Pneumomediastinum chest x ray
|
Pneumomediastinum Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pneumomediastinum chest x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pneumomediastinum chest x ray |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pneumomediastinum chest x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
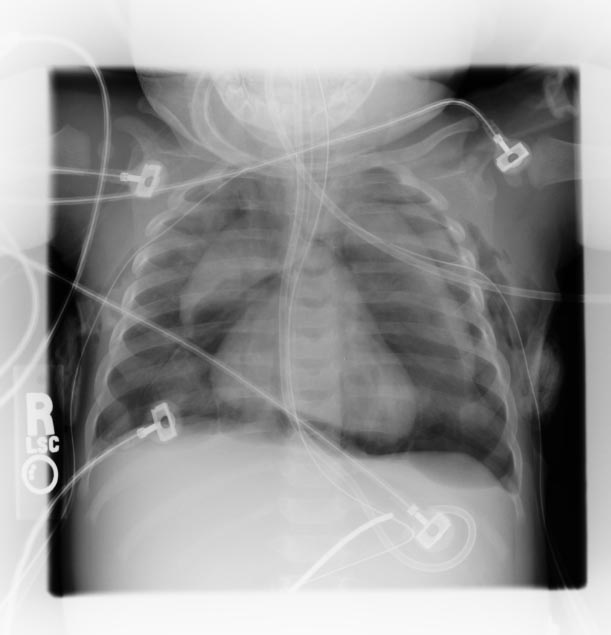
The diagnosis can be confirmed via chest X-ray showing a radiolucent outline around the heart and mediastinum or via CT scanning of the thorax. The presence of air within the connective tissue planes of the mediastinum can be seen on chest X-ray.
Chest X Ray
Radiological findings of pneumomediastinum are following:
- Subcutaneous emphysema.
- Naclerio V sign: Seen in pneumomediastinum occurring often secondary to an oesophageal rupture but it is not entirely specific to that condition.
- Gas anterior to pericardium: pneumopericardium.
- Gas around the pulmonary artery and main branches: ring around artery sign.
- Gas outlining major aortic branches: tubular artery sign.
- Gas outlining bronchial wall: double bronchial wall sign.
- Continuous diaphragm sign: due to gas trapped posterior to the pericardium.
- Gas between parietal pleura and diaphragm: extrapleural sign.
- Gas in pulmonary ligament.
Pediatric pneumomediastinum has different appearances:
- Elevated thymus: thymic wing sign/Spinnaker snail sign(thymus being outlined by air).
- Gas crossing the superior mediastinum: haystack sign (the heart appears like a haystack in a Monet painting).
-
Pneumomediastinum: Spinnaker sail sign (Image courtesy of RadsWiki)
-
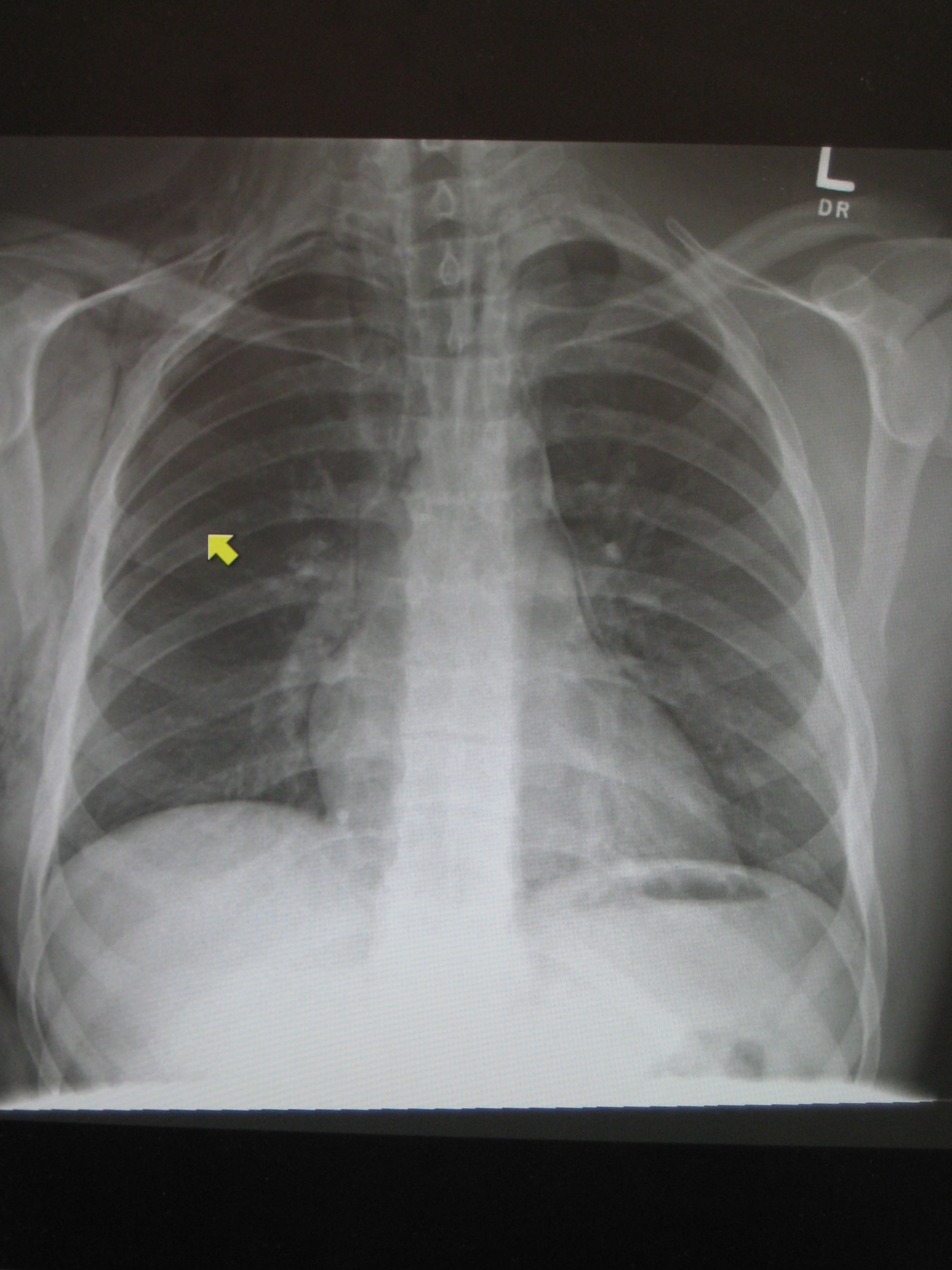
Pneumomediastinum and right sided pneumothorax post first rib fracture in a mountain biking accident.