding | ||
* Enhancement of the adjacent liver parenchyma due to reactive [[hyperaemia]] | * Enhancement of the adjacent liver parenchyma due to reactive [[hyperaemia]] | ||
* Tensile gallbladder fundus sign | * Tensile [[Gallbladder|gallbladder fundus]] sign | ||
** Fundus bulging the anterior abdominal wall | ** Fundus bulging the [[anterior abdominal wall]] | ||
| | | | ||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (23).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
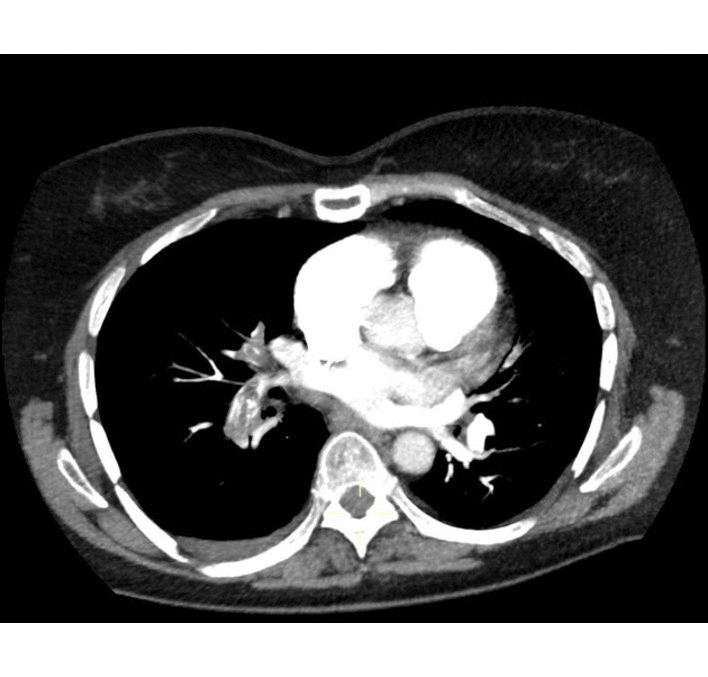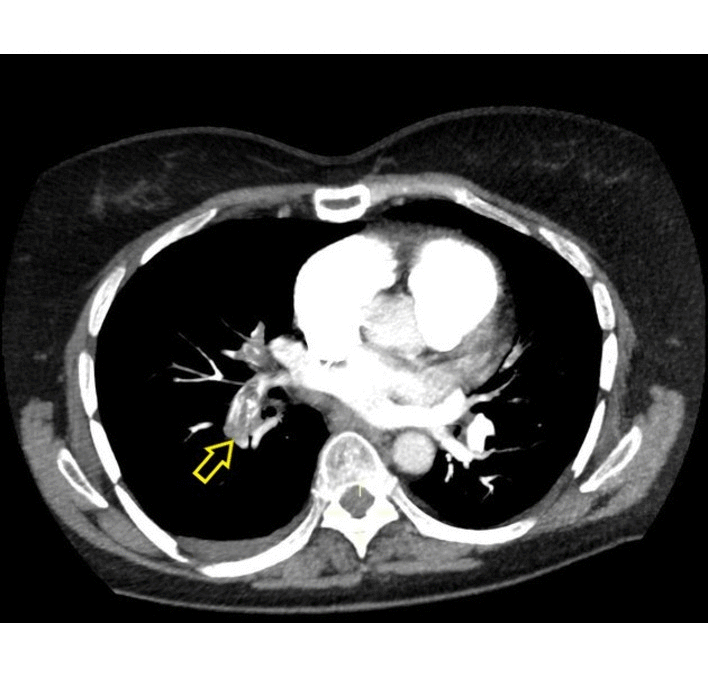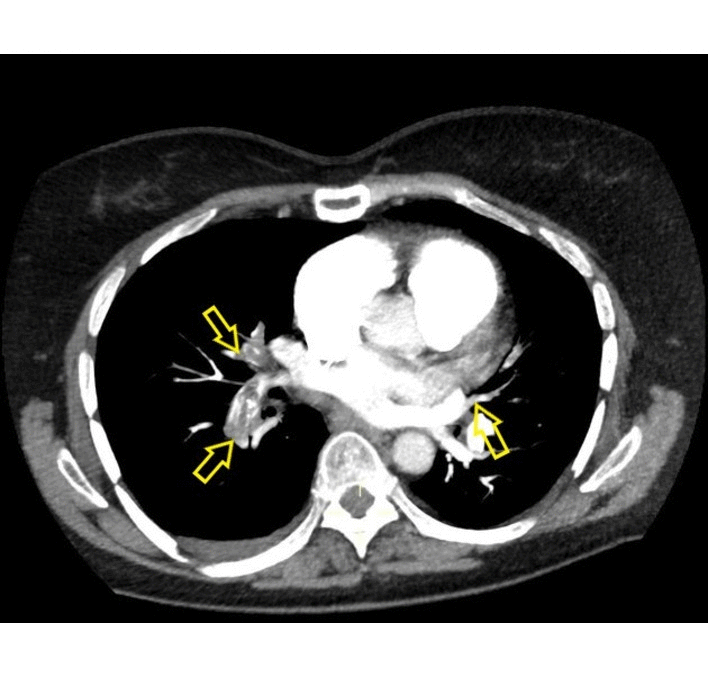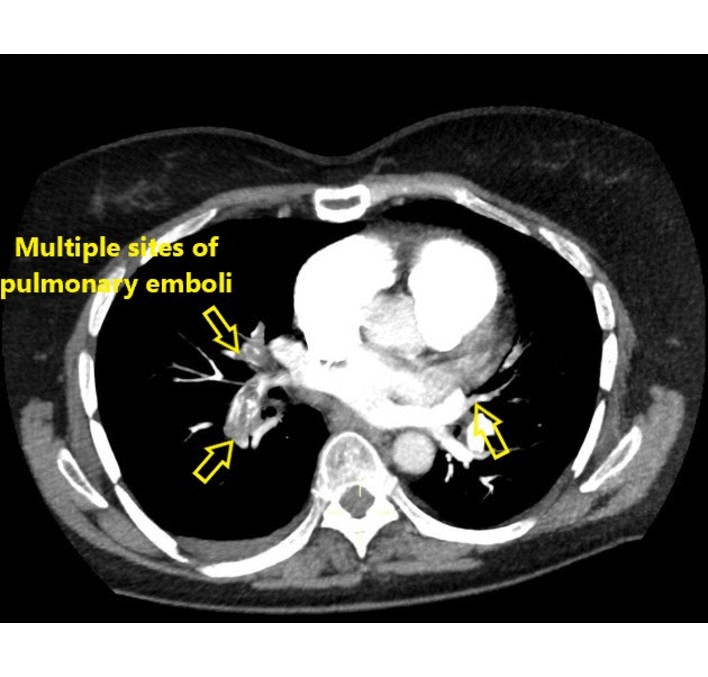
|[[Pulmonary emboli]] | | rowspan="3" style="background: #DCDCDC; " align="center" |<small><small>[[Pulmonary]]</small></small> | ||
![[Pulmonary emboli]] | |||
| | | | ||
* Filling defects within the pulmonary vasculature with acute [[pulmonary emboli]] | * Filling defects within the [[pulmonary vasculature]] with acute [[pulmonary emboli]] | ||
* Vascular CT signs include | * Vascular CT signs include | ||
** Direct pulmonary artery signs | ** Direct [[pulmonary artery]] signs | ||
*** Complete obstruction | *** Complete [[obstruction]] | ||
*** Partial obstruction | *** Partial obstruction | ||
*** Eccentric [[thrombus]] | *** Eccentric [[thrombus]] | ||
*** Calcified [[thrombus]]- calcific pulmonary emboli | *** Calcified [[thrombus]]- calcific pulmonary emboli | ||
*** Pulmonary arterial bands | *** [[Pulmonary artery|Pulmonary arterial]] bands | ||
*** Post stenotic dilatation | *** Post stenotic dilatation | ||
** Signs related to [[pulmonary hypertension]] | ** Signs related to [[pulmonary hypertension]] | ||
*** Enlargement of main pulmonary arteries | *** Enlargement of main [[pulmonary arteries]] | ||
*** Narrowing of the peripheral pulmonary arteries in affected segments | *** Narrowing of the [[Pulmonary arteries|peripheral pulmonary arteries]] in affected segments | ||
*** [[Pulmonary hypertension|Pulmonary arterial]] calcification | *** [[Pulmonary hypertension|Pulmonary arterial]] [[calcification]] | ||
*** Tortuous pulmonary vessels | *** Tortuous [[pulmonary vessels]] | ||
*** [[Right ventricular hypertrophy]] | *** [[Right ventricular hypertrophy]] | ||
** Signs of systemic collateral supply | ** Signs of systemic collateral supply | ||
| Line 105: | Line 173: | ||
* Parenchymal signs (often non-specific on their own) | * Parenchymal signs (often non-specific on their own) | ||
** [[Scars]] | ** [[Scars]] | ||
** Mosaic perfusion pattern | ** Mosaic [[perfusion]] pattern | ||
** Focal ground-glass opacities | ** Focal ground-glass opacities | ||
** | ** [[Bronchial]] anomalies | ||
| | | | ||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (24).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
!Shrinking lung syndrome | |||
| | | | ||
* Reduced lung volumes with [[diaphragmatic elevation]] | * Reduced [[lung volumes]] with [[diaphragmatic elevation]] | ||
* Occasional basal [[atelectasis]] | * Occasional basal [[atelectasis]] | ||
* No major [[Interstitial lung disease|parenchymal lung]] or [[pleural disease]] | * No major [[Interstitial lung disease|parenchymal lung]] or [[pleural disease]] | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
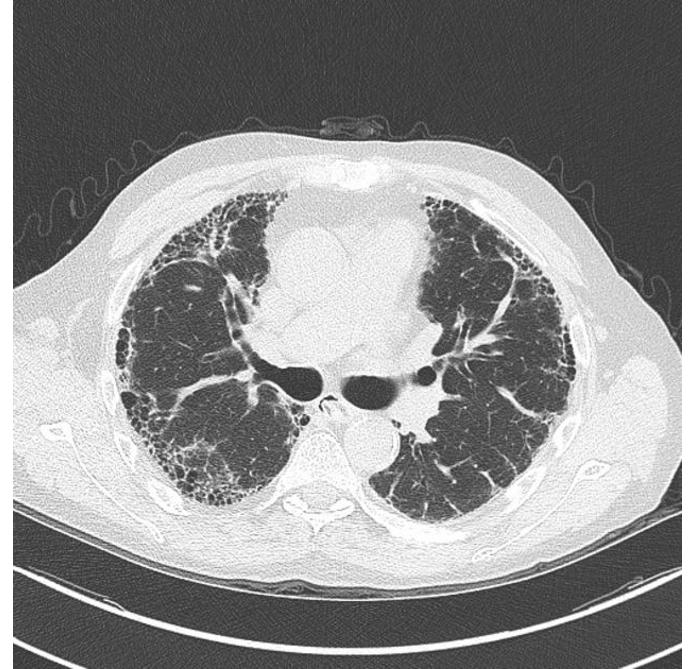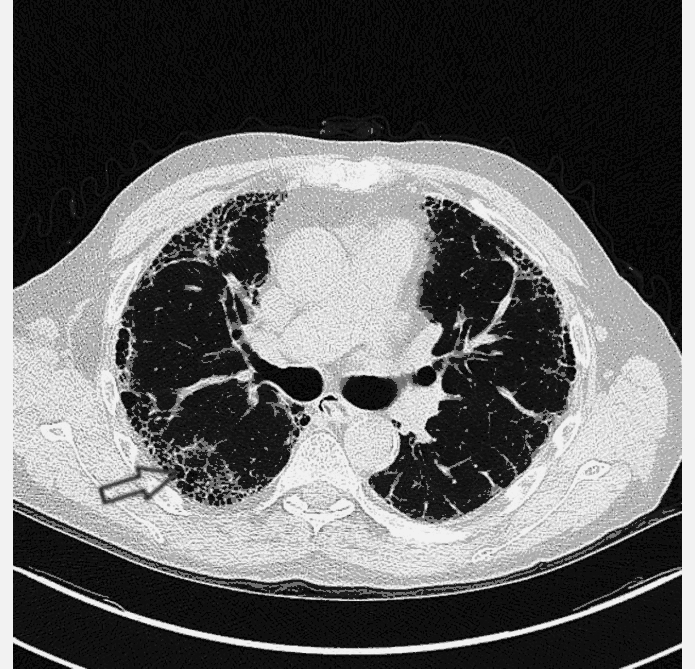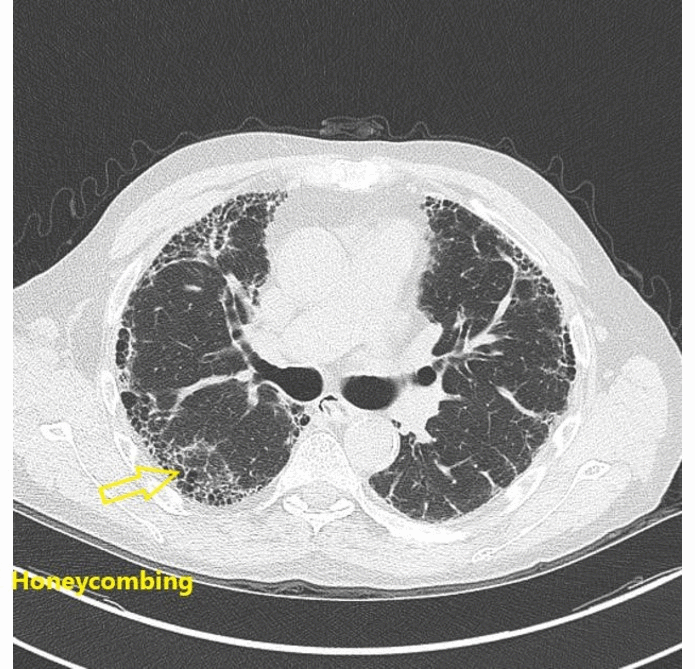
![[Pulmonary fibrosis]] | |||
| | | | ||
* Honeycombing | * Honeycombing | ||
