Ovarian germ cell tumor pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
===Pathogenesis=== | ===Pathogenesis=== | ||
*It is understood that [[ovarian]] [[germ cell]] [[tumors]] are the result of the [[Pathology|pathologic]] [[transformation]] of [[primordial germ cells]] during different stages of the development.<ref name="El-MaarriRijlaarsdam2015">{{cite journal|last1=El-Maarri|first1=Osman|last2=Rijlaarsdam|first2=Martin A.|last3=Tax|first3=David M. J.|last4=Gillis|first4=Ad J. M.|last5=Dorssers|first5=Lambert C. J.|last6=Koestler|first6=Devin C.|last7=de Ridder|first7=Jeroen|last8=Looijenga|first8=Leendert H. J.|title=Genome Wide DNA Methylation Profiles Provide Clues to the Origin and Pathogenesis of Germ Cell Tumors|journal=PLOS ONE|volume=10|issue=4|year=2015|pages=e0122146|issn=1932-6203|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0122146}}</ref><ref>{{cite book | last = Carcangiu | first = M. L. | title = WHO Classification of Tumours of Female Reproductive Organs | publisher = International Agency for Research on Cancer | location = Lyon | year = 2014 | isbn = 978-92-832-4487-5 }}</ref> | *It is understood that [[ovarian]] [[germ cell]] [[tumors]] are the result of the [[Pathology|pathologic]] [[transformation]] of [[primordial germ cells]] during different stages of the development.<ref name="El-MaarriRijlaarsdam2015">{{cite journal|last1=El-Maarri|first1=Osman|last2=Rijlaarsdam|first2=Martin A.|last3=Tax|first3=David M. J.|last4=Gillis|first4=Ad J. M.|last5=Dorssers|first5=Lambert C. J.|last6=Koestler|first6=Devin C.|last7=de Ridder|first7=Jeroen|last8=Looijenga|first8=Leendert H. J.|title=Genome Wide DNA Methylation Profiles Provide Clues to the Origin and Pathogenesis of Germ Cell Tumors|journal=PLOS ONE|volume=10|issue=4|year=2015|pages=e0122146|issn=1932-6203|doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0122146}}</ref><ref>{{cite book | last = Carcangiu | first = M. L. | title = WHO Classification of Tumours of Female Reproductive Organs | publisher = International Agency for Research on Cancer | location = Lyon | year = 2014 | isbn = 978-92-832-4487-5 }}</ref> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 40: | ||
*In 10% of the cases, the [[contralateral]] ovary carries a [[dermoid cyst]]. | *In 10% of the cases, the [[contralateral]] ovary carries a [[dermoid cyst]]. | ||
*In 40% of cases, they are accompanied by other types of [[germ cell]] [[tumors]].<ref name="KojimaharaNakahara2013">{{cite journal|last1=Kojimahara|first1=Takanobu|last2=Nakahara|first2=Kenji|last3=Takano|first3=Tadao|last4=Yaegashi|first4=Nobuo|last5=Nishiyama|first5=Hiroshi|last6=Fujimori|first6=Keiya|last7=Sato|first7=Naoki|last8=Terada|first8=Yukihiro|last9=Tase|first9=Toru|last10=Yokoyama|first10=Yoshihito|last11=Mizunuma|first11=Hideki|last12=Shoji|first12=Tadahiro|last13=Sugiyama|first13=Toru|last14=Kurachi|first14=Hirohisa|title=Yolk Sac Tumor of the Ovary: A Retrospective Multicenter Study of 33 Japanese Women by Tohoku Gynecologic Cancer Unit (TGCU)|journal=The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine|volume=230|issue=4|year=2013|pages=211–217|issn=1349-3329|doi=10.1620/tjem.230.211}}</ref> | *In 40% of cases, they are accompanied by other types of [[germ cell]] [[tumors]].<ref name="KojimaharaNakahara2013">{{cite journal|last1=Kojimahara|first1=Takanobu|last2=Nakahara|first2=Kenji|last3=Takano|first3=Tadao|last4=Yaegashi|first4=Nobuo|last5=Nishiyama|first5=Hiroshi|last6=Fujimori|first6=Keiya|last7=Sato|first7=Naoki|last8=Terada|first8=Yukihiro|last9=Tase|first9=Toru|last10=Yokoyama|first10=Yoshihito|last11=Mizunuma|first11=Hideki|last12=Shoji|first12=Tadahiro|last13=Sugiyama|first13=Toru|last14=Kurachi|first14=Hirohisa|title=Yolk Sac Tumor of the Ovary: A Retrospective Multicenter Study of 33 Japanese Women by Tohoku Gynecologic Cancer Unit (TGCU)|journal=The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine|volume=230|issue=4|year=2013|pages=211–217|issn=1349-3329|doi=10.1620/tjem.230.211}}</ref> | ||
==Genetics== | ==Genetics== | ||
*[[Ovarian]] [[germ cell]] [[tumors]] may be associated with [[cytogenetic]] abnormalities. | *[[Ovarian]] [[germ cell]] [[tumors]] may be associated with [[cytogenetic]] abnormalities. | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 21 March 2019
|
Ovarian germ cell tumor Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Ovarian germ cell tumor pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Ovarian germ cell tumor pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Ovarian germ cell tumor pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sahar Memar Montazerin, M.D.[2] Monalisa Dmello, M.B,B.S., M.D. [3]
Overveiw
The pathophysiology of ovarian germ cell tumors depends on the histological subtype. However, their origin is the primordial germ cells that transformed pathologically in different stages of development.
