Sleep apnea polysomnography
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
Sleep Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Sleep apnea polysomnography On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Sleep apnea polysomnography |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Sleep apnea polysomnography |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Saarah T. Alkhairy, M.D.
Overview
Polysomnography is diagnostic of sleep apnea and is recommended among all patients who are suspected to have sleep apnea during history-taking.
Polysomnography
- Also known as a sleep study
- Full-night, attended, in-laboratory polysomnography is considered the gold-standard diagnostic test for OSA
- It involves monitoring the patient during a full night's sleep:
- Brain activity
- Eye movements
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Amount of oxygen in the blood
- Air movement through the nose while breathing, snoring, and chest movements
- Split-night, attended, in-laboratory polysomnography
- This involves the diagnostic portion of the study performed during the first part of the night only
- Those patients who are diagnosed with OSA during the first part of the night and choose positive airway pressure therapy can have their positive airway pressure device titrated during the second part of the night[1]
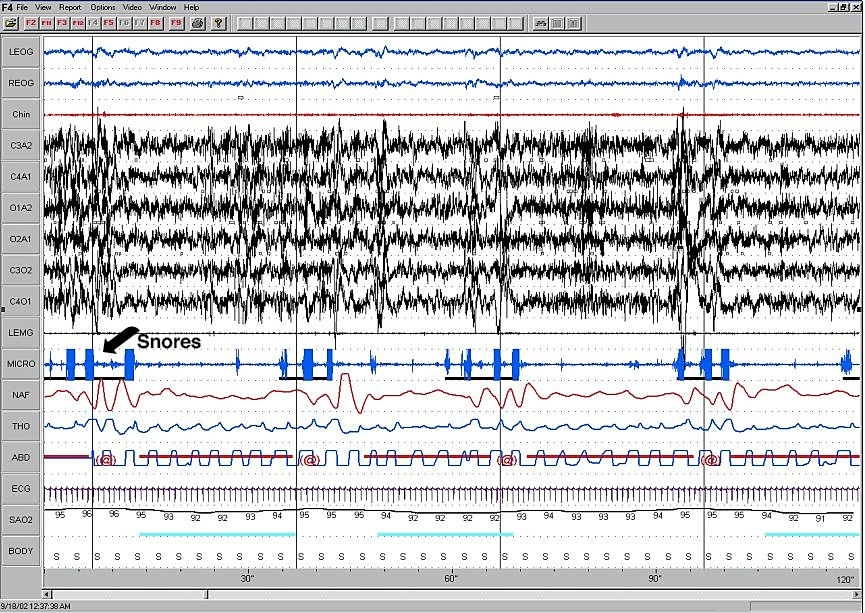
Two minute epoch representing continuous OSA
References
- ↑ Chesson AL, Ferber RA, Fry JM, Grigg-Damberger M, Hartse KM, Hurwitz TD; et al. (1997). "The indications for polysomnography and related procedures". Sleep. 20 (6): 423–87. PMID 9302726.