Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 x ray: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Mahshid) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1}} | {{Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}}{{ARK}}{{Ajay}} | ||
==Overview== | |||
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Findings on an x-ray suggestive of primary hyperparathyroidism includes subperiosteal [[bone resorption]], endoosteal [[bone resorption]], subchondral [[resorption]], subligamentous [[resorption]], intracortical [[resorption]], [[osteopenia]], [[Brown tumor|brown tumors]], salt and pepper sign in the skull (pepper pot skull), and [[chondrocalcinosis]]. | |||
==X Ray== | ==X Ray== | ||
* | An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Findings on an x-ray suggestive of primary hyperparathyroidism includes subperiosteal [[bone resorption]], endoosteal [[bone resorption]], subchondral [[resorption]], subligamentous [[resorption]], intracortical [[resorption]], [[osteopenia]], [[Brown tumor|brown tumors]], salt and pepper sign in the skull (pepper pot skull), and [[chondrocalcinosis]]. | ||
* X-ray is the preferred imaging for diagnosis of secondary hyperparathyroidism as majority of findings are radiological. | |||
* Findings in secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism are often associated with the [[osteosclerosis]] of renal [[osteodystrophy]], and the [[osteomalacia]] of [[vitamin D deficiency]] and includes subperiosteal [[bone resorption]],subchondral resorption, subligamentous resorption, severe [[osteopenia]], [[osteosclerosis]], [[brown tumor]], [[amyloid]] deposition, soft tissue and vascular [[calcification]], superior and inferior rib notching, and [[osteonecrosis]]. | |||
