WBR0986: Difference between revisions
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{WBRQuestion |QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 |MainCategory=Biochemistry |SubCategory=General Principles |MainCategory=Biochemistry |SubCategory=General Princip...") |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} | |QuestionAuthor= {{Rim}} (Reviewed by {{YD}}) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
|SubCategory=General Principles | |SubCategory=General Principles | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Biochemistry | |MainCategory=Biochemistry | ||
|SubCategory=General Principles | |SubCategory=General Principles | ||
|Prompt=A | |Prompt=A 10-month-old girl is brought to the physician's office for convulsions and generalized hypotonia. The mother states that her daughter's condition is associated with irritability and poor feeding. The girl's height and weight are below the lower threshold of growth on the height-weight chart. Laboratory work-up is remarkable for metabolic acidosis and elevated serum concentrations of LDH and ALT. A skeletal muscle biopsy demonstrates E1 subunit deficiency in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The physician advises the family to adhere to a strict diet. Which of the following amino acids should be included in this girl's diet? | ||
|Explanation= | |Explanation=Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex defects are associated with development of irritability, poor feeding, seizures, impaired psychomotor development, lactic acidosis, and elevated serum alanine concentration (accumulated pyruvate is shunted to lactate via LDH and to alanine via ALT). PDH deficiency is a genetic disorder that may be inherited in either an autosomal or X-linked pattern. This patient's diagnosis is first suspected by the findings on physical examination and lab work-up and further confirmed by genetic testing, which demonstrated E1 alpha gene defect. The majority of patients with PDH deficiency have E1 alpha gene defects (PDHA1), which are usually inherited in an X-linked pattern. Management of PDH deficiency includes a strict ketogenic diet (high intake of fat and/or ketogenic amino acids lysine and leucine). | ||
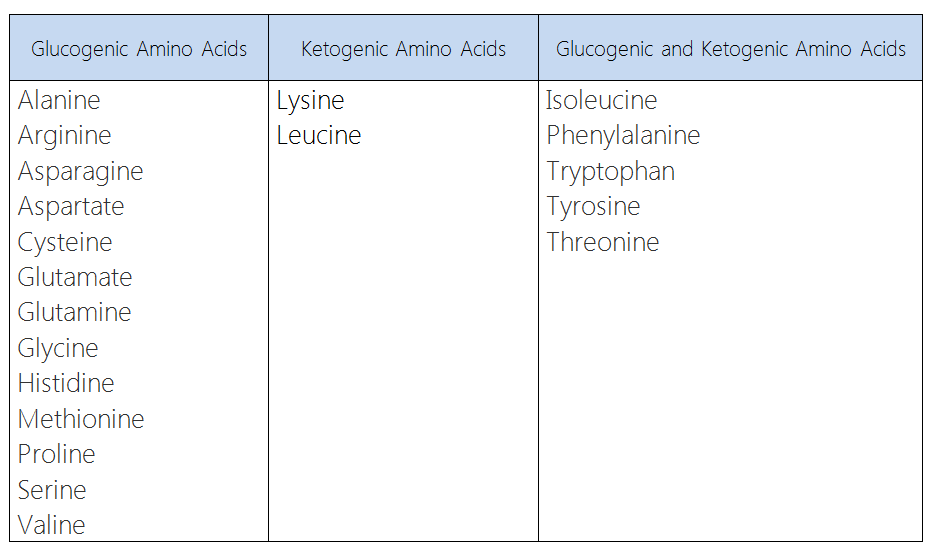
Amino acids are either ketogenic or glucogenic. Ketogenic amino acids are amino acids that give rise to fatty acid precursors (acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA) when metabolized. In contrast, glucogenic amino acids are amino acids that give rise to glucose (and consequently pyruvate) or can be converted to glucose (via gluconeogenesis) when metabolized. Only lycine and leucine are strictly ketogenic amino acids. All other amino acids are either only glucogenic or partly ketogenic and partly glucogenic.<br><br> | |||
Below is a table that classifies amino acids according to their catabolic class:<br> | |||
[[Image:Ketogenic and Glucogenic Amino Acids.png|600px]] | |||
|AnswerA=Methionine | |||
|AnswerAExp=[[Methionine]] is a glucogenic amino acid. | |||
|AnswerB=Valine | |||
|AnswerBExp=[[Valine]] is a glucogenic amino acid. | |||
|AnswerC=Isoleucine | |||
|AnswerCExp=[[Isoleucine]] is a glucogenic and ketogenic amino acid. A patient with [[pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency]] should adhere to a strict ketogenic diet. | |||
|AnswerD=Threonine | |||
|AnswerDExp=[[Threonine]] is a glucogenic and ketogenic amino acid. A patient with [[pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency]] should adhere to a strict ketogenic diet. | |||
|AnswerE=Lysine | |AnswerE=Lysine | ||
|AnswerEExp=[[ | |AnswerEExp=Only [[lysine]] and [[leucine]] are strictly ketogenic amino acids that are not metabolized by [[pyruvate dehydrogenase]]. Patients with pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency should adhere to a strict ketogenic diet that is rich in fat and the amino acids leucine and lysine. | ||
|EducationalObjectives=The majority of patients with PDH deficiency have E1 alpha gene defects (PDHA1), which are usually inherited in an X-linked pattern. Management of PDH deficiency includes a strict ketogenic diet (high intake of fat and/or ketogenic amino acids lysine and leucine). | |||
|References=Bindoff LA, Birch-Machin MA, Farnsworth L, et al. Familial intermittent ataxia due to a defect of the E1 component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. J Neurol Sci. 1989;93:311-8.<br> | |||
First Aid 2014 page 103 | |||
