Icatibant: Difference between revisions
Created page with "{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag= {{VP}} <!--Overview--> |genericName= |aOrAn= a |drugClass= bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist |indication= acute attacks..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 169: | Line 169: | ||
*Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. | *Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. | ||
T1 | |||
*The third trial was active-controlled and was comprised of 35 patients who received FIRAZYR 30 mg and 38 patients who received the comparator. Adverse reactions for FIRAZYR were similar in nature and frequency to those reported in Table 1. | |||
*In all three controlled trials, patients were eligible for treatment of subsequent attacks in an open-label extension. Patients were treated with FIRAZYR 30 mg and could receive up to 3 doses of FIRAZYR 30 mg administered at least 6 hours apart for each attack. A total of 225 patients were treated with 1,076 doses of 30 mg FIRAZYR for 987 attacks of acute HAE. Adverse reactions similar in nature and frequency were observed to those seen in the controlled phase of the trials. Other adverse reactions reported included rash, nausea, and headache in patients exposed to FIRAZYR. | |||
*The safety of self-administration was evaluated in a separate, open-label trial in 56 patients with HAE. In this trial, the safety profile of FIRAZYR in patients who self-administered FIRAZYR was similar in nature and frequency to that of patients whose therapy was administered by healthcare professionals. | |||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | <!--Postmarketing Experience--> | ||
| Line 237: | Line 181: | ||
|postmarketing= | |postmarketing= | ||
*Similar adverse reactions have been observed in postmarketing use as compared to the clinical trials. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. | |||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | <!--Drug Interactions--> | ||
| Line 295: | Line 187: | ||
|drugInteractions= | |drugInteractions= | ||
* | * ACE Inhibitors | ||
:* | :*FIRAZYR is a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist and thereby has the potential to have a pharmacodynamic interaction with ACE inhibitors where FIRAZYR may attenuate the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. Clinical trials to date have excluded subjects taking ACE inhibitors. | ||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | <!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
|useInPregnancyFDA= | |useInPregnancyFDA= | ||
* '''Pregnancy Category''' | * '''Pregnancy Category C''' | ||
*There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Icatibant was not teratogenic in rats or rabbits; however, it caused delayed parturition, fetal death, and pre-implantation loss in rats and premature birth, abortion, fetal death, and pre-implantation loss in rabbits. FIRAZYR should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. | |||
*Delayed parturition and fetal death in rats occurred at 0.5 and 2-fold, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (on an AUC basis at maternal doses of 1 and 3 mg/kg, respectively). Increased pre-implantation loss in rats occurred at 7-fold the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal dose of 10 mg/kg). In rabbits, premature birth and abortion rates increased at a dose that was less than 1/40th the MRHD (on a mg/m2 basis at a maternal dose of 0.1 mg/kg). Studies in rabbits also indicated that pre-implantation loss and increased fetal deaths occurred at 13-fold greater than the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal dose of 10 mg/kg). | |||
*Nonteratogenic effects: Impairment of pup air-righting reflex and decreased pup hair growth in rats occurred at 7-fold the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal dose of 10 mg/kg). | |||
|useInPregnancyAUS= | |useInPregnancyAUS= | ||
| Line 309: | Line 207: | ||
|useInLaborDelivery= | |useInLaborDelivery= | ||
There | |||
*There are no human studies that have investigated the effects of FIRAZYR on preterm labor or labor at term; however, animal studies showed that icatibant causes delayed parturition and associated fetal death in rats and premature birth and abortion in rabbits. Delayed parturition occurred in rats at 0.5-fold times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal dose of 1 mg/kg). | |||
|useInNursing= | |useInNursing= | ||
*Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when FIRAZYR is administered to a nursing woman. Icatibant is excreted into the milk of lactating rats. | |||
|useInPed= | |useInPed= | ||
*Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 18 years have not been established. | |||
|useInGeri= | |useInGeri= | ||
*Clinical studies of FIRAZYR did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Elderly patients are likely to have increased systemic exposure to FIRAZYR compared to younger (18-45 years) patients. Since other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in efficacy and safety between elderly and younger patients, no dose adjustment is recommended. | |||
