Strongyloidiasis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
This page is about clinical aspects of the disease. For microbiologic aspects of the causative organism(s), see Strongyloides stercoralis.
| Strongyloidiasis | |
| Classification and external resources | |
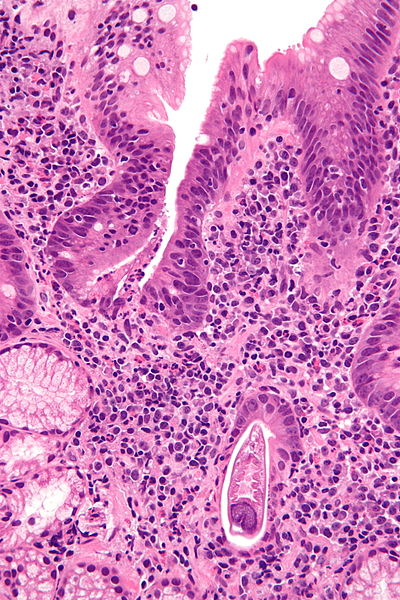
| |
|---|---|
| Micrograph showing strongyloidiasis; a fragment of a worm is seen in the lower right hand corner. H&E stain. Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AStrongyloides_-_very_high_mag_-_2.jpg |
For patient information, click here
|
Strongyloidiasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Strongyloidiasis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Strongyloidiasis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aditya Ganti M.B.B.S. [2]
Synonyms and keywords: Strongyloides infection, Hyperinfection syndrome, Intestinal strongyloidiasis, Infection by strongylus.
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | X-ray | CT scan| Ultrasound | Other Imaging findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies