Pancoast tumor chest x ray
|
Pancoast tumor Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pancoast tumor chest x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pancoast tumor chest x ray |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pancoast tumor chest x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mazia Fatima, MBBS [2]
Overveiw
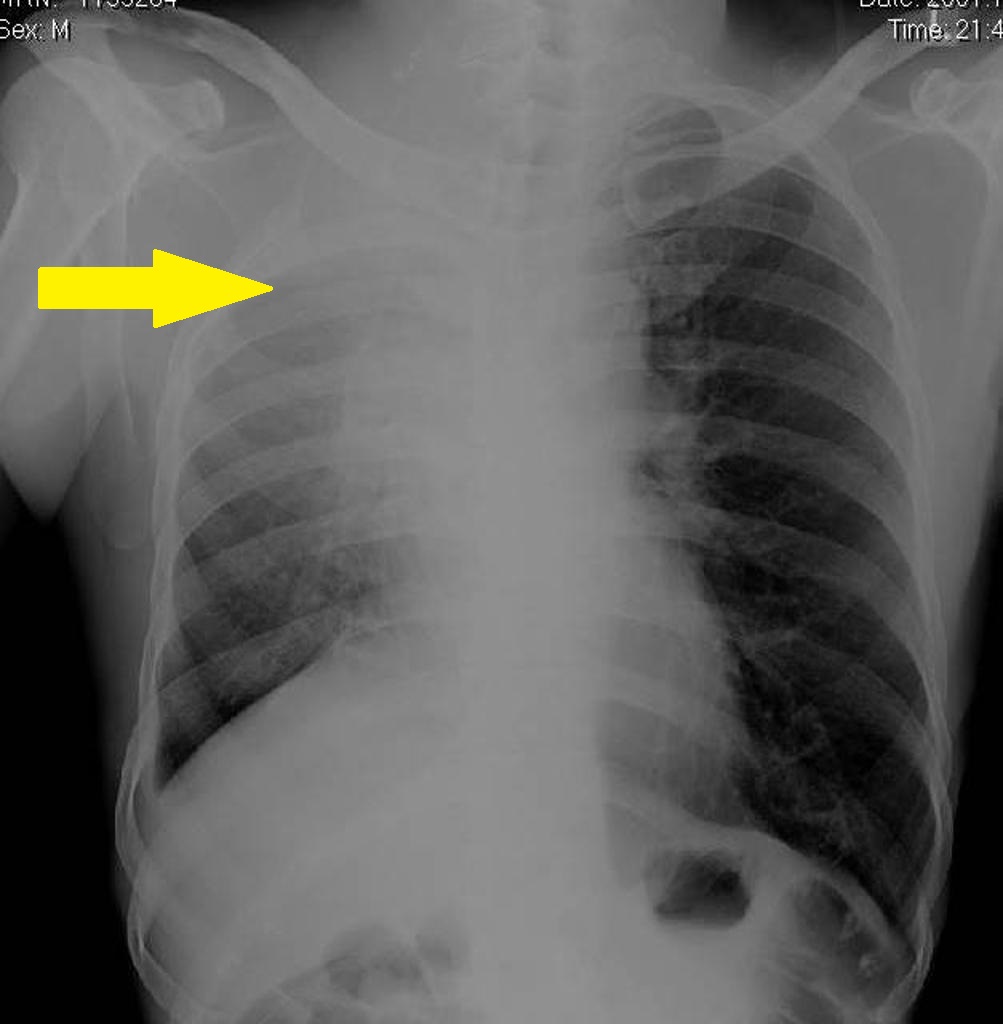
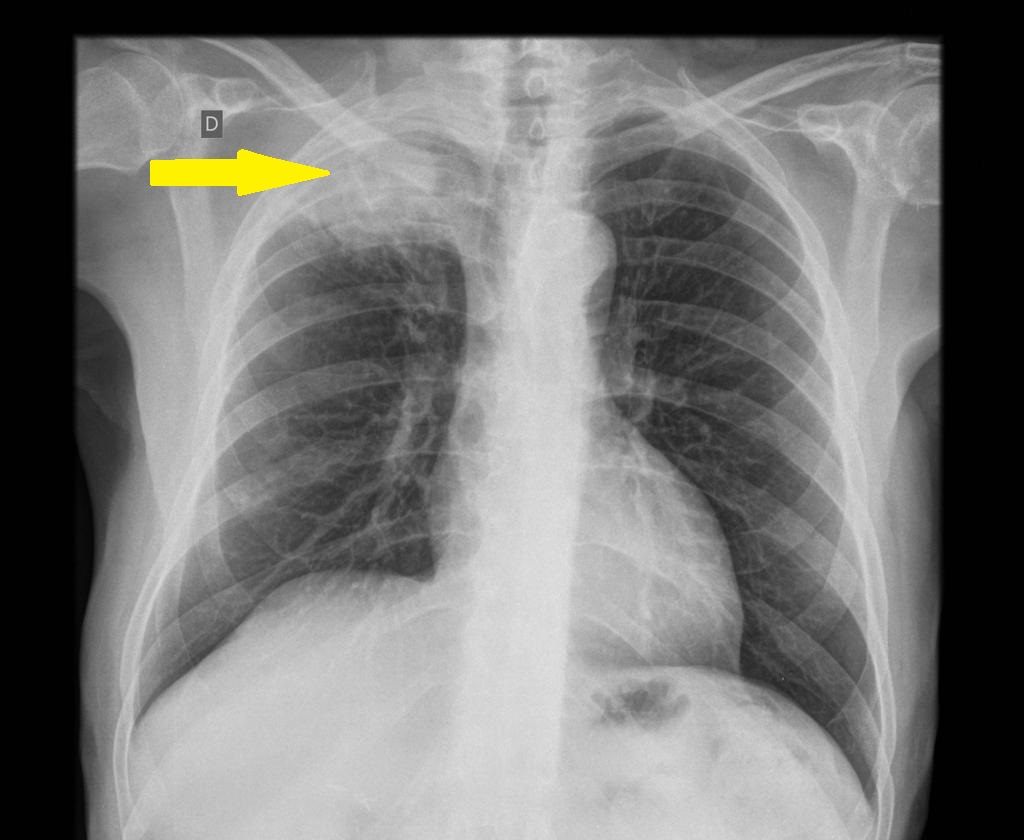
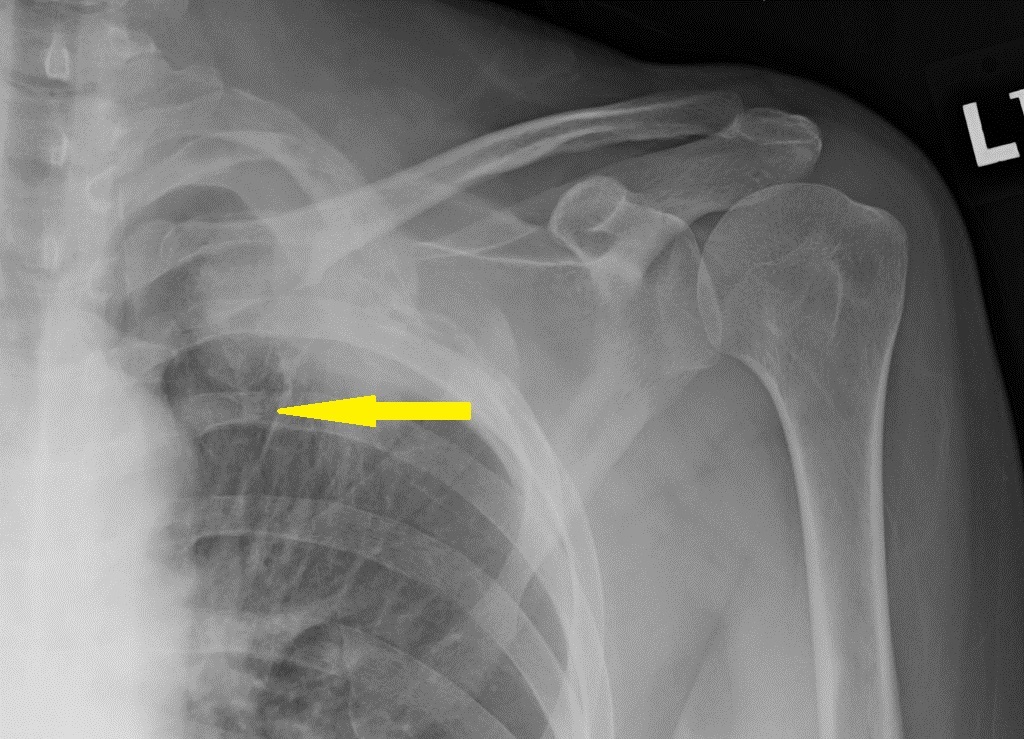
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of Pancoast tumor. Lordotic view on x-ray is helpful in visualizing Pancoast tumor because of its characteristic location in the apical portion of the lung. Findings on an x-ray suggestive of Pancoast tumor include opacity at the apex of the lung or in the superior sulcus area, the spread of the tumor can result in rib invasion that is observed as a bone destruction of posterior ribs, vertebral body infiltration, enlargement of the mediastinum.
Chest X-ray
- An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of Pancoast tumor.[1][2][3]
- Lordotic view on x-ray is helpful in visualizing Pancoast tumor because of its characteristic location in the apical portion of the lung.
- Findings on an x-ray suggestive of Pancoast tumor include:
- Opacity at the apex of the lung or in the superior sulcus area.
- Spread of the tumor can result in rib invasion that is observed as bone destruction of posterior ribs.
- Vertebral body infiltration
- Enlargement of the mediastinum.
References
- ↑ Bruzzi JF, Komaki R, Walsh GL, Truong MT, Gladish GW, Munden RF, Erasmus JJ (2008). "Imaging of non-small cell lung cancer of the superior sulcus: part 1: anatomy, clinical manifestations, and management". Radiographics. 28 (2): 551–60, quiz 620. doi:10.1148/rg.282075709. PMID 18349457.
- ↑ Foroulis CN, Zarogoulidis P, Darwiche K, Katsikogiannis N, Machairiotis N, Karapantzos I, Tsakiridis K, Huang H, Zarogoulidis K (September 2013). "Superior sulcus (Pancoast) tumors: current evidence on diagnosis and radical treatment". J Thorac Dis. 5 Suppl 4: S342–58. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.04.08. PMC 3791502. PMID 24102007.
- ↑ Marulli G, Battistella L, Mammana M, Calabrese F, Rea F (June 2016). "Superior sulcus tumors (Pancoast tumors)". Ann Transl Med. 4 (12): 239. doi:10.21037/atm.2016.06.16. PMC 4930518. PMID 27429965.