TIRAP: Difference between revisions
imported>Lrunge m (add links) |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''TIRAP''' is an adapter molecule associated with [[toll-like receptor]]s. | '''TIRAP''' is an adapter molecule associated with [[toll-like receptor]]s. | ||
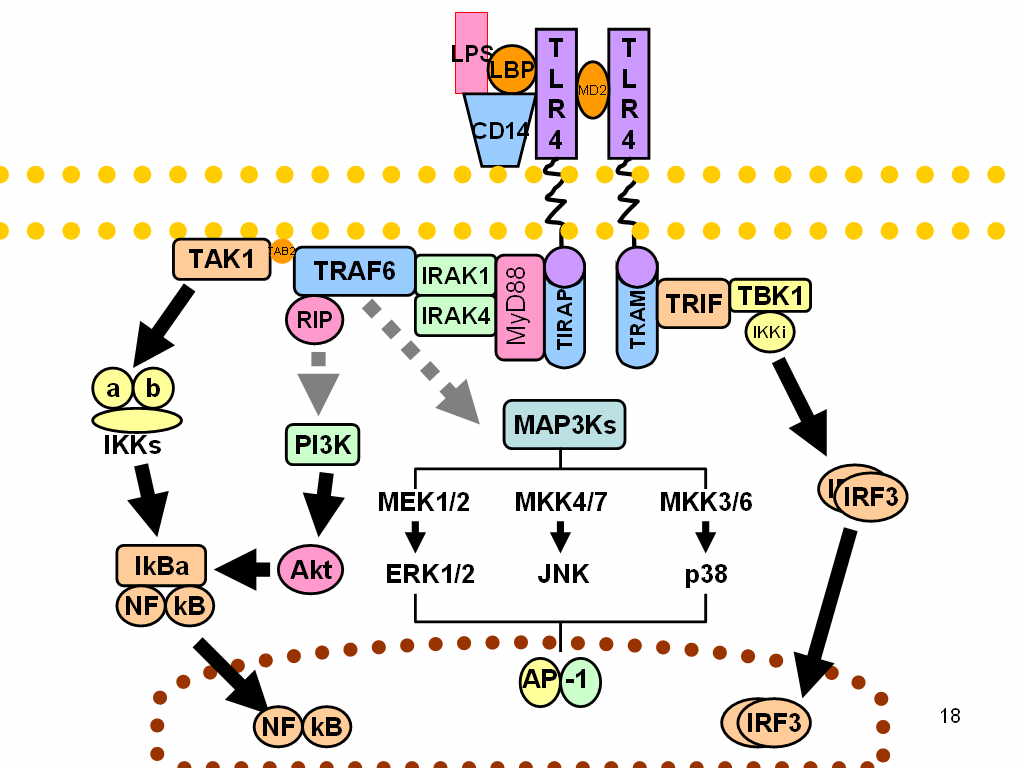
The innate immune system recognizes microbial pathogens through Toll-like receptors (TLRs), which identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Different TLRs recognize different pathogen-associated molecular patterns and all TLRs have a Toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain, which is responsible for signal transduction. The protein encoded by this gene is a TIR adaptor protein involved in the TLR4 signaling pathway of the immune system. It activates NF-kappa-B, MAPK1, MAPK3 and JNK, which then results in cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Alternative splicing of this gene results in several transcript variants; however, not all variants have been fully described. | The innate immune system recognizes microbial pathogens through Toll-like receptors (TLRs), which identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Different TLRs recognize different pathogen-associated molecular patterns and all TLRs have a Toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain, which is responsible for signal transduction. The protein encoded by this gene is a TIR adaptor protein involved in the TLR4 signaling pathway of the immune system. It activates [[NF-kappa-B]], [[MAPK1]], [[MAPK3]] and [[JNK]], which then results in cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Alternative splicing of this gene results in several transcript variants; however, not all variants have been fully described. | ||
[[Image:Toll-like receptor pathways revised.jpg|thumbnail|center|500px|Signaling pathway of toll-like receptors. Dashed grey lines represent unknown associations]] | [[Image:Toll-like receptor pathways revised.jpg|thumbnail|center|500px|Signaling pathway of toll-like receptors. Dashed grey lines represent unknown associations]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:47, 13 April 2018
| toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain containing adaptor protein | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | TIRAP |
| Entrez | 114609 |
| HUGO | 17192 |
| OMIM | 606252 |
| RefSeq | NM_148910 |
| UniProt | P58753 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 11 q24.2 |
TIRAP is an adapter molecule associated with toll-like receptors. The innate immune system recognizes microbial pathogens through Toll-like receptors (TLRs), which identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Different TLRs recognize different pathogen-associated molecular patterns and all TLRs have a Toll-interleukin 1 receptor (TIR) domain, which is responsible for signal transduction. The protein encoded by this gene is a TIR adaptor protein involved in the TLR4 signaling pathway of the immune system. It activates NF-kappa-B, MAPK1, MAPK3 and JNK, which then results in cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Alternative splicing of this gene results in several transcript variants; however, not all variants have been fully described.
See also
External links
- TIRAP+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| Stub icon | This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |