Glyceride
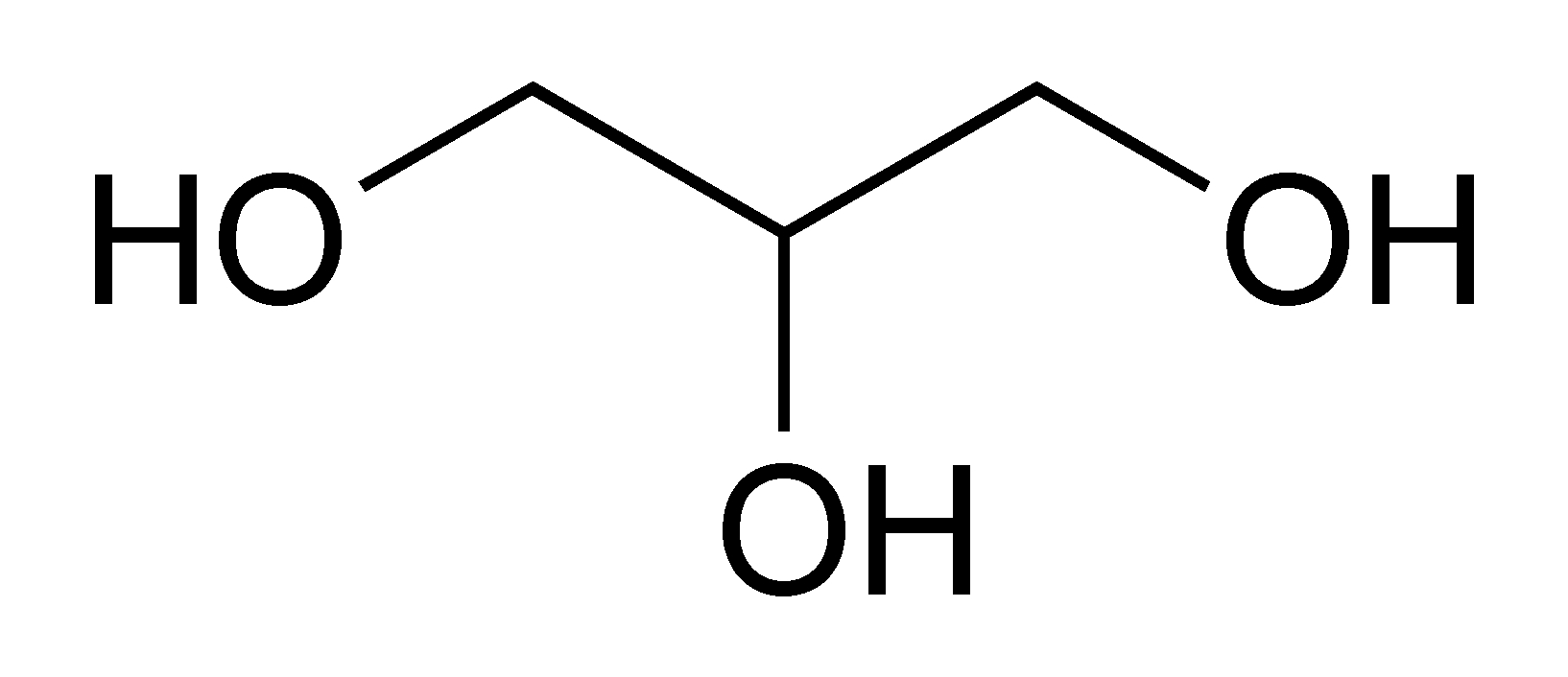

Glycerides, more correctly known as acylglycerols, are esters formed from glycerol and fatty acids.
Glycerol has three hydroxyl functional groups, which can be esterified with one, two, or three fatty acids to form monoglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides.
Vegetable oils and animal fats contain mostly triglycerides, but are broken down by natural enzymes (lipases) into mono- and diglycerides and free fatty acids.
Soaps are formed from the reaction of glycerides with sodium hydroxide. Glycerol is a product that can soften dehydrated skin by absorbing moisture from the air. If pure glycerol were left exposed to normal air, in 10 to 12 hours it would become 80% glycerol and 20% water by absorbing 1/5 of its weight in water.
da:Glycerid de:Acylglycerine eo:Glicerido ko:글리세라이드 it:Gliceridi he:גליצריד Template:WikiDoc Sources