Polio causes
|
Polio Microchapters |
|
Causes |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Polio causes On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Polio causes |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: João André Alves Silva, M.D. [2]
Overview
Polio is a highly infectious disease caused by Poliovirus that invades the nervous system. Poliovirus are small (27–30 nm), nonenveloped viruses with capsids enclosing a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome about 7,500 nucleotides long. Person-to-person spread of poliovirus via the fecal-oral route is the most important route of transmission, although the oral-oral route may account for some cases.
Taxonomy
Viruses; ssRNA viruses; ssRNA positive-strand viruses, no DNA stage; Picornavirales; Picornaviridae; Enterovirus; Poliovirus[1]
Biology
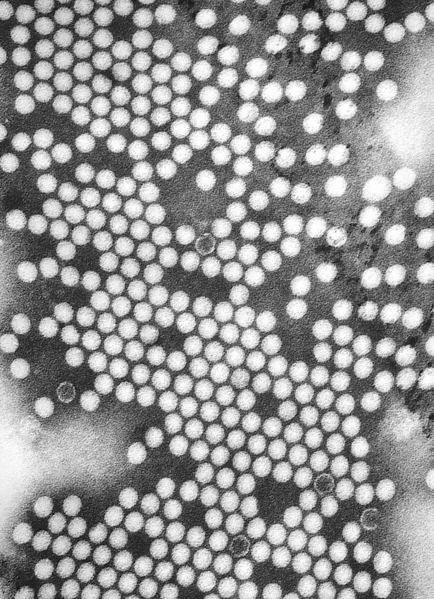 |
Poliovirus is a member of the genus enterovirus, family Picornaviridae. Enteroviruses are small, nonenveloped, positive stranded RNA viruses. Other members of the family include: Rhinovirus, Hepatovirus, Cardiovirus and Apthovirus. Poliovirus is a transient inhabitant of the gastrointestinal tract, stable at an acid pH.[3][4] Enteroviruses in general do not cause disease, or are responsible for mild symptoms. Disease syndromes resulting from viral spread to other secondary regions are rare. Despite rare, these syndromes may lead to severe disease complications, seldom with fatal outcomes.
There are three poliovirus serotype (P1, P2, and P3) that replicate efficiently in the gastrointestinal tract. There is minimal heterotypic immunity between the three serotypes. That is, immunity to one serotype does not produce significant immunity to the other serotypes. The poliovirus is rapidly inactivated by heat, formaldehyde, chlorine, and ultraviolet light.[3]
The characteristics of poliovirus make it a good model for viral study, specifically: high viral titers, stable capsid and ease of purification, along with a low bio-safety requirement.[4]
Structure
The genome of poliovirus consists of a single positive-sense RNA molecule, of approximately 7740 nucleotides. At the 5' end of the RNA molecule are coded 88 nucleotides that interact to form a clover leaf structure, which is involved in the replication process.[4] At the 3' end of the genome is encoded a poly Adenine sequence, which varies about 60 adenylate residues in length.[4] The translation of the genome is initiated by the attachment of the host cell's ribosomes to the often called internal ribosomal entry site (IRES). This is a specific RNA segment in the 5' end region of the RNA (not translated), where the host cell's translational ribosomes first attach, in order to initiate viral genome replication. The understanding of this mechanism has led to the establishment of a new mechanism of protein synthesis in eukaryotes.[4]
Tropism
Natural Reservoir
Humans are the only known reservoir of poliovirus, which is transmitted most frequently by persons with inapparent infections. There is no asymptomatic carrier state except in immune deficient persons.
References
- ↑ "Polyomavirus".
- ↑ "http://phil.cdc.gov/phil/details.asp". External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Polyomavirus" (PDF).
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Mueller S, Wimmer E, Cello J (2005). "Poliovirus and poliomyelitis: a tale of guts, brains, and an accidental event". Virus Res. 111 (2): 175–93. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2005.04.008. PMID 15885840.