===Primary hyperparathyroidism=== | |||
Finding in primary hyperparathyroidism includes:<ref name="pmid24614783">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lachungpa T, Sarawagi R, Chakkalakkoombil SV, Jayamohan AE |title=Imaging features of primary hyperparathyroidism |journal=BMJ Case Rep |volume=2014 |issue= |pages= |year=2014 |pmid=24614783 |pmc=3962932 |doi=10.1136/bcr-2013-203521 |url=}}</ref> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
!X-ray Findings | |||
!Description | |||
|- | |||
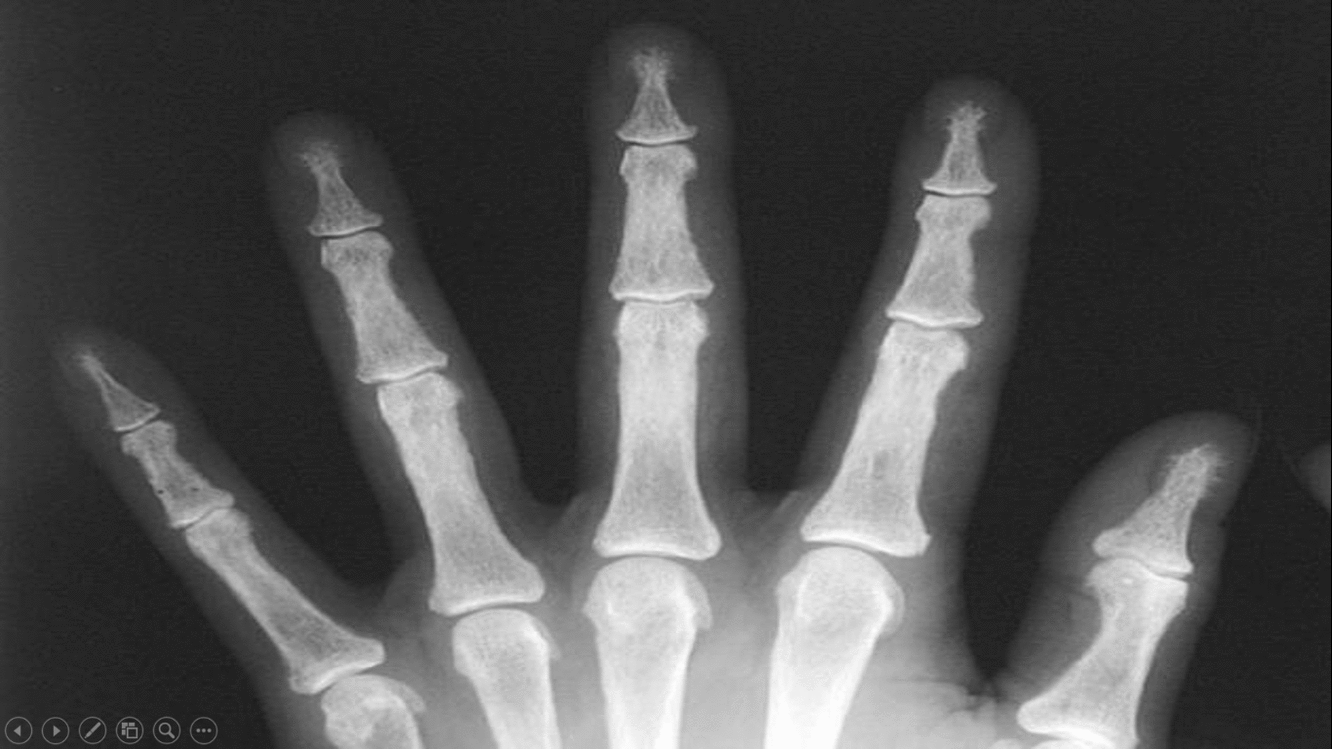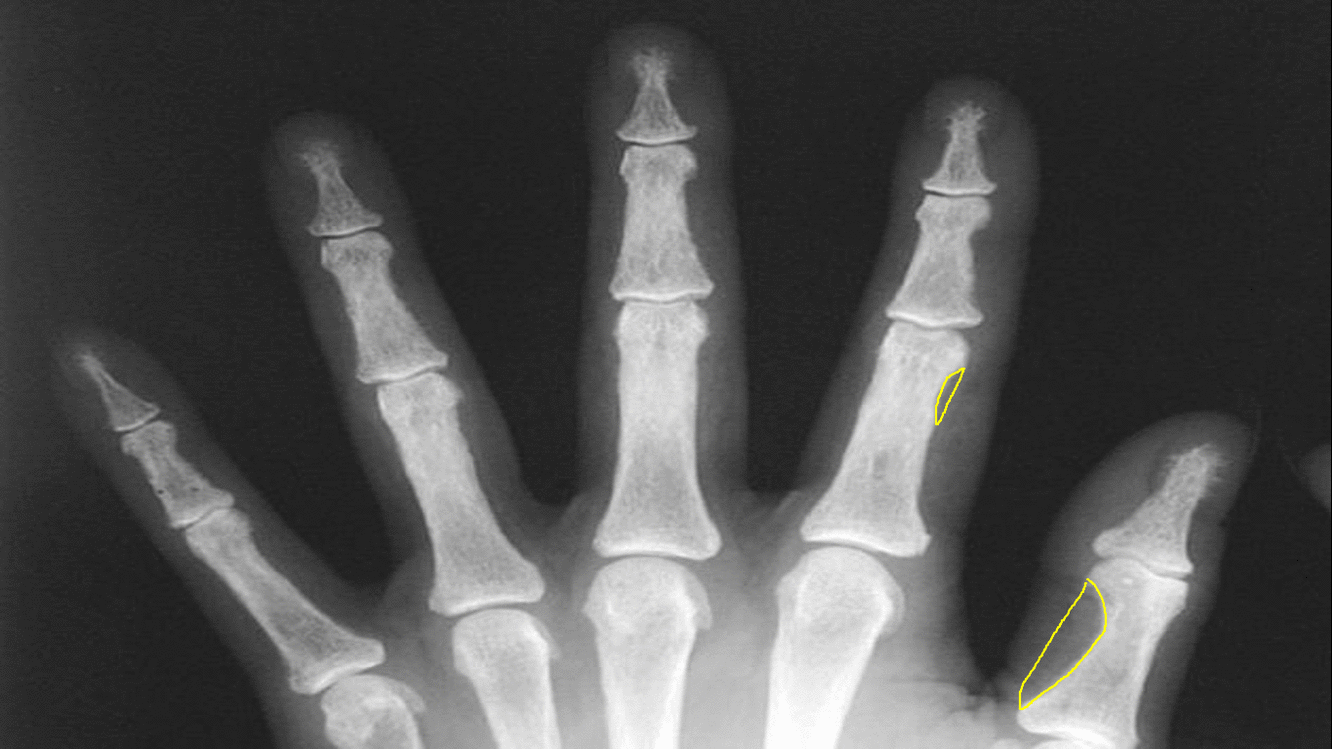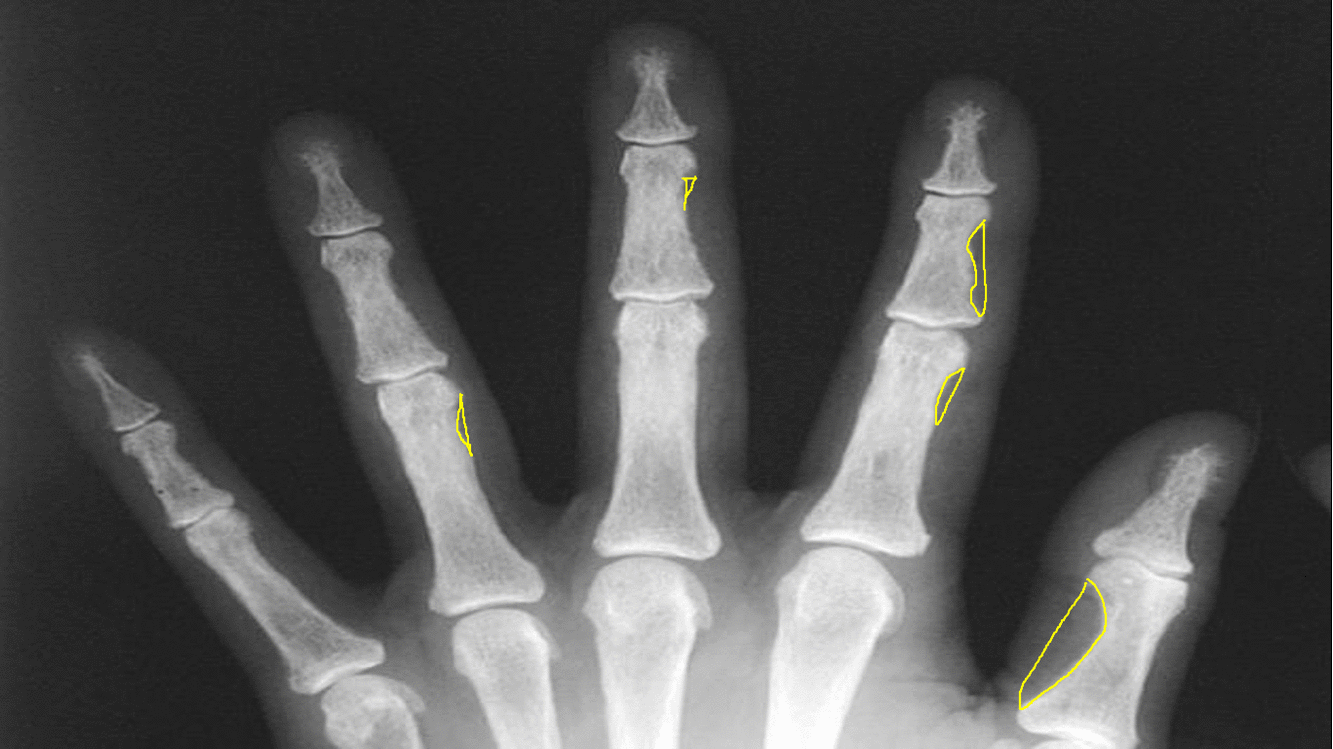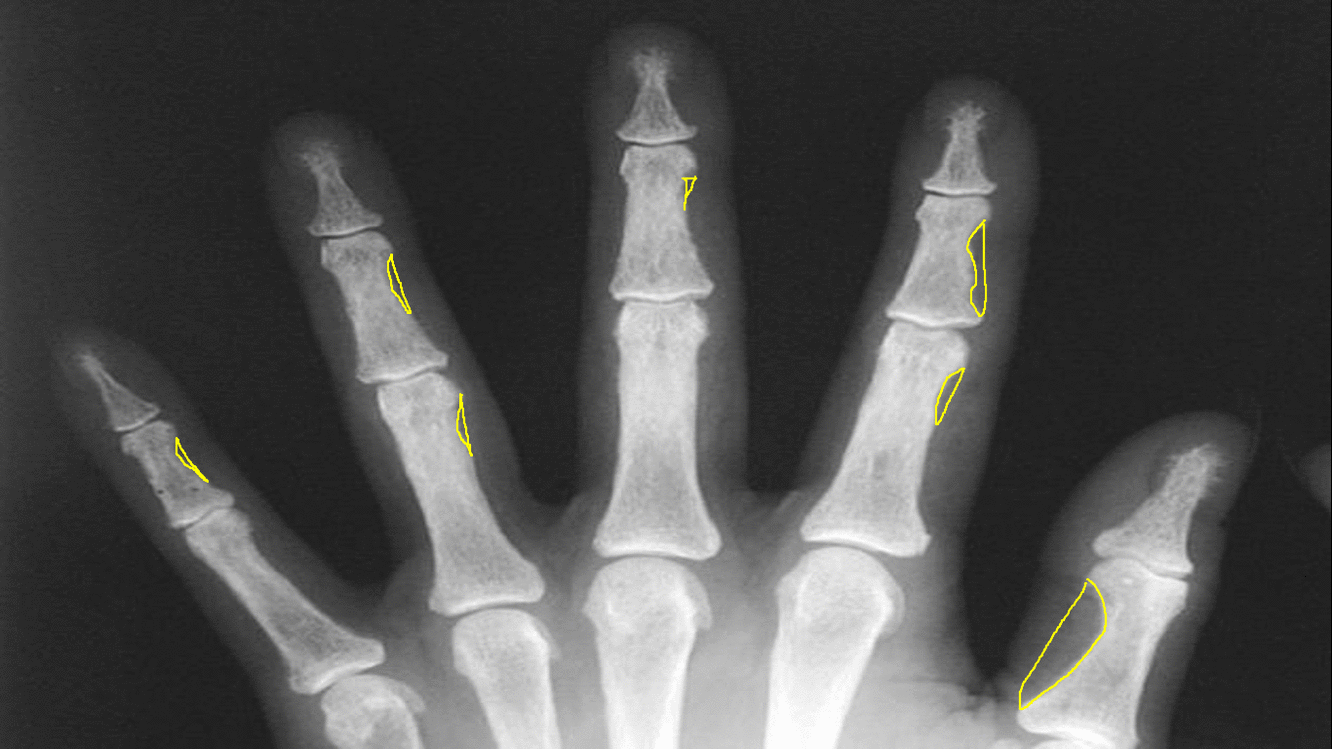
|Subperiosteal [[bone resorption]] | |||
| | |||
*Classically affects the radial aspects of the proximal and middle [[phalanges]] of the index and middle fingers | |||
*Medial aspect of [[tibia]], [[femur]], [[humerus]] | |||
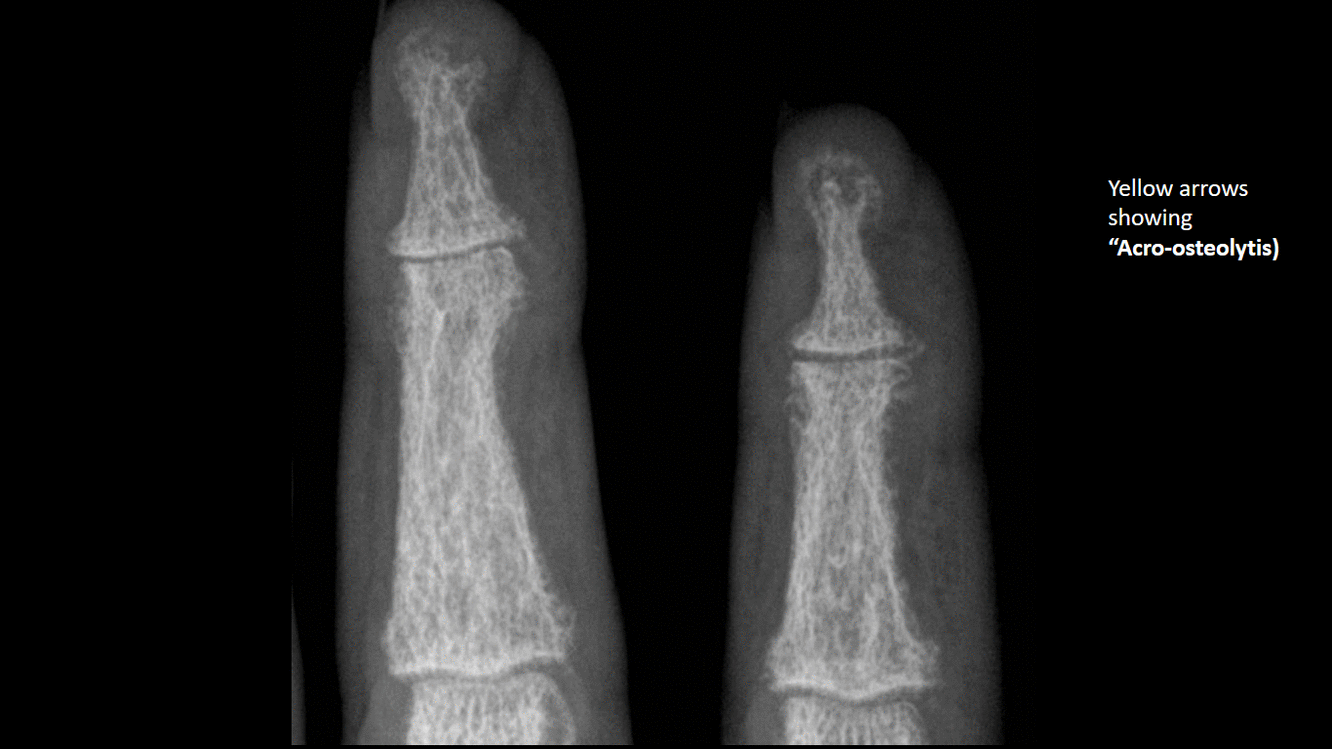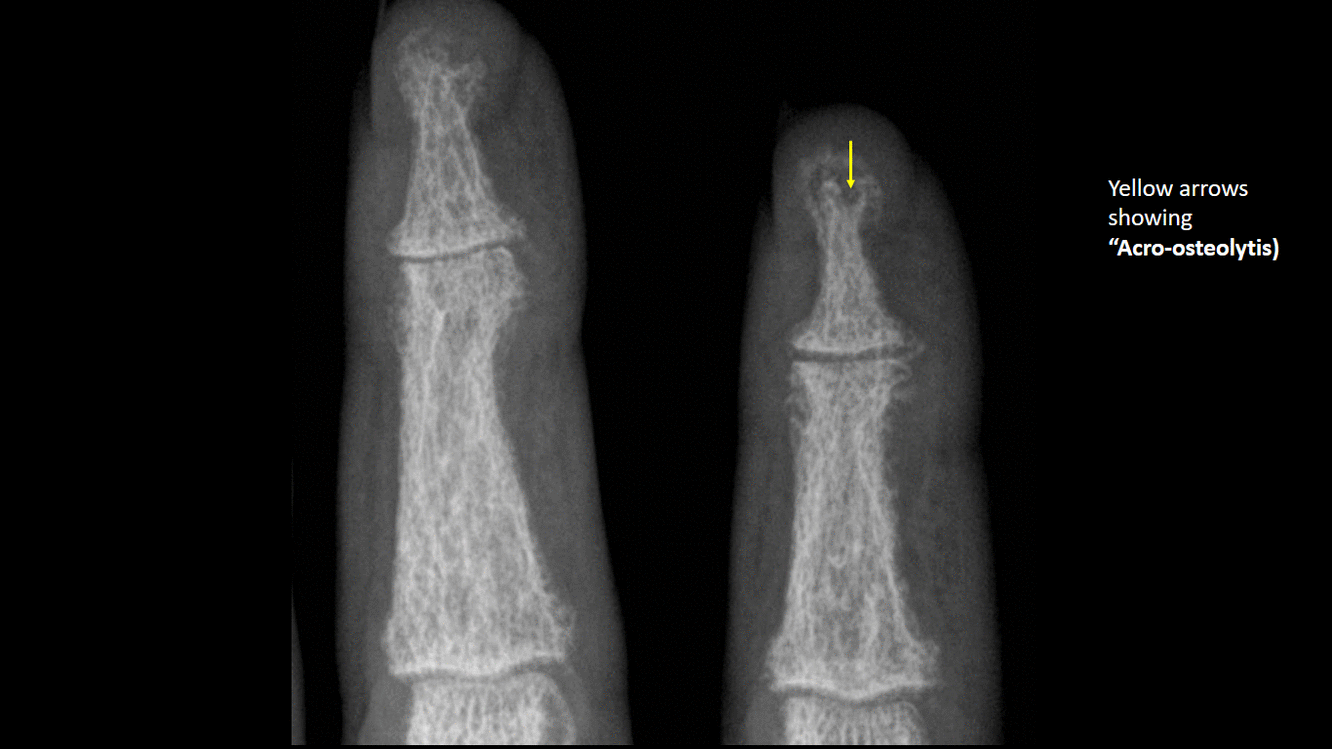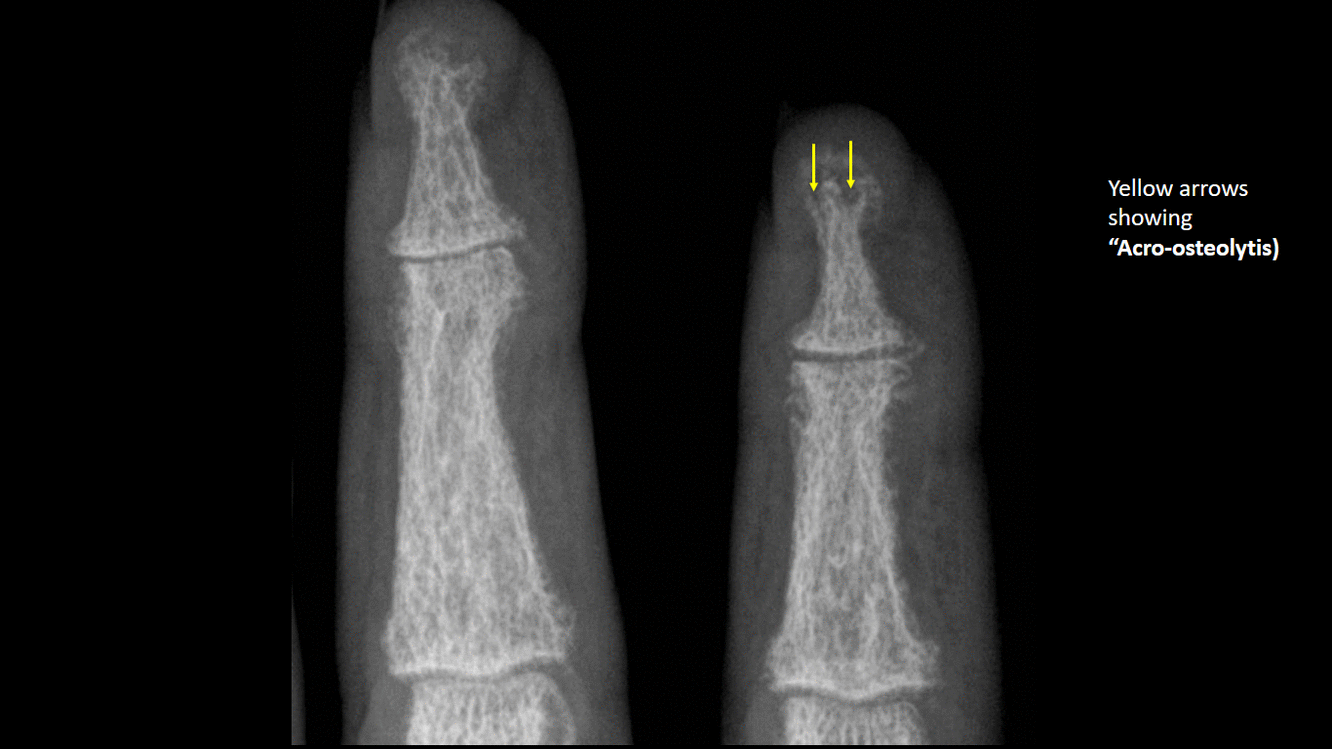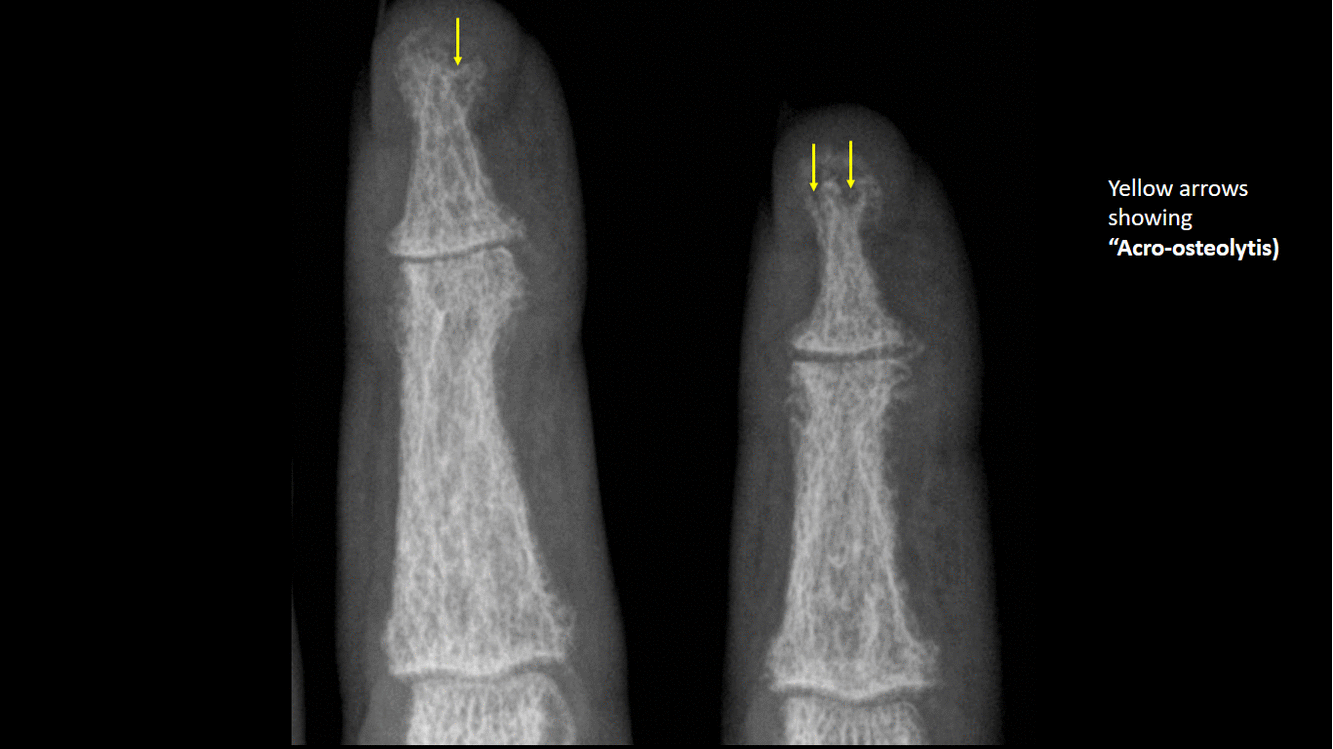
*Phalangeal tuft erosion (acro-osteolysis) | |||
*Lamina dura around teeth (floating teeth) | |||
|- | |||
|Endoosteal [[bone resorption]] | |||
| | |||
*Widening of [[medullary cavity]] | |||
*Thinning of the inner [[cortex]] | |||
|- | |||
|Subchondral [[resorption]] | |||
| | |||
*Lateral end of the [[Clavicle|clavicles]] | |||
*[[Pubic symphysis|Symphysis pubis]] | |||
*[[Sacroiliac joint|Sacroiliac joints]] | |||
|- | |||
|Subligamentous [[resorption]] | |||
| | |||
*[[Ischial tuberosity]] | |||
*Humeral tuberosity | |||
*[[Trochanters]] | |||
*Inferior surface of [[calcaneus]] | |||
*Inferior margin of lateral [[clavicle]] | |||
|- | |||
|Other findings | |||
| | |||
