|
|
| Line 11: |
Line 11: |
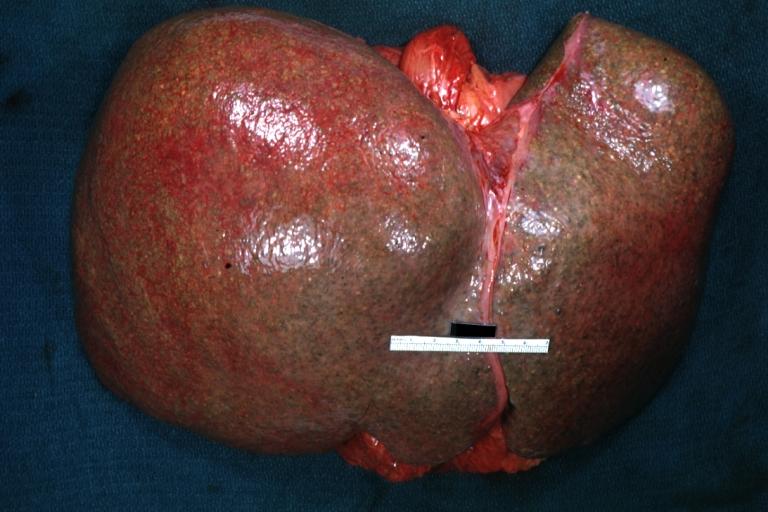
| {{SK}} Enlarged liver, Liver enlargement | | {{SK}} Enlarged liver, Liver enlargement |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview== | | ==[[Hepatomegaly overview|Overview]]== |
|
| |
|
| '''Hepatomegaly''' is the condition of having an enlarged [[liver]]. It is a nonspecific [[sign (medicine)| medical sign]] having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into [[infection]], direct toxicity, hepatic tumors, or [[metabolic disorder]]. Often, hepatomegaly will present as an [[abdominal mass]]. Depending on the cause, it may sometimes present along with [[jaundice]].
| | ==[[Hepatomegaly historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== |
|
| |
|
| ==Palpable Liver without Hepatic Pathology== | | ==[[Hepatomegaly classification|Classification]]== |
|
| |
|
| *Normal variant
| | ==[[Hepatomegaly pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== |
| *Thin or flaccid abdominal wall
| |
| *Depressed right diaphragm (e.g., [[emphysema]])
| |
| *Subdiaphragmatic lesion (e.g., [[abscess]])
| |
| *Riedel's lobe
| |
|
| |
|
| ==True Hepatic Enlargement== | | ==[[Hepatomegaly causes|Causes]]== |
|
| |
|
| ===Inflammatory liver disease=== | | ==[[Hepatomegaly differential diagnosis|Differentiating Hepatomegaly from other Diseases]]== |
| *[[Hepatitis]]
| |
| :*Infectious
| |
| :*:*Bacterial
| |
| :*:*:*[[Glandular fever]] ([[Infectious mononucleosis]]) This is caused by the [[Epstein-Barr Virus]] ([[EBV]]).
| |
| :*:*:*[[Malaria]]
| |
| :*:*:*[[Hydatid cyst]]
| |
| :*:*:*[[Leptospirosis]]
| |
| :*:*:*[[Actinomycosis]]
| |
| :*:*Viral
| |
| :*:*:*[[Hepatitis A]]
| |
| :*:*:*[[Hepatitis B]]
| |
| :*:*:*[[HIV]]
| |
| :*:*[[Schistosomiasis]]
| |
| :*:*Others
| |
| :*Alcoholic hepatitis
| |
| :*Other toxins induced hepatitis
| |
| :*Drug-induced hepatitis
| |
| :*Autoimmune hepatitis
| |
| :*Steatohepatitis
| |
| :*[[Steatosis]]
| |
| :*Others
| |
| *Abscess
| |
| :*Pyogenic
| |
| :*Amebic
| |
| *[[Cholangitis]]
| |
| :*Suppurative
| |
| :*Sclerosing
| |
| *Pericholangitis (especially related to [[ulcerative colitis]])
| |
|
| |
|
| ===[[Chronic liver disease]] and [[cirrhosis]]===
| | ==[[Hepatomegaly epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== |
| *Alcoholic
| |
| *Posthepatitic
| |
| *Postnecrotic
| |
| *Cholestatic
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Cirrhotic=== | | ==[[Hepatomegaly risk factors|Risk Factors]]== |
| *Portal
| |
| *Biliary
| |
| *Cardiac
| |
| :*[[Tricuspid insufficiency]]
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Metabolic disorders=== | | ==[[Hepatomegaly screening|Screening]]== |
| *[[Hemochromatosis]]
| |
|
| |
|
| ===[[Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency]]=== | | ==[[Hepatomegaly natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== |
| *[[Wilson's disease]]
| |
| *[[Cystic fibrosis]]
| |
| | |
| ===Other causes===
| |
| *Extrahepatic biliary obstruction
| |
| :*[[Choledocholithiasis]]
| |
| :*Biliary stricture
| |
| :*[[Pancreatitis]]
| |
| :*[[Carcinoma]]
| |
| :*:*[[Bile duct]]s ([[cholangiocarcinoma]])
| |
| :*:*Head of pancreas
| |
| :*:*[[Ampulla of Vater]]
| |
| :*External compression
| |
| *Hepatic congestion
| |
| :*[[Congestive heart failure]]
| |
| :*[[Constrictive pericarditis]]
| |
| :*[[Budd-Chiari syndrome]] (hepatic outflow obstruction, [[hepatic vein obstruction]])
| |
| :*:*Thrombosis
| |
| :*:*[[Tumor]]
| |
| :*:*Web ([[inferior vena cava]])
| |
| *Veno-occlusive disease
| |
| :*Jamaican herbal tea
| |
| :*After bone-marrow transplantation
| |
| *Infiltrative disorders, storage diseases
| |
| :*Lipid accumulation
| |
| :*:*[[Fatty liver]]
| |
| :*:*:*Alcohol
| |
| :*:*:*[[Diabetes mellitus]]
| |
| :*:*:*[[Obesity]]
| |
| :*:*:*Severe protein malnutrition ([[Kwashiorkor]]: dietary protein deficiency)
| |
| :*:*:*Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
| |
| :*:*:*Jejunoileal bypass
| |
| :*:*:*Parenteral hyperalimentation
| |
| :*:*:*[[Corticosteroid]]s, [[Cushing's syndrome]]
| |
| :*:*:*Fatty liver of pregnancy
| |
| :*:*:*Massive [[tetracycline]] therapy
| |
| :*:*:*Toxins (e.g., [[carbon tetrachloride]], dichlorodiphenyl trichloroethane)
| |
| :*:*:*[[Reye's syndrome]]
| |
| :*:*[[Lipid storage disease]] (especially [[Gaucher's disease]], [[Niemann-Pick disease]])
| |
| :*Glycogen accumulation
| |
| :*:*[[Glycogen storage disease]]
| |
| :*:*Diabetic glycogenosis
| |
| :*Granulomatous infiltration (especially [[sarcoidosis]], [[miliary tuberculosis]], disseminated fungal diseases, some drug reactions)
| |
| :*Myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative disorders
| |
| :*:*[[Lymphoma]]
| |
| :*:*[[Myeloid metaplasia]]
| |
| :*:*[[Multiple myeloma]]
| |
| :*:*[[Leukemia]]
| |
| :*[[Amyloidosis]]
| |
| :*[[Congenital hepatic fibrosis]]
| |
| :*[[Hemochromatosis]]
| |
| :*[[Wilson's disease]]
| |
| *[[Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency]]
| |
| :*[[Hurler's syndrome]]
| |
| *Neoplasms
| |
| :*Primary
| |
| :*:*Malignant
| |
| :*:*:[[Hepatocellular carcinoma]]
| |
| :*:*:[[Cholangiocarcinoma]]
| |
| :*:*:[[Angiosarcoma]]
| |
| :*:*Benign
| |
| :*:*:[[Hepatic adenoma]]
| |
| :*:*:[[Hemangioma]]
| |
| :*:*:[[Focal nodular hyperplasia]]
| |
| :*:*:[[Adenoma]]
| |
| :*Metastatic
| |
| :*:*[[Pancreas]]
| |
| :*:*[[Colon]]
| |
| :*:*[[Lung]]
| |
| :*:*[[Breast]]
| |
| :*:*[[Stomach]]
| |
| :*:*[[Kidney]]
| |
| :*:*[[Esophagus]]
| |
| :*:*[[Carcinoid]]
| |
| *Cysts
| |
| :*Congenital
| |
| :*:*Solitary
| |
| :*:*Polycystic
| |
| :*Acquired (especially echinococcal)
| |
| *[[Hunter syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Zellweger's syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I deficiency]]
| |
| *[[Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency]]
| |
| *[[Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency]]
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Diagnosis== | | ==Diagnosis== |
| After a thorough [[medical history]] and [[physical examination]], [[blood test]]s should be drawn. An important series of blood tests are the [[liver function test]]s, which give a good impression of the patient's broad metabolic picture.
| |
|
| |
| An [[ultrasound]] of the liver can reliably detect a dilated [[biliary duct]] system, which helps distinguish [[parenchyma]]l liver disease from extrahepatic bile duct obstruction. Ultrasound can also detect the characteristic texture of a [[liver cirrhosis|cirrhotic liver]], and can guide [[fine needle aspiration]] of [[cyst]]s, [[abscess]]es and tumors.
| |
|
| |
| [[Computed tomography]] (CT) can help obtain more accurate [[anatomy|anatomical]] information, and is unaffected by the [[obesity]] or the presence of bowel gases.
| |
|
| |
| ==Mnemonics for Hepatomegaly==
| |
|
| |
|
| '''V I N D I C A T E'''
| | [[Hepatomegaly diagnostic criteria|Diagnostic Criteria]] | [[Hepatomegaly history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Hepatomegaly physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Hepatomegaly laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Hepatomegaly electrocardiogram|EKG]] | [[Hepatomegaly CT|CT]] | [[Hepatomegaly MRI|MRI]] | [[Hepatomegaly echocardiography or ultrasound|Echocardiography or Ultrasound]] | [[Hepatomegaly other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Hepatomegaly other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] |
|
| |
|
| [[Image:Vindicate.jpg|center|thumb|700px]]
| | ==Treatment== |
|
| |
|
| | [[Hepatomegaly medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Hepatomegaly surgery|Surgery]] | [[Hepatomegaly primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Hepatomegaly secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Hepatomegaly cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Hepatomegaly future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] |
|
| |
|
| | ==Case Studies== |
| | [[Hepatomegaly case study one|Case #1]] |
|
| |
|
| ==See also== | | ==Related Chapters== |
| * [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | | * [[Hepatosplenomegaly]] |
|
| |
|