Pancoast tumor echocardiography or ultrasound: Difference between revisions
Mazia Fatima (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Pancoast tumor}} | {{Pancoast tumor}} | ||
{{CMG}}{{AE}}{{Mazia}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Mazia}} | ||
==Overveiw== | ==Overveiw== | ||
Pancoast tumor, a subtype of lung cancer located at the lung apex. On endobronchial and endoscopic ultrasound, characteristic findings of lung cancer may include: enlarged lymph nodes and local invasion to adjacent bronchial structures and mediastinum. Endobronchial ultrasound is a first-line diagnostic modality for mediastinal staging.<ref name="pmid24484269">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kinsey CM, Arenberg DA |title=Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for non-small cell lung cancer staging |journal=Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. |volume=189 |issue=6 |pages=640–9 |year=2014 |pmid=24484269 |doi=10.1164/rccm.201311-2007CI |url=}}</ref> | Pancoast tumor, a subtype of [[lung cancer]] located at the [[lung]] [[apex]]. On endobronchial and endoscopic [[ultrasound]], characteristic findings of [[lung cancer]] may include: [[enlarged lymph nodes]] and local [[invasion]] to adjacent [[bronchial]] structures and [[mediastinum]]. Endobronchial [[ultrasound]] is a first-line diagnostic modality for [[mediastinal]] [[Staging (pathology)|staging]].<ref name="pmid24484269">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kinsey CM, Arenberg DA |title=Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for non-small cell lung cancer staging |journal=Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. |volume=189 |issue=6 |pages=640–9 |year=2014 |pmid=24484269 |doi=10.1164/rccm.201311-2007CI |url=}}</ref> | ||
==Ultrasound== | ==Ultrasound== | ||
*Endobronchial ultrasound is a first-line diagnostic modality for mediastinal staging.<ref name="pmid24484269">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kinsey CM, Arenberg DA |title=Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for non-small cell lung cancer staging |journal=Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. |volume=189 |issue=6 |pages=640–9 |year=2014 |pmid=24484269 |doi=10.1164/rccm.201311-2007CI |url=}}</ref> | *Endobronchial [[ultrasound]] is a first-line [[diagnostic]] modality for [[mediastinal]] [[Cancer staging|staging]].<ref name="pmid24484269">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kinsey CM, Arenberg DA |title=Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for non-small cell lung cancer staging |journal=Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. |volume=189 |issue=6 |pages=640–9 |year=2014 |pmid=24484269 |doi=10.1164/rccm.201311-2007CI |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Common features of endobronchial ultrasound, include: <ref name="cancer"> Tests for non-small cell lung cancer. American Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.org/cancer/lungcancer-non-smallcell/detailedguide/non-small-cell-lung-cancer-diagnosis Accessed on February 25, 2016</ref> | *Common features of endobronchial [[ultrasound]], include:<ref name="cancer">Tests for non-small cell lung cancer. American Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.org/cancer/lungcancer-non-smallcell/detailedguide/non-small-cell-lung-cancer-diagnosis Accessed on February 25, 2016</ref> | ||
:*Evaluation of lymph nodes and other structures in the mediastinum | :*Evaluation of [[lymph nodes]] and other structures in the [[mediastinum]] | ||
:*Mediastinum invasion staging | :*[[Mediastinum]] [[invasion]] [[Cancer staging|staging]] | ||
:*Determination of management strategy | :*Determination of management strategy | ||
:*Real time evaluation of structures | :*Real time evaluation of structures | ||
:*Sensitivity 90% and specificity of 97% | :*[[Sensitivity]] 90% and [[specificity]] of 97% | ||
