Chest pain x ray: Difference between revisions
Aisha Adigun (talk | contribs) (→X Ray) |
Aisha Adigun (talk | contribs) (→X Ray) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
**Palla's sign: enlarged right descending pulmonary artery | **Palla's sign: enlarged right descending pulmonary artery | ||
**Pneumothorax<ref name="SharmaJindal2008">{{cite journal|last1=Sharma|first1=Anita|last2=Jindal|first2=Parul|title=Principles of diagnosis and management of traumatic pneumothorax|journal=Journal of Emergencies, Trauma and Shock|volume=1|issue=1|year=2008|pages=34|issn=0974-2700|doi=10.4103/0974-2700.41789}}</ref> | |||
**Absent [[lung]] markings | |||
**White [[Pleural cavity|pleural]] lines | |||
**[[Mediastinum]] deviation to the opposite side | |||
**[[Atelectasis]] | |||
**Air fluid level in [[Pleural cavity|pleural]] space | |||
**Outline of [[Thoracic diaphragm|diaphragm]] under the heart | |||
**[[Deep sulcus sign]] | |||
**Increased rib separation | |||
**Ipsilateral flattening of [[heart]] border | |||
**Midiaphragmatic [[depression]] | |||
[[File:Tension-pneumothorax-1.jpg|thumb|center|369x369px|Pneumothorax [https://radiopaedia.org/cases/tension-pneumothorax-1 Source:Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 8250]]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 19:10, 30 August 2020
|
Chest pain Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Chest pain x ray On the Web |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aisha Adigun, B.Sc., M.D.[2]
Overview
There are no x-ray findings associated with [disease name].
OR
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of [disease name]. Findings on an x-ray suggestive of/diagnostic of [disease name] include [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
There are no x-ray findings associated with [disease name]. However, an x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of complications of [disease name], which include [complication 1], [complication 2], and [complication 3].
X Ray
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of common causes of chest pain. Findings on an x-ray include:
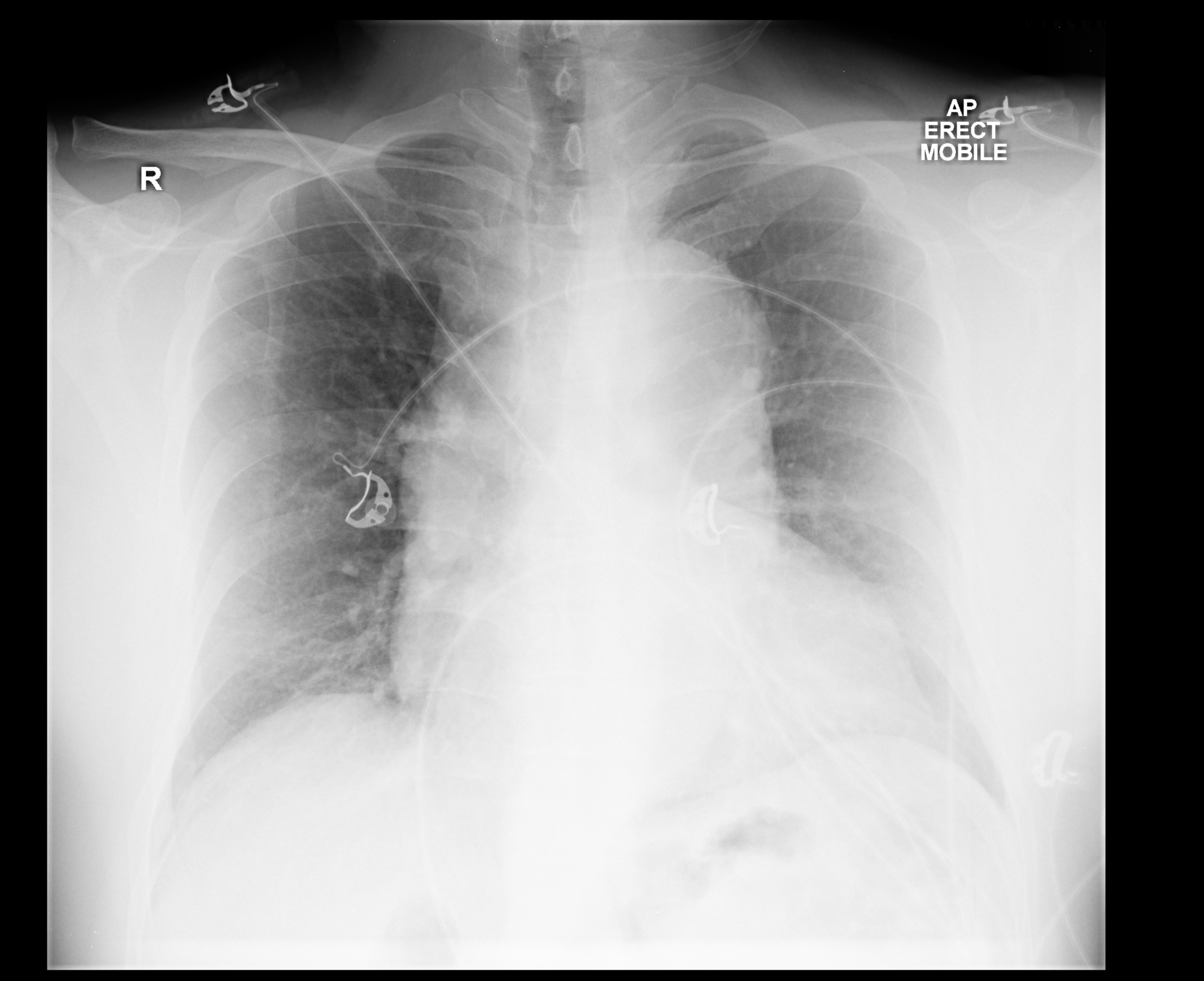
- Aortic dissection[1][2][3]
- Widened mediastinum, (> 8cm at the level of the aortic knob on portable AP chest radiographs)
- Left pleural effusion
- double and irregular aortic contour
- Displaced intimal calcification >5mm (ring sign)
- Esophageal and tracheal deviation to the right
- Blurred aortic knob
- Depression of left mainstem bronchus
- Apical capping on the left
- Loss of paratracheal stripe
- Pulmonary embolism[6][7][8][9]
- Hampton hump: peripheral wedge-shaped density above the diaphragm
- Westermark sign: vasoconstriction distal to the pulmonary embolus
- Elevated hemidiaphragm
- Pleural effusion
- Palla's sign: enlarged right descending pulmonary artery
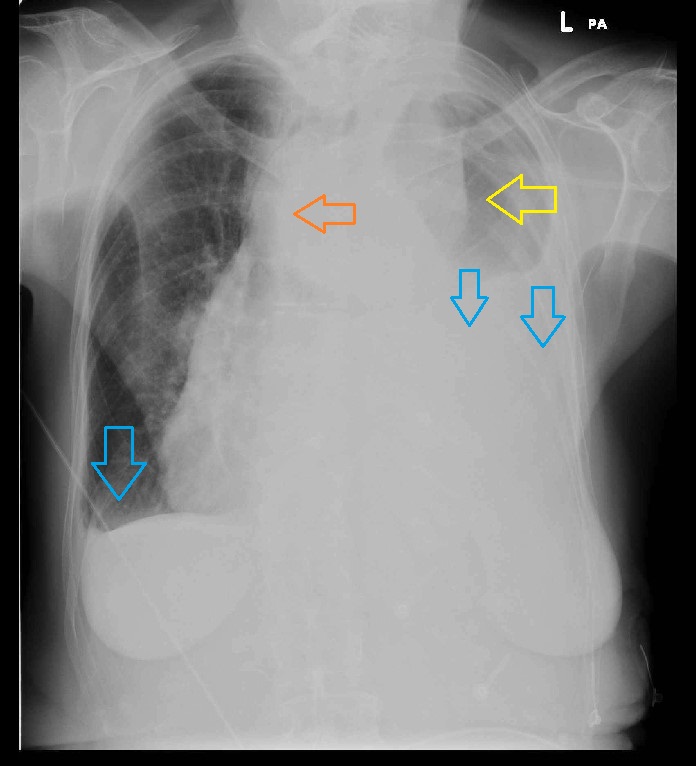
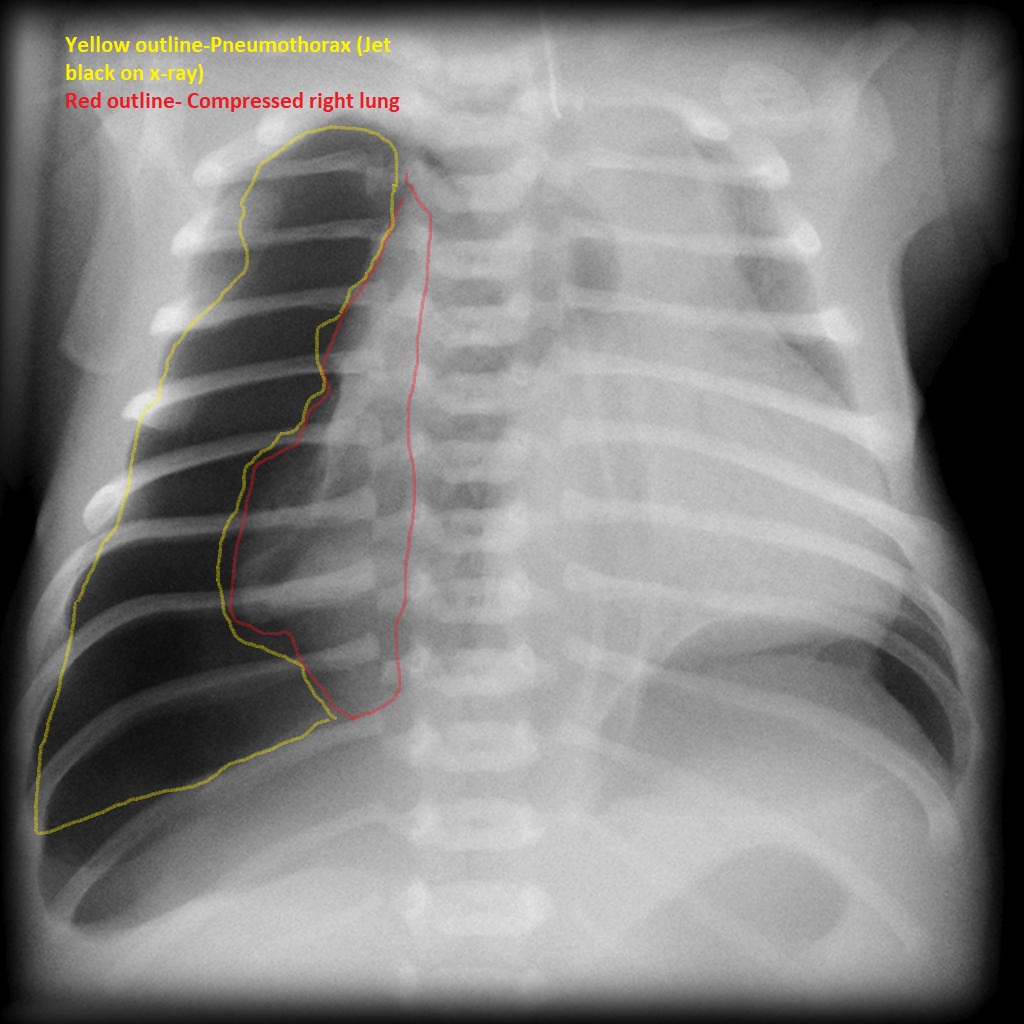
- Pneumothorax[10]
- Absent lung markings
- White pleural lines
- Mediastinum deviation to the opposite side
- Atelectasis
- Air fluid level in pleural space
- Outline of diaphragm under the heart
- Deep sulcus sign
- Increased rib separation
- Ipsilateral flattening of heart border
- Midiaphragmatic depression
References
- ↑ de Lacey G, Morley S et-al. The Chest X-Ray: A Survival Guide. Saunders Ltd. ISBN:0702030465.
- ↑ Lai V, Tsang WK, Chan WC, Yeung TW (August 2012). "Diagnostic accuracy of mediastinal width measurement on posteroanterior and anteroposterior chest radiographs in the depiction of acute nontraumatic thoracic aortic dissection". Emerg Radiol. 19 (4): 309–15. doi:10.1007/s10140-012-1034-3. PMC 3396328. PMID 22415593.
- ↑ Gleeson CE, Spedding RL, Harding LA, et al The mediastinum—Is it wide? Emergency Medicine Journal 2001;18:183-185.
- ↑ Case courtesy of Dr Wayland Wang, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 50763
- ↑ Case courtesy of Dr Devanshi Pathania, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 68763
- ↑ Worsley DF, Alavi A, Aronchick JM, Chen JT, Greenspan RH, Ravin CE (October 1993). "Chest radiographic findings in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: observations from the PIOPED Study". Radiology. 189 (1): 133–6. doi:10.1148/radiology.189.1.8372182. PMID 8372182.
- ↑ Rossi SE, Goodman PC, Franquet T (June 2000). "Nonthrombotic pulmonary emboli". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 174 (6): 1499–508. doi:10.2214/ajr.174.6.1741499. PMID 10845470.
- ↑ CHANG CH, DAVIS WC (April 1965). "A ROENTGEN SIGN OF PULMONARY INFARCTION". Clin Radiol. 16: 141–7. doi:10.1016/s0009-9260(65)80007-1. PMID 14272525.
- ↑ Palla A, Donnamaria V, Petruzzelli S, Rossi G, Riccetti G, Giuntini C (September 1983). "Enlargement of the right descending pulmonary artery in pulmonary embolism". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 141 (3): 513–7. doi:10.2214/ajr.141.3.513. PMID 6603760.
- ↑ Sharma, Anita; Jindal, Parul (2008). "Principles of diagnosis and management of traumatic pneumothorax". Journal of Emergencies, Trauma and Shock. 1 (1): 34. doi:10.4103/0974-2700.41789. ISSN 0974-2700.