Pathophysiology
Pathogenesis
- It is understood that ovarian germ cell tumors are the result of the pathologic transformation of primordial germ cells during different stages of the development.[1][2]
| Germ cell | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathogenesis | Malignant transformation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mature teratoma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tumors esxpressing transcription factors of pluripotency | Tumors with primitive embryonic ectoderm, mesoderm, and/or endoderm differentiation | Tumors with extraembroyonic differentiation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dysgerminoma/Embryonal carcinoma | Immature teratoma | Yolk sac tumor/Choriocarcinoma | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mature teratoma
- Mature teratomas are benign tumors originating from pathologic development of primordial germ cells.[3]
- It originates from a single germ cell tumor after the first phase of meiosis.[4]
- These tumors contain the well-differentiated component of three germ layers.[3]
- Their usual location is the embryonic fusion line overhead and neck, mediastinum, a and presacral area and tend to present at a greater extent in the midline.
Dysgerminoma
- Dysgerminoma arises from primordial germ cells, which are gonadal cells that are normally involved in the gametogenesis.[1]
- The majority of dysgerminomas in women present in the stage 1A.[5]
- Bilateral invovlement occurs in 10% to 15% of the cases.
- In < 15% of the affected cases, elements of other germ cell tumors can also be found.[6]
Yolk sac tumor
- These tumors develop from differentiation of primitive germ cells in the direction of yolk sac or vitelline structures.[7]
- They tend to grow very rapidly.[8]
- Bilateral involvement occurs in less than 5% of the cases.
- In 10% of the cases, the contralateral ovary carries a dermoid cyst.
- In 40% of cases, they are accompanied by other types of germ cell tumors.[9]
Genetics
- Ovarian germ cell tumors may be associated with cytogenetic abnormalities.
- Immature teratomas may be associated with chromosomal changes such as:[10]
- Gain of all or parts of
- 1p
- 16p
- 19
- 22q
- Gain of all or parts of
- Dysgerminomas may be associated with gain or loss of complete or partial chromosomal materials such as:[10]
- Gain of:
- 1p
- 6p
- 12p
- 12q
- 15q
- 20q
- 21q
- 22q
- Whole of chromosome 7
- Whole of chromosome 8
- Whole of chromosome 17
- Whole of chromosome 19
- Losses from 13q
- Gain of:
- Yolk sac tumor is associated with gaining of the 12p chromosome in 75% of the cases.[10]
- It may also be associated with chromosomal changes such as:
- Gain of 1q
- It may also be associated with chromosomal changes such as:
Associated Conditions
Conditions associated with mature teratoma include:
- Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis (although very rarely)[11]
- Rarely, they contain pituitary cells capable of prolactin production and is associated with prolactinoma.[12]
Polyembryoma may be associated with Klinefelter syndrome.[13]
Gross Pathology
| Ovarian germ cell tumor subtype | Features on Gross Pathology |
| Dysgerminonma | |
| Embryonal Carcinoma |
|
| Endodermal sinus tumor or yolk sac tumors | |
| Mixed germ cell tumors | |
| Polyembryoma |
|
| Teratoma |
Teratoma-mature
Teratoma-immature
Teratoma-monodermal
|
Microscopic Pathology
| Ovarian germ cell tumor subtype | Features on Histopathological Microscopic Analysis | Image |
| Dysgerminomas |
|
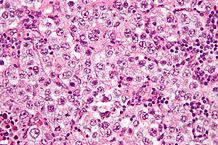 |
| Embryonal carcinoma | 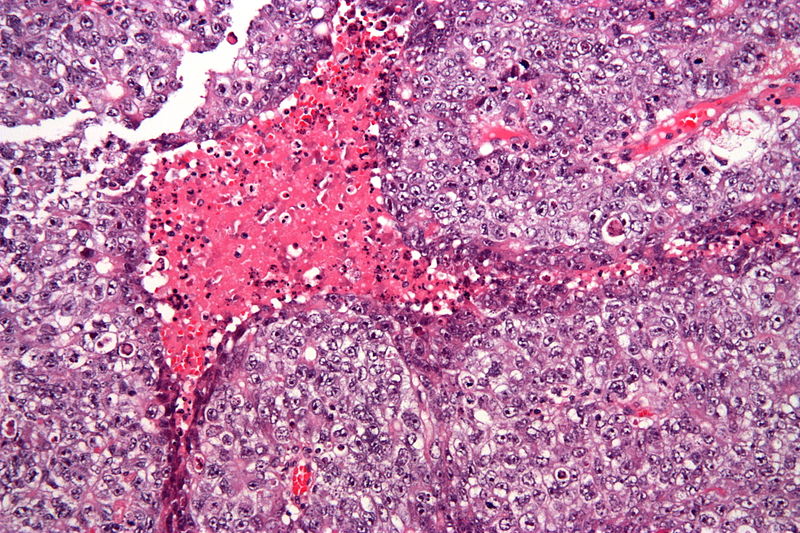 | |
| Endodermal sinus tumor or yolk sac tumors |  | |
| Polyemryoma |
|
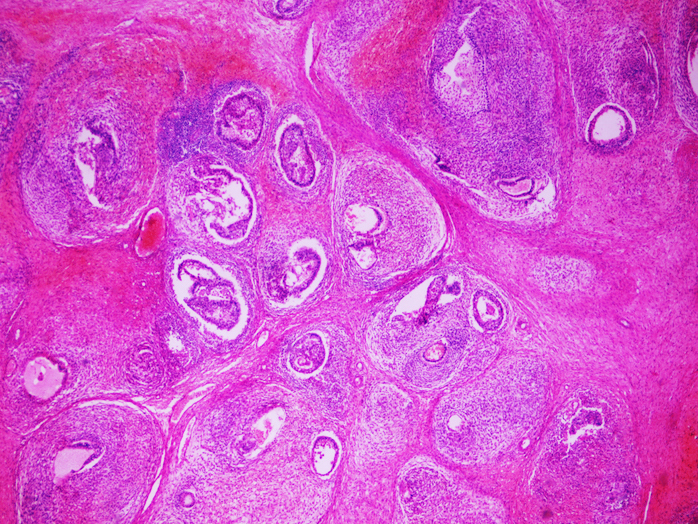 |
| Teratoma |
Mature teratoma
Immature teratoma |
 |
Immunohistochemistry
Dysgerminoma
- Dysgerminoma is positive for:[20]
- OCT4 (this marker is a key diagnostic factor for the diagnosis of dysgerminoma)
Embryonal carcinoma
Endodermal sinus tumor
- Yolk sac tumors are positive for:[20][21]
- AFP
- Cytokeratin (AE1/AE3)
- Placental-like alkaline phosphatase in 50% of the individuals.
- SALL4 (nuclear) in > 90% of the cases.
- GPC3
Non-gestational chriocarcinoma
- These tumors stain for keratins strongly.[22]
- AE1
- AE3
- CAM5
- Trophoblastic cells are positive for CD10.
- Tumor may be positive for:
Polyembryoma
- Embryoid body of the tumor may be positive for Glypican3.[26]
Teratoma
- Usually, teratomas are diagnosed histologically and routine use of immunohistochemistry is not needed. However it may be needed in the diagnosis of immature and monodermal types.
- Neuronal elements of mature or immature teratomas are positive for:[27]
- Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)
- neuron specific enolase (NSE)
- S-100
- Monodermal teratoma[17]
- Carcinoid tumor may be positive for serotonin and hormonal peptides.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 El-Maarri, Osman; Rijlaarsdam, Martin A.; Tax, David M. J.; Gillis, Ad J. M.; Dorssers, Lambert C. J.; Koestler, Devin C.; de Ridder, Jeroen; Looijenga, Leendert H. J. (2015). "Genome Wide DNA Methylation Profiles Provide Clues to the Origin and Pathogenesis of Germ Cell Tumors". PLOS ONE. 10 (4): e0122146. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122146. ISSN 1932-6203.