*On ultrasound (endobronchial ultrasound), | *On [[ultrasound]] (endobronchial [[ultrasound]]), findings of Pancoast tumor may include:<ref name="lung cancer">Lung cancer staging. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lung_cancer_staging Accessed on February 25,2016</ref> | ||
:*Enlarged lymph nodes | :*[[Enlarged lymph nodes]] | ||
:*Local invasion to adjacent bronchial structures and mediastinum | :*Local [[invasion]] to adjacent [[bronchial]] structures and [[mediastinum]] | ||
* The table below summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of both ultrasound modalities, for the diagnostic assessment of | * The table below summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of both [[ultrasound]] modalities, for the [[diagnostic]] assessment of Pancoast tumor. | ||
::{| style="border:1px solid black; border-collapse:collapse" border="1" cellpadding="5" | ::{| style="border:1px solid black; border-collapse:collapse" border="1" cellpadding="5" | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 300px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Disadvantages}} | ! style="background: #4479BA; width: 300px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Disadvantages}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold; text-align:center;"| Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold; text-align:center;" | Endobronchial [[ultrasound]] (EBUS) | ||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;"| | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Direct visualization of lymph node stations | *Direct visualization of [[lymph node]] stations | ||
*Complements endoscopic ultrasound: covers lymph node stations 2R and 4R which are difficult to access by endoscopic ultrasound | *Complements [[endoscopic ultrasound]]: covers [[lymph node]] stations 2R and 4R which are difficult to access by [[endoscopic ultrasound]] | ||
*Lower false-negative rate than with blind transbronchial fine needle aspiration and fewer complications | *Lower [[false-negative]] rate than with blind transbronchial [[fine needle aspiration]] and fewer [[complications]] | ||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;"| | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | | ||
*More invasive than endoscopic ultrasound, few practitioners, but rapidly growing in popularity | *More [[invasive]] than [[endoscopic ultrasound]], few practitioners, but rapidly growing in popularity | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold; text-align:center;"| [[Endoscopic ultrasound]] (EUS) | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold; text-align:center;" | [[Endoscopic ultrasound]] (EUS) | ||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;"| | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Least invasive modality | *Least [[invasive]] modality | ||
*Uses the esophagus to access mediastinal lymph nodes | *Uses the [[esophagus]] to access [[mediastinal]] [[lymph nodes]] | ||
*Excellent for staging lymph nodes | *Excellent for [[Staging (pathology)|staging]] [[lymph nodes]] | ||
*Useful for station 2L and 4L, L adrenal, celiac lymph node | *Useful for station 2L and 4L, L [[adrenal]], [[celiac]] [[lymph node]] | ||
|style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;"| | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" | | ||
*Cannot reliably access right sided paratracheal lymph node stations 2 R and 4R | *Cannot reliably access right sided [[Paratracheal lymph nodes|paratracheal]] [[Lymph nodes|lymph node]] stations 2 R and 4R | ||
*Accurate discrimination of primary hilar tumors and involved lymph nodes is important | *Accurate discrimination of primary [[Hilar|hilar tumors]] and involved [[lymph nodes]] is important | ||
|} | |} | ||
<div align="left"> | <div align="left"> | ||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | <gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | ||
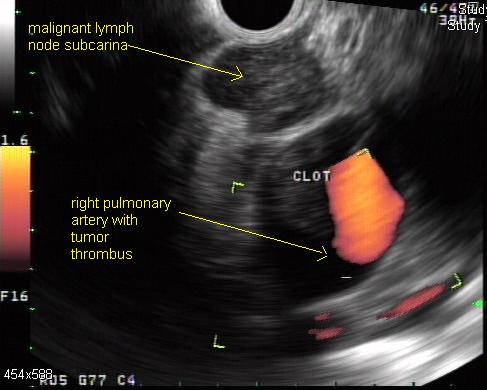
Image:Eus doppler mediastinal lymph node.JPG | Doppler endoscopic ultrasound: mediastinal lymph node | Image:Eus doppler mediastinal lymph node.JPG | Doppler endoscopic ultrasound: mediastinal lymph node | ||
