Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis diagnostic study of choice: Difference between revisions
Nazia Fuad (talk | contribs) |
Aditya Ganti (talk | contribs) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{CMG}}; {{APM}} {{AE}} {{KW}}, {{ADS}}, | {{CMG}}; {{APM}} {{AE}} {{KW}}, {{ADS}}, | ||
{{AEL}} | {{AEL}}, {{N.F}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Rapid diagnosis of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is very crucial to save kidneys function | Rapid diagnosis of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is very crucial to save kidneys function. It includes blood workup and renal [[biopsy]].Renal [[biopsy]] will provide the definitive diagnosis about the extent of involvement. Sometimes the result can be delayed ,in such cases the emperative therapy should be started to prevent [[end stage renal disease]]. | ||
== Diagnostic study of choice == | |||
==== Renal biopsy: ==== | ==== Renal biopsy: ==== | ||
* Renal biopsy will provide the most accurate reslt. | * [[Renal biopsy]] will provide the most accurate reslt. | ||
* Renal biopsy will give accurate information about the extent of the disease and therapy can be planned accordingly. | * [[Renal biopsy]] will give accurate information about the extent of the disease and therapy can be planned accordingly. | ||
* | * Findings include:<ref name="pmid12631105">{{cite journal |vauthors=Jennette JC |title=Rapidly progressive crescentic glomerulonephritis |journal=Kidney Int. |volume=63 |issue=3 |pages=1164–77 |date=March 2003 |pmid=12631105 |doi=10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00843.x |url=}}</ref> | ||
** Diffuse inflammation in glomeruli with rupture and damage to glomerular basement membrane. | ** Diffuse [[inflammation]] in [[glomeruli]] with rupture and damage to [[glomerular]] basement membrane. | ||
** Crescents are present in the Bowmans space. | ** [[Crescents]] are present in the [[Bowmans space]]. | ||
** Renal vessels can show transmural vasculitis, with necrosis and lymphocyte infiltrates. | ** Renal vessels can show [[transmural]] [[vasculitis]], with [[necrosis]] and [[lymphocyte]] infiltrates. | ||
** Tubular necrosis may also be present. | ** [[Tubular]] necrosis may also be present. | ||
** Interstitial granulomas in the glomeruli indicate Wegener’s granulomatosis. | ** [[Interstitial granulomas]] in the [[glomeruli]] indicate [[Wegener’s granulomatosis]]. | ||
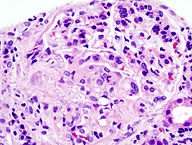
[[File:192px-Crescentic glomerulonephritis (1).jpg|200px|center|thumb| Microscopic findings of RPGN Source:By Nephron - Own work<ref>https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=17591464 </ref>]] | |||
=====Immunoflourescence===== | =====Immunoflourescence===== | ||
*In type I RPGN- diffuse and linear deposition of [[Immunoglobulin G|IgG]] along the [[GBM]]. | *In type I RPGN- diffuse and linear deposition of [[Immunoglobulin G|IgG]] along the [[GBM]]. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 28: | ||
*'''Electron microscopy''' | *'''Electron microscopy''' | ||
*In type I and type III, no electron dense deposits are seen. | *In type I and type III, no electron dense deposits are seen. | ||
**In type II RPGN, subepithelial electron dense deposits indiacting the presence of [[Immune complex|immune complexes]] are seen. | **In type II RPGN, [[subepithelial]] electron dense deposits indiacting the presence of [[Immune complex|immune complexes]] are seen. | ||
===== Serologic studies ===== | ===== Serologic studies ===== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 43: | ||
* Microscopic [[hematuria]] | * Microscopic [[hematuria]] | ||
*[[ Red cell casts]] indicates [[glomerular]] [[inflammation]] | *[[ Red cell casts]] indicates [[glomerular]] [[inflammation]] | ||
* Erythrocyte sedimentation, elevated with active disease. | * [[Erythrocyte sedimentation]], elevated with active disease. | ||
* C-reactive protein: levels are elevated and correspond with disease activity. | * [[C-reactive protein]]: levels are elevated and correspond with disease activity. | ||
*[[ Antinuclear antibody]] (ANA).High ANA titer is present in systemic lupus erythematosus. | *[[ Antinuclear antibody]] (ANA).High ANA titer is present in [[systemic lupus erythematosus]]. | ||
. | . | ||
Latest revision as of 18:10, 27 July 2018
|
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis diagnostic study of choice On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis diagnostic study of choice |
|
FDA on Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis diagnostic study of choice |
|
CDC on Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis diagnostic study of choice |
|
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis diagnostic study of choice in the news |
|
Blogs on Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis diagnostic study of choice |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Ali Poyan Mehr, M.D. [2] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Krzysztof Wierzbicki M.D. [3], Amandeep Singh M.D.[4],
Ahmed Elsaiey, MBBCH [5], Nazia Fuad M.D.
Overview
Rapid diagnosis of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is very crucial to save kidneys function. It includes blood workup and renal biopsy.Renal biopsy will provide the definitive diagnosis about the extent of involvement. Sometimes the result can be delayed ,in such cases the emperative therapy should be started to prevent end stage renal disease.
Diagnostic study of choice
Renal biopsy:
- Renal biopsy will provide the most accurate reslt.
- Renal biopsy will give accurate information about the extent of the disease and therapy can be planned accordingly.
- Findings include:[1]
- Diffuse inflammation in glomeruli with rupture and damage to glomerular basement membrane.
- Crescents are present in the Bowmans space.
- Renal vessels can show transmural vasculitis, with necrosis and lymphocyte infiltrates.
- Tubular necrosis may also be present.
- Interstitial granulomas in the glomeruli indicate Wegener’s granulomatosis.
Immunoflourescence
- In type I RPGN- diffuse and linear deposition of IgG along the GBM.
- In ttype II RPGN- diffuse and irregular deposition of IgG and C3 in the mesangial matrix.
- In type III RPGN- no finding.
- Electron microscopy
- In type I and type III, no electron dense deposits are seen.
- In type II RPGN, subepithelial electron dense deposits indiacting the presence of immune complexes are seen.
Serologic studies
- Complete blood cell count (CBC) withdifferential,
- Anemia can be seen in patienst with renal failure or gastrointestinal tract bleeding.
- Eosinophilia greater than 13% suggest Churg-Strauss disease.
- Serum electrolytes
- BUN(blood urea nitrogen)
- Serum creatinine
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
- Creatine phosphokinase (CPK),
- The most common abnormality is an increased serum creatinine level
- Urinalysis with microscopy: Proteinuria equal to or greater than 2-3 g in 24 hours.
- Microscopic hematuria
- Red cell casts indicates glomerular inflammation
- Erythrocyte sedimentation, elevated with active disease.
- C-reactive protein: levels are elevated and correspond with disease activity.
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA).High ANA titer is present in systemic lupus erythematosus.
.
References
- ↑ Jennette JC (March 2003). "Rapidly progressive crescentic glomerulonephritis". Kidney Int. 63 (3): 1164–77. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00843.x. PMID 12631105.
- ↑ https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=17591464