Endotracheal tube
|
WikiDoc Resources for Endotracheal tube |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Endotracheal tube Most cited articles on Endotracheal tube |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Endotracheal tube |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Cochrane Collaboration on Endotracheal tube |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Endotracheal tube at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Endotracheal tube Clinical Trials on Endotracheal tube at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Endotracheal tube NICE Guidance on Endotracheal tube
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Endotracheal tube Discussion groups on Endotracheal tube Patient Handouts on Endotracheal tube Directions to Hospitals Treating Endotracheal tube Risk calculators and risk factors for Endotracheal tube
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Endotracheal tube |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
An endotracheal tube (also called an ET tube or ETT) is used in anaesthesia, intensive care and emergency medicine for airway management and mechanical ventilation. The tube is inserted into a patient's trachea in order to ensure that the airway is not closed off and that air is able to reach the lungs. The endotracheal tube is regarded as the most reliable available method for protecting a patient's airway.
Inventor
David S. Sheridan was the inventor of the modern "disposable" plastic endotracheal tube now used routinely in surgery. Previous to his invention, red rubber tubes were used, then sterilized, and re-used which often led to a high risk of infection. Mr Sheridan is credited with saving thousands of lives.
He also held more than 50 medical instrument patents. Mr Sheridan died April 29 2004 in Argyle, New York at the age of 95.
Intubation
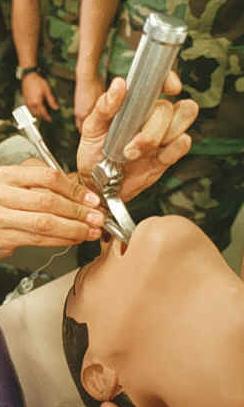
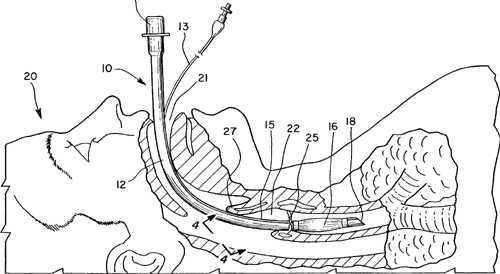
The process of inserting an ETT is called intubation. Intubation usually requires general anaesthesia and muscle relaxation but can be achieved in the awake patient with local anaesthesia or in an emergency without any anaesthesia, although this is extremely uncomfortable and generally avoided in other circumstances.
It is usually performed by visualising the larynx by means of a hand-held laryngoscope that has a variety of curved and straight blades, with a light source. Intubation can also be performed "blind" or with the use of the attendant's fingers (this is called digital intubation).
Intubation aids: A stylet can be used inside the endotracheal tube. The malleable metal stylet is a bendable piece of metal inserted into the ETT as to make the tube more stiff for easier insertion, or to provide more curvature to the tip in difficult cases. This is then removed after the intubation and a ventilator or self-inflating bag is attached to the ETT.
The goal is to position the end of the ETT 2 centimeters above the bifurcation of the lungs or the carina. If inserted too far into the trachea it often goes into the right main bronchus (the right main brochus is less angled than the left.
Indications of ETT:
1- Cardiac arrest,in which ventilation with mask either impossible or ineffective
2- Respiratory arrest, when the oxygenation with noninvasive methods is inadequate
3- Patient unable to protect airways(cardiac arrest, coma. areflexia)
4- general anesthesia
Types of tracheal tube
There are many types of Endotracheal tubes (ETT). Endotracheal tubes range in size from 2-10.5 mm in internal diameter (ID) - different sizes are chosen based on the patient's body size with the smaller sizes being used for paediatric and neonatal patients.
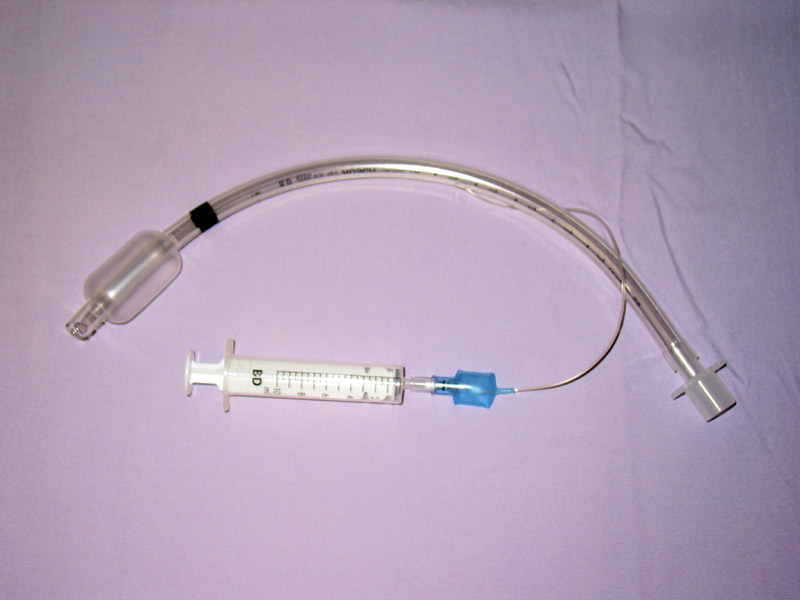
Tubes larger than 6 mm ID tend to have an inflatable cuff, but modern dates nearly all tubes can come with cuff. there are quite a few types of endotracheal tubes - oral un-cuffed, oral cuffed, Rae tube, Nasal tube, Nasal-Rae tube, reinforced tube, double-lumen tubes, tracheostomy tubes, laser tubes, septiflex, flexometallic, portex plain and red rubber cuffed et
Intra-thoracic Surgery
Dr. Robertshaw developed a double-lumen endo-bronchial tube for intra-thoracic surgery. These tubes allow single-lung ventilation whilst the other lung can be collapsed to make surgery easier and re-inflated as surgery finishes to check for fistulas (tears) etc.
Yet another type of endotracheal tube has a small second lumen with an opening situated right above the inflatable cuff, which can be used for suction of the nasopharngeal area and above the cuff to aid extubation (removal). This allows a suction system to be connected to the ETT to allow for suctioning of secretions which sit above the cuff which helps reduce the risk of chest infections in long-term intubated patients.
However the preferable method in these cases is to insert a shortened version of the tube via a tracheostomy, i.e. an opening into the trachea via neck. Patients can live with these respiratory aids permanently, although the majority are temporary airway adjuncts.
-
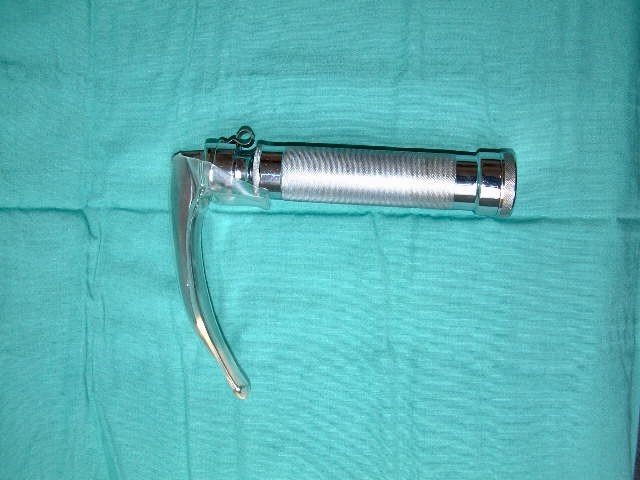
Macintosh pattern laryngoscope
-
Endotracheal tube
See Also
External Links
- Kimberly-Clark* Microcuff* Endotracheal Tube
- Portex Endotracheal tubes
- Mallincrodt Endotracheal tubes
- Other Endotracheal tubes & holders