Hyoscyamine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Protected "Hyoscyamine": Bot: Protecting all pages from category Drug ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite))) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|aOrAn= | |aOrAn= | ||
an | |||
|drugClass= | |drugClass= | ||
[[antimuscarinic]] | |||
|indication= | |indication= | ||
adjunctive therapy in the treatment of [[peptic ulcer]] and [[irritable bowel syndrome]] (irritable [[colon]], spastic [[colon]], mucous [[colitis]]), [[acute entercolitis]] and other functional [[gastrointestinal]] disorders, in symptomatic relief of [[biliary]] and [[renal colic]] and drying agent in the relief of symptoms of [[acute rhinitis]] | |||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |hasBlackBoxWarning= | ||
|adverseReactions= | |adverseReactions= | ||
diminished sweating, [[xerostomia]], [[dizziness]], [[somnolence]], [[blurred vision]], [[mydriasis]], delay when starting to pass urine | |||
<!--Black Box Warning--> | <!--Black Box Warning--> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 44: | ||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |fdaLIADAdult= | ||
=====Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of Peptic ulcer and Irritable bowel syndrome===== | |||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :*1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours. | ||
===== | =====Symptomatic relief of Biliary and Renal colic===== | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :*1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours. | ||
===== | =====Drying agent in Acute Rhinitis===== | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :*1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours. | ||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
| Line 82: | Line 68: | ||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | |offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | |||
=====Anesthesia - Bradyarrhythmia===== | |||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :*Hyoscyamine sulfate injection is used in adults for the reduction of drug-induced bradycardia during surgery. | ||
===== | =====Anesthesia - Excessive salivation; Prophylaxis===== | ||
* Dosing Information | |||
:*Hyoscyamine sulfate injection is used in adults during induction of anesthesia and intubation as a pre-operative medication for reduction of salivary, tracheobronchial, and pharyngeal secretions. | |||
===== | =====Biliary colic, With morphine or other narcotics; Adjunct===== | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :*Hyoscyamine sulfate is used as an adjunct with morphine or other narcotics in the symptomatic treatment of biliary colic . | ||
<!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | <!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | ||
| Line 118: | Line 98: | ||
|fdaLIADPed= | |fdaLIADPed= | ||
===== | =====Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of Peptic ulcer and Irritable bowel syndrome===== | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* | :* Children 12 years of age and older: 1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours. Children 2 to under 12 years of age: 1/2 to 1 tablet every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24 hours. | ||
===== | =====Symptomatic relief of Biliary and Renal colic===== | ||
* Dosing Information | |||
:*Children 12 years of age and older: 1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours. Children 2 to under 12 years of age: 1/2 to 1 tablet every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24 hours. | |||
=====Drying agent in Acute Rhinitis===== | |||
* Dosing Information | |||
* | :*Children 12 years of age and older: 1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours. Children 2 to under 12 years of age: 1/2 to 1 tablet every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24 hours. | ||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | ||
| Line 153: | Line 127: | ||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | ||
| Line 168: | Line 134: | ||
|contraindications= | |contraindications= | ||
*Glaucoma, obstructive uropathy (for example, bladder neck obstruction due to prostatic hypertrophy); obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract (as in achalasia, pyloroduodenal stenosis); paralytic ileus; intestinal atony of elderly or debilitated patients; unstable cardiovascular status; severe ulcerative colitis; toxic megacolon; myasthenia gravis; myocardial ischemia. | *[[Glaucoma]], [[obstructive uropathy]] (for example, bladder neck obstruction due to [[prostatic hypertrophy]]); obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract (as in [[achalasia]], pyloroduodenal [[stenosis]]); [[paralytic ileus]]; intestinal atony of elderly or debilitated patients; unstable cardiovascular status; severe [[ulcerative colitis]]; [[toxic megacolon]]; [[myasthenia gravis]]; [[myocardial ischemia]]. | ||
<!--Warnings--> | <!--Warnings--> | ||
| Line 176: | Line 142: | ||
====Precautions==== | ====Precautions==== | ||
*In the presence of high environmental temperature, heat prostration can occur with drug use (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating). Diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. In this instance, treatment with this drug would be inappropriate and possibly harmful. Like other anticholinergic agents, ANASPAZ may produce drowsiness or blurred vision. In this event, the patient should be warned not to engage in activities requiring mental alertness such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or to perform hazardous work while taking this drug. | *In the presence of high environmental temperature, heat prostration can occur with drug use ([[fever]] and [[heat stroke]] due to decreased sweating). [[Diarrhea]] may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with [[ileostomy]] or [[colostomy]]. In this instance, treatment with this drug would be inappropriate and possibly harmful. Like other [[anticholinergic]] agents, ANASPAZ may produce [[drowsiness]] or [[blurred vision]]. In this event, the patient should be warned not to engage in activities requiring mental alertness such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or to perform hazardous work while taking this drug. | ||
*Anticholinergic psychosis has been reported in sensitive individuals given anticholinergic drugs. CNS signs and symptoms include confusion, disorientation, short term memory loss, hallucinations, dysarthria, ataxia, coma, euphoria, decreased anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, agitation and mannerisms, and inappropriate affect. These CNS signs and symptoms usually resolve 12 to 48 hours after drug discontinuation. | *[[Anticholinergic]] [[psychosis]] has been reported in sensitive individuals given [[anticholinergic]] drugs. CNS signs and symptoms include confusion, disorientation, short term memory loss, [[hallucinations]], [[dysarthria]], [[ataxia]], [[coma]], euphoria, decreased [[anxiety]], [[fatigue]], [[insomnia]], agitation and mannerisms, and inappropriate affect. These CNS signs and symptoms usually resolve 12 to 48 hours after drug discontinuation. | ||
*Elderly patients may react with excitement, agitation, drowsiness, and other unfavorable manifestations to even small doses of ANASPAZ. | *Elderly patients may react with excitement, agitation, [[drowsiness]], and other unfavorable manifestations to even small doses of ANASPAZ. | ||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | <!--Adverse Reactions--> | ||
| Line 188: | Line 154: | ||
|clinicalTrials= | |clinicalTrials= | ||
*Not all the following adverse reactions have been associated with ANASPAZ, but have been reported for drugs in the same pharmacological class, with anticholinergic / antispasmodic action. Adverse reactions may include dryness of the mouth, urinary hesitancy, urinary retention, tachycardia, palpitations, blurred vision, mydriasis, cycloplegia, increased intraocular pressure, dry eyes, headache, nervousness, drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, mental confusion and/or excitement (especially in geriatric patients), flushing, insomnia, fever, altered sense of taste, nausea, vomiting, dysphagia, heartburn, constipation, bloated feeling, suppression of lactation, impotence, and decreased sweating. Allergic reactions or drug idiosyncrasies such as anaphylaxis, urticaria and other dermal manifestations may also occur. | *Not all the following adverse reactions have been associated with ANASPAZ, but have been reported for drugs in the same pharmacological class, with anticholinergic / antispasmodic action. Adverse reactions may include [[dryness of the mouth]], [[urinary hesitancy]], [[urinary