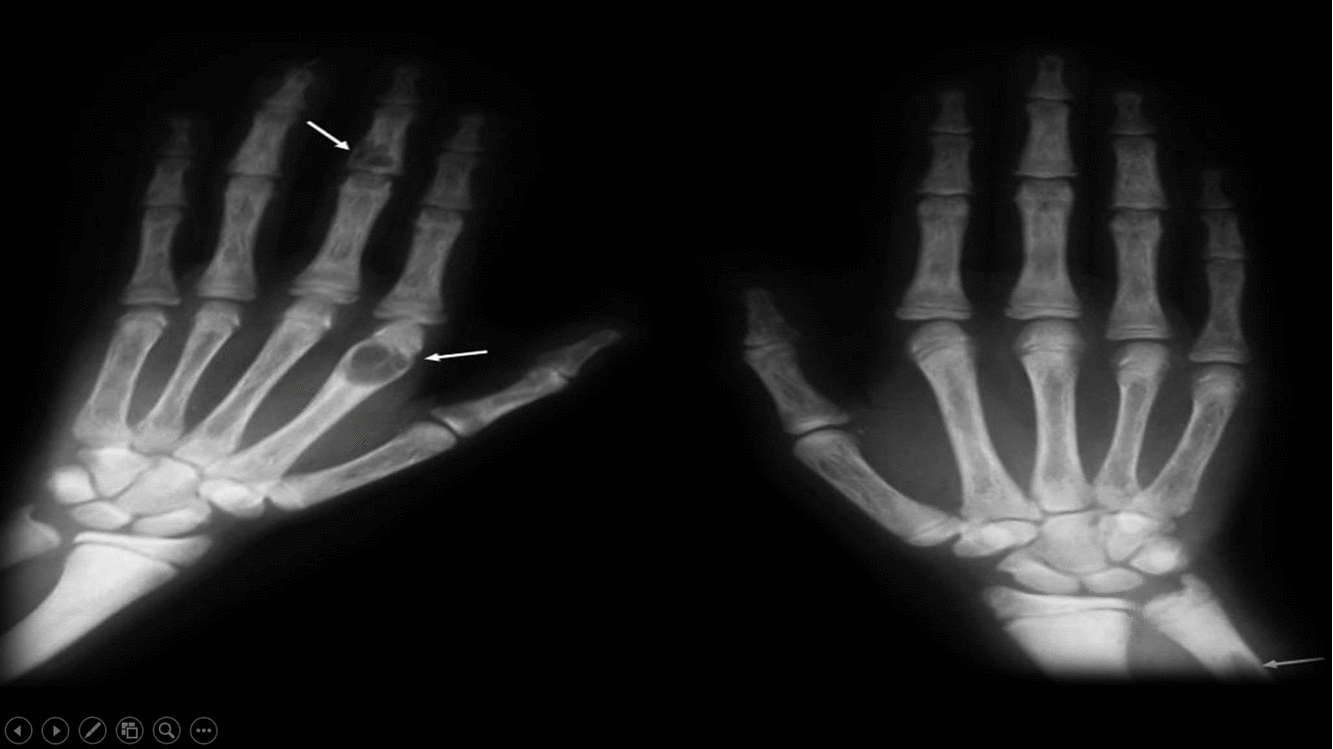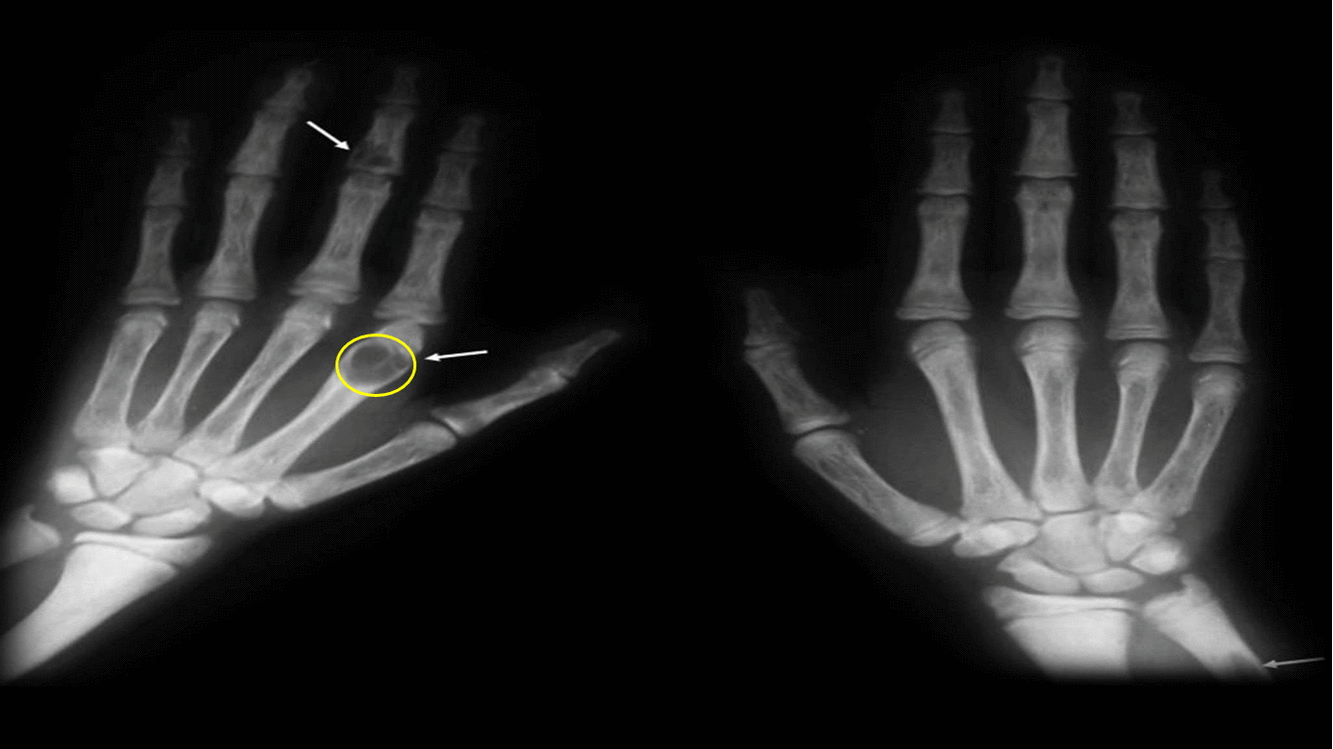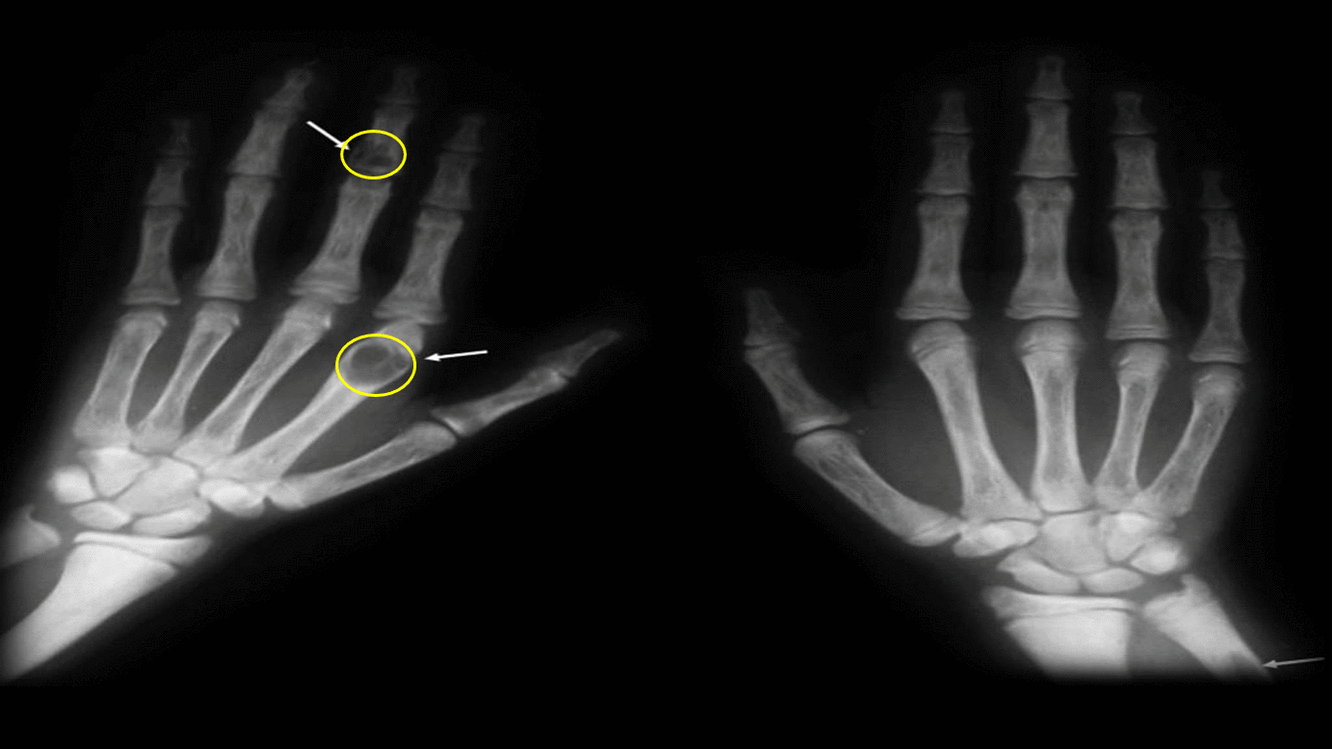
*Intracortical [[resorption]]: cigar/oval-shaped or tunnel-shaped radiolucency in the cortex | |||
*[[Osteopenia]] | |||
*[[Brown tumor|Brown tumors]] | |||
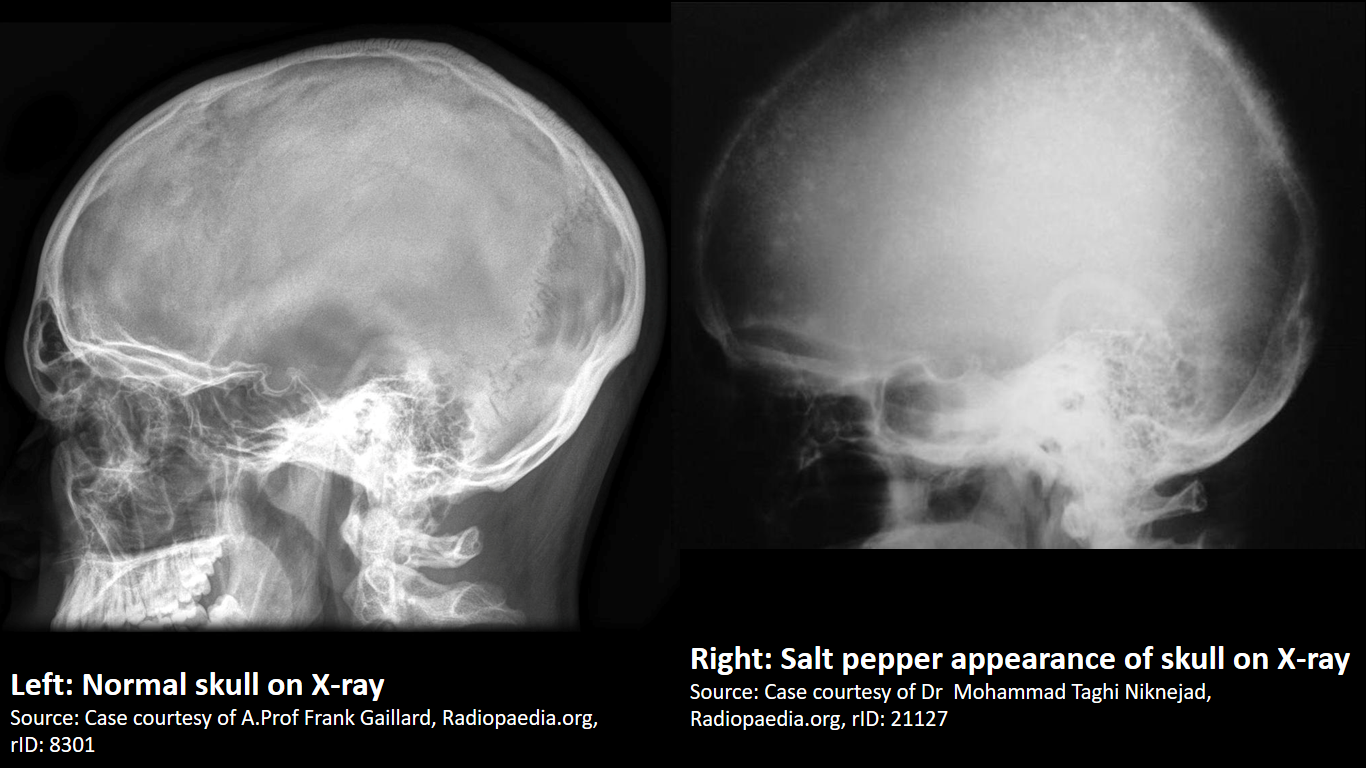
*Salt and pepper sign in the skull (pepper pot skull) | |||
*[[Chondrocalcinosis]] | |||
|} | |||
[[image:Subperiosteal bone resorption.gif|thumb|center|500px|Subperiosteal bone resorption - [https://radiopaedia.org/articles/subperiosteal-bone-resorption Source:Radiopedia]]] | |||
[[image:Brown tumor.gif|thumb|center|500px|Brown tumors - [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/renal-osteodystrophy-and-brown-tumours-1 Source:Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopedia]]] | |||
