Cardiac tumors pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
'''Papillary fibroelastoma''' | '''Papillary fibroelastoma''' | ||
:*[[primary tumors of the heart|Primary tumor of the heart]] that typically involves one of the valves of the [[heart]] | :*[[primary tumors of the heart|Primary tumor of the heart]] that typically involves one of the valves of the [[heart]] | ||
:* | :*Papillary fibroelastoma is generally considered benign, and represents 10% of all primary tumors of the heart | ||
:*Papillary fibroelastoma are the third most common type of primary tumor of the heart, behind [[myxoma|cardiac myxomas]] and cardiac fibromas.<ref name="Matsumoto-2007">{{cite journal | author=Matsumoto N, Sato Y, Kusama J, Matsuo S, Kinukawa N, Kunimasa T, Ichiyama I, Takahashi H, Kimura S, Orime Y, Saito S. | title=Multiple papillary fibroelastomas of the aortic valve: case report. | journal=Int J Cardiol | year=2007 | volume=122 | issue=1 | pages=e1-3 | id=PMID 17196273}}</ref> | :*Papillary fibroelastoma are the third most common type of primary tumor of the heart, behind [[myxoma|cardiac myxomas]] and cardiac fibromas.<ref name="Matsumoto-2007">{{cite journal | author=Matsumoto N, Sato Y, Kusama J, Matsuo S, Kinukawa N, Kunimasa T, Ichiyama I, Takahashi H, Kimura S, Orime Y, Saito S. | title=Multiple papillary fibroelastomas of the aortic valve: case report. | journal=Int J Cardiol | year=2007 | volume=122 | issue=1 | pages=e1-3 | id=PMID 17196273}}</ref> | ||
:*The pathogenesis of papillary fibroelastoma is characterised by the mechanical effects of the tumor and the transient occlusion of the [[left coronary artery|left main coronary artery]] (by the tumor), while a heart attack or sudden cardiac death may be due to embolisation of a portion of the tumor into a coronary artery.<ref name="Takada-2000">{{cite journal | author=Takada A, Saito K, Ro A, Tokudome S, Murai T. | title= Papillary fibroelastoma of the aortic valve: a sudden death case of coronary embolism with myocardial infarction.| journal=Forensic Sci Int | year=2000 | volume=113 | issue=1-3 | pages=209-14 | id=PMID 10978627}}</ref> | |||
===Gross Pathology=== | ===Gross Pathology=== | ||
Revision as of 14:09, 2 May 2016
|
Cardiac tumors Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Cardiac tumors pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cardiac tumors pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cardiac tumors pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]; Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S.
Overview
Pathophysiology
Papillary fibroelastoma
- Primary tumor of the heart that typically involves one of the valves of the heart
- Papillary fibroelastoma is generally considered benign, and represents 10% of all primary tumors of the heart
- Papillary fibroelastoma are the third most common type of primary tumor of the heart, behind cardiac myxomas and cardiac fibromas.[1]
- The pathogenesis of papillary fibroelastoma is characterised by the mechanical effects of the tumor and the transient occlusion of the left main coronary artery (by the tumor), while a heart attack or sudden cardiac death may be due to embolisation of a portion of the tumor into a coronary artery.[2]
Gross Pathology
Image shown below is courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
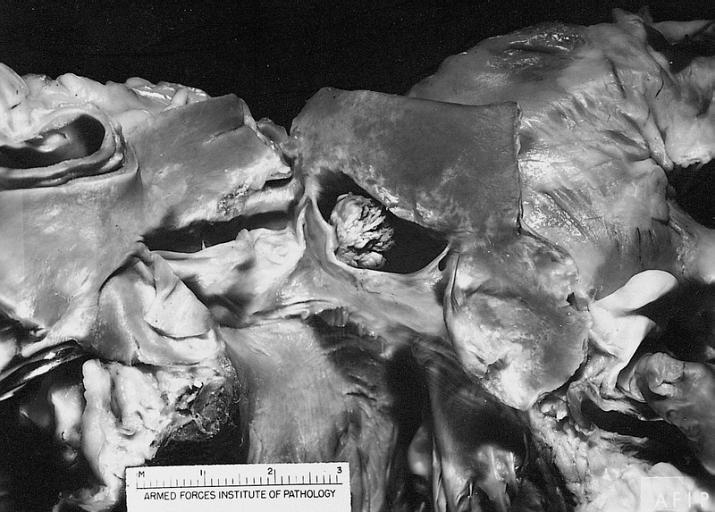
HEART: Metastatic Tumor: Gross very unusual large metastatic carcinoid in right atrium
-
Cardiac Myxoma A gelatinous tumor is attached by a narrow pedicle to the atrial septum. The myxoma has an irregular surface and nearly fills the left atrium.
-
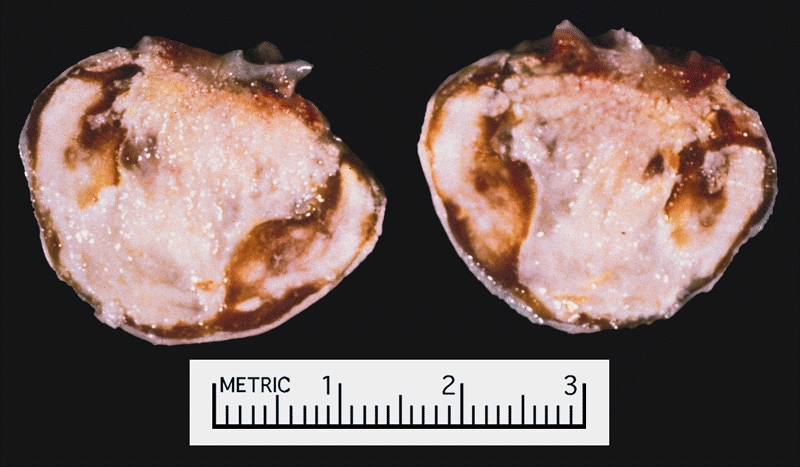
Cardiac Myxoma There was a calcified right atrial mass on the X ray of a 47-year-old man. Resection demonstrated a smooth-surfaced tumor. The gritty material seen microscopically on cut section was calcified and ossified myxoma.
-
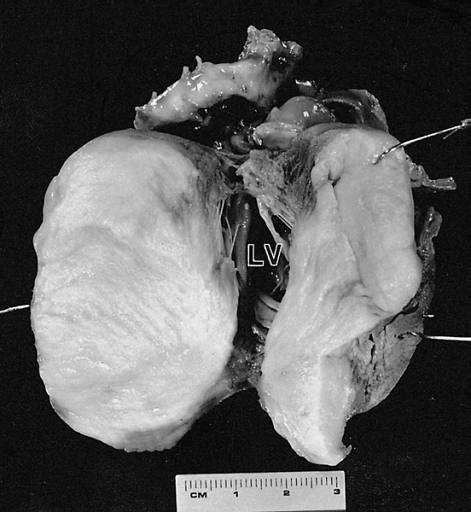
Cardiac Fibroma Cut surface of the tumor shown in figure 6-2. The left ventricular (LV) cavity is present behind the mass. The patient was a 4-month-old child who died suddenly without a previous medical history.
-
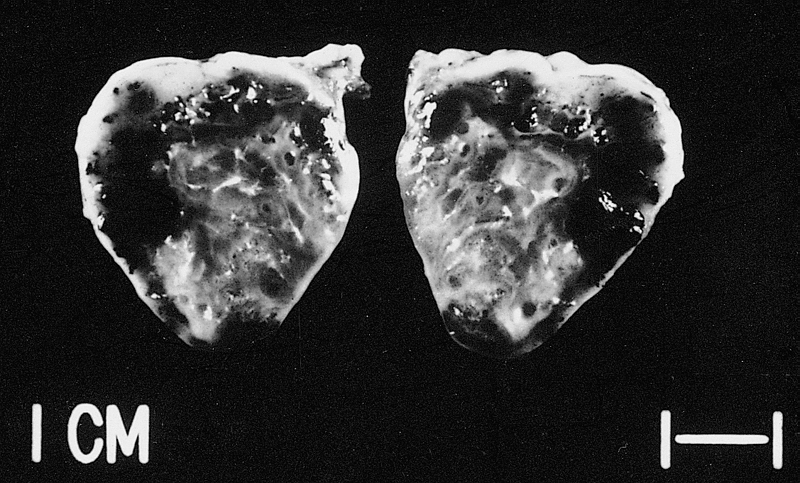
This tumor was resected from the right atrium of a 1-year-old boy with pericardial effusions. Note areas of hemorrhage and dilated vessels. The patient was well 49 months postoperatively.
-
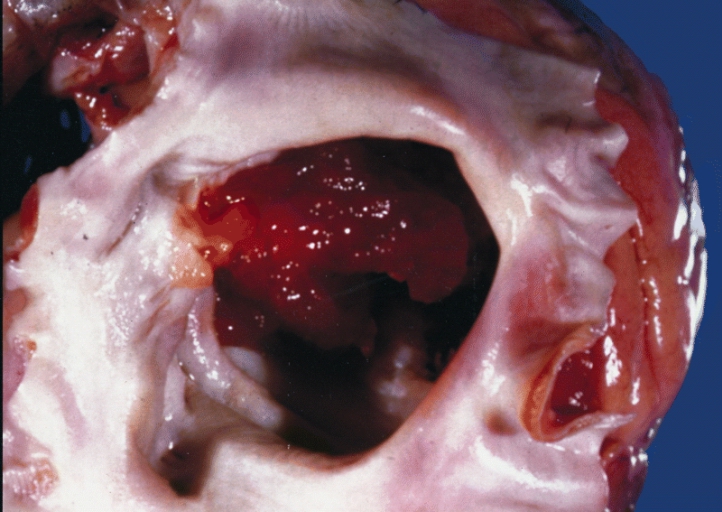
Papillary fibroelastomas are often on the arterial surface and may project into the coronary ostium, causing ostial occlusion. This tumor is in the noncoronary sinus.
References
- ↑ Matsumoto N, Sato Y, Kusama J, Matsuo S, Kinukawa N, Kunimasa T, Ichiyama I, Takahashi H, Kimura S, Orime Y, Saito S. (2007). "Multiple papillary fibroelastomas of the aortic valve: case report". Int J Cardiol. 122 (1): e1–3. PMID 17196273.
- ↑ Takada A, Saito K, Ro A, Tokudome S, Murai T. (2000). "Papillary fibroelastoma of the aortic valve: a sudden death case of coronary embolism with myocardial infarction". Forensic Sci Int. 113 (1–3): 209–14. PMID 10978627.