Sideroblastic anemia: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} +, -{{EH}} +, -{{EJ}} +, -{{Editor Help}} +, -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
'''For patient information click [[Sideroblastic anemia (patient information)|here]]''' | |||
{{Infobox_Disease | | {{Infobox_Disease | | ||
Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | ||
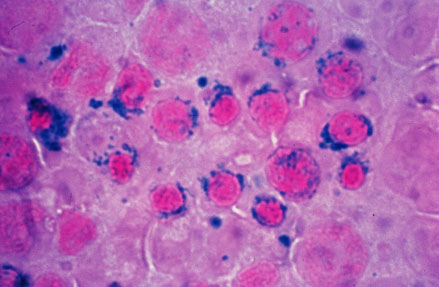
Image = Sideroblastic (microcytic) anemia.jpg | | Image = Sideroblastic (microcytic) anemia.jpg | | ||
Caption = Sideroblastic (microcytic) anemia| | Caption = Sideroblastic (microcytic) anemia| | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Sideroblastic anemia}} | |||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{N.F}} | |||
{{SK}} Sideroblastic anaemia | |||
== [[Sideroblastic anemia overview|Overview]] == | |||
== | == [[Sideroblastic anemia historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | ||
== | == [[Sideroblastic anemia classification|Classification]] == | ||
== | == [[Sideroblastic anemia pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]] == | ||
== | == [[Sideroblastic anemia causes|Causes]] == | ||
== | == [[Sideroblastic anemia differential diagnosis|Differentiating Sideroblastic Anemia from other Diseases]] == | ||
== | == [[Sideroblastic anemia epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | ||
== [[Sideroblastic anemia risk factors|Risk Factors]] == | |||
== [[Sideroblastic anemia screening|Screening]] == | |||
== [[Sideroblastic anemia natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]] == | |||
== Diagnosis == | |||
[[Sideroblastic anemia diagnostic study of choice|Diagnostic study of choice]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia x ray|X Ray]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia CT|CT]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia MRI|MRI]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia echocardiography or ultrasound|Ultrasound]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia other imaging findings|Other Imaging Studies]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] | |||
== Treatment == | |||
[[Sideroblastic anemia medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia surgery|Surgery]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia cost-effectiveness of therapy | Cost Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Sideroblastic anemia future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] | |||
==Case Studies== | |||
[[Sideroblastic anemia case study one|Case #1]] | |||
==Related Chapters== | |||
* [[Anemia]] | * [[Anemia]] | ||
* [[Siderosis]] | * [[Siderosis]] | ||
{{Hematology}} | {{Hematology}} | ||
| Line 58: | Line 55: | ||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | {{WikiDoc Sources}} | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Up-To-Date]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Hematology]] | [[Category:Hematology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:11, 30 July 2020
For patient information click here
| Sideroblastic anemia | |
 | |
|---|---|
| Sideroblastic (microcytic) anemia |
|
Sideroblastic anemia Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Sideroblastic anemia On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Sideroblastic anemia |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Nazia Fuad M.D.
Synonyms and keywords: Sideroblastic anaemia
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Sideroblastic Anemia from other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
Diagnostic study of choice | History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | X Ray | CT | MRI | Ultrasound | Other Imaging Studies | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention | Cost Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies