ACC AHA guideline on the primary prevention of hypercholestrolemia
Template:Hypercholesterolemia Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Primary Prevention in Adult ≥21 Years With LDL–C ≥190 mg/dL
- Adults ≥21 years of age with primary, severe elevations of LDL–C (≥190 mg/dL) have a high lifetime risk for ASCVD events and require even more substantial reductions in their LDL–C levels and intensive management of other risk factors to reduce their ASCVD event. It is reasonable to use high-intensity statin therapy to achieve at least a 50% reduction. In addition to a maximally tolerated dose of statin, nonstatin cholesterol-lowering medications are often needed to lower LDL–C to acceptable levels in these individuals.
- Because the hypercholesterolemia in these high-risk individuals is often genetically determined, family screening is especially important in this group to identify additional family members who would benefit from assessment and early treatment.
- Secondary causes of severe elevations of LDL–C ≥190 mg/dL and triglycerides ≥500 mg/dL often contribute to the magnitude of the hyperlipidemia and should be evaluated and treated appropriately. The most frequently encountered secondary conditions were excessive alcohol intake, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and overt albuminuria.
| Secondary Cause | Elevated LDL–C | Elevated Triglycerides |
| Diet | Saturated or trans fats, weight gain, anorexia | Weight gain, very low-fat diets, high intake of refined carbohydrates, excessive alcohol intake |
| Drugs | Diuretics, cyclosporine, glucocorticoids, amiodarone | Oral estrogens, glucocorticoids, bile acid sequestrants, protease inhibitors, retinoic acid, anabolic steroids, sirolimus, raloxifene, tamoxifen, beta blockers (not carvedilol), thiazides |
| Diseases | Biliary obstruction, nephrotic syndrome | Nephrotic syndrome, chronic renal failure, lipodystrophies |
| Disorders and altered states of metabolism | Hypothyroidism, obesity, pregnancy* | Diabetes (poorly controlled), hypothyroidism, obesity; pregnancy* |
* Cholesterol and triglycerides rise progressively throughout pregnancy (81); treatment with statins, niacin, and ezetimibe are contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
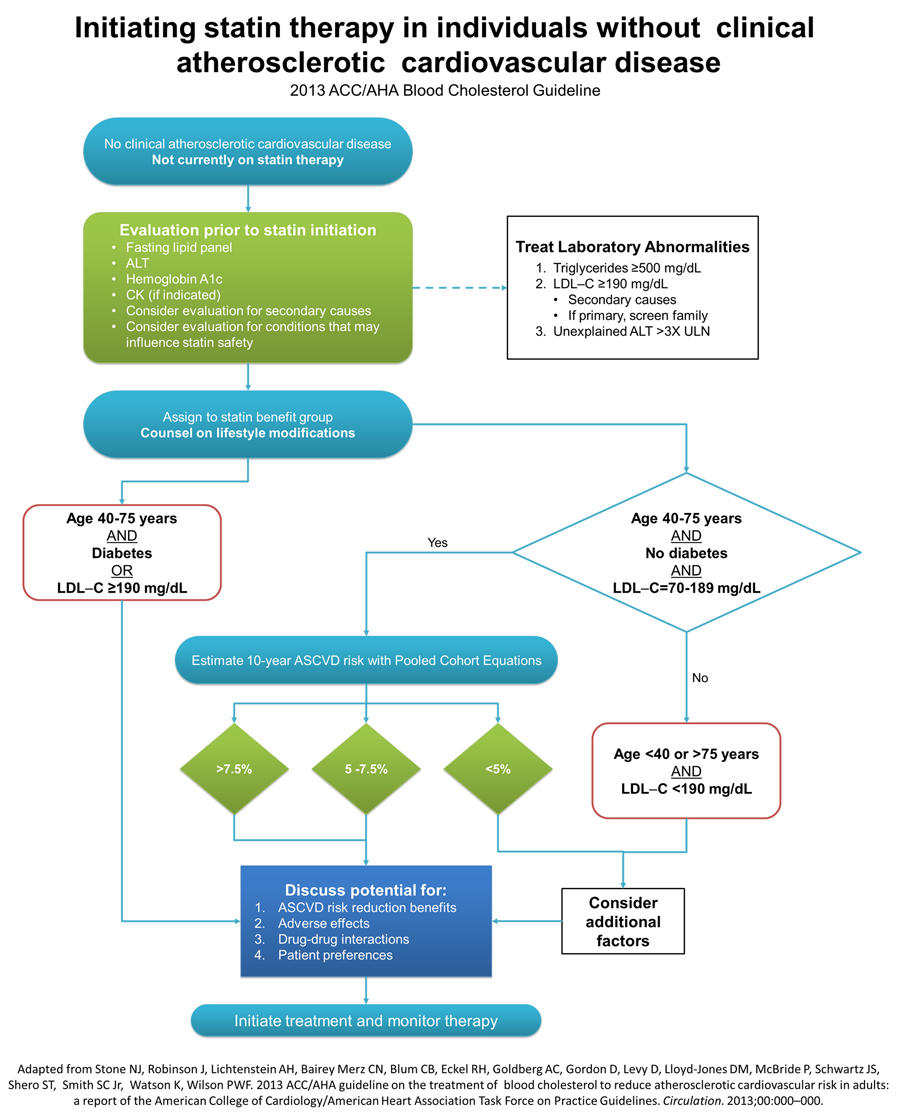
Initiating and Management of Statin Therapy in Individuals Without Clinical ASCVD
Clinical ASCVD is defined as acute coronary syndromes or history of MI, stable or unstable angina, coronary revascularization, stroke, or TIA presumed to be of atherosclerotic origin, and peripheral arterial disease or revascularization.