** Fibrotic cystic changes | ** Fibrotic cystic changes | ||
* Traction bronchiectasis | * Traction [[bronchiectasis]] | ||
** Dilatation of [[bronchi]] and [[bronchioles]] within fibrotic lung tissue | ** Dilatation of [[bronchi]] and [[bronchioles]] within fibrotic lung tissue | ||
* Lung architectural distortion | * Lung architectural distortion | ||
* Reticulation | * Reticulation | ||
* Interlobular septal thickening | * Interlobular septal thickening | ||
| | | | ||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (25).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Acute pericarditis]] | | rowspan="2" style="background: #DCDCDC; " align="center" |<small><small>[[Cardiac]]</small></small> | ||
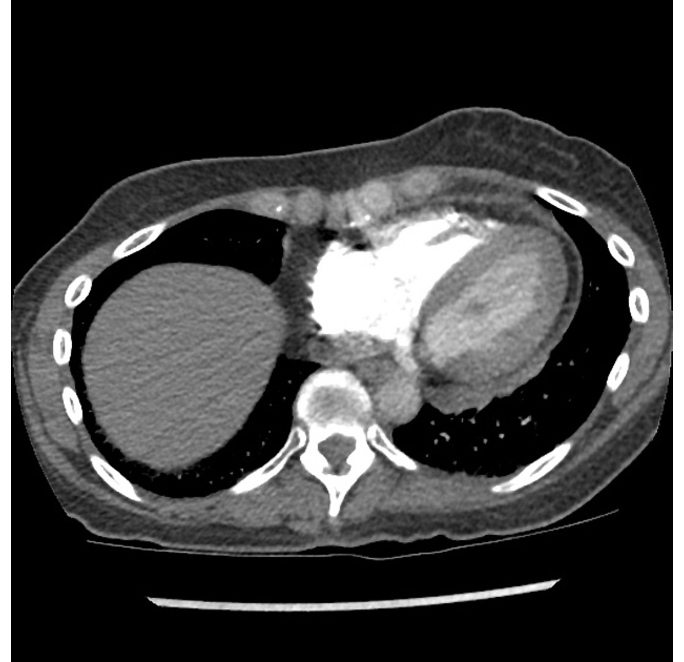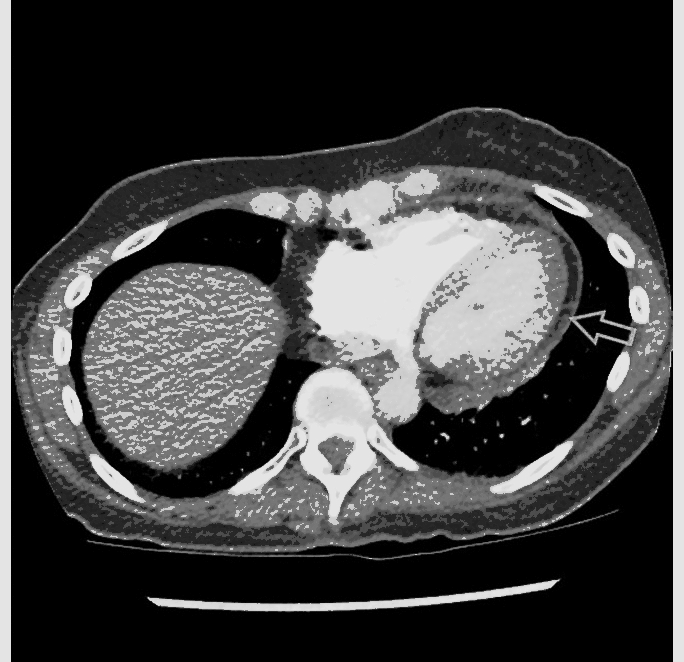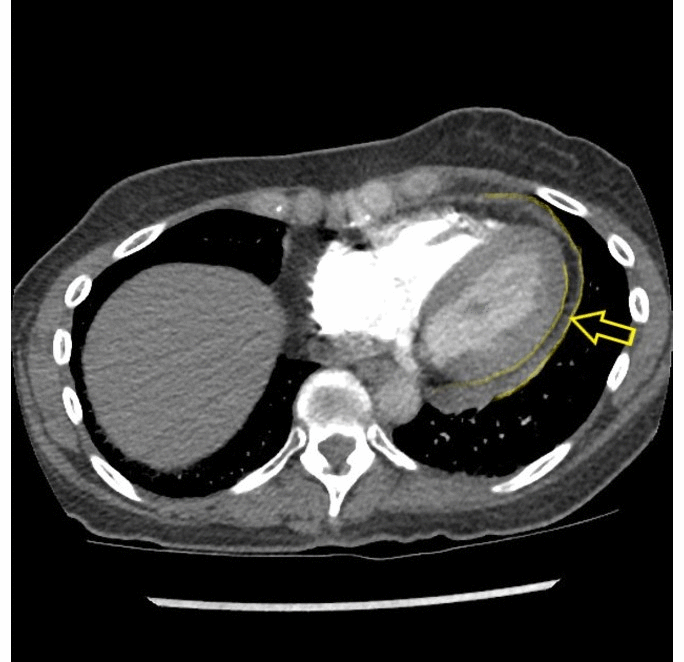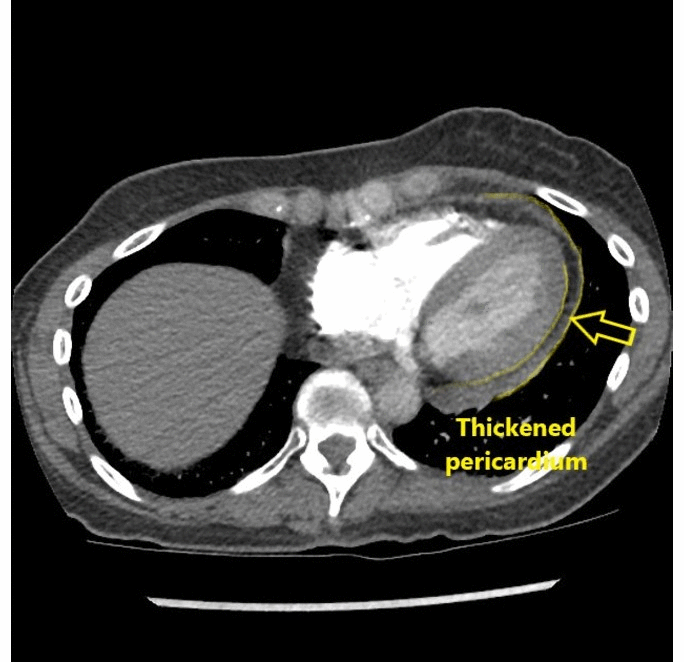
![[Acute pericarditis]] | |||
| | | | ||
* Enhancement of the thickened [[pericardium]] | * Enhancement of the thickened [[pericardium]] | ||
| | | | ||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (26).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
![[Pericardial effusion]] | |||
| | | | ||
* | * Fluid density material surrounding the [[heart]] | ||
| | | | ||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (27).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Stroke]] | | style="background: #DCDCDC; " align="center" |<small><small>[[Neurological]]</small></small> | ||
![[Stroke]] | |||
| | | | ||
* Early sign | * Early sign | ||
** A hyperdense segment of a vessel, representing direct | ** A hyperdense segment of a [[vessel]], representing direct [[Visualization (cam)|visualization]] of the [[Intravascular coagulation|intravascular thrombus]] | ||
* Early hyperacute | * Early hyperacute | ||
** Loss of grey-white matter differentiation | ** Loss of grey-white matter differentiation | ||
** Hypoattenuation of deep nuclei | ** Hypoattenuation of deep nuclei | ||
** Cortical hypodensity with associated parenchymal swelling with resultant gyral effacement | ** Cortical hypodensity with associated [[Parenchyma|parenchymal]] swelling with resultant gyral effacement | ||
** Elevation of the attenuation of the cortex | ** Elevation of the attenuation of the [[cortex]] | ||
| | |||
[[File:Webp.net-gifmaker (28).gif|thumb|300px|<SMALL><SMALL>''[https://radiopaedia.org/ Adapted from Radiopaedia]''</SMALL></SMALL>]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:20, 1 February 2018
|
Systemic lupus erythematosus Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Systemic lupus erythematosus from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Systemic lupus erythematosus CT On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Systemic lupus erythematosus CT |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Systemic lupus erythematosus |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Systemic lupus erythematosus CT |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mahshid Mir, M.D. [2]
Overview
On abdominal CT-scan, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) may be characterized by hepatosplenomegaly, pancreatic parenchymal enlargement, and ascites. On cardiac CT-scan, SLE may be characterized by enhancement of the thickened pericardium. On brain CT-scan, SLE may be characterized by brain atrophy, stroke patterns like cortical hypodensity, and increased attenuation of the cortex.
