Pulsus bisferiens: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
===Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy=== | ===Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy=== | ||
[[File:Double-peak pulse.jpg| | [[File:Double-peak pulse.jpg|400px|right]] | ||
Pulsus bisferiens is due to [[systolic anterior motion]] (SAM) of the mitral valve. Because the mitral valve leaflet doesn't get pulled into the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) until after the [[aortic valve]] opens, the initial upstroke of the arterial pulse pressure will be normal. When the mitral valve leaflet gets pushed into the LVOT, the arterial pulse will momentarily collapse and will later be followed by a second rise in the pulse pressure, as the left ventricular pressure overcomes the increased obstruction caused by the SAM of the mitral valve. This can be seen on the physical examination as a double tap upon palpation of the apical impulse and as a double pulsation upon palpation of the carotid pulse, known as ''[[pulsus bisferiens]]''or a "[[spike and dome pattern]]" to the carotid pulse. | Pulsus bisferiens is due to [[systolic anterior motion]] (SAM) of the mitral valve. Because the mitral valve leaflet doesn't get pulled into the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) until after the [[aortic valve]] opens, the initial upstroke of the arterial pulse pressure will be normal. When the mitral valve leaflet gets pushed into the LVOT, the arterial pulse will momentarily collapse and will later be followed by a second rise in the pulse pressure, as the left ventricular pressure overcomes the increased obstruction caused by the SAM of the mitral valve. This can be seen on the physical examination as a double tap upon palpation of the apical impulse and as a double pulsation upon palpation of the carotid pulse, known as ''[[pulsus bisferiens]]'' or a "[[spike and dome pattern]]" to the carotid pulse. | ||
==Causes Of Pulsus Bisferiens== | ==Causes Of Pulsus Bisferiens== | ||
===Overview=== | ===Overview=== | ||
Pulsus bisferiens classically detected in patients with mixed [[aortic insufficiency]] and [[aortic stenosis]], but it may also be found in isolated severe [[aortic insufficiency]], and [[hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy]]. | |||
===Life Threatening Causes=== | ===Life Threatening Causes=== | ||
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated. Pulsus | Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated. Pulsus bisferiens in itself is not a life threatening condition, but in most of cases it indicate [[aortic insufficiency]], and further investigations should be done. | ||
===Common Causes=== | ===Common Causes=== | ||
The most common cause of pulsus | The most common cause of pulsus bisferiens is sever [[aortic insufficiency]] , other causes include: | ||
*[[ | *[[Aortic valve regurgitation]] Mixed with [[aortic stenosis]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy]] | ||
=== Causes by Organ System === | === Causes by Organ System === | ||
| Line 44: | Line 34: | ||
{|style="width:70%; height:100px" border="1" | {|style="width:70%; height:100px" border="1" | ||
|style="height:100px"; style="width:25%" border="1" bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | '''Cardiovascular''' | |style="height:100px"; style="width:25%" border="1" bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | '''Cardiovascular''' | ||
|style="height:100px"; style="width:75%" border="1" bgcolor="Beige" | [[ | |style="height:100px"; style="width:75%" border="1" bgcolor="Beige" | Sever [[aortic insufficiency]], [[aortic valve regurgitation]] Mixed with [[aortic stenosis]], [[hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | ||
| Line 126: | Line 116: | ||
|-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | ||
| '''Pulmonary''' | | '''Pulmonary''' | ||
|bgcolor="Beige"| | |bgcolor="Beige"| No underlying causes | ||
|- | |- | ||
|-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | |-bgcolor="LightSteelBlue" | ||
| Line 156: | Line 146: | ||
=== Causes in Alphabetical Order === | === Causes in Alphabetical Order === | ||
*[[ | *[[Aortic insufficiency]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Aortic valve regurgitation]] Mixed with [[aortic stenosis]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy]] | ||
==Related chapters== | ==Related chapters== | ||
*[[Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy]] | *[[Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:51, 25 November 2013
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Synonyms and keywords: Bisferious pulse, biphasic pulse, spike and dome pattern
Overview

Pulsus bisferiens is a sign where, on palpation of the pulse, a double peak in the aortic waveform is observed with each cardiac cycle.
Bisferious means striking twice. Therefore, pulsus bisferiens is a type of aortic waveform which has two systolic peaks separated by distinct mid-systolic dip
Pathophysiology
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
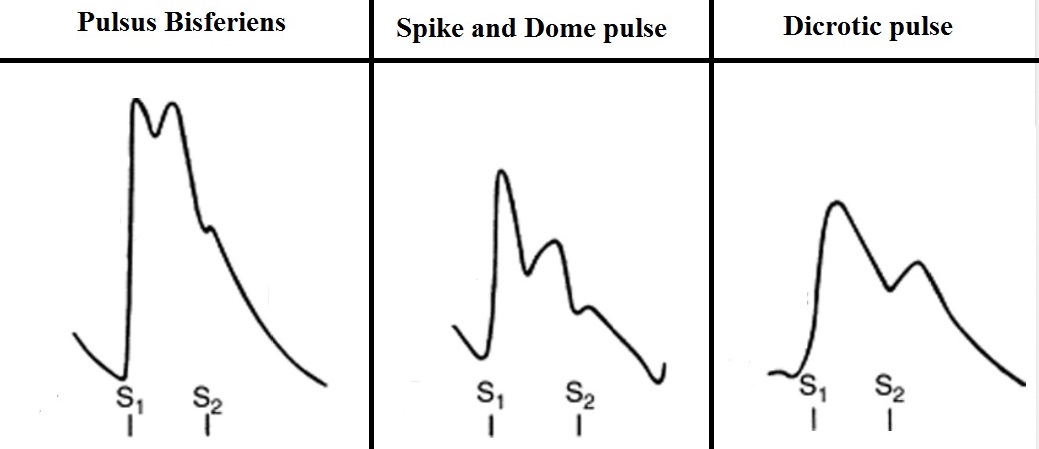
Pulsus bisferiens is due to systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve. Because the mitral valve leaflet doesn't get pulled into the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) until after the aortic valve opens, the initial upstroke of the arterial pulse pressure will be normal. When the mitral valve leaflet gets pushed into the LVOT, the arterial pulse will momentarily collapse and will later be followed by a second rise in the pulse pressure, as the left ventricular pressure overcomes the increased obstruction caused by the SAM of the mitral valve. This can be seen on the physical examination as a double tap upon palpation of the apical impulse and as a double pulsation upon palpation of the carotid pulse, known as pulsus bisferiens or a "spike and dome pattern" to the carotid pulse.
Causes Of Pulsus Bisferiens
Overview
Pulsus bisferiens classically detected in patients with mixed aortic insufficiency and aortic stenosis, but it may also be found in isolated severe aortic insufficiency, and hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy.
Life Threatening Causes
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated. Pulsus bisferiens in itself is not a life threatening condition, but in most of cases it indicate aortic insufficiency, and further investigations should be done.
Common Causes
The most common cause of pulsus bisferiens is sever aortic insufficiency , other causes include:
- Aortic valve regurgitation Mixed with aortic stenosis
Causes by Organ System
| Cardiovascular | Sever aortic insufficiency, aortic valve regurgitation Mixed with aortic stenosis, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy |
| Chemical / poisoning | No underlying causes |
| Dermatologic | No underlying causes |
| Drug and Toxin Side Effect | No underlying causes |
| Ear Nose Throat | No underlying causes |
| Endocrine | No underlying causes |
| Environmental | No underlying causes |
| Gastroenterologic | No underlying causes |
| Genetic | [No underlying causes |
| Hematologic | No underlying causes |
| Iatrogenic | No underlying cause |
| Infectious Disease | No underlying causes |
| Musculoskeletal / Ortho | No underlying causes |
| Neurologic | No underlying cause |
| Nutritional / Metabolic | No underlying cause |
| Obstetric/Gynecologic | No underlying cause |
| Oncologic | No underlying causes |
| Opthalmologic | No underlying causes |
| Overdose / Toxicity | [No underlying causes |
| Psychiatric | No underlying causes |
| Pulmonary | No underlying causes |
| Renal / Electrolyte | No underlying causes |
| Rheum / Immune / Allergy | No underlying causes |
| Sexual | No underlying causes |
| Trauma | No underlying causes |
| Urologic | No underlying causes |
| Miscellaneous | No underlying causes |
Causes in Alphabetical Order
- Aortic valve regurgitation Mixed with aortic stenosis