|
|
| Line 15: |
Line 15: |
| {{CMG}} | | {{CMG}} |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview==
| |
| '''Sideroblastic anemia''' is caused by the abnormal production of [[red blood cell]]s as part of [[myelodysplastic syndrome]], which can evolve into [[hematological malignancy|hematological malignancies]] (especially [[acute myelogenous leukemia]]). Thus, the body has iron available, but cannot incorporate it into hemoglobin.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Causes==
| |
| The common feature of these causes is a failure to completely form [[heme]] - whose biosynthesis takes place partly in the [[mitochondrion]]. This leads to deposits of iron in the [[mitochondria]] that form a ring around the [[Cell nucleus|nucleus]] of the developing [[red blood cell]]. Sometimes the disorder represents a stage in evolution of a generalized bone marrow disorder that may ultimately terminate in acute leukemia.
| |
| * Toxins: [[lead]] or [[zinc]] poisoning
| |
| * Drug-induced: [[ethanol]], [[isoniazid]], [[chloramphenicol]], [[cycloserine]]
| |
| * Nutritional: [[pyridoxine]] or [[copper]] deficiency
| |
| * Genetic: ALA synthase deficiency ([[X-linked]])
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Diagnosis== | | ==Related Chapters== |
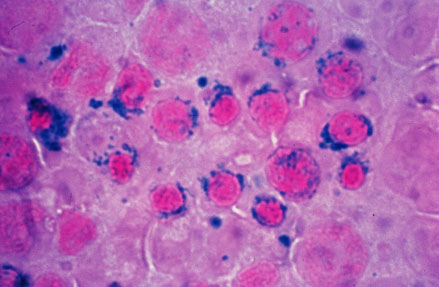
| Ringed sideroblasts are seen in the bone marrow.
| |
| | |
| ==Laboratory findings==
| |
| * Increased [[ferritin]] levels
| |
| * Decreased [[total iron-binding capacity]]
| |
| * [[Hematocrit]] of about 20-30%
| |
| * Serum Iron: High
| |
| * High [[transferrin saturation]]
| |
| * The [[mean corpuscular volume]] or MCV is usually normal or slightly increased; although it may occasionally be low, leading to confusion with iron deficiency.{{ref|Laboratory_findings}}
| |
| * With [[lead poisoning]], see coarse basophilic stippling of red blood cells on peripheral blood smear
| |
| * Specific test: Prussian Blue stain of RBC in marrow. Shows ringed sideroblasts.
| |
| | |
| ==Treatment==
| |
| Occasionally, the anemia is so severe that support with transfusion is required. These patients usually do not respond to [[erythropoietin]] therapy.{{ref|Laboratory_findings}}Some cases have been reported that the anemia is reversed or heme level is improved through use of moderate to high doses of Pyrodoxine (Vitamin B6.) In severe cases of SBA Bone Marrow Transplant is also an option with limited information about the success rate. Some cases are listed on MedLine and various other medical cites.
| |
| | |
| ==See also==
| |
| * [[Anemia]] | | * [[Anemia]] |
| * [[Siderosis]] | | * [[Siderosis]] |
|
| |
|
| == References ==
| |
| {{reflist|2}}
| |
|
| |
|
| {{Hematology}} | | {{Hematology}} |