Key CT Findings in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
On CT-scan, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) may be characterized by the following features, based on the organ system involvement:[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11]
More common complications
| Organ | Disease | CT | Preview |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal | Hepatitis |
|
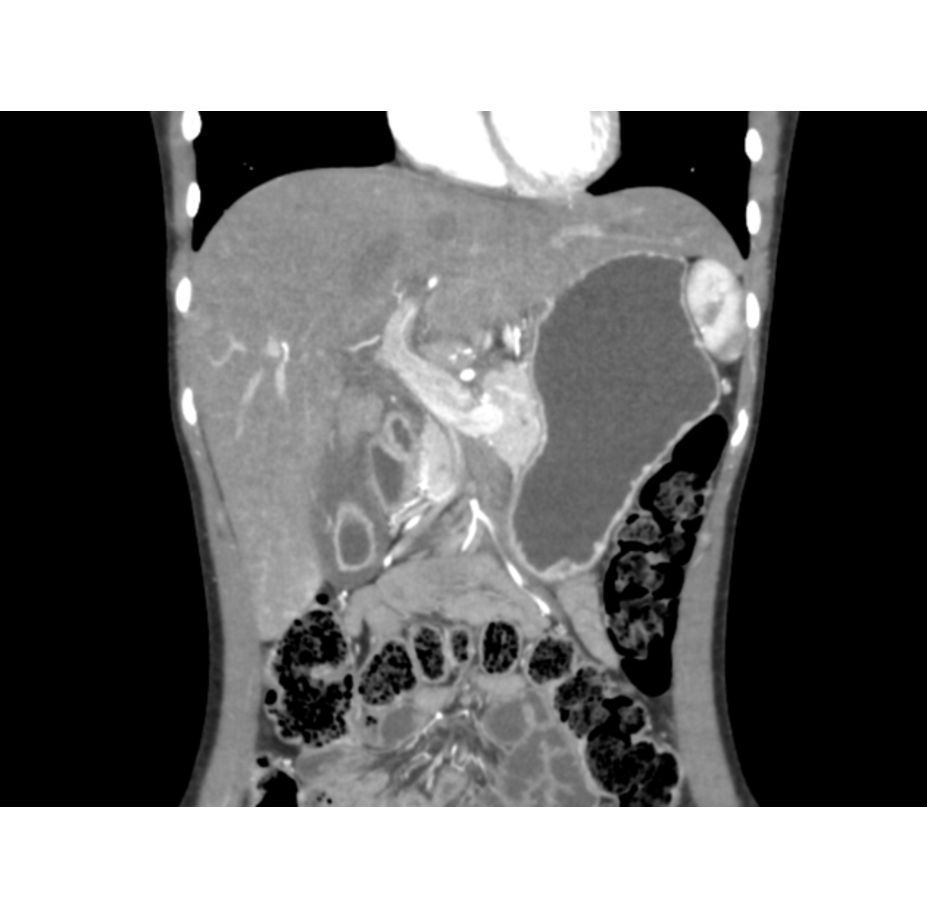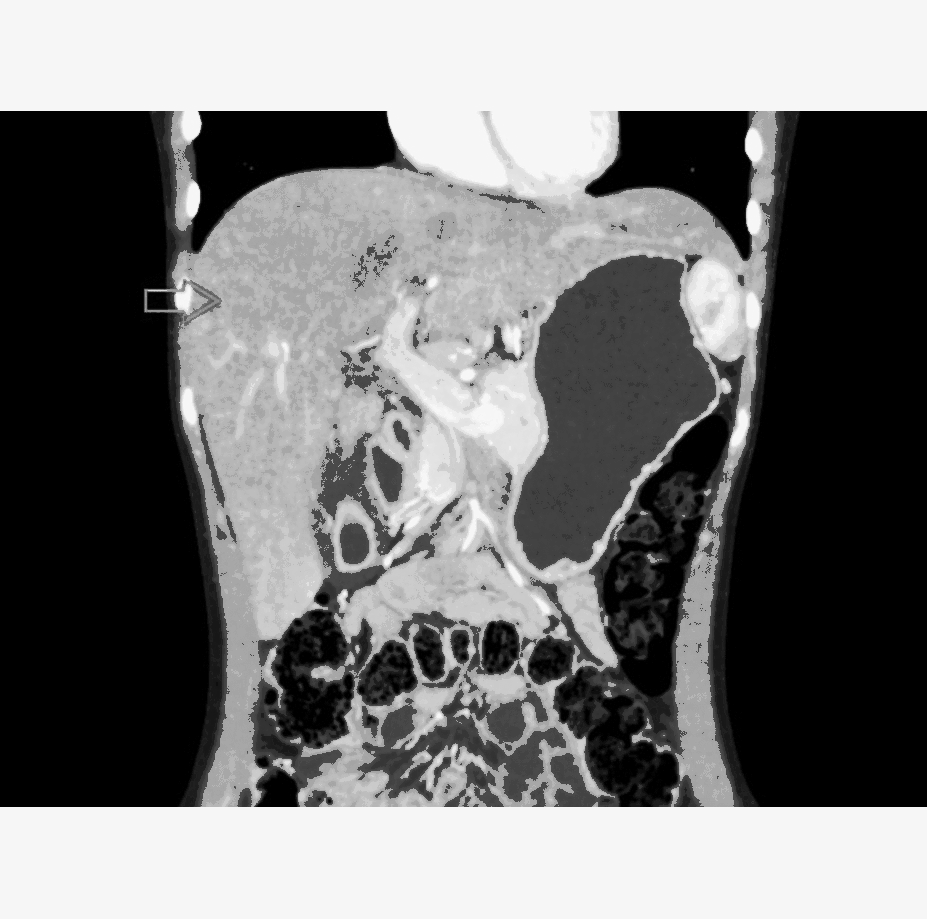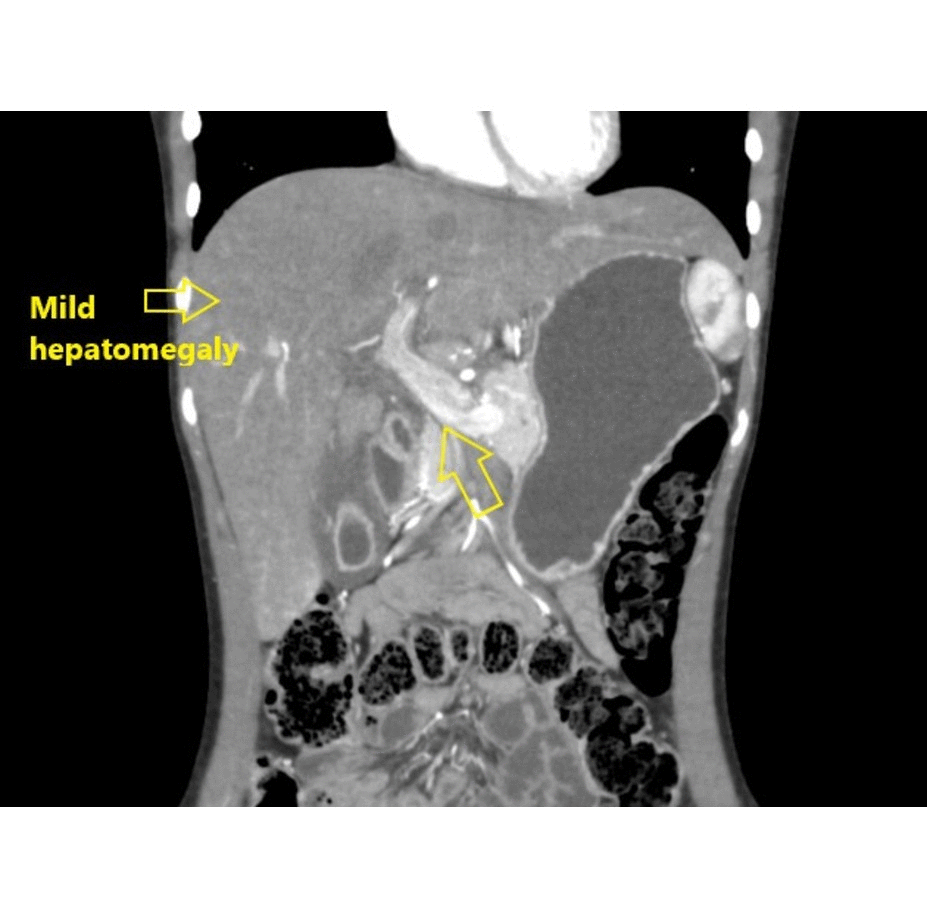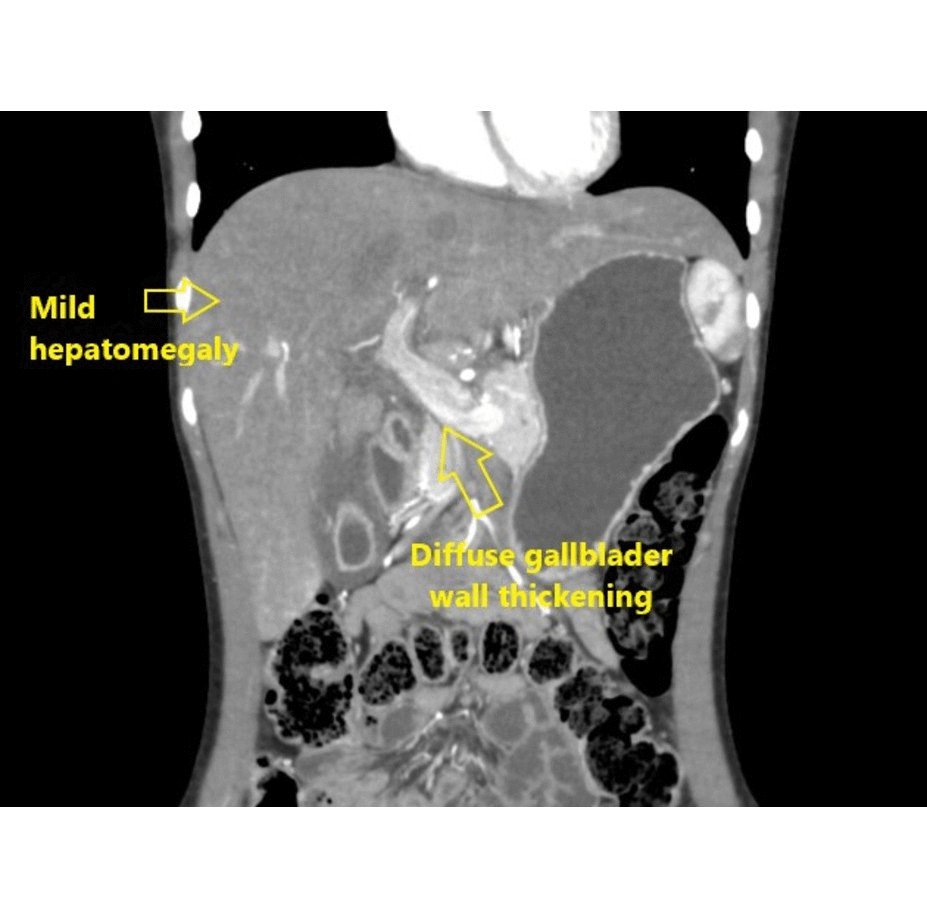 |
| Mesenteric vasculitis |
|
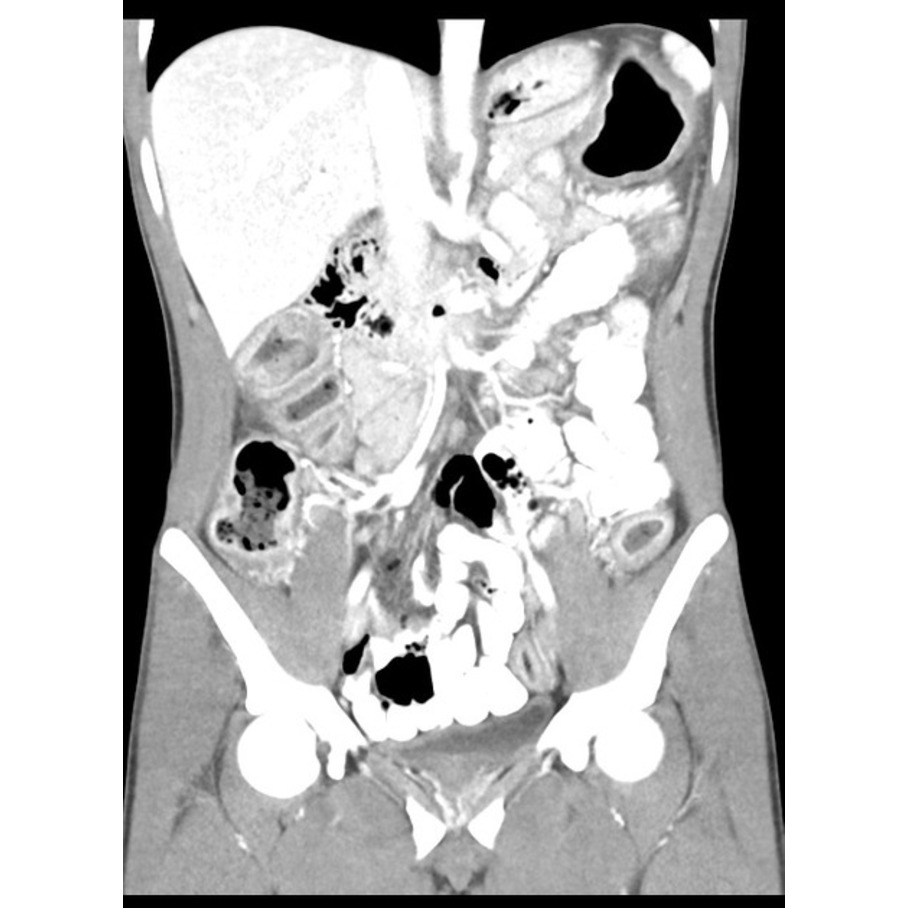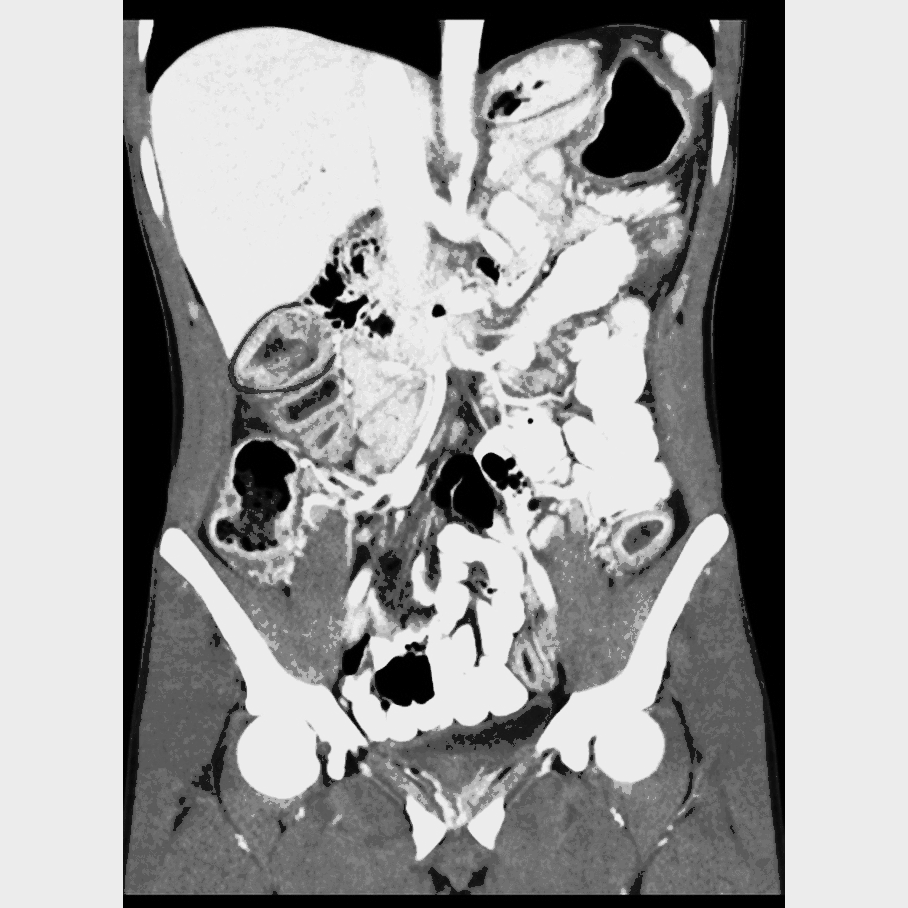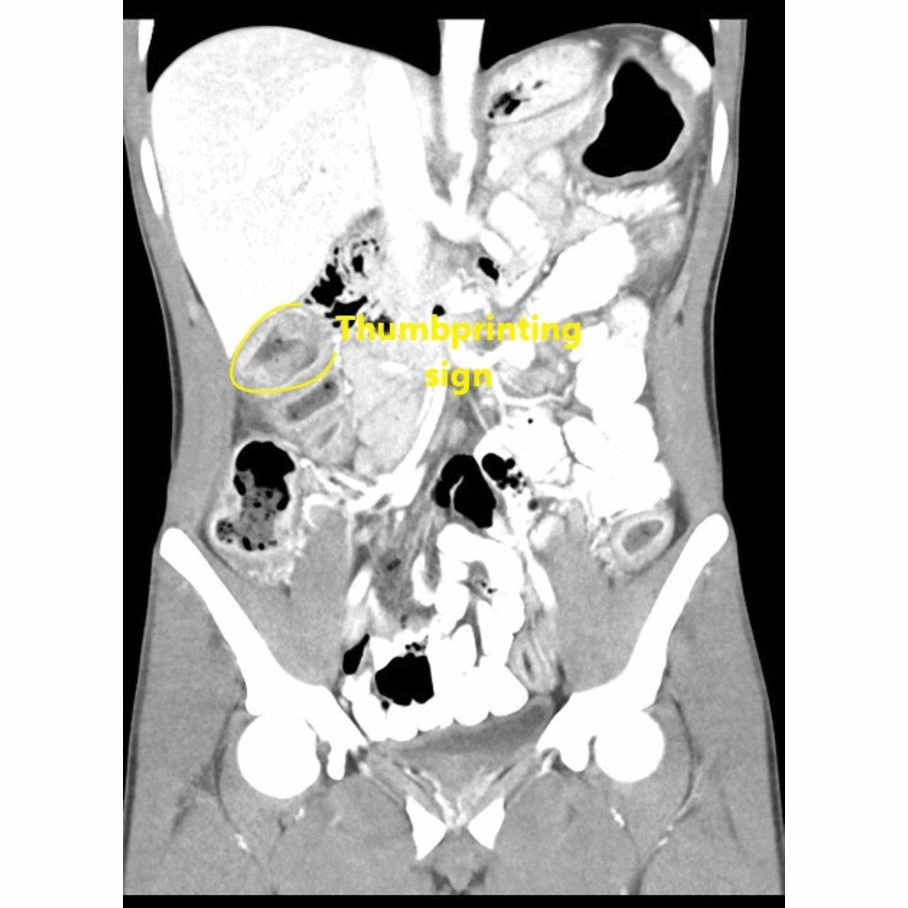 | |
| Kidney | Nephritis |
|
 |
| Pulmonary | Pleural effusion |
|
