Lead poisoning differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ {{Lead poisoning}} {{CMG}}; {{AE}} ==Overview== [Disease name] must be differentiated from other diseases that cause [clinical feature 1], [clinical feature 2], an...") |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
[Disease name] must be differentiated from [[differential dx1], [differential dx2], and [differential dx3]. | [Disease name] must be differentiated from [[differential dx1], [differential dx2], and [differential dx3]. | ||
==Diagnosis== | |||
===Symptoms=== | |||
The symptoms of chronic lead poisoning include neurological problems, such as | |||
reduced cognitive abilities | |||
*[[Nausea]] | |||
*[[Abdominal pain]] | |||
*[[Irritability]] | |||
*[[Insomnia]] | |||
*[[Mettalic taste]] | |||
*excess [[lethargy]] | |||
*[[Hyperactivity]] | |||
*[[Chest pain]] | |||
* [[headache]] | |||
* [[seizure]] | |||
* [[coma]] | |||
There are also associated gastrointestinal problems, such as | |||
* [[constipation]] | |||
* [[diarrhea]] | |||
* [[vomiting]] | |||
* [[poor appetite]] | |||
* [[weight loss]] | |||
Other associated effects are | |||
* [[anemia]] | |||
* kidney problems | |||
* reproductive problems | |||
===Physical examination=== | |||
* [[Burton's line]] | |||
* [[Peripheral neuropathy]] | |||
* [[Wrist drop]] | |||
* [[learning disability]] | |||
===Laboratory tests=== | |||
* Basophilic stippling of red blood cells | |||
* [[Iron deficiency anemia]] (microcytosis and hypochromia) | |||
* Elevated serum lead levels | |||
* K-fluorescent X-ray metering can measure bone-lead. | |||
Shown below is an image depicting basophilic stippling in a blood smear of a patient with lead poisoning.<br> | |||
[[File:Lead poisoning - blood film.jpg|Basophilic stippling in a blood smear of a patient with lead poisoning]] | |||
==Differentiating X from other Diseases== | ==Differentiating X from other Diseases== | ||
Revision as of 20:21, 29 May 2018
|
Lead poisoning Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Lead poisoning differential diagnosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Lead poisoning differential diagnosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Lead poisoning differential diagnosis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:
Overview
[Disease name] must be differentiated from other diseases that cause [clinical feature 1], [clinical feature 2], and [clinical feature 3], such as [differential dx1], [differential dx2], and [differential dx3].
OR
[Disease name] must be differentiated from [[differential dx1], [differential dx2], and [differential dx3].
Diagnosis
Symptoms
The symptoms of chronic lead poisoning include neurological problems, such as reduced cognitive abilities
- excess lethargy
There are also associated gastrointestinal problems, such as
Other associated effects are
- kidney problems
- reproductive problems
Physical examination
Laboratory tests
- Basophilic stippling of red blood cells
- Iron deficiency anemia (microcytosis and hypochromia)
- Elevated serum lead levels
- K-fluorescent X-ray metering can measure bone-lead.
Shown below is an image depicting basophilic stippling in a blood smear of a patient with lead poisoning.
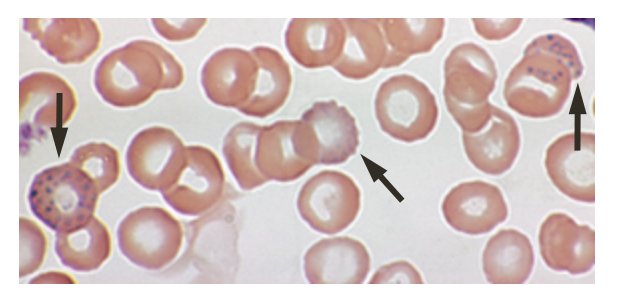
Differentiating X from other Diseases
- [Disease name] must be differentiated from other diseases that cause [clinical feature 1], [clinical feature 2], and [clinical feature 3], such as [differential dx1], [differential dx2], and [differential dx3].
- [Disease name] must be differentiated from [differential dx1], [differential dx2], and [differential dx3].
- As [disease name] manifests in a variety of clinical forms, differentiation must be established in accordance with the particular subtype. [Subtype name 1] must be differentiated from other diseases that cause [clinical feature 1], such as [differential dx1] and [differential dx2]. In contrast, [subtype name 2] must be differentiated from other diseases that cause [clinical feature 2], such as [differential dx3] and [differential dx4].
Preferred Table
| Diseases | Clinical manifestations | Para-clinical findings | Gold standard | Additional findings | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Physical examination | ||||||||||||||
| Lab Findings | Imaging | Histopathology | |||||||||||||
| Symptom 1 | Symptom 2 | Symptom 3 | Physical exam 1 | Physical exam 2 | Physical exam 3 | Lab 1 | Lab 2 | Lab 3 | Imaging 1 | Imaging 2 | Imaging 3 | ||||
| Differential Diagnosis 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Differential Diagnosis 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Differential Diagnosis 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Diseases | Symptom 1 | Symptom 2 | Symptom 3 | Physical exam 1 | Physical exam 2 | Physical exam 3 | Lab 1 | Lab 2 | Lab 3 | Imaging 1 | Imaging 2 | Imaging 3 | Histopathology | Gold standard | Additional findings |
| Differential Diagnosis 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Differential Diagnosis 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Differential Diagnosis 6 | |||||||||||||||