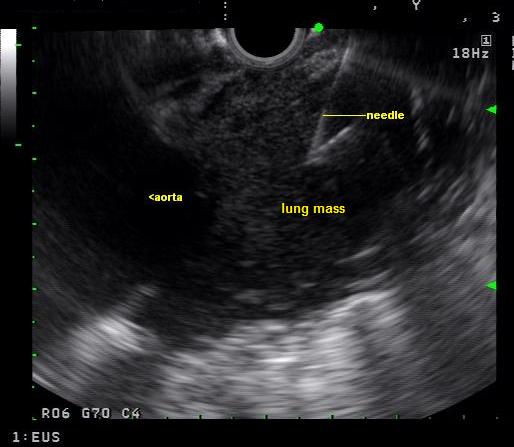
Image:Lul mass linear eus 1.jpg|Endoscopic ultrasound: A biopsy window is found and an fine needle aspiration advanced into the mass | Image:Lul mass linear eus 1.jpg|Endoscopic ultrasound: A biopsy window is found and an fine needle aspiration advanced into the mass | ||
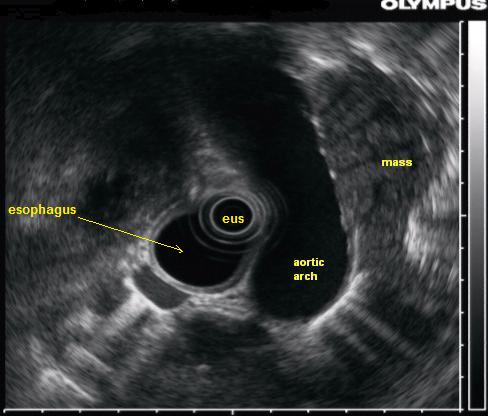
Image:Lul mass radial eus.jpg | Endoscopic ultrasound: A lung mass which is partially behind the aorta is seen with endoscopic ultrasound | Image:Lul mass radial eus.jpg | Endoscopic ultrasound: A lung mass which is partially behind the aorta is seen with endoscopic ultrasound | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:07, 16 March 2018
|
Pancoast tumor Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pancoast tumor echocardiography or ultrasound On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pancoast tumor echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pancoast tumor echocardiography or ultrasound |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mazia Fatima, MBBS [2]
Overveiw
Pancoast tumor, a subtype of lung cancer located at the lung apex. On endobronchial and endoscopic ultrasound, characteristic findings of lung cancer may include: enlarged lymph nodes and local invasion to adjacent bronchial structures and mediastinum. Endobronchial ultrasound is a first-line diagnostic modality for mediastinal staging.[1]
Ultrasound
- Endobronchial ultrasound is a first-line diagnostic modality for mediastinal staging.[1]
- Common features of endobronchial ultrasound, include:[2]
- Evaluation of lymph nodes and other structures in the mediastinum
- Mediastinum invasion staging
- Determination of management strategy
- Real time evaluation of structures
- Sensitivity 90% and specificity of 97%
- On ultrasound (endobronchial ultrasound), findings of Pancoast tumor may include:[3]
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Local invasion to adjacent bronchial structures and mediastinum
- The table below summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of both ultrasound modalities, for the diagnostic assessment of Pancoast tumor.
Procedure Advantages Disadvantages Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) - Direct visualization of lymph node stations
- Complements endoscopic ultrasound: covers lymph node stations 2R and 4R which are difficult to access by endoscopic ultrasound
- Lower false-negative rate than with blind transbronchial fine needle aspiration and fewer complications
- More invasive than endoscopic ultrasound, few practitioners, but rapidly growing in popularity
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) - Least invasive modality
- Uses the esophagus to access mediastinal lymph nodes
- Excellent for staging lymph nodes
- Useful for station 2L and 4L, L adrenal, celiac lymph node
- Cannot reliably access right sided paratracheal lymph node stations 2 R and 4R
- Accurate discrimination of primary hilar tumors and involved lymph nodes is important
-
Doppler endoscopic ultrasound: mediastinal lymph node
-
Endoscopic ultrasound: A biopsy window is found and an fine needle aspiration advanced into the mass
-
Endoscopic ultrasound: A lung mass which is partially behind the aorta is seen with endoscopic ultrasound
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kinsey CM, Arenberg DA (2014). "Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for non-small cell lung cancer staging". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 189 (6): 640–9. doi:10.1164/rccm.201311-2007CI. PMID 24484269.
- ↑ Tests for non-small cell lung cancer. American Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.org/cancer/lungcancer-non-smallcell/detailedguide/non-small-cell-lung-cancer-diagnosis Accessed on February 25, 2016
- ↑ Lung cancer staging. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lung_cancer_staging Accessed on February 25,2016