|useInGender= | |useInGender= | ||
| Line 327: | Line 229: | ||
|useInRenalImpair= | |useInRenalImpair= | ||
*Although a formal renal impairment study has not been conducted, 10 of 37 patients treated with FIRAZYR had [[hepatorenal syndrome]] with [[glomerular filtration rate]] (GFR) below 60 mL/min. FIRAZYR is cleared non-renally and hence it is not expected to show any change in systemic exposure in patients with impaired renal function. No dose adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment. | |||
|useInHepaticImpair= | |useInHepaticImpair= | ||
*FIRAZYR was studied in patients with mild to moderate (Child Pugh scores of 5 to 8) hepatic impairment. No change in systemic exposure is noted in these patient populations. No dose adjustment is required in patients with hepatic impairment. | |||
|useInReproPotential= | |useInReproPotential= | ||
| Line 341: | Line 245: | ||
|administration= | |administration= | ||
* Intravenous | * Intravenous | ||
| Line 349: | Line 251: | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | <!--IV Compatibility--> | ||
| Line 364: | Line 264: | ||
===Acute Overdose=== | ===Acute Overdose=== | ||
* In a clinical study evaluating a 90 mg dose (30 mg in each of 3 subcutaneous sites), the adverse event profile was similar to that seen with 30 mg administered in a single subcutaneous site. | |||
* | *In another clinical study, a dose of 3.2 mg/kg administered intravenously (approximately 8 times the therapeutic dose for HAE) caused erythema, itching and hypotension in healthy subjects. No therapeutic intervention was necessary. | ||
===Chronic Overdose=== | ===Chronic Overdose=== | ||
| Line 382: | Line 278: | ||
|drugBox= | |drugBox= | ||
{{Drugbox2 | |||
| Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| Watchedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 461936569 | |||
| IUPAC_name = (2S)-2-<nowiki>[[</nowiki>(3aS,7aS)-1-[2-[(2S)-2-<nowiki>[[</nowiki>(2S)-<BR/>2-<nowiki>[[</nowiki>2-<nowiki>[[</nowiki>(4R)-1-[1-[2-<nowiki>[[</nowiki>(2R)-2-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)<BR/>pentanoyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]pyrrolidine-<BR/>2-carbonyl]-4-hydroxypyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-<BR/>3-thiophen-2-ylpropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]<BR/>3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline-3-carbonyl]<BR/>2,3,3a,4,5,6,7,7a-octahydroindole-2-carbonyl]amino]-<BR/>5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoic acid | |||
| image = Icatibant00.png | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| tradename = Firazyr | |||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|international|icatibant}} | |||
| licence_EU = Firazyr | |||
| licence_US = Icatibant | |||
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | |||
| pregnancy_US = C | |||
| pregnancy_category = | |||
| legal_AU = <!-- S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9 or Unscheduled--> | |||
| legal_CA = <!-- Schedule I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII --> | |||
| legal_UK = <!-- GSL, P, POM, CD, or Class A, B, C --> | |||
| legal_US = Rx-only | |||
| legal_status = | |||
| routes_of_administration = subcutaneous | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = | |||
| protein_bound = | |||
| metabolism = | |||
| elimination_half-life = | |||
| excretion = | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|changed|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 130308-48-4 | |||
| ATC_prefix = B06 | |||
| ATC_suffix = AC02 | |||
| ATC_supplemental = | |||
| PubChem = 71364 | |||
| IUPHAR_ligand = 667 | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank = DB06196 | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 16736634 | |||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | |||
| ChEBI = 68556 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = 7PG89G35Q7 | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL = 1743581 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| C=59 | H=89 | N=19 | O=13 | S=1 | |||
| molecular_weight = 1304.52 g/mol | |||
| smiles = C1CC[C@H]2[C@@H](C1)CC(N2C(=O)C3CC4=CC=CC=C4CN3C(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CC5=CC=CS5)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C6C[C@H](CN6C(=O)C7CCCN7C(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)[C@@H](CCCN=C(N)N)N)O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)O | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C59H89N19O13S/c60-37(14-5-19-67-57(61)62)48(82)72-38(15-6-20-68-58(63)64)52(86)75-22-8-18-43(75)54(88)77-30-35(80)26-44(77)50(84)70-28-47(81)71-40(27-36-13-9-23-92-36)49(83)74-41(31-79)53(87)76-29-34-12-2-1-10-32(34)24-46(76)55(89)78-42-17-4-3-11-33(42)25-45(78)51(85)73-39(56(90)91)16-7-21-69-59(65)66/h1-2,9-10,12-13,23,33,35,37-46,79-80H,3-8,11,14-22,24-31,60H2,(H,70,84)(H,71,81)(H,72,82)(H,73,85)(H,74,83)(H,90,91)(H4,61,62,67)(H4,63,64,68)(H4,65,66,69)/t33-,35+,37+,38-,39-,40-,41-,42-,43-,44-,45?,46+/m0/s1 | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey = QURWXBZNHXJZBE-OVZQYVDUSA-N | |||
}} | |||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | <!--Mechanism of Action--> | ||
| Line 388: | Line 340: | ||
|mechAction= | |mechAction= | ||
* | * Icatibant is a competitive antagonist selective for the bradykinin B2 receptor, with an affinity similar to bradykinin. Hereditary angioedema is caused by an absence or dysfunction of C1-esterase-inhibitor, a key regulator of the Factor XII/kallikrein proteolytic cascade that leads to bradykinin production. Bradykinin is a vasodilator which is thought to be responsible for the characteristic HAE symptoms of localized swelling, inflammation, and pain. Icatibant inhibits bradykinin from binding the B2 receptor and thereby treats the clinical symptoms of an acute, episodic attack of HAE. | ||
<!--Structure--> | <!--Structure--> | ||
| Line 394: | Line 346: | ||
|structure= | |structure= | ||
* | * FIRAZYR (icatibant) is a synthetic decapeptide with five non-proteinogenic amino acids. The chemical structure of icatibant acetate is presented in Figure 1. | ||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | : [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
*Chemical name: D-Arginyl-L-arginyl-L-prolyl-L[(4R)-4-hydroxyprolyl]-glycyl-L[3-(2-thienyl)alanyl]-L-seryl-D-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-3-ylcarbonyl)-L[(3aS,7aS)-octahydroindol-2-ylcarbonyl]-L-arginine, acetate salt | |||
*FIRAZYR is provided as a sterile, isotonic, and buffered solution of icatibant acetate in a single-use, prefilled syringe for subcutaneous administration. Each mL of the solution contains 10 mg of icatibant (free base). Each prefilled syringe delivers 3 mL of solution equivalent to a 30 mg icatibant dose. The solution is clear and colorless. | |||
*The solution also contains sodium chloride, glacial acetic acid, sodium hydroxide and water for injection with a pH of approximately 5.5. The solution does not contain preservatives. | |||
*Pharmacological class: Icatibant is a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist. | |||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | <!--Pharmacodynamics--> | ||
| Line 402: | Line 362: | ||
|PD= | |PD= | ||
*Following bradykinin challenge, intravenous administration of FIRAZYR caused dose and time-dependent inhibition of development of bradykinin-induced hypotension, vasodilation, and reflex tachycardia in healthy young subjects. FIRAZYR intravenous doses of 0.4 and 0.8 mg/kg infused over 4 hours inhibited response to bradykinin challenge for 6 to 8 hours following completion of the infusion. Based on exposure-response analysis, a subcutaneous dose of 30 mg FIRAZYR is predicted to be effective against bradykinin challenge for at least 6 hours. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. | |||
*The effect of FIRAZYR 30 and 90 mg following a single subcutaneous injection on QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized, placebo-, and active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) four-period crossover thorough QT study in 72 healthy subjects. In a study with demonstrated ability to detect small effects, the upper bound of the one-sided 95% confidence interval for the largest placebo adjusted, baseline-corrected QTc based on individual correction method (QTcI) was below 10 ms, the threshold for regulatory concern. The dose of 90 mg is adequate to represent the high exposure clinical scenario. | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | <!--Pharmacokinetics--> | ||
Revision as of 20:18, 12 February 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Icatibant is a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adults 18 years of age and older. Common adverse reactions include pyrexia, transaminase increase, dizziness, and rash.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Hereditary Angioedema
- The recommended dose of FIRAZYR is 30 mg administered by subcutaneous (SC) injection in the abdominal area. Additional doses may be administered at intervals of at least 6 hours if response is inadequate or if symptoms recur. No more than 3 doses may be administered in any 24 hour period.
- FIRAZYR should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The drug solution should be clear and colorless. Do not administer if the product contains particulates or is discolored.
- Attach the provided 25 gauge needle to the syringe hub and screw on securely. Do not use a different needle. Disinfect the injection site and administer FIRAZYR by subcutaneous injection over at least 30 seconds.
- Patients may self-administer FIRAZYR upon recognition of symptoms of an HAE attack after training under the guidance of a healthcare professional [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Icatibant in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Icatibant in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Icatibant in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Icatibant in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Icatibant in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- None.
Warnings
Precautions
- Laryngeal Attacks
- Given the potential for airway obstruction during acute laryngeal HAE attacks, patients should be advised to seek medical attention in an appropriate healthcare facility immediately in addition to treatment with FIRAZYR.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
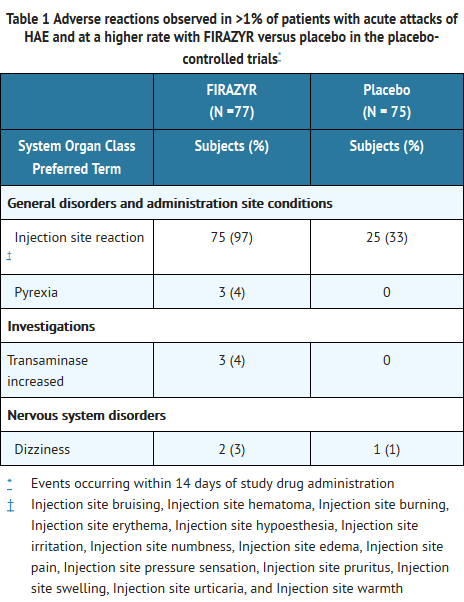
- The safety of icatibant was evaluated in three controlled trials that included 223 patients who received FIRAZYR 30 mg (n=113), placebo (n=75), or comparator (n=38). The mean age at study entry was 38 years (range 18 to 83 years), 64% were female, and 95% were white. The data described below represent adverse reactions observed from the two placebo-controlled trials, consisting of 77 patients who received FIRAZYR at a dose of 30 mg SC, and 75 who received placebo.
- The most frequently reported adverse reactions (occurring in greater than 1% of patients and at a higher rate with FIRAZYR versus placebo) are shown in Table 1.
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
T1
- The third trial was active-controlled and was comprised of 35 patients who received FIRAZYR 30 mg and 38 patients who received the comparator. Adverse reactions for FIRAZYR were similar in nature and frequency to those reported in Table 1.
- In all three controlled trials, patients were eligible for treatment of subsequent attacks in an open-label extension. Patients were treated with FIRAZYR 30 mg and could receive up to 3 doses of FIRAZYR 30 mg administered at least 6 hours apart for each attack. A total of 225 patients were treated with 1,076 doses of 30 mg FIRAZYR for 987 attacks of acute HAE. Adverse reactions similar in nature and frequency were observed to those seen in the controlled phase of the trials. Other adverse reactions reported included rash, nausea, and headache in patients exposed to FIRAZYR.
- The safety of self-administration was evaluated in a separate, open-label trial in 56 patients with HAE. In this trial, the safety profile of FIRAZYR in patients who self-administered FIRAZYR was similar in nature and frequency to that of patients whose therapy was administered by healthcare professionals.
Postmarketing Experience
- Similar adverse reactions have been observed in postmarketing use as compared to the clinical trials. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Drug Interactions
- ACE Inhibitors
- FIRAZYR is a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist and thereby has the potential to have a pharmacodynamic interaction with ACE inhibitors where FIRAZYR may attenuate the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. Clinical trials to date have excluded subjects taking ACE inhibitors.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Icatibant was not teratogenic in rats or rabbits; however, it caused delayed parturition, fetal death, and pre-implantation loss in rats and premature birth, abortion, fetal death, and pre-implantation loss in rabbits. FIRAZYR should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- Delayed parturition and fetal death in rats occurred at 0.5 and 2-fold, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (on an AUC basis at maternal doses of 1 and 3 mg/kg, respectively). Increased pre-implantation loss in rats occurred at 7-fold the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal dose of 10 mg/kg). In rabbits, premature birth and abortion rates increased at a dose that was less than 1/40th the MRHD (on a mg/m2 basis at a maternal dose of 0.1 mg/kg). Studies in rabbits also indicated that pre-implantation loss and increased fetal deaths occurred at 13-fold greater than the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal dose of 10 mg/kg).
- Nonteratogenic effects: Impairment of pup air-righting reflex and decreased pup hair growth in rats occurred at 7-fold the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal dose of 10 mg/kg).
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Icatibant in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
- There are no human studies that have investigated the effects of FIRAZYR on preterm labor or labor at term; however, animal studies showed that icatibant causes delayed parturition and associated fetal death in rats and premature birth and abortion in rabbits. Delayed parturition occurred in rats at 0.5-fold times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal dose of 1 mg/kg).
Nursing Mothers
- Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when FIRAZYR is administered to a nursing woman. Icatibant is excreted into the milk of lactating rats.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 18 years have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of FIRAZYR did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Elderly patients are likely to have increased systemic exposure to FIRAZYR compared to younger (18-45 years) patients. Since other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in efficacy and safety between elderly and younger patients, no dose adjustment is recommended.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Icatibant with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Icatibant with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
- Although a formal renal impairment study has not been conducted, 10 of 37 patients treated with FIRAZYR had hepatorenal syndrome with glomerular filtration rate (GFR) below 60 mL/min. FIRAZYR is cleared non-renally and hence it is not expected to show any change in systemic exposure in patients with impaired renal function. No dose adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
- FIRAZYR was studied in patients with mild to moderate (Child Pugh scores of 5 to 8) hepatic impairment. No change in systemic exposure is noted in these patient populations. No dose adjustment is required in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Icatibant in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Icatibant in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Icatibant in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Icatibant in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
- In a clinical study evaluating a 90 mg dose (30 mg in each of 3 subcutaneous sites), the adverse event profile was similar to that seen with 30 mg administered in a single subcutaneous site.
- In another clinical study, a dose of 3.2 mg/kg administered intravenously (approximately 8 times the therapeutic dose for HAE) caused erythema, itching and hypotension in healthy subjects. No therapeutic intervention was necessary.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Icatibant in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- Icatibant is a competitive antagonist selective for the bradykinin B2 receptor, with an affinity similar to bradykinin. Hereditary angioedema is caused by an absence or dysfunction of C1-esterase-inhibitor, a key regulator of the Factor XII/kallikrein proteolytic cascade that leads to bradykinin production. Bradykinin is a vasodilator which is thought to be responsible for the characteristic HAE symptoms of localized swelling, inflammation, and pain. Icatibant inhibits bradykinin from binding the B2 receptor and thereby treats the clinical symptoms of an acute, episodic attack of HAE.
Structure
- FIRAZYR (icatibant) is a synthetic decapeptide with five non-proteinogenic amino acids. The chemical structure of icatibant acetate is presented in Figure 1.
- Chemical name: D-Arginyl-L-arginyl-L-prolyl-L[(4R)-4-hydroxyprolyl]-glycyl-L[3-(2-thienyl)alanyl]-L-seryl-D-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-3-ylcarbonyl)-L[(3aS,7aS)-octahydroindol-2-ylcarbonyl]-L-arginine, acetate salt
- FIRAZYR is provided as a sterile, isotonic, and buffered solution of icatibant acetate in a single-use, prefilled syringe for subcutaneous administration. Each mL of the solution contains 10 mg of icatibant (free base). Each prefilled syringe delivers 3 mL of solution equivalent to a 30 mg icatibant dose. The solution is clear and colorless.
- The solution also contains sodium chloride, glacial acetic acid, sodium hydroxide and water for injection with a pH of approximately 5.5. The solution does not contain preservatives.
- Pharmacological class: Icatibant is a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist.
Pharmacodynamics
- Following bradykinin challenge, intravenous administration of FIRAZYR caused dose and time-dependent inhibition of development of bradykinin-induced hypotension, vasodilation, and reflex tachycardia in healthy young subjects. FIRAZYR intravenous doses of 0.4 and 0.8 mg/kg infused over 4 hours inhibited response to bradykinin challenge for 6 to 8 hours following completion of the infusion. Based on exposure-response analysis, a subcutaneous dose of 30 mg FIRAZYR is predicted to be effective against bradykinin challenge for at least 6 hours. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
- The effect of FIRAZYR 30 and 90 mg following a single subcutaneous injection on QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized, placebo-, and active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) four-period crossover thorough QT study in 72 healthy subjects. In a study with demonstrated ability to detect small effects, the upper bound of the one-sided 95% confidence interval for the largest placebo adjusted, baseline-corrected QTc based on individual correction method (QTcI) was below 10 ms, the threshold for regulatory concern. The dose of 90 mg is adequate to represent the high exposure clinical scenario.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Icatibant in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Icatibant in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Icatibant in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Icatibant Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Icatibant |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Icatibant |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Icatibant in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Icatibant interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Icatibant |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Icatibant |Label Name=Icatibant11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Icatibant |Label Name=Icatibant11.png
}}