- ↑ Carcangiu, M. L. (2014). WHO Classification of Tumours of Female Reproductive Organs. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer. ISBN 978-92-832-4487-5.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Vural, F.; Vural, B.; Paksoy, N. (2015). "Vaginal teratoma: A case report and review of the literature". Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 35 (7): 757–758. doi:10.3109/01443615.2015.1004525. ISSN 0144-3615.
- ↑ Linder, David; McCaw, Barbara Kaiser; Hecht, Frederick (1975). "Parthenogenic Origin of Benign Ovarian Teratomas". New England Journal of Medicine. 292 (2): 63–66. doi:10.1056/NEJM197501092920202. ISSN 0028-4793.
- ↑ A L Husaini H, Soudy H, El Din Darwish A, Ahmed M, Eltigani A, A L Mubarak M, Sabaa AA, Edesa W, A L-Tweigeri T, Al-Badawi IA (December 2012). "Pure dysgerminoma of the ovary: a single institutional experience of 65 patients". Med. Oncol. 29 (4): 2944–8. doi:10.1007/s12032-012-0194-z. PMID 22407668. Vancouver style error: missing comma (help)
- ↑ Gordon A, Lipton D, Woodruff JD (October 1981). "Dysgerminoma: a review of 158 cases from the Emil Novak Ovarian Tumor Registry". Obstet Gynecol. 58 (4): 497–504. PMID 7279343.
- ↑ Young, Robert H. (2014). "The Yolk Sac Tumor". International Journal of Surgical Pathology. 22 (8): 677–687. doi:10.1177/1066896914558265. ISSN 1066-8969.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 8.8 8.9 Shaaban, Akram M.; Rezvani, Maryam; Elsayes, Khaled M.; Baskin, Henry; Mourad, Amr; Foster, Bryan R.; Jarboe, Elke A.; Menias, Christine O. (2014). "Ovarian Malignant Germ Cell Tumors: Cellular Classification and Clinical and Imaging Features". RadioGraphics. 34 (3): 777–801. doi:10.1148/rg.343130067. ISSN 0271-5333.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Kojimahara, Takanobu; Nakahara, Kenji; Takano, Tadao; Yaegashi, Nobuo; Nishiyama, Hiroshi; Fujimori, Keiya; Sato, Naoki; Terada, Yukihiro; Tase, Toru; Yokoyama, Yoshihito; Mizunuma, Hideki; Shoji, Tadahiro; Sugiyama, Toru; Kurachi, Hirohisa (2013). "Yolk Sac Tumor of the Ovary: A Retrospective Multicenter Study of 33 Japanese Women by Tohoku Gynecologic Cancer Unit (TGCU)". The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine. 230 (4): 211–217. doi:10.1620/tjem.230.211. ISSN 1349-3329.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Kraggerud SM, Szymanska J, Abeler VM, Kaern J, Eknaes M, Heim S, Teixeira MR, Tropé CG, Peltomäki P, Lothe RA (June 2000). "DNA copy number changes in malignant ovarian germ cell tumors". Cancer Res. 60 (11): 3025–30. PMID 10850452.
- ↑ Dalmau, Josep; Gleichman, Amy J; Hughes, Ethan G; Rossi, Jeffrey E; Peng, Xiaoyu; Lai, Meizan; Dessain, Scott K; Rosenfeld, Myrna R; Balice-Gordon, Rita; Lynch, David R (2008). "Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis: case series and analysis of the effects of antibodies". The Lancet Neurology. 7 (12): 1091–1098. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70224-2. ISSN 1474-4422.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Kallenberg, GA; Pesce, CM; Norman, B; Ratner, RE; Silverberg, SG (1991). "Ectopic hyperprolactinemia resulting from an ovarian teratoma". International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics. 34 (2): 194–195. doi:10.1016/0020-7292(91)90266-8. ISSN 0020-7292.
- ↑ Lisa Beresford, Conrad V. Fernandez, Elizabeth Cummings, Susan Sanderson, Wei Ming-Yu & Michael Giacomantonio (2003). "Mediastinal polyembryoma associated with Klinefelter syndrome". Journal of pediatric hematology/oncology. 25 (4): 321–323. PMID 12679648. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Chen, Vivien W.; Ruiz, Bernardo; Killeen, Jeffrey L.; Cot�, Timothy R.; Wu, Xiao Cheng; Correa, Catherine N.; Howe, Holly L. (2003). "Pathology and classification of ovarian tumors". Cancer. 97 (S10): 2631–2642. doi:10.1002/cncr.11345. ISSN 0008-543X. replacement character in
|last4=at position 4 (help) - ↑ Oliva, Esther; Young, Robert H. (2014). "Germ cell tumours of the ovary: selected topics". Diagnostic Histopathology. 20 (9): 364–375. doi:10.1016/j.mpdhp.2014.07.003. ISSN 1756-2317.
- ↑ Yayla Abide, Çiğdem; Bostancı Ergen, Evrim (2018). "Retrospective analysis of mature cystic teratomas in a single center and review of the literature". Journal of Turkish Society of Obstetric and Gynecology. 15 (2): 95–98. doi:10.4274/tjod.86244. ISSN 1307-699X.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Outwater, Eric K.; Siegelman, Evan S.; Hunt, Jennifer L. (2001). "Ovarian Teratomas: Tumor Types and Imaging Characteristics". RadioGraphics. 21 (2): 475–490. doi:10.1148/radiographics.21.2.g01mr09475. ISSN 0271-5333.
- ↑ Mature teratoma. http://librepathology.org/wiki/index.php/Teratoma#Mature_teratoma. URL Accessed on November 12, 2015
- ↑ Ulbright TM (February 2005). "Germ cell tumors of the gonads: a selective review emphasizing problems in differential diagnosis, newly appreciated, and controversial issues". Mod. Pathol. 18 Suppl 2: S61–79. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800310. PMID 15761467.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Pectasides, D.; Pectasides, E.; Kassanos, D. (2008). "Germ cell tumors of the ovary". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 34 (5): 427–441. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2008.02.002. ISSN 0305-7372.
- ↑ Cao, Dengfeng; Guo, Shuangping; Allan, Robert W.; Molberg, Kyle H.; Peng, Yan (2009). "SALL4 Is a Novel Sensitive and Specific Marker of Ovarian Primitive Germ Cell Tumors and Is Particularly Useful in Distinguishing Yolk Sac Tumor From Clear Cell Carcinoma". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 33 (6): 894–904. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318198177d. ISSN 0147-5185.
- ↑ Ordi J, Romagosa C, Tavassoli FA, Nogales F, Palacin A, Condom E, Torné A, Cardesa A (February 2003). "CD10 expression in epithelial tissues and tumors of the gynecologic tract: a useful marker in the diagnosis of mesonephric, trophoblastic, and clear cell tumors". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 27 (2): 178–86. PMID 12548163.
- ↑ Banet, Natalie; Gown, Allen M.; Shih, Ie-Ming; Kay Li, Qing; Roden, Richard B.S.; Nucci, Marisa R.; Cheng, Liang; Przybycin, Christopher G.; Nasseri-Nik, Niloofar; Wu, Lee-Shu-Fune; Netto, George J.; Ronnett, Brigitte M.; Vang, Russell (2015). "GATA-3 Expression in Trophoblastic Tissues". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 39 (1): 101–108. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000315. ISSN 0147-5185.
- ↑ Miettinen, Markku; Wang, Zengfeng; McCue, Peter A.; Sarlomo-Rikala, Maarit; Rys, Janusz; Biernat, Wojciech; Lasota, Jerzy; Lee, Yi-Shan (2014). "SALL4 Expression in Germ Cell and Non–Germ Cell Tumors". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 38 (3): 410–420. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000116. ISSN 0147-5185.
- ↑ Niehans GA, Manivel JC, Copland GT, Scheithauer BW, Wick MR (September 1988). "Immunohistochemistry of germ cell and trophoblastic neoplasms". Cancer. 62 (6): 1113–23. PMID 2457424.
- ↑ Preda, Ovidiu; Nicolae, Alina; Aneiros-Fernández, José; Borda, Angela; Nogales, Francisco F (2011). "Glypican 3 is a sensitive, but not a specific, marker for the diagnosis of yolk sac tumours". Histopathology. 58 (2): 312–314. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2010.03735.x. ISSN 0309-0167.
- ↑ Takayama, Yoshiyasu; Matsumura, Nozomi; Nobusawa, Sumihito; Ikota, Hayato; Minegishi, Takashi; Yokoo, Hideaki (2015). "Immunophenotypic features of immaturity of neural elements in ovarian teratoma". Virchows Archiv. 468 (3): 337–343. doi:10.1007/s00428-015-1891-8. ISSN 0945-6317.