|RightAnswer=E | |RightAnswer=E | ||
|WBRKeyword=Pyruvate dehydrogenase, | |WBRKeyword=Pyruvate dehydrogenase, Lysine, Leucine, Ketogenic amino acid, Enzyme, Enzyme deficiency, Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency, Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency | ||
|Approved=No | |Approved=No | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:17, 28 October 2020
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1] (Reviewed by Yazan Daaboul, M.D.)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Biochemistry |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::General Principles |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 10-month-old girl is brought to the physician's office for convulsions and generalized hypotonia. The mother states that her daughter's condition is associated with irritability and poor feeding. The girl's height and weight are below the lower threshold of growth on the height-weight chart. Laboratory work-up is remarkable for metabolic acidosis and elevated serum concentrations of LDH and ALT. A skeletal muscle biopsy demonstrates E1 subunit deficiency in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. The physician advises the family to adhere to a strict diet. Which of the following amino acids should be included in this girl's diet?]] |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Methionine |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::Methionine is a glucogenic amino acid.]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Valine |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::Valine is a glucogenic amino acid.]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Isoleucine |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Isoleucine is a glucogenic and ketogenic amino acid. A patient with pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency should adhere to a strict ketogenic diet.]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Threonine |
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::Threonine is a glucogenic and ketogenic amino acid. A patient with pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency should adhere to a strict ketogenic diet.]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Lysine |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::Only lysine and leucine are strictly ketogenic amino acids that are not metabolized by pyruvate dehydrogenase. Patients with pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency should adhere to a strict ketogenic diet that is rich in fat and the amino acids leucine and lysine.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::E |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex defects are associated with development of irritability, poor feeding, seizures, impaired psychomotor development, lactic acidosis, and elevated serum alanine concentration (accumulated pyruvate is shunted to lactate via LDH and to alanine via ALT). PDH deficiency is a genetic disorder that may be inherited in either an autosomal or X-linked pattern. This patient's diagnosis is first suspected by the findings on physical examination and lab work-up and further confirmed by genetic testing, which demonstrated E1 alpha gene defect. The majority of patients with PDH deficiency have E1 alpha gene defects (PDHA1), which are usually inherited in an X-linked pattern. Management of PDH deficiency includes a strict ketogenic diet (high intake of fat and/or ketogenic amino acids lysine and leucine).
Amino acids are either ketogenic or glucogenic. Ketogenic amino acids are amino acids that give rise to fatty acid precursors (acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA) when metabolized. In contrast, glucogenic amino acids are amino acids that give rise to glucose (and consequently pyruvate) or can be converted to glucose (via gluconeogenesis) when metabolized. Only lycine and leucine are strictly ketogenic amino acids. All other amino acids are either only glucogenic or partly ketogenic and partly glucogenic. Below is a table that classifies amino acids according to their catabolic class: |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Pyruvate dehydrogenase, WBRKeyword::Lysine, WBRKeyword::Leucine, WBRKeyword::Ketogenic amino acid, WBRKeyword::Enzyme, WBRKeyword::Enzyme deficiency, WBRKeyword::Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency, WBRKeyword::Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |