Betamethasone valerate (topical): Difference between revisions
Adeel Jamil (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Gerald Chi- (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|authorTag={{AJ}} | |authorTag={{AJ}} | ||
|genericName=Betamethasone valerate | |genericName=Betamethasone valerate | ||
|aOrAn= | |aOrAn=an | ||
|drugClass=adrenal glucocorticoid | |drugClass=[[adrenal|adrenal glucocorticoid]]and [[endocrinology|endocrine-metabolic agent]] | ||
|indicationType=treatment | |indicationType=treatment | ||
|indication= | |indication=the relief of [[inflammatory]] and [[pruritus|pruritic]] manifestations of [[dermatitis|corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses]] | ||
|adverseReactions=hypertension, skin atrophy, erythema, striae, folliculitis, vesicles in skin, pruritus of skin, | |adverseReactions=[[hypertension]], [[atrophy|skin atrophy]], [[erythema]], [[striae]], [[folliculitis]], [[vesicles|vesicles in skin]], [[pruritus|pruritus of skin]], [[skin|stinging of skin]], [[depression]], and [[euphoria]] | ||
|blackBoxWarningTitle=Warning Title | |blackBoxWarningTitle=Warning Title | ||
|blackBoxWarningBody=<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">Condition Name:</span></i> (Content) | |blackBoxWarningBody=<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">Condition Name:</span></i> (Content) | ||
|fdaLIADAdult=* Topical corticosteroids are indicated for the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses. | |fdaLIADAdult=* [[corticosteroids|Topical corticosteroids]] are indicated for the relief of the [[inflammatory]] and [[pruritus|pruritic]] manifestations of [[dermatitis|corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses]]. | ||
=====Dosing Information===== | =====Dosing Information===== | ||
* Apply a thin film of Betamethasone Valerate Cream or Ointment to the affected skin areas one to three times a day. Dosage once or twice a day is often effective. | * Apply a thin film of Betamethasone Valerate Cream or [[Ointment]] to the affected [[skin]] areas one to three times a day. Dosage once or twice a day is often effective. | ||
* Apply a few drops of Betamethasone Valerate [[Lotion]] to the affected area and [[massage]] lightly until it disappears. Apply twice daily, in the morning and at night. Dosage may be increased in stubborn cases. Following improvement, apply once daily. For the most effective and economical use, apply nozzle very close to affected area and gently squeeze bottle. | |||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Betamethasone valerate in adult patients. | |||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Betamethasone valerate in adult patients. | |||
|fdaLIADPed=There is limited information regarding <i>FDA-Labeled Use</i> of Betamethasone valerate in pediatric patients. | |||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Betamethasone valerate in pediatric patients. | |||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Betamethasone valerate in pediatric patients. | |||
|contraindications=* Topical corticosteroids are contraindicated in those patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the components of the preparation. | |contraindications=* Topical corticosteroids are contraindicated in those patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the components of the preparation. | ||
|warnings======PRECAUTIONS===== | |warnings======PRECAUTIONS===== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
* General: | * General: | ||
:* Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids has produced reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria in some patients. | :* Systemic absorption of [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] has produced reversible [[HPA axis|hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression]], manifestations of [[Cushing's syndrome]], [[hyperglycemia]], and [[glucosuria]] in some patients. | ||
:* Conditions which augment systemic absorption include the application of the more potent steroids, use over large surface areas, prolonged use, and the addition of occlusive dressings. | :* Conditions which augment systemic absorption include the application of the more [[steroids|potent steroids]], use over large surface areas, prolonged use, and the addition of occlusive dressings. | ||
:* Therefore, patients receiving a large dose of a potent topical steroid applied to a large surface area should be evaluated periodically for evidence of HPA axis suppression by using the urinary free cortisol and ACTH stimulation tests. If HPA axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or substitute to a less potent steroid. | :* Therefore, patients receiving a large dose of a [[corticosteroids|potent topical steroid]] applied to a large surface area should be evaluated periodically for evidence of [[HAP axis|HPA axis suppression]] by using the [[cortisol|urinary free cortisol]] and [[ACTH|ACTH stimulation tests]]. If [[HPA axis|HPA axis suppression]] is noted, an attempt should be made to [[withdraw]] the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or substitute to a less potent [[steroid]]. | ||
:* Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of the drug. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of steroid withdrawal may occur, requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids. | :* Recovery of [[HPA axis|HPA axis function]] is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of the drug. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of [[steroid|steroid withdrawal]] may occur, requiring [[corticosteroids|supplemental systemic corticosteroids]]. | ||
:* Pediatric patients may absorb proportionally larger amounts of topical corticosteroids and thus be more susceptible to systemic toxicity | :* Pediatric patients may absorb proportionally larger amounts of [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] and thus be more susceptible to systemic [[toxicity]]. | ||
:* If irritation develops, topical corticosteroids should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. | :* If [[irritation]] develops, [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. | ||
:* In the presence of dermatological | :* In the presence of [[dermatitis|dermatological infection]]s, the use of an appropriate [[antifungal]] or [[antibiotics|antibacterial agent]] should be instituted. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, the [[corticosteroid]] should be discontinued until the [[infection]] has been adequately controlled. | ||
|clinicalTrials=* The following local adverse reactions are reported infrequently with topical corticosteroids, but may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: burning, itching, irritation, dryness, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, maceration of the skin, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae and miliaria. | |clinicalTrials=* The following local adverse reactions are reported infrequently with [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]], but may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: [[burning]], [[itching]], [[irritation]], [[dryness]], [[folliculitis]], [[hypertrichosis]], [[acne|acneiform eruptions]], [[hypopigmentation]], [[perioral dermatitis]], [[allergic contact dermatitis]], [[maceration|maceration of the skin]], [[dermatitis|secondary infection]], [[atrophy|skin atrophy]], [[striae]] and [[miliaria]]. | ||
|postmarketing=( | |postmarketing=(There is limited information regarding <i>Postmarketing Experience</i> of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label.) | ||
|drugInteractions= | |drugInteractions=There is limited information regarding <i>Drug Interactions</i> of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label. | ||
|FDAPregCat=C | |||
|useInPregnancyFDA=====TeratogenicEffects===== | |||
* [[Corticosteroids]] are generally [[teratogenic]] in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. The more [[corticosteroids|potent corticosteroids]] have been shown to be [[teratogenic]] after [[dermis|dermal application]] in laboratory animals. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in [[pregnant]] women on [[teratogenic]] effects from topically applied [[corticosteroids]]. Therefore, [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] should be used during [[pregnancy]] only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Drugs of this class should not be used extensively on [[pregnant]] patients, in large amounts, or for prolonged periods of time. | |||
|useInPregnancyAUS=* '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | |||
| | There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Betamethasone valerate in women who are pregnant. | ||
| | |useInLaborDelivery=There is no FDA guidance on use of Betamethasone valerate during labor and delivery. | ||
|useInNursing=* It is not known whether topical administration of [[corticosteroids]] could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in [[breast milk]]. Systemically administered [[corticosteroids]] are secreted into [[breast milk]] in quantities not likely to have a deleterious effect on the [[infant]]. Nevertheless, caution should be exercised when [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] are administered to a [[nursing]] woman. | |||
|useInPed=* [[Pediatric]] patients may demonstrate greater susceptibility to [[HPA axis|topical corticosteroid-induced HPA axis suppression]] and [[Cushing's syndrome]] than mature patients because of a larger skin surface area to body weight ratio. | |||
* | * [[HPA axis|Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression]], [[Cushing's syndrome]], and [[intracranial hypertension]] have been reported in children receiving [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]]. Manifestations of [[adrenal|adrenal suppression]] in children include [[growth retardation|linear growth retardation]], delayed weight gain, [[cortisol|low plasma cortisol levels]], and absence of response to [[ACTH|ACTH stimulation]]. Manifestations of [[intracranial hypertension]] include [[fontanelles|bulging fontanelles]], [[headaches]], and [[papilledema|bilateral papilledema]]. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
* Administration of [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] to [[pediatric]] patients should be limited to the least amount compatible with an effective therapeutic regimen. Chronic [[corticosteroid]] therapy may interfere with the growth and development of children. | |||
|useInGeri=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate with respect to geriatric patients. | |||
* Administration of topical corticosteroids to pediatric patients should be limited to the least amount compatible with an effective therapeutic regimen. Chronic corticosteroid therapy may interfere with the growth and development of children. | |useInGender=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate with respect to specific gender populations. | ||
|useInGeri= | |useInRace=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate with respect to specific racial populations. | ||
|useInGender= | |useInRenalImpair=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate in patients with renal impairment. | ||
|useInRace= | |useInHepaticImpair=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate in patients with hepatic impairment. | ||
|useInRenalImpair= | |useInReproPotential=There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate in women of reproductive potentials and males. | ||
|useInHepaticImpair= | |useInImmunocomp=There is no FDA guidance one the use of Betamethasone valerate in patients who are immunocompromised. | ||
|useInReproPotential= | |||
|useInImmunocomp= | |||
|othersTitle=Others | |othersTitle=Others | ||
|administration=* Topical | |administration=* Topical | ||
|IVCompat= | |monitoring=There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label. | ||
|IVCompat=There is limited information regarding <i>IV Compatibility</i> of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label. | |||
|overdose=* Topically applied corticosteroids can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to produce systemic effects. | |overdose=* Topically applied corticosteroids can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to produce systemic effects. | ||
|drugBox={{Drugbox2 | |drugBox={{Drugbox2 | ||
| verifiedrevid = | | Watchedfields = changed | ||
| IUPAC_name = | | verifiedrevid = 459977512 | ||
| image = | | IUPAC_name = (8''S'',9''R'',10''S'',11''S'',13''S'',14''S'',16''S'',17''R'')-9-fluoro- 11,17-dihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13,16-trimethyl- 6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro- 3''H''-cyclopenta[''a'']phenanthren-3-one | ||
| | | image = Betamethasone.png | ||
| image2 = Betamethasone2.png | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | <!--Clinical data--> | ||
| tradename = | | tradename = Celestone | ||
| | | Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|betamethasone}} | ||
| | | pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | ||
| | | pregnancy_US = C | ||
| | | pregnancy_category = | ||
| legal_status = | | legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S4 / S8 --> | ||
| routes_of_administration = | | legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD --> | ||
| legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only --> | |||
| legal_status = Rx-only | |||
| routes_of_administration = Oral,Topical,IM | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | <!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | ||
| bioavailability = | | bioavailability = ? | ||
| metabolism = | | metabolism = [[hepatic]] [[CYP3A4]] | ||
| elimination_half-life = | | elimination_half-life = 36-54 hours | ||
| excretion = | | excretion = [[Renal]] (in urine) | ||
<!--Identifiers--> | <!--Identifiers--> | ||
| CAS_number_Ref = | | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | ||
| CAS_number = | | CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | ||
| ATC_prefix = | | CAS_number = 378-44-9 | ||
| ATC_suffix = | | ATC_prefix = A07 | ||
| | | ATC_suffix = EA04 | ||
| | | ATC_supplemental = {{ATC|C05|AA05}} {{ATC|D07|AC01}} {{ATC|H02|AB01}} {{ATC|R01|AD06}} {{ATC|R03|BA04}} {{ATC|S01|BA06}} {{ATC|S02|BA07}} {{ATC|S03|BA03}} | ||
| DrugBank_Ref = | | PubChem = 9782 | ||
| DrugBank = | | DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | ||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = | | DrugBank = DB00443 | ||
| ChemSpiderID = | | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| UNII_Ref = | | ChemSpiderID = 9399 | ||
| UNII = | | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | ||
| KEGG_Ref = | | UNII = 9842X06Q6M | ||
| KEGG = | | KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | ||
| ChEBI_Ref = | | KEGG = D00244 | ||
| ChEBI = | | ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | ||
| ChEMBL_Ref = | | ChEBI = 3077 | ||
| ChEMBL = | | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | ||
| ChEMBL = 632 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | <!--Chemical data--> | ||
| C= | H= | | | C=22 | H=29 | F=1 | O=5 | ||
| molecular_weight = | | molecular_weight = 392.461 | ||
| smiles = | | smiles = O=C(CO)[C@]3(O)[C@]2(C[C@H](O)[C@]4(F)[C@@]/1(\C(=C/C(=O)\C=C\1)CC[C@H]4[C@@H]2C[C@@H]3C)C)C | ||
| InChI = | | InChI = 1/C22H29FO5/c1-12-8-16-15-5-4-13-9-14(25)6-7-19(13,2)21(15,23)17(26)10-20(16,3)22(12,28)18(27)11-24/h6-7,9,12,15-17,24,26,28H,4-5,8,10-11H2,1-3H3/t12-,15-,16-,17-,19-,20-,21-,22-/m0/s1 | ||
| InChIKey = | | InChIKey = UREBDLICKHMUKA-DVTGEIKXBT | ||
| StdInChI_Ref = | | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| StdInChI = | | StdInChI = 1S/C22H29FO5/c1-12-8-16-15-5-4-13-9-14(25)6-7-19(13,2)21(15,23)17(26)10-20(16,3)22(12,28)18(27)11-24/h6-7,9,12,15-17,24,26,28H,4-5,8,10-11H2,1-3H3/t12-,15-,16-,17-,19-,20-,21-,22-/m0/s1 | ||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = | | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| StdInChIKey = | | StdInChIKey = UREBDLICKHMUKA-DVTGEIKXSA-N | ||
}} | }} | ||
|mechAction=* | |mechAction=* [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] share [[anti-inflammatory]], [[antipruritic]] and [[vasoconstrictive]] actions. | ||
* The mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity of the topical corticosteroids is unclear. Various laboratory methods, including vasoconstrictor assays, are used to compare and predict potencies and/or clinical efficacies of the topical corticosteroids. There is some evidence to suggest that a recognizable correlation exists between vasoconstrictor potency and therapeutic efficacy in man. | * The mechanism of [[anti-inflammatory]] activity of the [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] is unclear. Various laboratory methods, including vasoconstrictor assays, are used to compare and predict potencies and/or clinical efficacies of the [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]]. There is some evidence to suggest that a recognizable correlation exists between [[vasoconstrictor]] [[potency]] and [[efficacy|therapeutic efficacy]] in man. | ||
|structure=* Betamethasone Valerate Cream, Ointment and Lotion contain betamethasone valerate USP, a synthetic adrenocorticosteroid for dermatologic use. Betamethasone, an analog of prednisolone, has a high degree of glucocorticoid activity and a slight degree of mineralocorticoid activity. | |structure=* Betamethasone Valerate Cream, [[Ointment]] and [[Lotion]] contain betamethasone valerate USP, a [[cortisol|synthetic adrenocorticosteroid]] for [[dermatologic]] use. Betamethasone, an analog of [[prednisolone]], has a high degree of [[glucocorticoid]] activity and a slight degree of [[mineralocorticoid]] activity. | ||
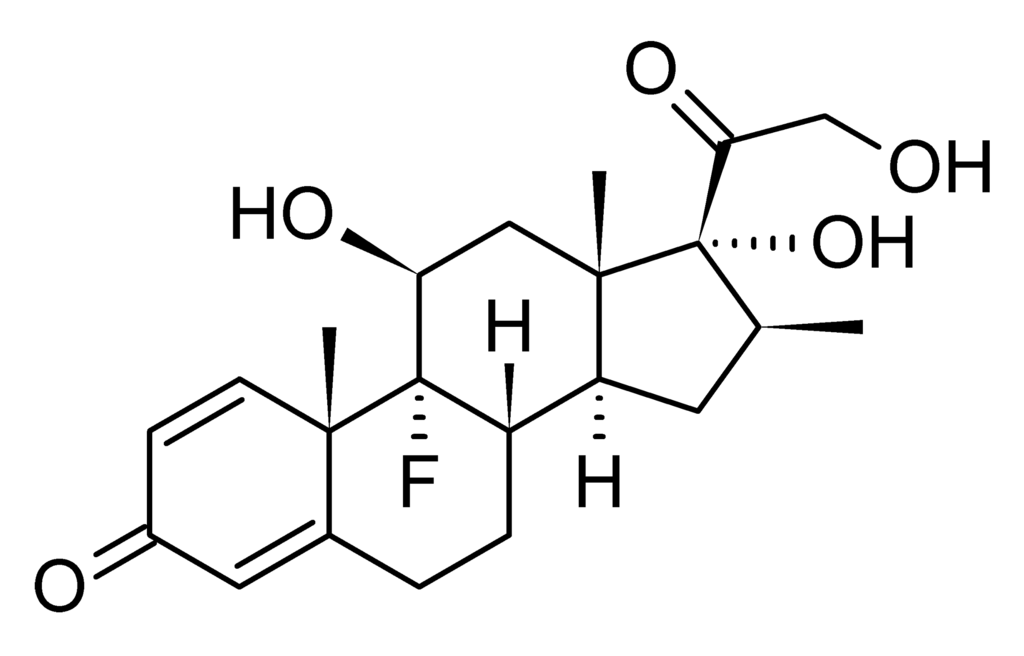
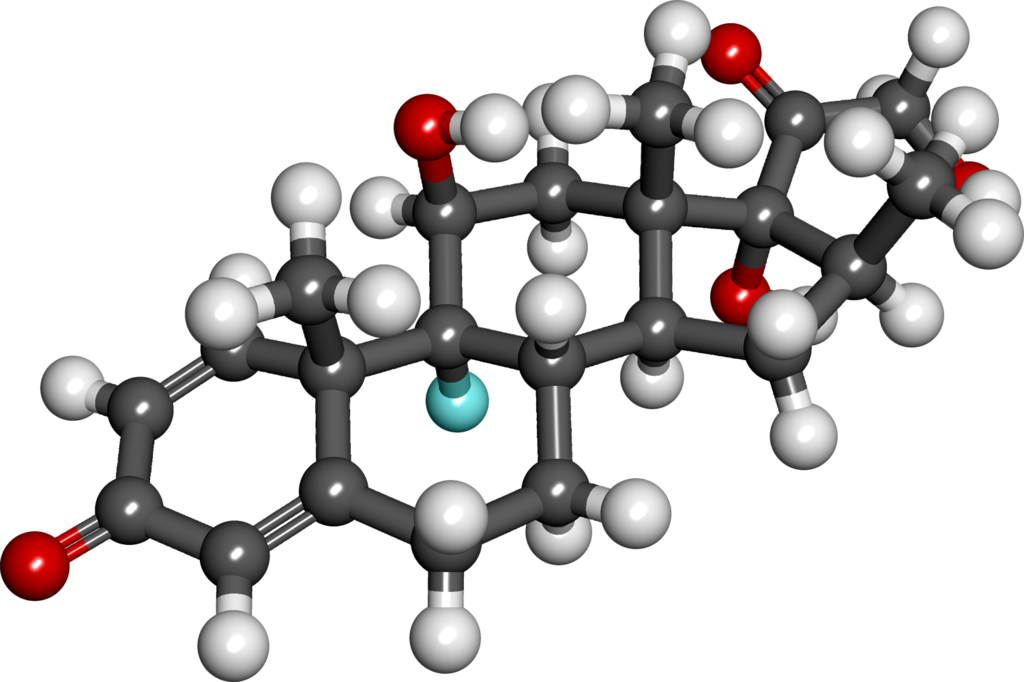
* Betamethasone valerate is a white to practically white odorless crystalline powder practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetone and chloroform, soluble in alcohol, and slightly soluble in benzene and ether. Chemically, it is 9-fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16β-methylpregna-1, 4-diene-3,20-dione 17-valerate. The structural formula is: | * Betamethasone valerate is a white to practically white odorless crystalline powder practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetone and chloroform, soluble in alcohol, and slightly soluble in benzene and ether. Chemically, it is 9-fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16β-methylpregna-1, 4-diene-3,20-dione 17-valerate. The structural formula is: | ||
[[File:Betamethasone valerate structure.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
|PD=* The following tests may be helpful in evaluating the HPA axis suppression: | |PD=* The following tests may be helpful in evaluating the HPA axis suppression: | ||
:* Urinary free cortisol test | :* [[Cortisol|Urinary free cortisol test]] | ||
:* ACTH stimulation test | :* [[ACTH stimulation test]] | ||
|PK=* The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors including the vehicle, the integrity of the epidermal barrier, and the use of occlusive dressings. | |PK=* The extent of [[percutaneous]] absorption of [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] is determined by many factors including the vehicle, the integrity of the [[skin|epidermal barrier]], and the use of occlusive dressings. | ||
* Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin increase percutaneous absorption. Occlusive dressings substantially increase the percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids. Thus, occlusive dressings may be a valuable therapeutic adjunct for treatment of resistant dermatoses. | * [[corticosteroids|Topical corticosteroids]]can be absorbed from normal intact [[skin]]. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the [[skin]] increase [[percutaneous]] absorption. Occlusive dressings substantially increase the [[percutaneous]] absorption of[[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]]. Thus, occlusive dressings may be a valuable [[therapeutic]] adjunct for [[dermatitis|treatment of resistant dermatoses]]. | ||
* Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are bound to plasma proteins in varying degrees. Corticosteroids are metabolized primarily in the liver and are then excreted by the kidneys. Some of the topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile. | * Once absorbed through the [[skin]], [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] are handled through [[pharmacokinetic]] pathways similar to systemically administered [[corticosteroids]]. [[Corticosteroids]] are bound to [[plasma proteins]] in varying degrees. [[Corticosteroids]] are metabolized primarily in the [[liver]] and are then excreted by the [[kidneys]]. Some of the [[corticosteroids|topical corticosteroids]] and their metabolites are also excreted into the [[bile]]. | ||
|nonClinToxic= | |nonClinToxic=There is limited information regarding <i>Nonclinical Toxicology</i> of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label. | ||
|clinicalStudies======Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility===== | |clinicalStudies======Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility===== | ||
* Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential or the effect on fertility of topical corticosteroids. | * Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the [[carcinogenic]] potential or the effect on [[fertility]] of topical [[corticosteroids]]. | ||
* Studies to determine mutagenicity with [[prednisolone]] and hydrocortisone have revealed negative results. | |||
|howSupplied=[[File:Betamethasone valerate how supplied table.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
E. FOUGERA & CO. | |||
A division of | A division of | ||
Fougera | Fougera | ||
PHARMACEUTICALS INC. | PHARMACEUTICALS INC. | ||
Melville, NY 11747 | Melville, NY 11747 | ||
|storage=* Store at room temperature 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F). | |storage=* Store at room temperature 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F). | ||
|fdaPatientInfo=* Patients using topical corticosteroids should receive the following information and instructions: | |fdaPatientInfo=* Patients using topical corticosteroids should receive the following information and instructions: | ||
:* This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes. | :* This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the [[eyes]]. | ||
:* Patients should be advised not to use this medication for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed. | :* Patients should be advised not to use this medication for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed. | ||
:* The treated skin area should not be bandaged or otherwise covered or wrapped as to be occlusive unless directed by the physician. | :* The treated [[skin]] area should not be [[bandage|bandaged]] or otherwise covered or wrapped as to be occlusive unless directed by the physician. | ||
:* Patients should report any signs of local adverse reactions especially under occlusive dressing. | :* Patients should report any signs of local adverse reactions especially under occlusive dressing. | ||
:* Parents of pediatric patients should be advised not to use tight-fitting diapers or plastic pants on a child being treated in the diaper area, as these garments may constitute occlusive dressings. | :* Parents of [[pediatric]] patients should be advised not to use tight-fitting diapers or plastic pants on a child being treated in the diaper area, as these garments may constitute occlusive dressings. | ||
|alcohol=Alcohol-Betamethasone valerate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |alcohol=Alcohol-Betamethasone valerate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | ||
|brandNames=* Celestone® | |||
|nlmPatientInfo=(Link to patient information page) | |nlmPatientInfo=(Link to patient information page) | ||
|drugShortage=Drug Shortage | |drugShortage=Drug Shortage | ||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 01.png | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 02.png | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 03.png | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 04.png | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 05.png | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 06.png | |||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 06:37, 18 May 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Adeel Jamil, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Betamethasone valerate (topical) is an adrenal glucocorticoidand endocrine-metabolic agent that is FDA approved for the treatment of the relief of inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses. Common adverse reactions include hypertension, skin atrophy, erythema, striae, folliculitis, vesicles in skin, pruritus of skin, stinging of skin, depression, and euphoria.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Topical corticosteroids are indicated for the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses.
Dosing Information
- Apply a thin film of Betamethasone Valerate Cream or Ointment to the affected skin areas one to three times a day. Dosage once or twice a day is often effective.
- Apply a few drops of Betamethasone Valerate Lotion to the affected area and massage lightly until it disappears. Apply twice daily, in the morning and at night. Dosage may be increased in stubborn cases. Following improvement, apply once daily. For the most effective and economical use, apply nozzle very close to affected area and gently squeeze bottle.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Betamethasone valerate in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Betamethasone valerate in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Betamethasone valerate in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Betamethasone valerate in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Betamethasone valerate in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Topical corticosteroids are contraindicated in those patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the components of the preparation.
Warnings
PRECAUTIONS
- General:
- Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids has produced reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria in some patients.
- Conditions which augment systemic absorption include the application of the more potent steroids, use over large surface areas, prolonged use, and the addition of occlusive dressings.
- Therefore, patients receiving a large dose of a potent topical steroid applied to a large surface area should be evaluated periodically for evidence of HPA axis suppression by using the urinary free cortisol and ACTH stimulation tests. If HPA axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or substitute to a less potent steroid.
- Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of the drug. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of steroid withdrawal may occur, requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids.
- Pediatric patients may absorb proportionally larger amounts of topical corticosteroids and thus be more susceptible to systemic toxicity.
- If irritation develops, topical corticosteroids should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
- In the presence of dermatological infections, the use of an appropriate antifungal or antibacterial agent should be instituted. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, the corticosteroid should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The following local adverse reactions are reported infrequently with topical corticosteroids, but may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: burning, itching, irritation, dryness, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, maceration of the skin, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae and miliaria.
Postmarketing Experience
(There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label.)
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Drug Interactions of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
TeratogenicEffects=
- Corticosteroids are generally teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. The more potent corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic after dermal application in laboratory animals. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women on teratogenic effects from topically applied corticosteroids. Therefore, topical corticosteroids should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Drugs of this class should not be used extensively on pregnant patients, in large amounts, or for prolonged periods of time.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Betamethasone valerate in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Betamethasone valerate during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in breast milk. Systemically administered corticosteroids are secreted into breast milk in quantities not likely to have a deleterious effect on the infant. Nevertheless, caution should be exercised when topical corticosteroids are administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Pediatric patients may demonstrate greater susceptibility to topical corticosteroid-induced HPA axis suppression and Cushing's syndrome than mature patients because of a larger skin surface area to body weight ratio.
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, Cushing's syndrome, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in children receiving topical corticosteroids. Manifestations of adrenal suppression in children include linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, low plasma cortisol levels, and absence of response to ACTH stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include bulging fontanelles, headaches, and bilateral papilledema.
- Administration of topical corticosteroids to pediatric patients should be limited to the least amount compatible with an effective therapeutic regimen. Chronic corticosteroid therapy may interfere with the growth and development of children.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betamethasone valerate in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Betamethasone valerate in patients who are immunocompromised.
Others
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Topical
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label.
Overdosage
- Topically applied corticosteroids can be absorbed in sufficient amounts to produce systemic effects.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- topical corticosteroids share anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and vasoconstrictive actions.
- The mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity of the topical corticosteroids is unclear. Various laboratory methods, including vasoconstrictor assays, are used to compare and predict potencies and/or clinical efficacies of the topical corticosteroids. There is some evidence to suggest that a recognizable correlation exists between vasoconstrictor potency and therapeutic efficacy in man.
Structure
- Betamethasone Valerate Cream, Ointment and Lotion contain betamethasone valerate USP, a synthetic adrenocorticosteroid for dermatologic use. Betamethasone, an analog of prednisolone, has a high degree of glucocorticoid activity and a slight degree of mineralocorticoid activity.
- Betamethasone valerate is a white to practically white odorless crystalline powder practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetone and chloroform, soluble in alcohol, and slightly soluble in benzene and ether. Chemically, it is 9-fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-16β-methylpregna-1, 4-diene-3,20-dione 17-valerate. The structural formula is:

Pharmacodynamics
- The following tests may be helpful in evaluating the HPA axis suppression:
Pharmacokinetics
- The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors including the vehicle, the integrity of the epidermal barrier, and the use of occlusive dressings.
- Topical corticosteroidscan be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin increase percutaneous absorption. Occlusive dressings substantially increase the percutaneous absorption oftopical corticosteroids. Thus, occlusive dressings may be a valuable therapeutic adjunct for treatment of resistant dermatoses.
- Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are bound to plasma proteins in varying degrees. Corticosteroids are metabolized primarily in the liver and are then excreted by the kidneys. Some of the topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Betamethasone valerate in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
- Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential or the effect on fertility of topical corticosteroids.
- Studies to determine mutagenicity with prednisolone and hydrocortisone have revealed negative results.
How Supplied

E. FOUGERA & CO. A division of Fougera PHARMACEUTICALS INC. Melville, NY 11747
Storage
- Store at room temperature 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F).
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Betamethasone valerate (topical) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Betamethasone valerate (topical) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Patients using topical corticosteroids should receive the following information and instructions:
- This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes.
- Patients should be advised not to use this medication for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed.
- Patients should report any signs of local adverse reactions especially under occlusive dressing.
- Parents of pediatric patients should be advised not to use tight-fitting diapers or plastic pants on a child being treated in the diaper area, as these garments may constitute occlusive dressings.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Betamethasone valerate interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Celestone®
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Betamethasone valerate (topical) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Betamethasone valerate (topical) |Label Name=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 01.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Betamethasone valerate (topical) |Label Name=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 02.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Betamethasone valerate (topical) |Label Name=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 03.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Betamethasone valerate (topical) |Label Name=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 04.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Betamethasone valerate (topical) |Label Name=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 05.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Betamethasone valerate (topical) |Label Name=Betamethasone valerate drug lable 06.png
}}