T wave
|
WikiDoc Resources for T wave |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on T wave at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on T wave at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on T wave
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating T wave Risk calculators and risk factors for T wave
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
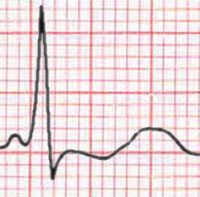
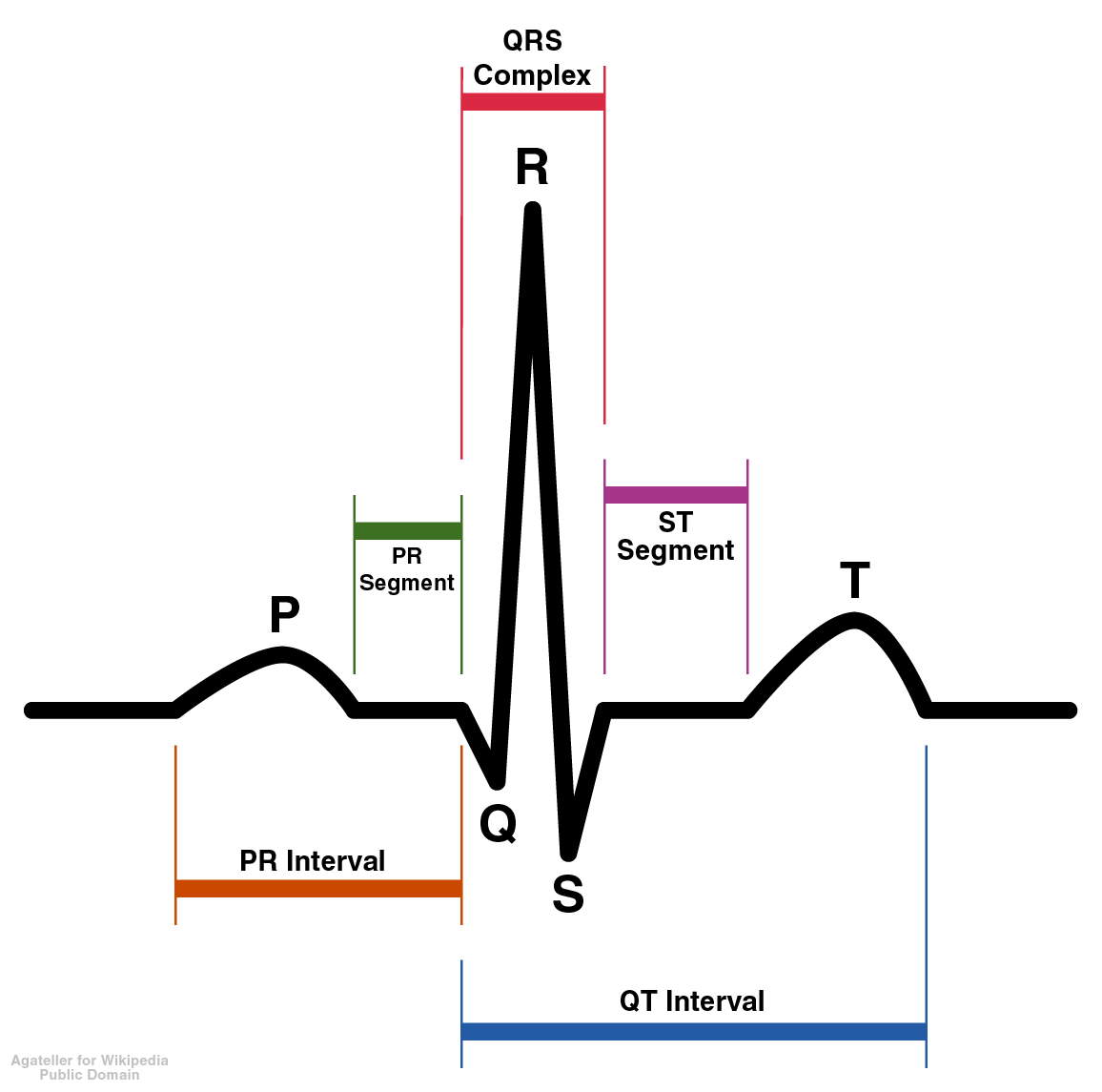
The T wave represents the repolarization (or recovery) of the ventricles. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the absolute refractory period. The last half of the T wave is referred to as the relative refractory period (or vulnerable period).
Orientation of T waves
Normal Orientation
General
- Normally upright in leads 1 and 2 and in the chest leads over the left ventricle.
Precordial Leads
- Lead V1 may have a positive, negative, or biphasic T wave.
- The T wave in V1 may be inverted at any age (is more often inverted than upright) and the T in V2 can normally be inverted.