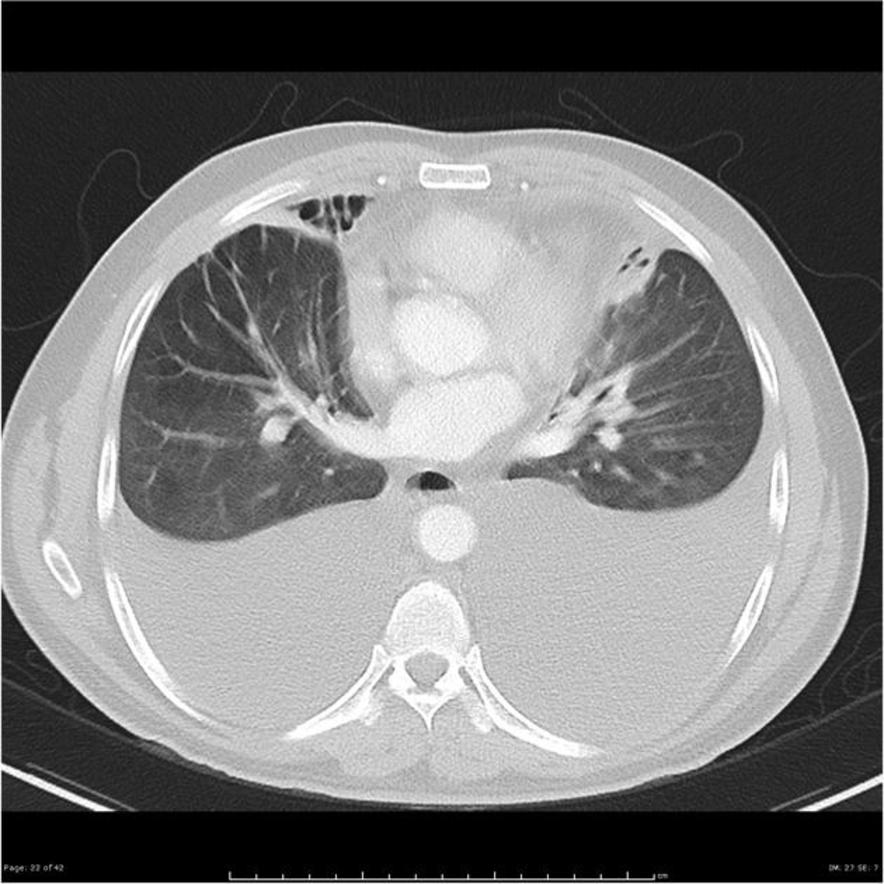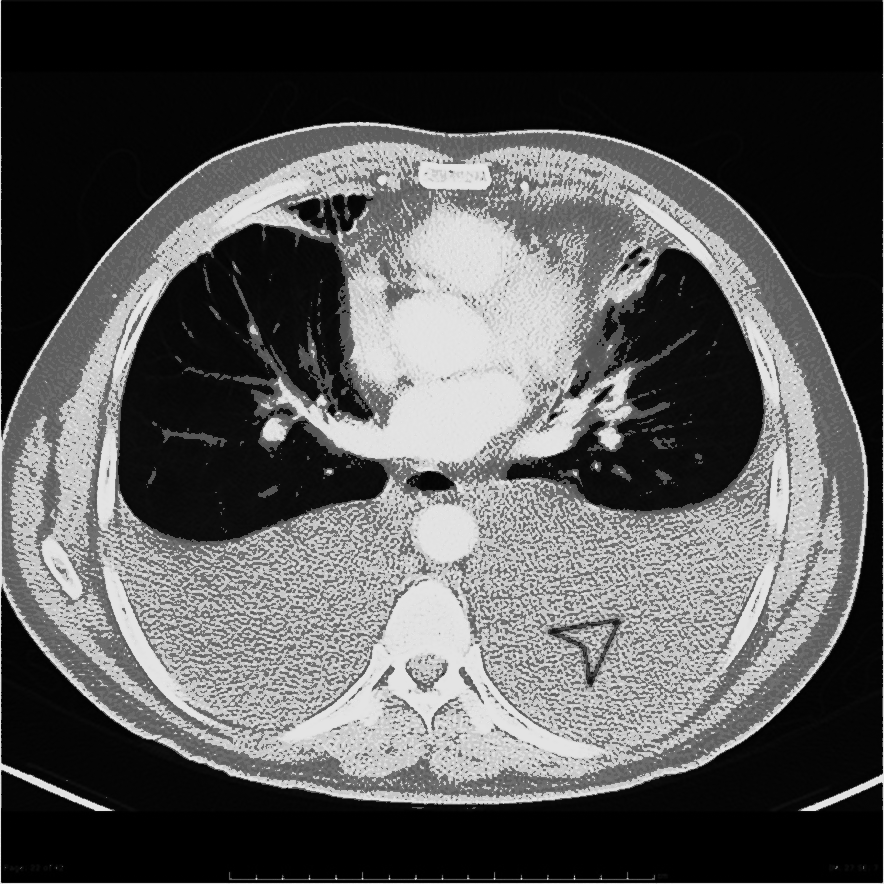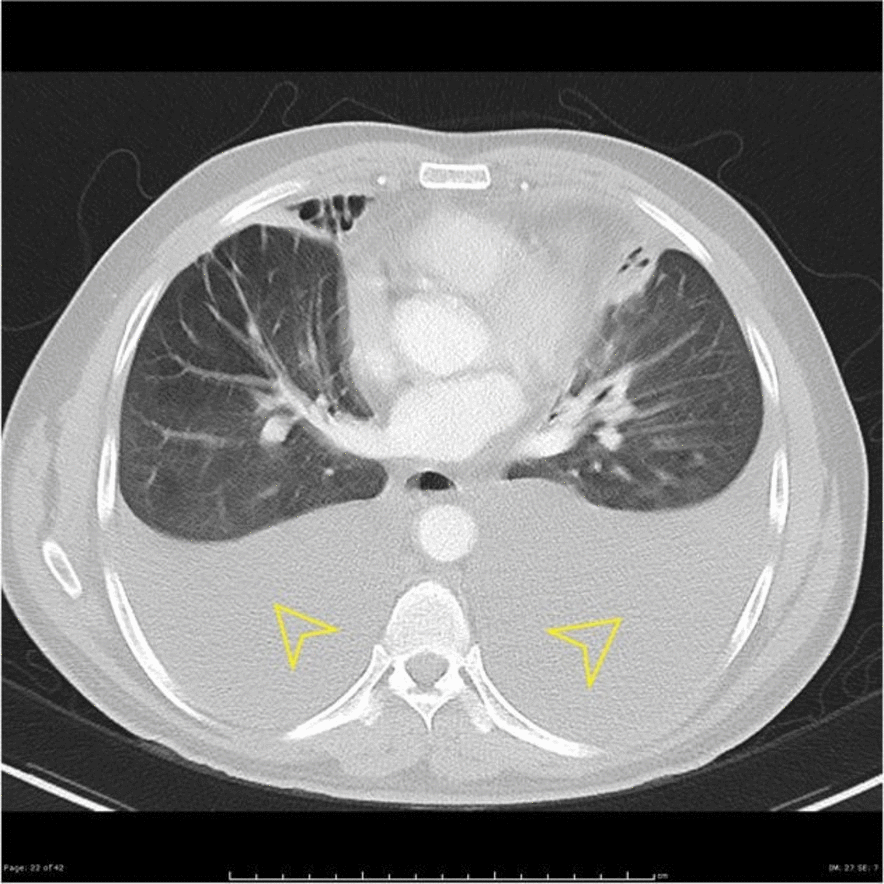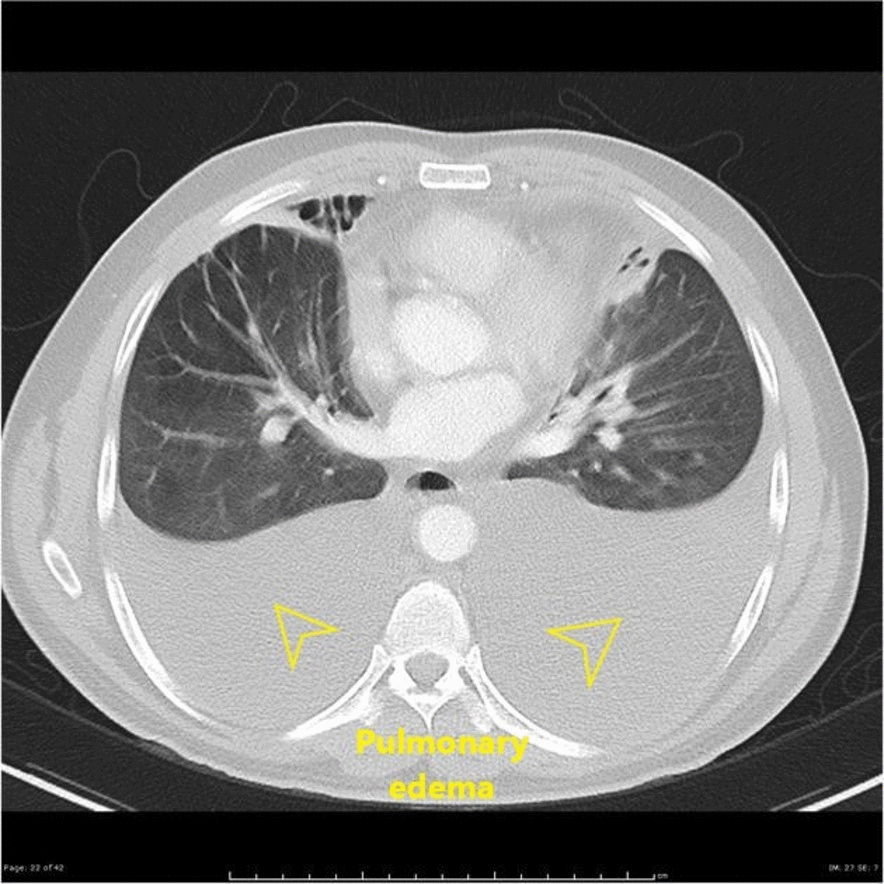 |
| Pulmonary hypertension |
|
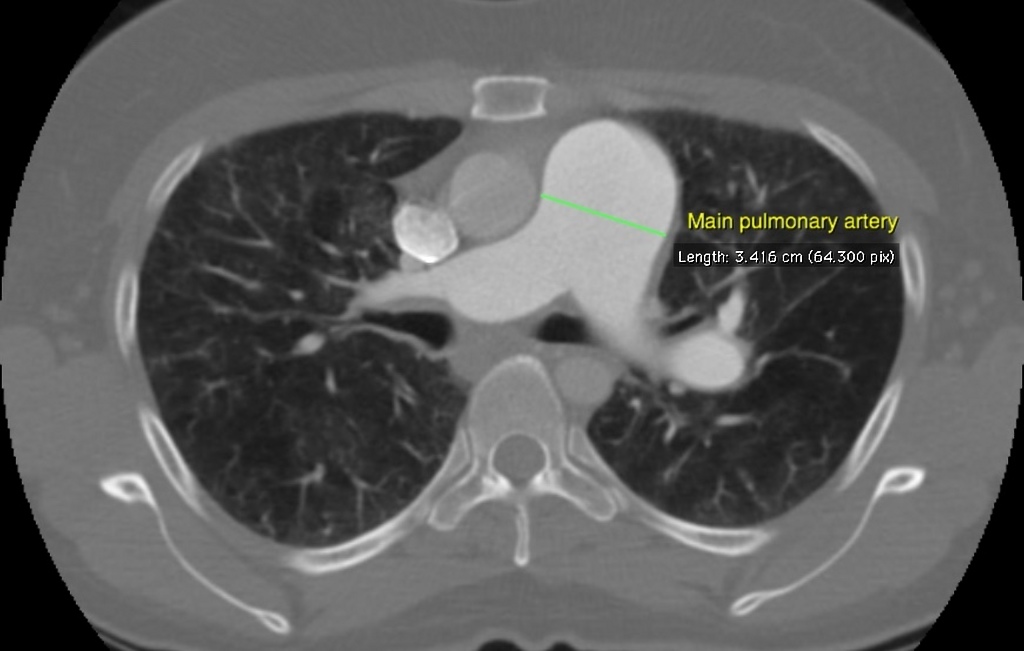 | |
| Pneumonitis |
|
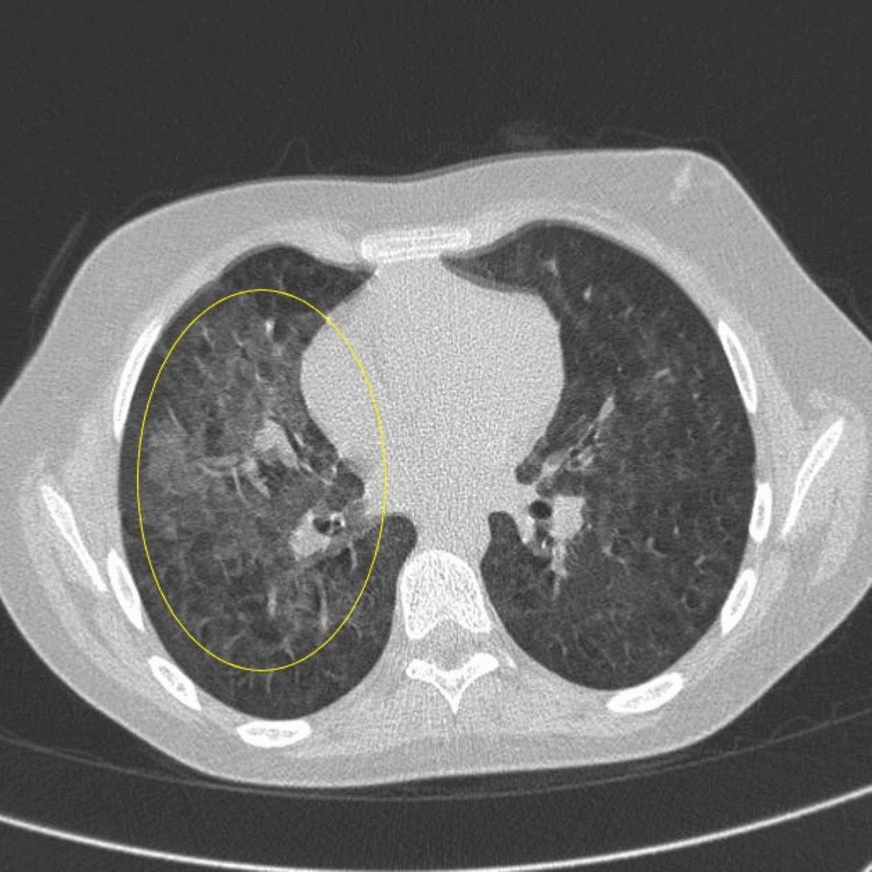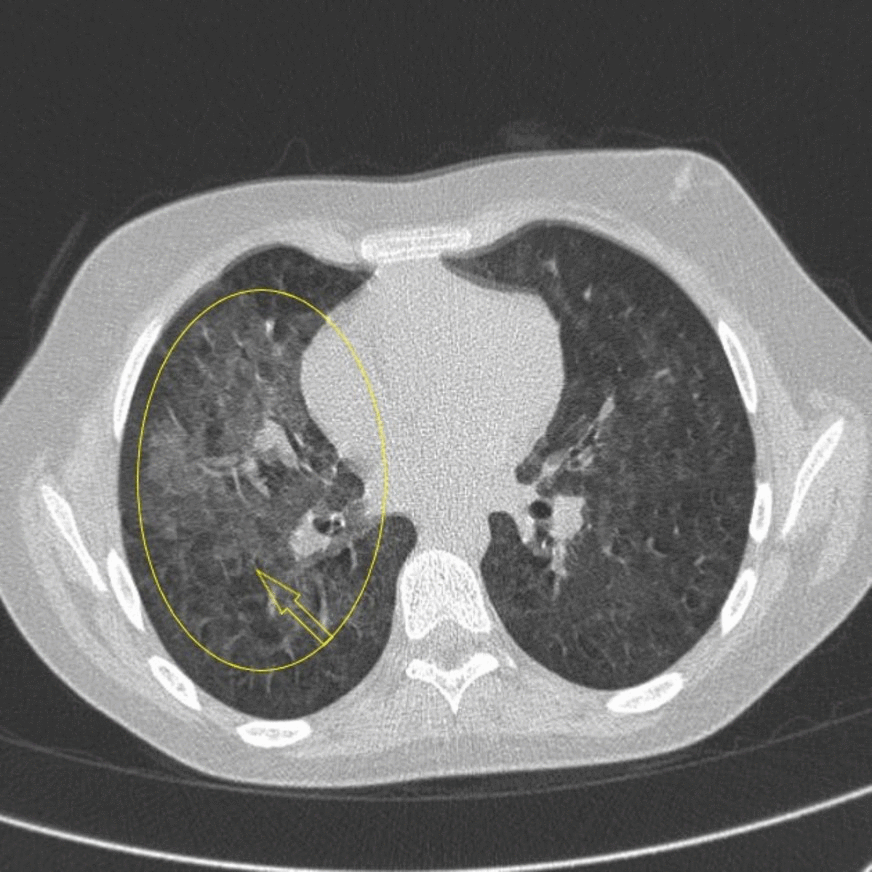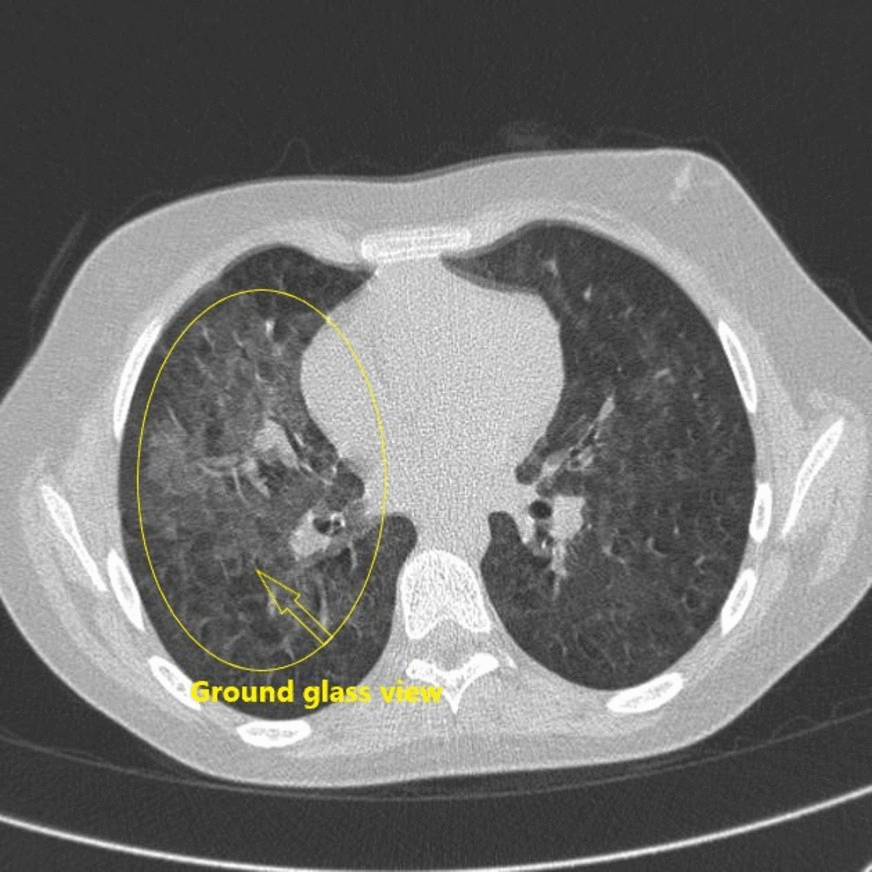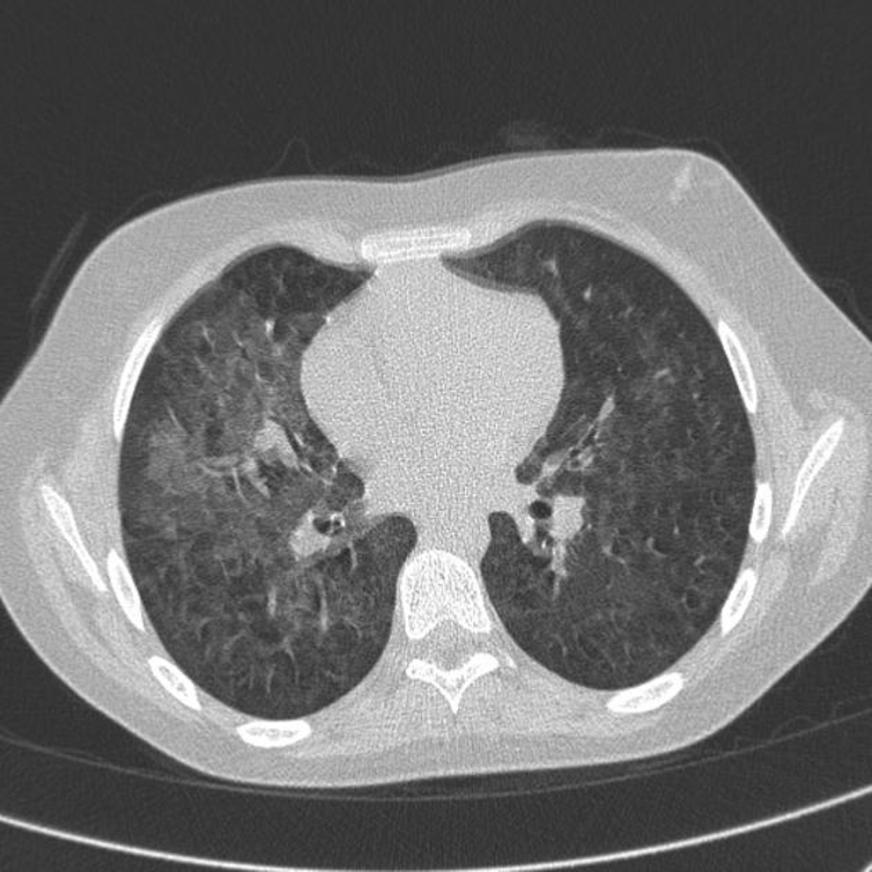 | |
| Neurological | Genreral |
|
Less common complications
| Organ | Disease | CT | Preview |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal | Intestinal pseudo-obstruction |
|
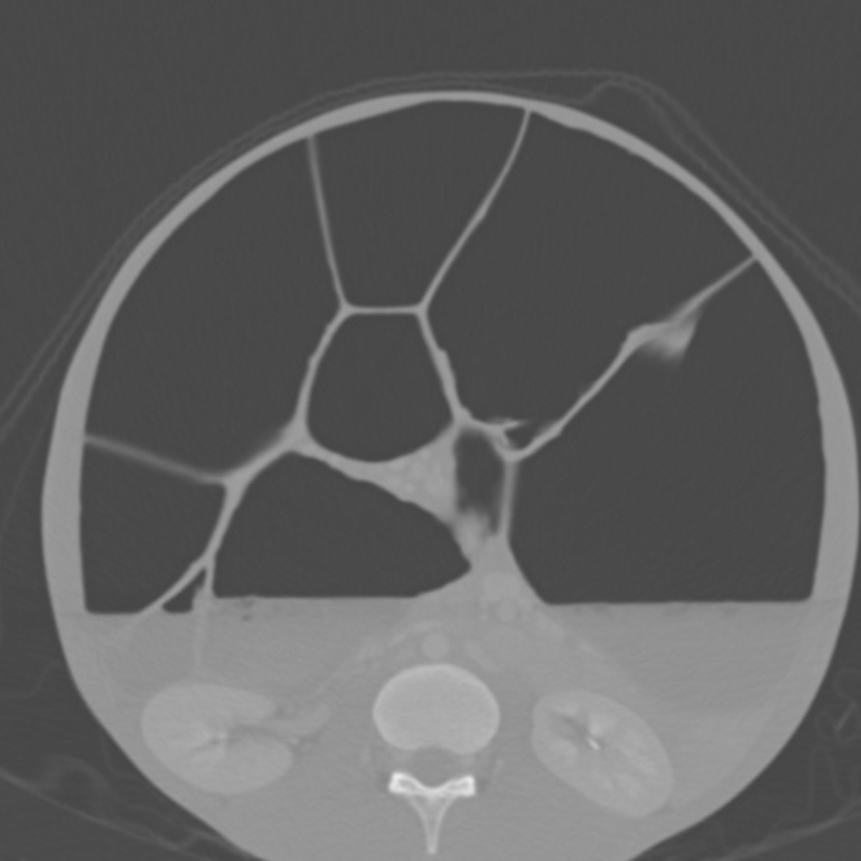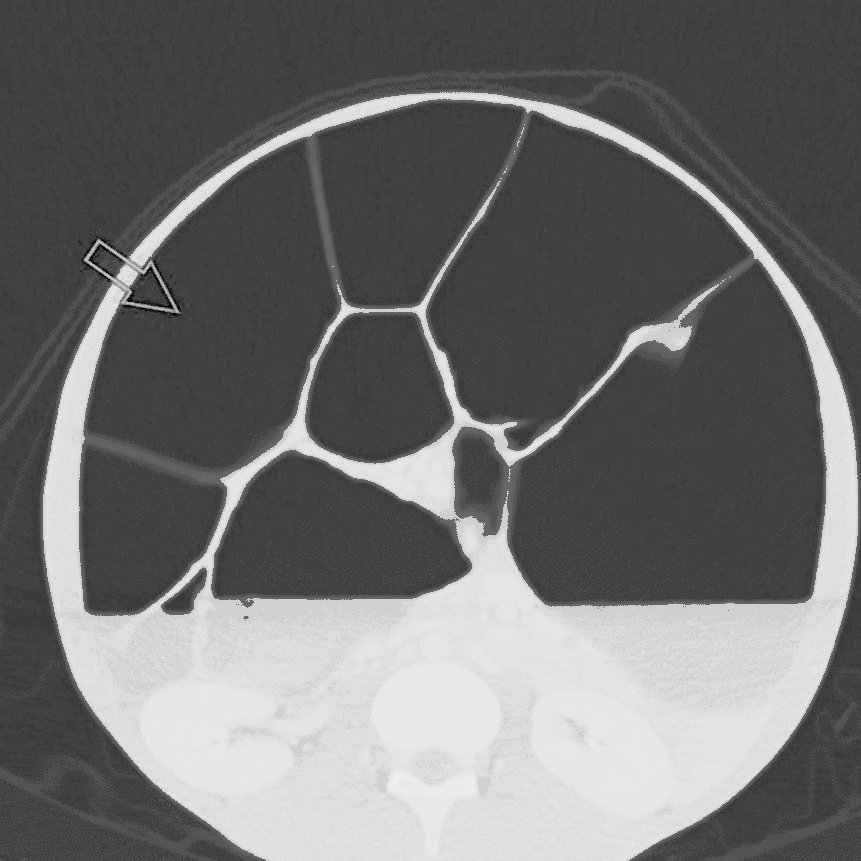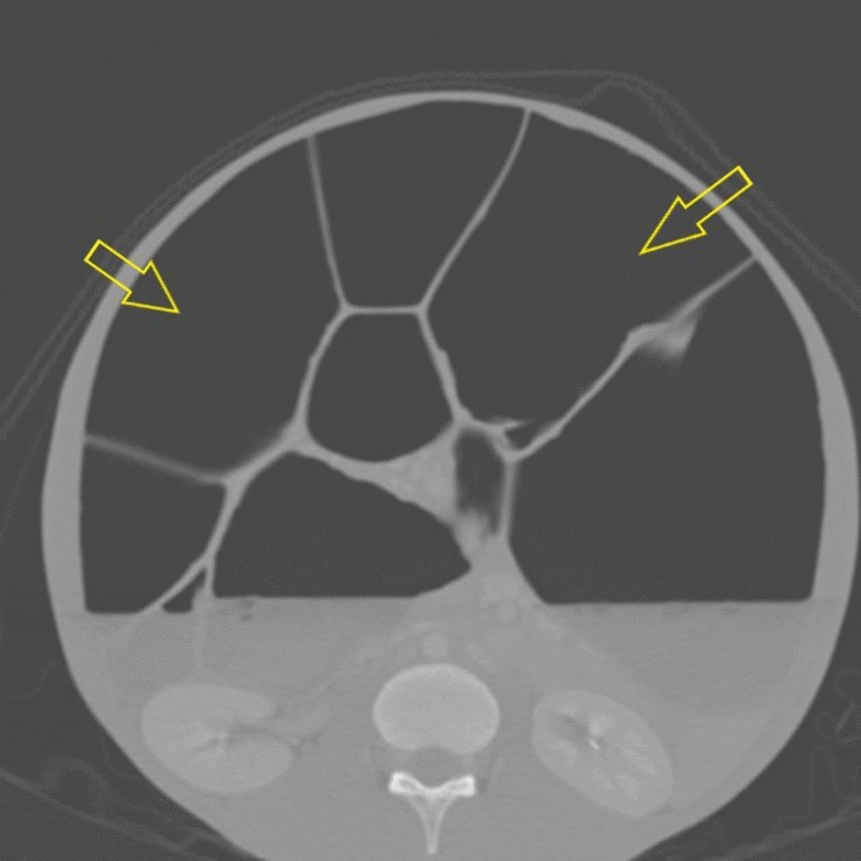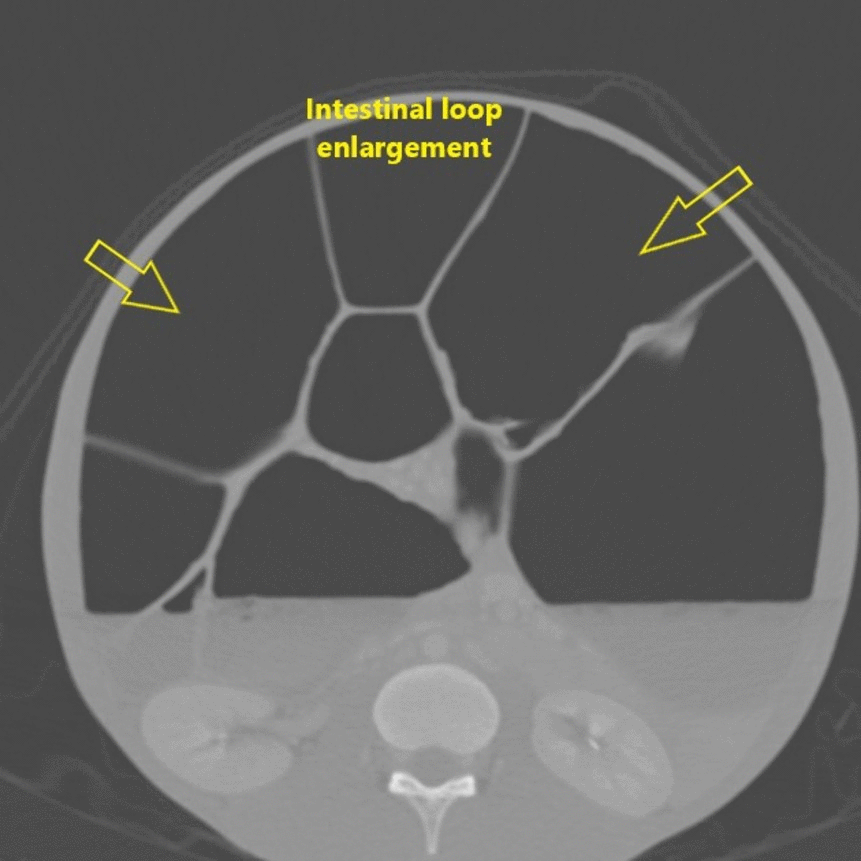 |
