Colistimethate sodium
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Kiran Singh, M.D. [2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Colistimethate sodium is an antibiotic that is FDA approved for the treatment of acute or chronic infections due to sensitive strains of certain gram-negative bacilli. Common adverse reactions include gastrointestinal upset,slurred speech, dizziness, vertigo, paresthesia,urticaria, rash,respiratory distress apnea, fever.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- Colistimethate for injection is indicated for the treatment of acute or chronic infections due to sensitive strains of certain gram-negative bacilli. It is particularly indicated when the infection is caused by sensitive strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This antibiotic is not indicated for infections due to Proteus or Neisseria. Colistimethate for injection has proven clinically effective in treatment of infections due to the following gram-negative organisms: Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Colistimethate for injection may be used to initiate therapy in serious infections that are suspected to be due to gram-negative organisms and in the treatment of infections due to susceptible gram-negative pathogenic bacilli.
- To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of colistimethate for injection and other antibacterial drugs, colistimethate for injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Dosage
Adults and Pediatric Patients—Intravenous or Intramuscular Administration: The dose of colistimethate for injection should be 2.5 to 5 mg/kg per day of colistin base in 2 to 4 divided doses for patients with normal renal function, depending on the severity of the infection.
- In obese individuals, dosage should be based on ideal body weight.
- The daily dose and frequency should be reduced for the patients with renal impairment. Suggested modifications of dosage schedule for patients with renal impairment are presented in table 1.


Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Colistimethate sodium in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Colistimethate sodium in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Indications
- Colistimethate for injection is indicated for the treatment of acute or chronic infections due to sensitive strains of certain gram-negative bacilli. It is particularly indicated when the infection is caused by sensitive strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This antibiotic is not indicated for infections due to Proteus or Neisseria. Colistimethate for injection has proven clinically effective in treatment of infections due to the following gram-negative organisms: Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Colistimethate for injection may be used to initiate therapy in serious infections that are suspected to be due to gram-negative organisms and in the treatment of infections due to susceptible gram-negative pathogenic bacilli.
- To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of colistimethate for injection and other antibacterial drugs, colistimethate for injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Dosage
Pediatric Patients—Intravenous or Intramuscular Administration: The dose of colistimethate for injection should be 2.5 to 5 mg/kg per day of colistin base in 2 to 4 divided doses for patients with normal renal function, depending on the severity of the infection.
- In obese individuals, dosage should be based on ideal body weight.
- The daily dose and frequency should be reduced for the patients with renal impairment. Suggested modifications of dosage schedule for patients with renal impairment are presented in table 1.


Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Colistimethate sodium in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Colistimethate sodium in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- The use of colistimethate for injection is contraindicated for patients with a history of sensitivity to the drug or any of its components.
Warnings
- Maximum daily dose calculated from colistin base activity should not exceed 5 mg/kg/day with normal renal function.
- Transient neurological disturbances may occur. These include circumoral paresthesia or numbness, tingling or formication of the extremities, generalized pruritus, vertigo, dizziness, and slurring of speech. For these reasons, patients should be warned not to drive vehicles or use hazardous machinery while on therapy. Reduction of dosage may alleviate symptoms. Therapy need not be discontinued, but such patients should be observed with particular care.
- Nephrotoxicity can occur and is probably a dose-dependent effect of colistimethate sodium. These manifestations of nephrotoxicity are reversible following discontinuation of the antibiotic.
- Overdosage can result in renal insufficiency, muscle weakness, and apnea.
- Respiratory arrest has been reported following intramuscular administration of colistimethate sodium. Impaired renal function increases the possibility of apnea and neuromuscular blockade following administration of colistimethate sodium. Therefore, it is important to follow recommended dosing guidelines.
- Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including colistimethate for injection, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
- C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
- If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been reported:
- Gastrointestinal - gastrointestinal upset
- Nervous System - tingling of extremities and tongue, slurred speech, dizziness, vertigo and paresthesia
- Body as a Whole - fever
- Laboratory Deviations - increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN), elevated creatinine and decreased creatinine clearance
- Respiratory System - respiratory distress and apnea
- Renal System - nephrotoxicity and decreased urine output
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Colistimethate sodium in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- Certain other antibiotics (aminoglycosides and polymyxin) have also been reported to interfere with the nerve transmission at the neuromuscular junction. Based on this reported activity, they should not be given concomitantly with colistimethate for injection except with the greatest caution.
- Curariform muscle relaxants (e.g., tubocurarine) and other drugs, including ether, succinylcholine, gallamine, decamethonium and sodium citrate, potentiate the neuromuscular blocking effect and should be used with extreme caution in patients being treated with colistimethate for injection.
- Sodium cephalothin may enhance the nephrotoxicity of colistimethate for injection. The concomitant use of sodium cephalothin and colistimethate for injection should be avoided.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Colistimethate sodium in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
Teratogenic Effects-Pregnancy Category C
- Colistimethate sodium given intramuscularly during organogenesis to rabbits at 4.15 and 9.3 mg/kg resulted in talipes varus in 2.6% and 2.9% of fetuses, respectively. These doses are 0.25 and 0.55 times the maximum daily human dose based on mg/m2. In addition, increased resorption occurred at 9.3 mg/kg. Colistimethate sodium was not teratogenic in rats at 4.15 or 9.3 mg/kg. These doses are 0.13 and 0.30 times the maximum daily human dose based on mg/m2. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Since colistimethate sodium is transferred across the placental barrier in humans, it should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Colistimethate sodium during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether colistimethate sodium is excreted in human breast milk. However, colistin sulphate is excreted in human breast milk. Therefore, caution should be exercised when colistimethate sodium is administered to nursing women.
Pediatric Use
- In clinical studies, colistimethate sodium was administered to the pediatric population (neonates, infants, children and adolescents). Although adverse reactions appear to be similar in the adult and pediatric populations, subjective symptoms of toxicity may not be reported by pediatric patients. Close clinical monitoring of pediatric patients is recommended.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of colistimethate sodium did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colistimethate sodium with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colistimethate sodium with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colistimethate sodium in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colistimethate sodium in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Colistimethate sodium in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Colistimethate sodium in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Colistimethate sodium in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Colistimethate sodium in the drug label.
Overdosage
- Overdosage with colistimethate sodium can cause neuromuscular blockade characterized by paresthesia, lethargy, confusion, dizziness, ataxia, nystagmus, disorders of speech and apnea. Respiratory muscle paralysis may lead to apnea, respiratory arrest and death. Overdosage with the drug can also cause acute renal failure, manifested as decreased urine output and increases in serum concentrations of BUN and creatinine.
- As in any case of overdose, colistimethate sodium therapy should be discontinued and general supportive measures should be utilized.
- It is unknown whether colistimethate sodium can be removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis in overdose cases.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Colistimethate sodium Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
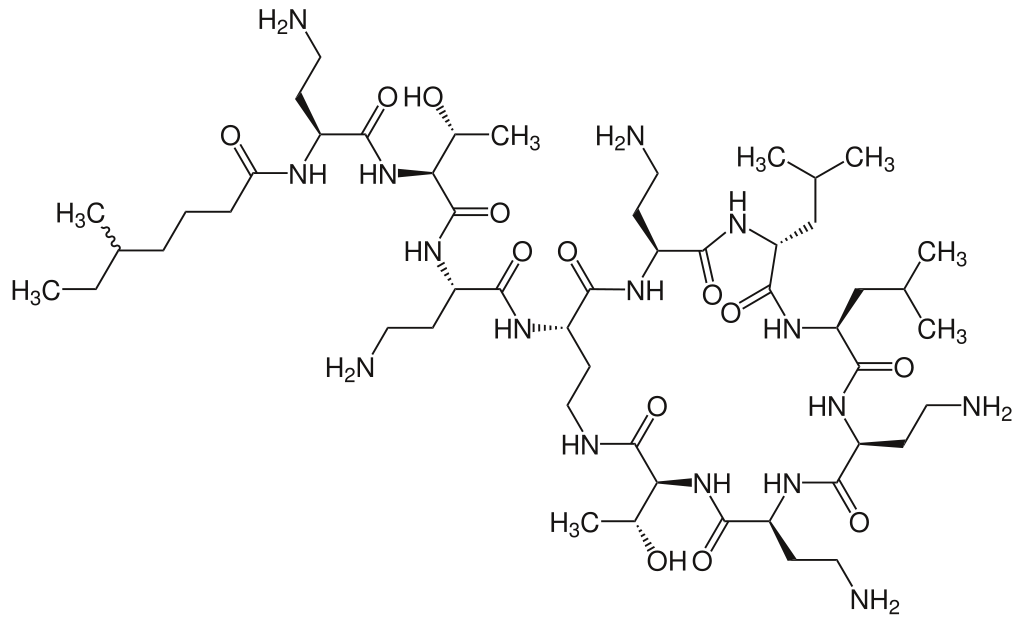
Structure
- Colistimethate for Injection, USP is a sterile parenteral antibiotic product which, when reconstituted, is suitable for intramuscular or intravenous administration.
- Each vial contains colistimethate sodium or pentasodium colistinmethanesulfonate (150 mg colistin base activity). The sodium content is approximately 0.099 mg (0.0043 mEq) of sodium per milligram of colistin.
- Colistimethate Sodium, USP is pentasodium 4-3-hydroxy-1-1-3-(1-hydroxyethyl)-12,15-bis(2-methylpropyl)-2,5,8,11,14,17,20-heptaoxo-6,9,18-tris2-(sulfonatomethylamino)ethyl-1,4,7,10,13,16,19-heptazacyclotricos-21-ylamino-1-oxo-4-(sulfonatomethylamino)butan-2-ylamino-1-oxobutan-2-ylamino-3-(6-methyloctanoylamino)-4-oxobutylaminomethanesulfonate.
- Colistimethate Sodium, USP is a polypeptide antibiotic with an approximate molecular weight of 1750. The molecular formula is C58H105N16Na5O28S5 and the structural formula is represented below:

- Colistimethate for Injection, USP is a white to slightly yellow lyophilized cake. The color of the reconstituted solution is clear colorless to pale yellow and essentially free from particles.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Colistimethate sodium in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Colistimethate sodium in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Long-term animal carcinogenicity studies and genetic toxicology studies have not been performed with colistimethate sodium. There were no adverse effects on fertility or reproduction in rats at doses of 9.3 mg/kg/day (0.30 times the maximum daily human dose when based on mg/m2).
Clinical Studies
- Typical serum and urine levels following a single 150 mg dose of colistimethate for injection IM or IV in normal adult subjects are shown in figure1.

- Higher serum levels were obtained at 10 minutes following IV administration. Serum concentration declined with a half-life of 2 to 3 hours following either intravenous or intramuscular administration in adults and in the pediatric population, including premature infants.
- Average urine levels ranged from about 270 mcg/mL at 2 hours to about 15 mcg/mL at 8 hours after intravenous administration and from 200 to about 25 mcg/mL during a similar period following intramuscular administration.
Microbiology
- Colistimethate sodium is a surface active agent which penetrates into and disrupts the bacterial cell membrane. It has been shown to have bactericidal activity against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections:
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms
- Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Susceptibility Tests
- Colistimethate sodium is no longer listed as an antimicrobial for routine testing and reporting by clinical microbiology laboratories.
How Supplied
- Colistimethate for Injection, USP is supplied in vials containing colistimethate sodium (equivalent to 150 mg colistin base activity per vial) as follows:

- Colistimethate for Injection, USP is a white to slightly yellow lyophilized cake.
Storage
- Store dry powder at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F).
- Store reconstituted solution in refrigerator at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) or between 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) and use within 7 days.
- Sterile, Nonpyrogenic, Preservative-free.
- The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Colistimethate sodium |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel


{{#ask: Label Page::Colistimethate sodium |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Information for Patients
- Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including colistimethate for injection should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When colistimethate for injection is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by colistimethate for injection or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Colistimethate sodium interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- COLISTIMETHATE ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "COLISTIMETHATE- colistimethate sodium injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Colistimethate sodium |Label Name=Colistimethate sodium11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Colistimethate sodium |Label Name=Colistimethate sodium11.png
}}