Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (-O H) attached to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol (C6H5OH).

Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have relatively higher acidities due to the aromatic ring tightly coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually comprised between 10 and 12). Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a negative phenolate ion.
Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.
Synthesis of phenols
Several laboratory methods for the synthesis of phenols:
- by an ester rearrangement in the Fries rearrangement
- by a rearrangement of N-phenylhydroxylamines in the Bamberger rearrangement
- by hydrolysis of phenolic esters or ethers
- by reduction of quinones
- by replacement of an aromatic amine by an hydroxyl group with water and sodium bisulfite in the Bucherer reaction
- by hydrolysis of diazonium salts
- by oligomerisation with formaldehyde + base catalysed reaction with epichlorohydrine to epoxi resin components
- by reaction with acetone/ketones to e.g. Bisphenol A, an important monomer for resins, e.g. polycarbonate(PC), epoxi resins
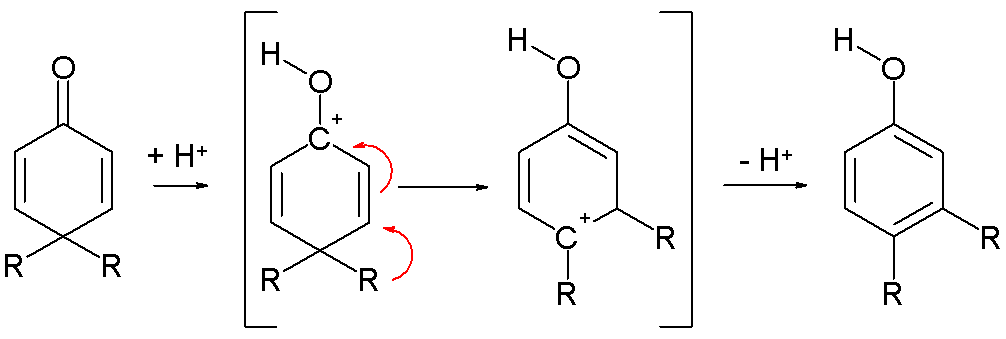
- by a rearrangement reaction of dienones [1] in the dienone phenol rearrangement [2]:
Reactions of phenols
Phenols react in a wide variety of ways.
- Esterification reactions and ether formation
- Electrophilic aromatic substitutions as the hydroxyl group is activating, for example synthesis of calixarenes [3]
- Reaction of naphtols and hydrazines and sodium bisulfite in the Bucherer carbazole synthesis
- Oxidative cleavage, for instance cleavage of 1,2-dihydroxybenzene to the monomethylester of 2,4 hexadienedioic acid with oxygen, copper chloride in pyridine [4]
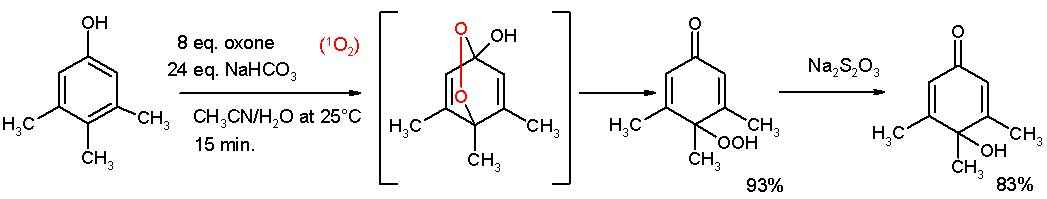
- Oxidative de-aromatization to quinones also known as the Teuber reaction. Oxidizing reagents are Fremy's salt [5] and oxone [6]. In reaction depicted below 3,4,5-trimethylphenol reacts with singlet oxygen generated from oxone/sodium carbonate in an acetonitrile/water mixture to a para-peroxyquinole. This hydroperoxide is oxidized to the quinole with sodium thiosulphate.
- Phenols are oxidized to benzenediols in the Elbs persulfate oxidation
- Phenolate anions (deriving from phenols by the loss of H+) can act as ligands towards metal cations
Phenolic compounds
- For a full list, see Category:Phenols
| Phenol | the parent compound, used as an disinfectant and for chemical synthesis |
| BHT | (butylated hydroxytoluene) - a fat-soluble antioxidant and food additive |
| Capsaicin | the pungent compound of chilli peppers |
| Bisphenol A | and other bisphenols produced from ketones and phenol / cresol |
| Chavibetol | from betel, used as a flavouring |
| Cresol | found in coal tar and creosote |
| Estradiol | estrogen - hormones |
| Eugenol | the main constituent of the essential oil of clove |
| Gallic acid | found in gallnuts |
| Guaiacol | (2-methoxyphenol) - has a smokey flavor, and is found in roasted coffee, whisky, and smoke |
| 4-Nonylphenol | a breakdown product of detergents and nonoxynol-9 |
| Orthophenyl phenol | a fungicide used for waxing citrus fruits |
| Picric acid | (trinitrophenol) - an explosive material |
| Phenolphthalein | pH indicator |
| Polyphenol | e.g. flavonoids and tannins |
| Raspberry ketone | a compound with an intense raspberry smell |
| Serotonin / dopamine / adrenaline / noradrenaline | natural neurotransmitters |
| Thymol | (2-Isopropyl-5-methyl phenol) - an antiseptic that is used in mouthwashes |
| Tyrosine | an amino acid |
| Xylenol | - |
Medicinals
| Cannabinoids | the active constituents of cannabis |
| Diethylstilbestrol | a synthetic estrogen with a stilbene structure |
| L-DOPA | a synthetic estrogen with a stilbene structure |
| Methyl salicylate | the major constituent of the essental oil of wintergreen |
| Propofol | a short-acting intravenous anesthetic agent |
| Psilocin | a hallucinogenic alkaloid of Psilocybe mushrooms |
| Salicylic acid | a plant hormone used for its analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory properties, also a precursor compound to Aspirin |
| Trichlorophenylmethyliodosalicyl | the main component of TCP, an antiseptic. |
References
- ↑ related to quinones, see for example the Zincke-Suhl reaction
- ↑ Advanced organic Chemistry, Reactions, mechanisms and structure 3ed. page Jerry March ISBN 0-471-85472-7
- ↑ p-tert-butylcalix[8]arene, Organic Syntheses, CV 8, 80 Article
- ↑ 2,4-Hexadienedioic acid, monomethyl ester, (Z,Z)- Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 8, p.490 (1993); Vol. 66, p.180 (1988) Article
- ↑ 2,5-Cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione, 2,3,5-trimethyl Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 6, p.1010 (1988); Vol. 52, p.83 (1972) Abstract.
- ↑ Oxidative De-aromatization of para-Alkyl Phenols into para-Peroxyquinols and para-Quinols Mediated by Oxone as a Source of Singlet Oxygen M. Carmen Carreño, Marcos González-López, Antonio Urbano Angewandte Chemie International Edition Volume 45, Issue 17 , Pages 2737 - 2741 2006 Abstract
cs:Fenoly da:Fenoler de:Phenole et:Fenoolid it:Fenoli ko:페놀류 mk:Фенол (класа) he:פנול sk:Fenoly