| Acute pancreatitis | Abnormalities that may be seen in the pancreas include:
|
 | |
| Autosplenectomy |
 | ||
| Acute cholecystitis |
|
 | |
| Pulmonary | Pulmonary emboli |
|
 |
| Shrinking lung syndrome |
|
||
| Pulmonary fibrosis |
|
 | |
| Cardiac | Acute pericarditis |
|
 |
| Pericardial effusion |
|
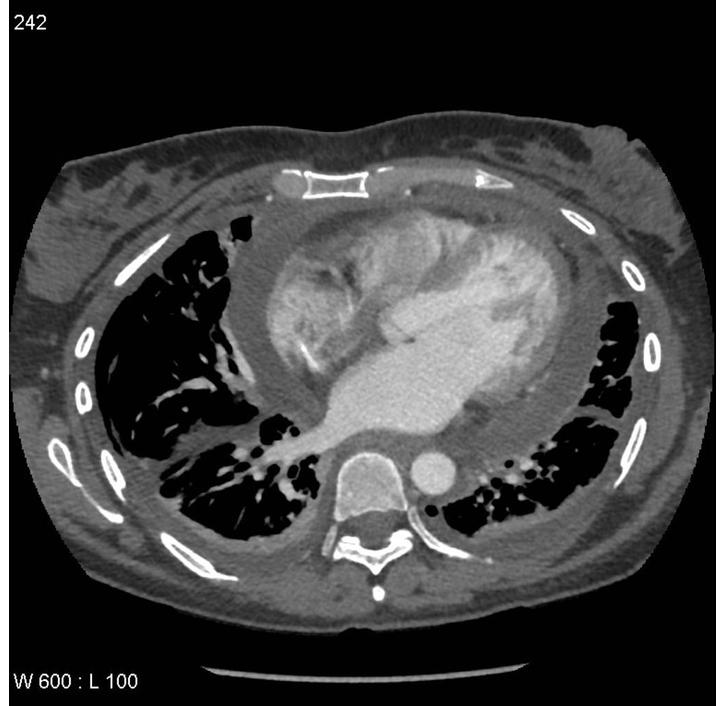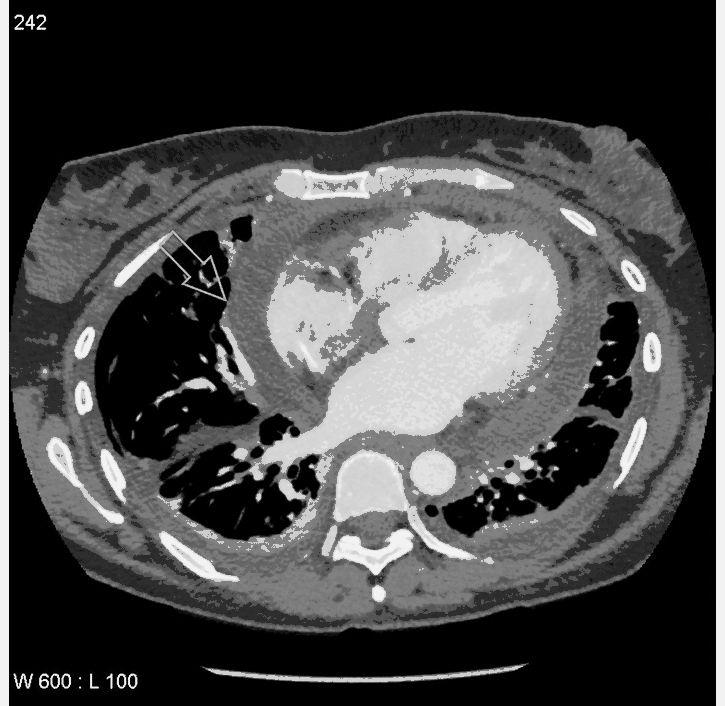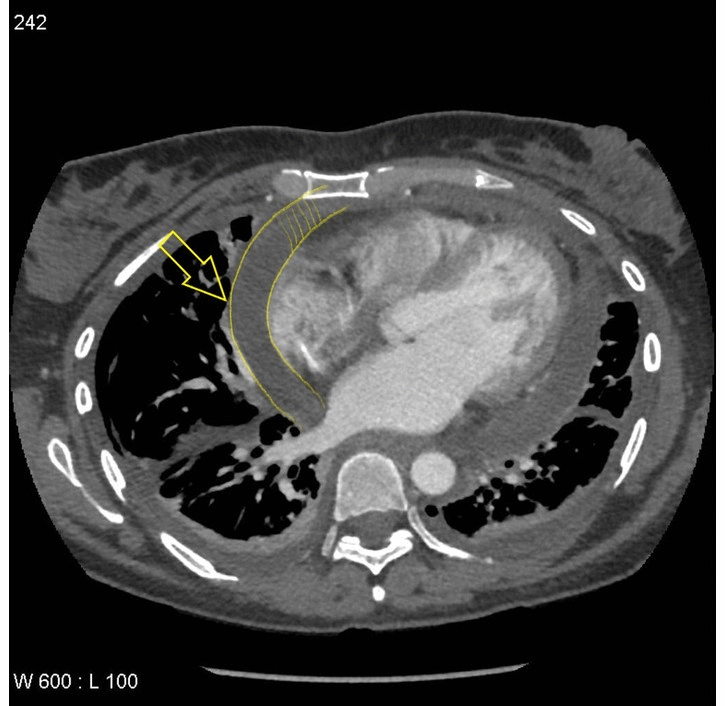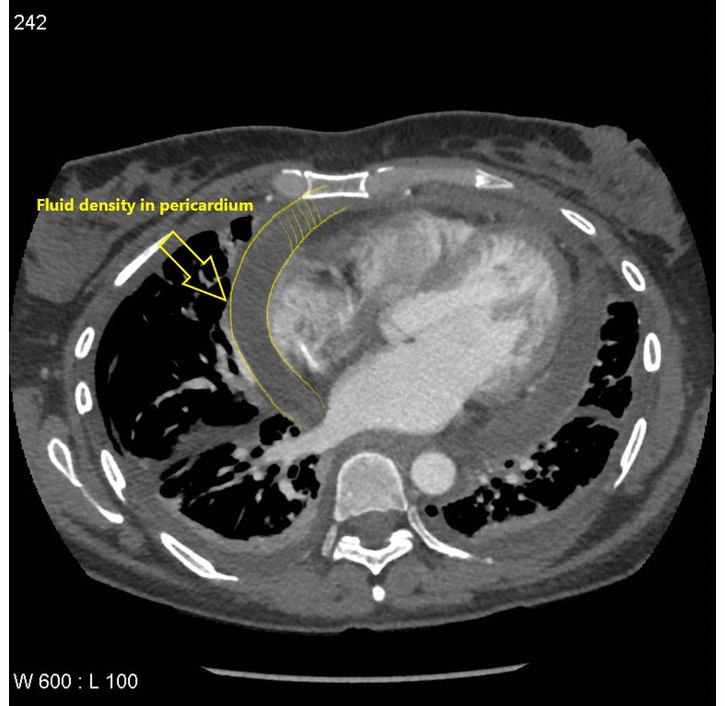 | |
| Neurological | Stroke |
|
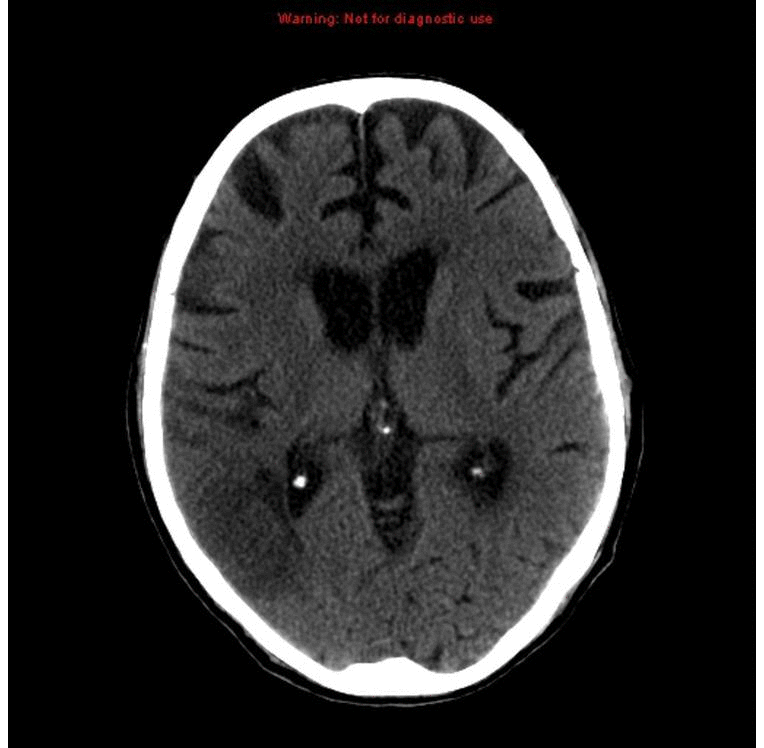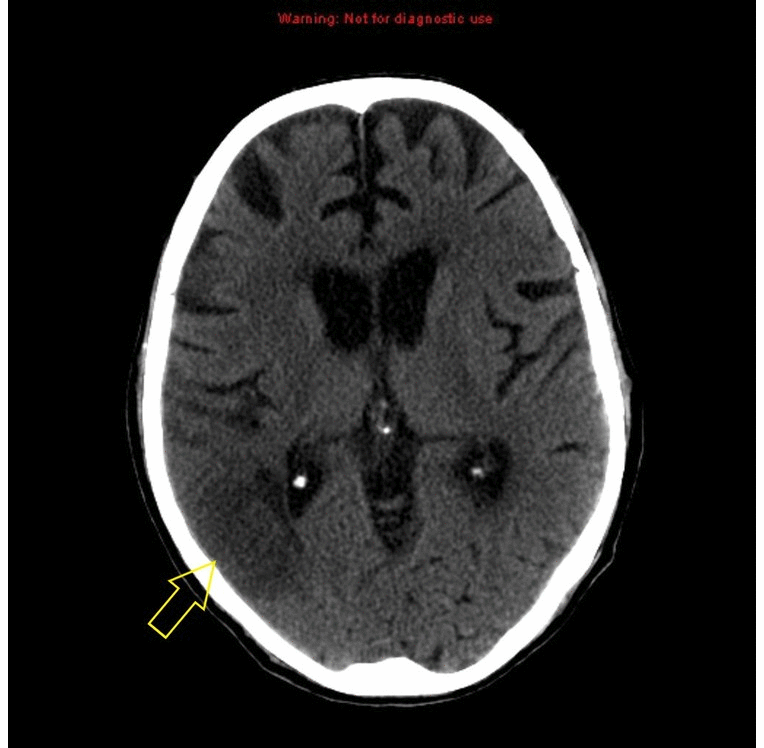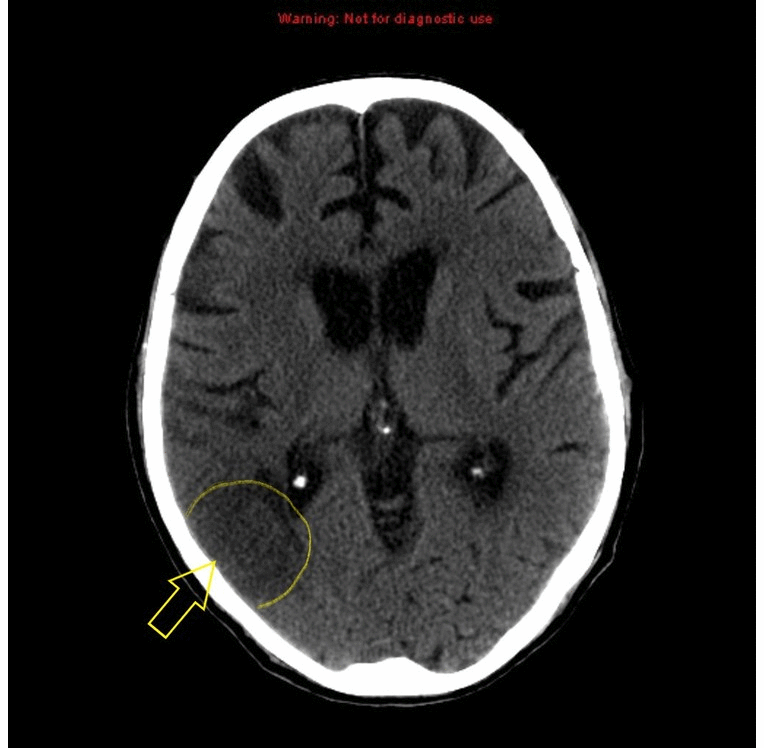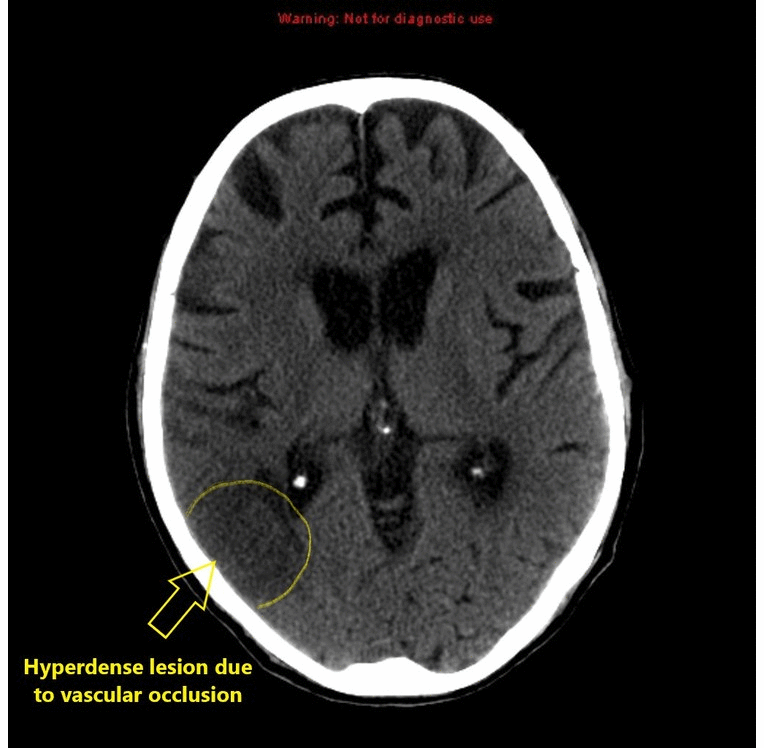 |
References
- ↑ Appenzeller S (2013). "Magnetic resonance imaging in systemic lupus erythematosus: where do we stand?". Cogn Behav Neurol. 26 (2): 53–4. doi:10.1097/WNN.0b013e31829d5b60. PMID 23812167.
- ↑ Thurman JM, Serkova NJ (2015). "Non-invasive imaging to monitor lupus nephritis and neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus". F1000Res. 4: 153. doi:10.12688/f1000research.6587.2. PMC 4536614. PMID 26309728.
- ↑ Lin K, Lloyd-Jones DM, Li D, Liu Y, Yang J, Markl M, Carr JC (2015). "Imaging of cardiovascular complications in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus". Lupus. 24 (11): 1126–34. doi:10.1177/0961203315588577. PMC 4567427. PMID 26038342.
- ↑ Sarbu N, Bargalló N, Cervera R (2015). "Advanced and Conventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Neuropsychiatric Lupus". F1000Res. 4: 162. doi:10.12688/f1000research.6522.2. PMC 4505788. PMID 26236469.
- ↑ Qin H, Guo Q, Shen N, Huang X, Wu H, Zhang M, Bao C, Chen S (2014). "Chest imaging manifestations in lupus nephritis". Clin. Rheumatol. 33 (6): 817–23. doi:10.1007/s10067-014-2586-2. PMID 24696368.
- ↑ Goh YP, Naidoo P, Ngian GS (2013). "Imaging of systemic lupus erythematosus. Part II: gastrointestinal, renal, and musculoskeletal manifestations". Clin Radiol. 68 (2): 192–202. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2012.06.109. PMID 22901453.
- ↑ Gal Y, Twig G, Mozes O, Greenberg G, Hoffmann C, Shoenfeld Y (2013). "Central nervous system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: an imaging challenge". Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 15 (7): 382–6. PMID 23943987.
- ↑ Shirato M, Hisa N, Fujikura Y, Ohkuma K, Kutsuki S, Hiramatsu K (1992). "[Imaging diagnosis of lupus enteritis--especially about sonographic findings]". Nihon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi (in Japanese). 52 (10): 1394–9. PMID 1448334.
- ↑ Adachi JD, Lau A (2014). "Systemic lupus erythematosus, osteoporosis, and fractures". J. Rheumatol. 41 (10): 1913–5. doi:10.3899/jrheum.140919. PMID 25275093.
- ↑ Curiel R, Akin EA, Beaulieu G, DePalma L, Hashefi M (2011). "PET/CT imaging in systemic lupus erythematosus". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1228: 71–80. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06076.x. PMID 21718325.
- ↑ Goh YP, Naidoo P, Ngian GS (2013). "Imaging of systemic lupus erythematosus. Part I: CNS, cardiovascular, and thoracic manifestations". Clin Radiol. 68 (2): 181–91. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2012.06.110. PMID 22901452.