retention]], [[tachycardia]], [[palpitations]], blurred vision, [[mydriasis]], [[cycloplegia]], increased [[intraocular pressure]], dry eyes, [[headache]], [[nervousness]], [[drowsiness]], [[dizziness]], [[weakness]], mental confusion and/or excitement (especially in geriatric patients), [[flushing]], [[insomnia]], fever, altered sense of taste, [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[dysphagia]], [[heartburn]], [[constipation]], bloated feeling, suppression of [[lactation]], [[impotence]], and decreased sweating. Allergic reactions or drug idiosyncrasies such as [[anaphylaxis]], [[urticaria]] and other dermal manifestations may also occur. | ||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | <!--Postmarketing Experience--> | ||
| Line 200: | Line 166: | ||
|drugInteractions= | |drugInteractions= | ||
*Additive adverse effects resulting from cholinergic blockade may occur when ANASPAZ is administered concomitantly with other anti-muscarinics, amantadine, haloperidol, phenothiazines, monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants or some antihistamines. | *Additive adverse effects resulting from [[cholinergic]] blockade may occur when ANASPAZ is administered concomitantly with other anti-[[muscarinics]], [[amantadine]], [[haloperidol]], [[phenothiazines]], [[monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors]], [[tricyclic antidepressants]] or some [[antihistamines]]. | ||
*Antacids may interfere with the absorption of ANASPAZ; take ANASPAZ before meals and antacids after meals. | *[[Antacids]] may interfere with the absorption of ANASPAZ; take ANASPAZ before meals and [[antacids]] after meals. | ||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | <!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
| Line 231: | Line 197: | ||
*This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. | *This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. | ||
*Sedating drugs may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly; elderly patients generally should be started on low doses of ANASPAZ and observed | *Sedating drugs may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly; elderly patients generally should be started on low doses of ANASPAZ and observed closely. | ||
|useInGender= | |useInGender= | ||
| Line 256: | Line 222: | ||
* Oral | * Oral | ||
|monitoring= | |monitoring= | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | <!--IV Compatibility--> | ||
| Line 279: | Line 241: | ||
====Signs and Symptoms==== | ====Signs and Symptoms==== | ||
*The signs and symptoms of overdose include headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, dry mouth, difficulty in swallowing, dilated pupils, blurred vision, urinary retention, hot dry and flushed skin, tachycardia, hypertension, hypotension, respiratory depression, CNS stimulation, fever, ataxia, excitation, lethargy, stupor, coma, and paralysis (with large overdoses). | *The signs and symptoms of overdose include [[headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[dizziness]], [[dry mouth]], difficulty in swallowing, [[dilated pupils]], blurred vision, [[urinary retention]], hot dry and flushed skin, [[tachycardia]], [[hypertension]], [[hypotension]], [[respiratory depression]], [[CNS stimulation]], [[fever]], [[ataxia]], excitation, [[lethargy]], stupor, [[coma]], and [[paralysis]] (with large overdoses). | ||
*The LD50 for hyoscyamine in rats is 375 mg/kg. | *The LD50 for hyoscyamine in rats is 375 mg/kg. | ||
| Line 285: | Line 247: | ||
====Management==== | ====Management==== | ||
*General measures such as emesis or gastric lavage and administration of activated charcoal should be undertaken immediately. Supportive therapy is given as needed, including artificial respiration if required. Physostigmine may be given by intravenous injection to reverse severe anticholinergic symptoms. | *General measures such as [[emesis]] or [[gastric lavage]] and administration of [[activated charcoal]] should be undertaken immediately. Supportive therapy is given as needed, including artificial respiration if required. [[Physostigmine]] may be given by intravenous injection to reverse severe [[anticholinergic]] symptoms. | ||
*Hyoscyamine sulfate is dialyzable. | *Hyoscyamine sulfate is dialyzable. | ||
| Line 299: | Line 261: | ||
|drugBox= | |drugBox= | ||
{{Drugbox2 | |||
| Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 461742575 | |||
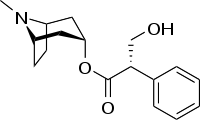
| IUPAC_name = (8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate | |||
| image = Hyoscyamine.png | |||
| width = 200px | |||
| image2 = Hyoscyamine1.png | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| tradename = Anaspaz, Levbid, Levsin | |||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|hyoscyamine}} | |||
| MedlinePlus = a684010 | |||
| pregnancy_category = C | |||
| legal_AU = S4 | |||
| legal_US = Prescription only | |||
| routes_of_administration = Oral, Injection | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = 50% Protein binding | |||
| metabolism = Hepatic | |||
| elimination_half-life = 3–5 hrs. | |||
| excretion = Urine | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 101-31-5 | |||
| ATC_prefix = A03 | |||
| ATC_suffix = BA03 | |||
| PubChem = 154417 | |||
| PubChem_Ref = {{pubchemcite|correct}} | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank = DB00424 | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 10246417 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = PX44XO846X | |||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEBI = 17486 | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL = 1697729 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| C=17 | H=23 | N=1 | O=3 | |||
| molecular_weight = 289.375 g/mol | |||
| smiles = CN3[C@H]1CC[C@@H]3C[C@@H](C1)OC(=O)[C@H](CO)c2ccccc2 | |||
| InChI = 1/C17H23NO3/c1-18-13-7-8-14(18)10-15(9-13)21-17(20)16(11-19)12-5-3-2-4-6-12/h2-6,13-16,19H,7-11H2,1H3/t13-,14+,15+,16-/m1/s1 | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C17H23NO3/c1-18-13-7-8-14(18)10-15(9-13)21-17(20)16(11-19)12-5-3-2-4-6-12/h2-6,13-16,19H,7-11H2,1H3/t13-,14+,15+,16-/m1/s1 | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey = RKUNBYITZUJHSG-FXUDXRNXSA-N | |||
}} | |||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | <!--Mechanism of Action--> | ||
| Line 305: | Line 317: | ||
|mechAction= | |mechAction= | ||
* ANASPAZ inhibits specifically the actions of acetylcholine on structures innervated by postganglionic cholinergic nerves and on smooth muscles that respond to acetylcholine but lack cholinergic innervation. These peripheral cholinergic receptors are present in the autonomic effector cells of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, the sino-atrial node, the atrioventricular node and exocrine glands. At therapeutic doses, it is completely devoid of any action in the autonomic ganglia. ANASPAZ inhibits gastrointestinal propulsive motility and decreases gastric acid secretion. ANASPAZ also controls excessive pharyngeal, tracheal and bronchial secretions. ANASPAZ is absorbed totally and completely by sublingual administration as well as oral administration. Once absorbed, ANASPAZ disappears rapidly from the blood and is distributed throughout the entire body. The half-life of ANASPAZ is 3.5 hours and the majority of drug is excreted in the urine unchanged within the first 12 hours, with a small amount hydrolyzed to tropic acid and tropine. Only traces of this drug are found in breast milk. ANASPAZ passes the blood-brain and placental barriers. | * ANASPAZ inhibits specifically the actions of [[acetylcholine]] on structures innervated by [[postganglionic]] cholinergic nerves and on smooth muscles that respond to [[acetylcholine]] but lack [[cholinergic]] innervation. These peripheral [[cholinergic]] receptors are present in the autonomic effector cells of [[smooth muscle]], [[cardiac muscle]], the [[sino-atrial node]], the [[atrioventricular node]] and [[exocrine glands]]. At therapeutic doses, it is completely devoid of any action in the [[autonomic ganglia]]. ANASPAZ inhibits [[gastrointestinal]] propulsive motility and decreases [[gastric acid]] secretion. ANASPAZ also controls excessive [[pharyngeal]], [[tracheal]] and [[bronchial]] secretions. ANASPAZ is absorbed totally and completely by [[sublingual]] administration as well as oral administration. Once absorbed, ANASPAZ disappears rapidly from the blood and is distributed throughout the entire body. The half-life of ANASPAZ is 3.5 hours and the majority of drug is excreted in the urine unchanged within the first 12 hours, with a small amount hydrolyzed to tropic acid and tropine. Only traces of this drug are found in breast milk. ANASPAZ passes the blood-brain and placental barriers. | ||
<!--Structure--> | <!--Structure--> | ||
| Line 314: | Line 326: | ||
*ANASPAZ is chemically pure 1-hyoscyamine sulfate, one of the principal anticholinergic/antispasmodic components of belladonna alkaloids. Chemically, it is benzeneacetic acid, α-(hydroxymethyl)-, 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1.]oct-3-yl ester, [3(S)-endo]-, sulfate (2:1), dihydrate with the chemical formula (C17H23NO3)2•H2SO4•2H2O | *ANASPAZ is chemically pure 1-hyoscyamine sulfate, one of the principal anticholinergic/antispasmodic components of belladonna alkaloids. Chemically, it is benzeneacetic acid, α-(hydroxymethyl)-, 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1.]oct-3-yl ester, [3(S)-endo]-, sulfate (2:1), dihydrate with the chemical formula (C17H23NO3)2•H2SO4•2H2O | ||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | <!--Pharmacodynamics--> | ||
| Line 345: | Line 355: | ||
|howSupplied= | |howSupplied= | ||
* ANASPAZ (l-hyoscyamine sulfate orally disintegrating tablets) 0.125mg is available as a compressed, light yellow, scored tablet, imprinted with the Ascher logo and 225/295 in bottles of 100 tablets (NDC 0225-0295-15) and 500 tablets (NDC 0225-0295-20). | *ANASPAZ (l-hyoscyamine sulfate orally disintegrating tablets) 0.125mg is available as a compressed, light yellow, scored tablet, imprinted with the Ascher logo and 225/295 in bottles of 100 tablets (NDC 0225-0295-15) and 500 tablets (NDC 0225-0295-20). | ||
*Store at room temperature - 59º - 86º F (15º - 30º C) in a dry place. | *Store at room temperature - 59º - 86º F (15º - 30º C) in a dry place. | ||
| Line 355: | Line 365: | ||
|fdaPatientInfo= | |fdaPatientInfo= | ||
*ANASPAZ may produce drowsiness, dizziness or blurred vision. Patients should observe caution before operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or performing other tasks requiring mental alertness. | *ANASPAZ may produce [[drowsiness]], [[dizziness]] or [[blurred vision]]. Patients should observe caution before operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or performing other tasks requiring mental alertness. | ||
*Use of ANASPAZ may decrease sweating resulting in heat prostration, fever or heat stroke; febrile patients or those who may be exposed to elevated environmental temperatures should use caution. | *Use of ANASPAZ may decrease sweating resulting in heat prostration, fever or heat stroke; febrile patients or those who may be exposed to elevated environmental temperatures should use caution. | ||
| Line 374: | Line 384: | ||
|lookAlike= | |lookAlike= | ||
<!--Drug Shortage Status--> | <!--Drug Shortage Status--> | ||
| Line 402: | Line 410: | ||
{{LabelImage | {{LabelImage | ||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}} | |fileName={{PAGENAME}}01.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:29, 20 August 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Hyoscyamine is an antimuscarinic that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of adjunctive therapy in the treatment of peptic ulcer and irritable bowel syndrome (irritable colon, spastic colon, mucous colitis), acute entercolitis and other functional gastrointestinal disorders, in symptomatic relief of biliary and renal colic and drying agent in the relief of symptoms of acute rhinitis. Common adverse reactions include diminished sweating, xerostomia, dizziness, somnolence, blurred vision, mydriasis, delay when starting to pass urine.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of Peptic ulcer and Irritable bowel syndrome
- Dosing Information
- 1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours.
Symptomatic relief of Biliary and Renal colic
- Dosing Information
- 1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours.
Drying agent in Acute Rhinitis
- Dosing Information
- 1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Hyoscyamine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Anesthesia - Bradyarrhythmia
- Dosing Information
- Hyoscyamine sulfate injection is used in adults for the reduction of drug-induced bradycardia during surgery.
Anesthesia - Excessive salivation; Prophylaxis
- Dosing Information
- Hyoscyamine sulfate injection is used in adults during induction of anesthesia and intubation as a pre-operative medication for reduction of salivary, tracheobronchial, and pharyngeal secretions.
