Steatosis
|
WikiDoc Resources for Steatosis |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Steatosis |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Steatosis at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Steatosis at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Steatosis
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Steatosis Discussion groups on Steatosis Directions to Hospitals Treating Steatosis Risk calculators and risk factors for Steatosis
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Steatosis |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:
Overview
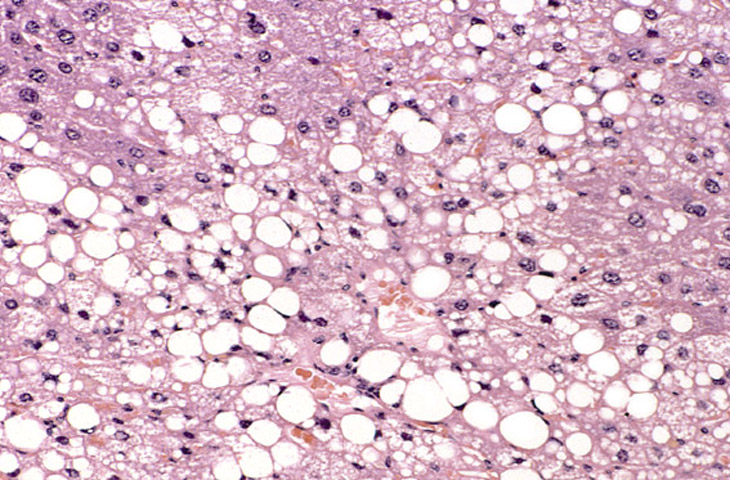
In cellular pathology, steatosis (also called fatty change) is the process describing the abnormal retention of lipids within a cell. It reflects an impairment of the normal processes of synthesis and breakdown of triglyceride fat. Excess lipid accumulates in vesicles that displace the cytoplasm. When the vesicles are large enough to distort the nucleus, the condition is known as macrovesicular steatosis, otherwise the condition is known as microvesicular steatosis. Whilst not particularly detrimental to the cell in mild cases, large accumulations can disrupt cell constituents, and in severe cases the cell may even burst.
The risk factors associated with steatosis are varied, and include diabetes mellitus,[1] protein malnutrition,[2] hypertension[3] cell toxins, obesity,[4] and anoxia.[5] As the liver is the primary organ of lipid metabolism it is most often associated with steatosis, however it may occur in any organ, commonly the kidneys, heart, and muscle.[5]
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Pathogenesis
No single mechanism leading to steatosis exists, rather a varied multitude of pathologies disrupt normal lipid movement through the cell and cause accumulation. These mechanisms can be separated on whether they ultimately cause an oversupply of lipid which can not be removed quickly enough (too much in), or whether they cause a failure in lipid breakdown (not enough being utilised).
Oversupply of lipid may occur due to obesity, insulin resistance, or alcoholism. Nutrient malnutrition may also cause the mobilisation of fat from adipocytes and create a local oversupply in the liver where lipid metabolism occurs. Excess alcohol over a long period of time can induce steatosis. The breakdown of large amounts of ethanol in alcoholic drinks produces large amounts of chemical energy, in the form of NADH, signalling to the cell to inhibit the breakdown of fatty acids (which also produces energy) and simultaneously increase the synthesis of fatty acids. This "false sense of energy" results in more lipid being created than is needed.
Failure of lipid metabolism can also lead to the mechanisms which would normally utilise or remove lipids becoming impaired, resulting in the accumulation of unused lipids in the cell. Certain toxins, such as alcohols, carbon tetrachloride, aspirin, and diphtheria toxin, interfere with cellular machinery involved in lipid metabolism. In those with Gaucher's disease, the lysosomes fail to degrade lipids and steatosis arises from the accumulation of glycolipids. Protein malnutrition, such as that seen in kwashiorkor, results in a lack of precursor apoproteins within the cell, therefore unused lipids which would normally participate in lipoprotein synthesis begin to accumulate.
Causes
Drug Side Effect
Differentiating Steatosis from Other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Appearance
Histologically, steatosis is physically apparent as lipid within membrane bound liposomes of parenchymal cells[5]. When this tissue is fixed and stained to be better viewed under a microscope, the lipid is usually dissolved by the solvents used to prepare the sample. As such, samples prepared this way will appear to have empty holes within the cells where the lipid has been cleared. Special lipid stains, such as Sudan stains and osmium tetroxide are able to retain and show up lipid droplets, hence more conclusively indicating the presence of lipids. Other intracellular accumulations, such as water or glycogen, can also appear as clear vacuoles, therefore it becomes necessary to use stains to better decide what is accumulating.
Grossly, steatosis causes organ enlargement and lightning in colour[5]. This is due to the high lipid content increasing the organ's volume and becoming visible to the unaided eye. In severe cases, the organ may become vastly enlarged, greasy, and yellow in appearance.
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Diagnosis
Diagnosis Criteria
History and Symptoms
Physical Examination
Laboratory Findings
Imaging Findings
Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy
Surgery
Prevention
Related Chapters
References
- ↑ Araya Q AV; et al. (2006). "Glucose tolerance alterations and frequency of metabolic syndrome among patients with non alcoholic fatty liver disease". Rev Med Chil. 134 (9): 1092-1098.
- ↑ Conde Martel A; et al. (1993). "Liver changes in protein malnutrition. An experimental study in rats". Nutr Hosp. 8 (6): 358-363.
- ↑ MJ Brookes, BT Cooper (2007). "Hypertension and fatty liver: guilty by association?". J Hum Hypertens. 21 (4): 264-270.
- ↑ S Saadeh (2007). "Nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease and obesity". Nutr Clin Pract. 22 (1): 1-10.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Cotran. Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease. Philadelphia: W.B Saunders Company. 0-7216-7335-X. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help)