[[image:Salt-and-pepper-sign-skull compared to normal skull.png|thumb|center|500px|Normal skull compared to Salt & pepper appearance of skull - [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/21127 Source:Radiopedia]]] | |||
[[image:Acro-osteolytis.gif|thumb|center|500px|Acro-osteolytis, terminal tufts erosion - [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/9738 Source:Case courtesy of Dr Andrew Dixon, Radiopedia]]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
| Line 17: | Line 65: | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Oncology]] | |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Endocrinology]] | |||
[[Category:Surgery]] | |||
Latest revision as of 02:46, 27 November 2017
|
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 x ray |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aravind Reddy Kothagadi M.B.B.S[2] Ajay Gade MD[3]]
Overview
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Findings on an x-ray suggestive of primary hyperparathyroidism includes subperiosteal bone resorption, endoosteal bone resorption, subchondral resorption, subligamentous resorption, intracortical resorption, osteopenia, brown tumors, salt and pepper sign in the skull (pepper pot skull), and chondrocalcinosis.
X Ray
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Findings on an x-ray suggestive of primary hyperparathyroidism includes subperiosteal bone resorption, endoosteal bone resorption, subchondral resorption, subligamentous resorption, intracortical resorption, osteopenia, brown tumors, salt and pepper sign in the skull (pepper pot skull), and chondrocalcinosis.
- X-ray is the preferred imaging for diagnosis of secondary hyperparathyroidism as majority of findings are radiological.
- Findings in secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism are often associated with the osteosclerosis of renal osteodystrophy, and the osteomalacia of vitamin D deficiency and includes subperiosteal bone resorption,subchondral resorption, subligamentous resorption, severe osteopenia, osteosclerosis, brown tumor, amyloid deposition, soft tissue and vascular calcification, superior and inferior rib notching, and osteonecrosis.
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Finding in primary hyperparathyroidism includes:[1]
| X-ray Findings | Description |
|---|---|
| Subperiosteal bone resorption | |
| Endoosteal bone resorption |
|
| Subchondral resorption |
|
| Subligamentous resorption |
|
| Other findings |
|
References
- ↑ Lachungpa T, Sarawagi R, Chakkalakkoombil SV, Jayamohan AE (2014). "Imaging features of primary hyperparathyroidism". BMJ Case Rep. 2014. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-203521. PMC 3962932. PMID 24614783.