- When the T in V1 is upright, it is almost never as tall as the T in V6.
- In infants and young children precordial T waves may be inverted.
- In adult males it is considered abnormal if the T waves are inverted as far to the left as lead V3.
- In adult females the T in V3 may be shallowly inverted.
aVF
- Normally upright in aVL and aVF if the QRS is > 5 mm tall but may be inverted if the R waves are smaller.
- It is not uncommon to have an isolated negative T wave in lead III, aVL, or aVF. Cardiologists are often asked to consult pre-operativley on the patient with the isolated flipped T in lead III.
aVR
- Normally inverted in aVR.
In The Presence of Conduction Delay
- When a conduction abnormality (e.g., left bundle branch block,right bundle branch block, or a paced rhythm) is present, the T wave should be deflected opposite the terminal deflection of the QRS complex. This is known as appropriate T wave discordance.
Differential Diagnosis of Inverted or Negative T waves:
- Coronary ischemia
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- CNS disorder.
Morphology of T waves
Shape
Notched
- Notched in children and in adults with Pericarditis
Differential diagnosis of the sharp, tented or pointed T wave
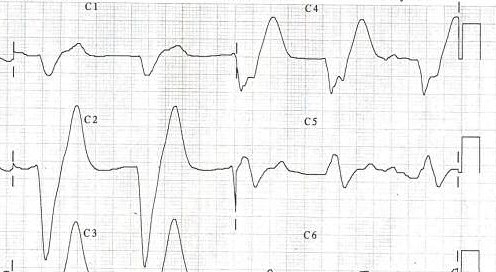
- Tall or "tented" symmetrical T waves may indicate hyperkalemia.
- One of the earliest electrocardiographic finding of acute myocardial infarction is sometimes the hyperacute T wave, which can be distinguished from hyperkalemia by the broad base and slight asymmetry.
- T waves can be sharply pointed in ischemia as well.
Height
The T wave is normally not taller than > 5 mm in any standard lead and not taller than > 10 mm in any precordial lead.
Differential diagnosis of the tall T wave:
- Hyperkalemia
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Myocardial Ischemia
- Myocardial infarction
- Ventricular strain
- Psychosis
- Cerebrovascular accident (usually inverted, widely splayed, frequently in subarrachnoid hemorrhages)
Differential diagnosis of the short or flat T wave:
- Coronary ischemia
- Hypokalemia.
- Obesity. This finding may reverse with weight loss
Cerebral T waves
Overview
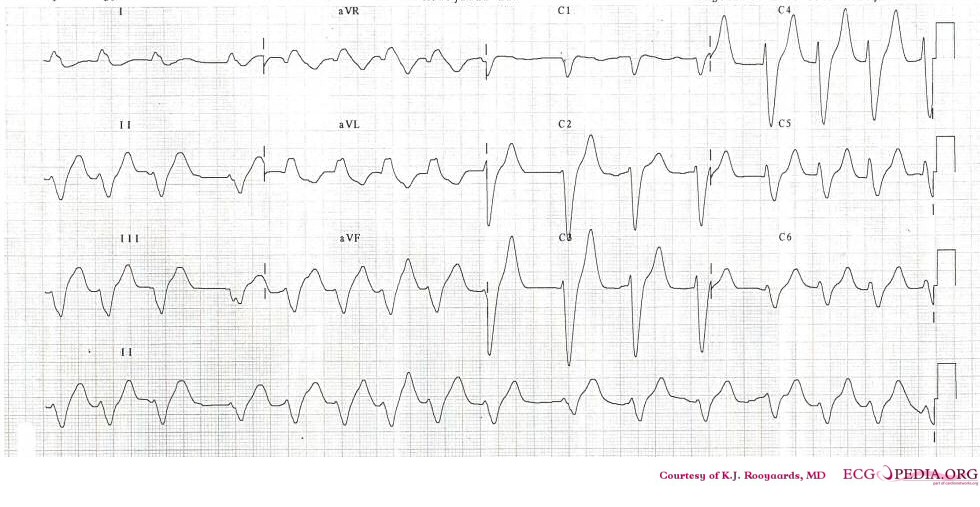
In 1954 George Burch described T wave abnormalities as myocardial ischemia mimics in patients with a variety of acute cerebral insults. His classic paper [1] published in May 1954 popularized the term cerebral T waves.
Examples
References
Additional resources
- ECGpedia: Course for interpretation of ECG
- The whole ECG - A basic ECG primer
- 12-lead ECG library
- Simulation tool to demonstrate and study the relation between the electric activity of the heart and the ECG
- ECG information from Children's Hospital Heart Center, Seattle
- ECG Challenge from the ACC D2B Initiative
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Diseases and Conditions Index
- A history of electrocardiography
- EKG Interpretations in infants and children