Chlorhexidine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 87% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
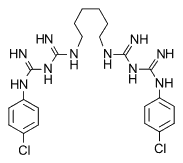
| Formula | C22H30Cl2N10 |
| Molar mass | 505.446 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Chlorhexidine |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Chlorhexidine Most cited articles on Chlorhexidine |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Chlorhexidine |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Chlorhexidine at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Chlorhexidine Clinical Trials on Chlorhexidine at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Chlorhexidine NICE Guidance on Chlorhexidine
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Chlorhexidine Discussion groups on Chlorhexidine Patient Handouts on Chlorhexidine Directions to Hospitals Treating Chlorhexidine Risk calculators and risk factors for Chlorhexidine
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Chlorhexidine |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Chlorhexidine is a chemical antiseptic. [1] It kills (is bactericidal to) both gram-positive and gram-negative microbes, although it is less effective with some gram-negative microbes. [2] It is also bacteriostatic.
The mechanism of action is believed to be membrane disruption, and not ATPase inactivation as previously thought.
Products containing chlorhexidine in high concentrations must be kept away from eyes (corneal ulcers) and the inner ear (deafness), although it is used in minute concentrations in some contact lens solutions.
Availability
It is sometimes marketed under the brand names Peridex, Periochip, Periogard Oral Rinse. In the UK it is sometimes marketed under the brand names Corsodyl or Chlorohex, in Germany as Chlorhexamed, in Australia as Savacol, in Venezuela as Perioxidina and in some Central American countries as Clorexil.
In some countries it is available by prescription only.
Dental applications
It is often used as an active ingredient in mouthwash designed to kill dental plaque and other oral bacteria. Chlorhexidine can thus be used to improve bad breath.[3]
Chlorhexidine based products are usually utilized to combat or prevent gum diseases such as gingivitis. According to Colgate [2], chlorhexidine gluconate has not been proven to reduce subgingivial calculus and in some studies actually increased deposits.
Deactivation
Chlorhexidine is deactivated by anionic compounds, including the anionic surfactants commonly used as detergents in toothpastes and mouthwashes. For this reason, chlorhexidine mouth rinses should be used at least 30 minutes after other dental products.[4] For best effectiveness, food, drink, smoking, and mouth rinses should be avoided for at least one hour after use.
Non-dental applications
Chlorhexidine is also used in non-dental applications, most notably under the brand names Oronine, Avagard, Hibiclens, Hibiscrub, ChloraPrep, BIOPATCH, and Exidine. It is also a component of the famous household antiseptic Savlon. It is used for general skin cleansing, a surgical scrub and a pre-operative skin preparation. Due to other chemicals listed as inactive ingredients, the cleanser solution is not suitable for use as mouthwash. It is often used as a rubbing agent prior to the use of hypodermic or intravenous needles in place of iodine. Chlorhexidine is contraindicated for use near the meninges, in the genital area, and near the eyes and ears. At the 2% concentration, it can cause serious and permanent injury on contact with the eye or if instilled through a perforated eardrum. As a scrub it is not recommended on persons under two months of age. It can be used also as spermatocidal agent.
References
- ↑ "Chlorhexidine Official FDA information, side effects and uses". Drug information Online. Drugs.com. Revised 11/2006. Retrieved 2007-10-08. Check date values in:
|date=(help) Drugs.com state that this information comes directly from the FDA - ↑ "THE MOST COMMON TOPICAL ANTIMICROBIALS". Care of the umbilical cord. World Health Organization. 1998. Retrieved 2007-10-08.
- ↑ http://www.freshbreath.ca/fbcpubs.html
- ↑ Denton W , Chlorhexidine In: Sterilisation and Preservation 5th Edition, Block SS, eds. Lippincott Williams & Williams, Philadelphia, 2001; 321-36.
External links
Template:Antiseptics and disinfectants
Template:Medicated dressings
Template:Throat preparations
Template:Otologicals
bg:Хлорхексидин
da:Klorhexidin
de:Chlorhexidin
el:Χλωρεξιδίνη
it:Clorexidina
hu:Klórhexidin
nl:Chloorhexidinedigluconaat
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 errors: dates
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Antiseptics
- Guanidines
- Oral hygiene