Biliary colic, With morphine or other narcotics; Adjunct
- Dosing Information
- Hyoscyamine sulfate is used as an adjunct with morphine or other narcotics in the symptomatic treatment of biliary colic .
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of Peptic ulcer and Irritable bowel syndrome
- Dosing Information
- Children 12 years of age and older: 1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours. Children 2 to under 12 years of age: 1/2 to 1 tablet every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24 hours.
Symptomatic relief of Biliary and Renal colic
- Dosing Information
- Children 12 years of age and older: 1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours. Children 2 to under 12 years of age: 1/2 to 1 tablet every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24 hours.
Drying agent in Acute Rhinitis
- Dosing Information
- Children 12 years of age and older: 1 or 2 tablets every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 12 tablets in 24 hours. Children 2 to under 12 years of age: 1/2 to 1 tablet every four hours or as needed. Do not exceed 6 tablets in 24 hours.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Hyoscyamine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Hyoscyamine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Glaucoma, obstructive uropathy (for example, bladder neck obstruction due to prostatic hypertrophy); obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract (as in achalasia, pyloroduodenal stenosis); paralytic ileus; intestinal atony of elderly or debilitated patients; unstable cardiovascular status; severe ulcerative colitis; toxic megacolon; myasthenia gravis; myocardial ischemia.
Warnings
Precautions
- In the presence of high environmental temperature, heat prostration can occur with drug use (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating). Diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. In this instance, treatment with this drug would be inappropriate and possibly harmful. Like other anticholinergic agents, ANASPAZ may produce drowsiness or blurred vision. In this event, the patient should be warned not to engage in activities requiring mental alertness such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or to perform hazardous work while taking this drug.
- Anticholinergic psychosis has been reported in sensitive individuals given anticholinergic drugs. CNS signs and symptoms include confusion, disorientation, short term memory loss, hallucinations, dysarthria, ataxia, coma, euphoria, decreased anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, agitation and mannerisms, and inappropriate affect. These CNS signs and symptoms usually resolve 12 to 48 hours after drug discontinuation.
- Elderly patients may react with excitement, agitation, drowsiness, and other unfavorable manifestations to even small doses of ANASPAZ.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Not all the following adverse reactions have been associated with ANASPAZ, but have been reported for drugs in the same pharmacological class, with anticholinergic / antispasmodic action. Adverse reactions may include dryness of the mouth, urinary hesitancy, urinary retention, tachycardia, palpitations, blurred vision, mydriasis, cycloplegia, increased intraocular pressure, dry eyes, headache, nervousness, drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, mental confusion and/or excitement (especially in geriatric patients), flushing, insomnia, fever, altered sense of taste, nausea, vomiting, dysphagia, heartburn, constipation, bloated feeling, suppression of lactation, impotence, and decreased sweating. Allergic reactions or drug idiosyncrasies such as anaphylaxis, urticaria and other dermal manifestations may also occur.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Hyoscyamine in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- Additive adverse effects resulting from cholinergic blockade may occur when ANASPAZ is administered concomitantly with other anti-muscarinics, amantadine, haloperidol, phenothiazines, monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants or some antihistamines.
- Antacids may interfere with the absorption of ANASPAZ; take ANASPAZ before meals and antacids after meals.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with ANASPAZ. It is also not known whether ANASPAZ can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. ANASPAZ should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Hyoscyamine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Hyoscyamine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- ANASPAZ is excreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when ANASPAZ is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 2 have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
- Sedating drugs may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly; elderly patients generally should be started on low doses of ANASPAZ and observed closely.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hyoscyamine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hyoscyamine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hyoscyamine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hyoscyamine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hyoscyamine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Hyoscyamine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Hyoscyamine in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Hyoscyamine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- The signs and symptoms of overdose include headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, dry mouth, difficulty in swallowing, dilated pupils, blurred vision, urinary retention, hot dry and flushed skin, tachycardia, hypertension, hypotension, respiratory depression, CNS stimulation, fever, ataxia, excitation, lethargy, stupor, coma, and paralysis (with large overdoses).
- The LD50 for hyoscyamine in rats is 375 mg/kg.
Management
- General measures such as emesis or gastric lavage and administration of activated charcoal should be undertaken immediately. Supportive therapy is given as needed, including artificial respiration if required. Physostigmine may be given by intravenous injection to reverse severe anticholinergic symptoms.
- Hyoscyamine sulfate is dialyzable.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Hyoscyamine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
| |
| |
Hyoscyamine
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | A03 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 289.375 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% Protein binding |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Half life | 3–5 hrs. |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
C |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | Oral, Injection |
Mechanism of Action
- ANASPAZ inhibits specifically the actions of acetylcholine on structures innervated by postganglionic cholinergic nerves and on smooth muscles that respond to acetylcholine but lack cholinergic innervation. These peripheral cholinergic receptors are present in the autonomic effector cells of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, the sino-atrial node, the atrioventricular node and exocrine glands. At therapeutic doses, it is completely devoid of any action in the autonomic ganglia. ANASPAZ inhibits gastrointestinal propulsive motility and decreases gastric acid secretion. ANASPAZ also controls excessive pharyngeal, tracheal and bronchial secretions. ANASPAZ is absorbed totally and completely by sublingual administration as well as oral administration. Once absorbed, ANASPAZ disappears rapidly from the blood and is distributed throughout the entire body. The half-life of ANASPAZ is 3.5 hours and the majority of drug is excreted in the urine unchanged within the first 12 hours, with a small amount hydrolyzed to tropic acid and tropine. Only traces of this drug are found in breast milk. ANASPAZ passes the blood-brain and placental barriers.
Structure
- Each ANASPAZ orally disintegrating tablet contains 1-hyoscyamine sulfate 0.125 mg. ANASPAZ may be taken orally (swallowed or chewed) or sublingually. ANASPAZ tablets are compressed, light yellow and scored with the Ascher logo on one side and 225/295 on the other. Inactive ingredients: DC Yellow #10, FDC yellow #6, lactose NF, magnesium stearate NF, mannitol USP, sorbitol NF, pre-gelatinized starch NF, stearic acid NF.
- ANASPAZ is chemically pure 1-hyoscyamine sulfate, one of the principal anticholinergic/antispasmodic components of belladonna alkaloids. Chemically, it is benzeneacetic acid, α-(hydroxymethyl)-, 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1.]oct-3-yl ester, [3(S)-endo]-, sulfate (2:1), dihydrate with the chemical formula (C17H23NO3)2•H2SO4•2H2O
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Hyoscyamine in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Hyoscyamine in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Hyoscyamine in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Hyoscyamine in the drug label.
How Supplied
- ANASPAZ (l-hyoscyamine sulfate orally disintegrating tablets) 0.125mg is available as a compressed, light yellow, scored tablet, imprinted with the Ascher logo and 225/295 in bottles of 100 tablets (NDC 0225-0295-15) and 500 tablets (NDC 0225-0295-20).
- Store at room temperature - 59º - 86º F (15º - 30º C) in a dry place.
- Dispense in tight, amber glass or opaque PE plastic containers.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Hyoscyamine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Hyoscyamine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Hyoscyamine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- ANASPAZ may produce drowsiness, dizziness or blurred vision. Patients should observe caution before operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or performing other tasks requiring mental alertness.
- Use of ANASPAZ may decrease sweating resulting in heat prostration, fever or heat stroke; febrile patients or those who may be exposed to elevated environmental temperatures should use caution.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Hyoscyamine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ANASPAZ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Hyoscyamine Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Hyoscyamine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Hyoscyamine |Label Name=Hyoscyamine01.png
}}