Chondrosarcoma: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Robot: Changing Category:DiseaseState to Category:Disease) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
MeshID = | | MeshID = | | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ | {{Chondrosarcoma}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
==[[Chondrosarcoma overview|Overview]]== | |||
== | ==[[Chondrosarcoma classification|Classification]]== | ||
==[[Chondrosarcoma historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | |||
== | ==[[Chondrosarcoma pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | ||
== | ==[[Chondrosarcoma epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology & Demographics]]== | ||
==[[Chondrosarcoma risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | |||
==[[Chondrosarcoma screening|Screening]]== | |||
==[[Chondrosarcoma causes|Causes]]== | |||
==[[Chondrosarcoma differential diagnosis|Differentiating Chondrosarcoma from other Diseases]]== | |||
== | ==[[Chondrosarcoma natural history|Natural History, Complications & Prognosis]]== | ||
==Diagnosis== | |||
[[Chondrosarcoma history and symptoms|History & Symptoms]] | [[Chondrosarcoma physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Chondrosarcoma staging|Staging]] | [[Chondrosarcoma laboratory tests|Lab Tests]] | [[Chondrosarcoma electrocardiogram|Electrocardiogram]] | [[Chondrosarcoma x ray|X Ray]] | [[Chondrosarcoma CT|CT]] | [[Chondrosarcoma MRI|MRI]] | [[Chondrosarcoma echocardiography or ultrasound|Echocardiography or Ultrasound]] | [[Chondrosarcoma other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Chondrosarcoma other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
[[Chondrosarcoma medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Chondrosarcoma surgery|Surgery]] | [[Chondrosarcoma primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Chondrosarcoma secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | |||
==Resources== | |||
== | |||
*[http://www.geocities.com/chondrosarcoma/ A Patient's Guide to Chondrosarcoma] | *[http://www.geocities.com/chondrosarcoma/ A Patient's Guide to Chondrosarcoma] | ||
*[http://health.groups.yahoo.com/group/Chondrosarcoma/ Chondrosarcoma Support Group at Yahoo!] | *[http://health.groups.yahoo.com/group/Chondrosarcoma/ Chondrosarcoma Support Group at Yahoo!] | ||
| Line 77: | Line 53: | ||
*[http://www.rnoh.nhs.uk/clinical_services/bone-tumour-tissue-cancer/ Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore] | *[http://www.rnoh.nhs.uk/clinical_services/bone-tumour-tissue-cancer/ Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore] | ||
[[de:Chondrosarkom]] | [[de:Chondrosarkom]] | ||
[[pl:Chrzęstniak mięsakowy]] | [[pl:Chrzęstniak mięsakowy]] | ||
[[pt:Condrosarcoma]] | [[pt:Condrosarcoma]] | ||
[[Category:Disease]] | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category:Oncology]] | [[Category:Oncology]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedics]] | |||
[[Category:Types of cancer]] | |||
[[Category:Skeletal disorders]] | |||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | |||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | |||
Revision as of 17:58, 19 January 2012
| Chondrosarcoma | |
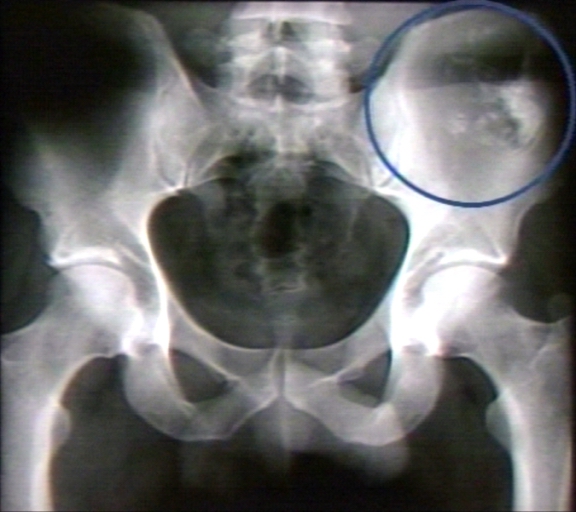 | |
|---|---|
| Chondrosarcoma: Ileum |
|
Chondrosarcoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Chondrosarcoma On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Chondrosarcoma |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Classification
Historical Perspective
Pathophysiology
Epidemiology & Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Causes
Differentiating Chondrosarcoma from other Diseases
Natural History, Complications & Prognosis
Diagnosis
History & Symptoms | Physical Examination | Staging | Lab Tests | Electrocardiogram | X Ray | CT | MRI | Echocardiography or Ultrasound | Other Imaging Findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention
Resources
- A Patient's Guide to Chondrosarcoma
- Chondrosarcoma Support Group at Yahoo!
- Adult Bone Cancer Survivors - Chondrosarcoma Survivors' Stories, Resources and Support Forum
- Chondrosarcoma of Bone Article written so patients can understand
- Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma by John Goldberg, MD and Holcombe Grier, MD
- A list where you can find a Sarcoma Center
- CancerBACUP Chondrosarcoma Info Page
- Bone Tumor.org Fact Page on Chondrosarcoma
- Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore