Strongyloidiasis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Name = Strongyloidiasis | | Name = Strongyloidiasis | | ||
Image = Strongyloides_-_very_high_mag_-_2.jpg | | Image = Strongyloides_-_very_high_mag_-_2.jpg | | ||
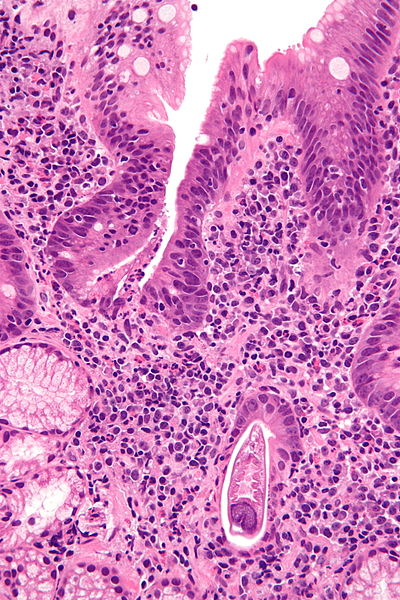
Caption = [[Micrograph]] showing strongyloidiasis; a fragment of a worm is seen in the lower right hand corner. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = [[Micrograph]] showing strongyloidiasis; a fragment of a worm is seen in the lower right hand corner. [[H&E stain]]. Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AStrongyloides_-_very_high_mag_-_2.jpg | | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''For patient information, click [[Strongyloidiasis (patient information)|here]]''' | '''For patient information, click [[Strongyloidiasis (patient information)|here]]''' | ||
{{Strongyloidiasis}} | {{Strongyloidiasis}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{ADG}} | ||
{{SK}} Strongyloides infection | {{SK}} Strongyloides infection, Hyperinfection syndrome, Intestinal strongyloidiasis, Infection by strongylus. | ||
==[[Strongyloidiasis overview|Overview]]== | ==[[Strongyloidiasis overview|Overview]]== | ||
==[[Strongyloidiasis historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | ==[[Strongyloidiasis historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | ||
==[[Strongyloidiasis classification|Classification]]== | |||
==[[Strongyloidiasis pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | ==[[Strongyloidiasis pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 24: | ||
==[[Strongyloidiasis differential diagnosis|Differentiating Strongyloidiasis from other Diseases]]== | ==[[Strongyloidiasis differential diagnosis|Differentiating Strongyloidiasis from other Diseases]]== | ||
==[[Strongyloidiasis epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | ==[[Strongyloidiasis epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | ||
==[[Strongyloidiasis risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | ==[[Strongyloidiasis risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | ||
== [[Strongyloidiasis screening|Screening]] == | |||
==[[Strongyloidiasis natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== | ==[[Strongyloidiasis natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== | ||
| Line 127: | Line 35: | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
[[Strongyloidiasis history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Strongyloidiasis physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Strongyloidiasis laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Strongyloidiasis imaging findings|Imaging | [[Strongyloidiasis history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Strongyloidiasis physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Strongyloidiasis laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Strongyloidiasis x ray|X-ray]] | [[Strongyloidiasis CT|CT scan]]| [[Strongyloidiasis ultrasound|Ultrasound]] | [[Strongyloidiasis other imaging findings|Other Imaging findings]] | [[Strongyloidiasis other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
[[Strongyloidiasis medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Strongyloidiasis prevention|Prevention]] | [[Strongyloidiasis cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Strongyloidiasis future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] | [[Strongyloidiasis medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Strongyloidiasis surgery|Surgery]] | [[Strongyloidiasis primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Strongyloidiasis secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Strongyloidiasis cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Strongyloidiasis future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] | ||
==Case Studies== | ==Case Studies== | ||
| Line 141: | Line 49: | ||
[[Category:Disease]] | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category:Emergency mdicine]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | [[Category:Infectious disease]] | ||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:Dermatology]] | |||
[[Category:Neurology]] | |||
[[Category:Pulmonology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:19, 30 July 2020
This page is about clinical aspects of the disease. For microbiologic aspects of the causative organism(s), see Strongyloides stercoralis.
| Strongyloidiasis | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| |
|---|---|
| Micrograph showing strongyloidiasis; a fragment of a worm is seen in the lower right hand corner. H&E stain. Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AStrongyloides_-_very_high_mag_-_2.jpg |
For patient information, click here
|
Strongyloidiasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Strongyloidiasis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Strongyloidiasis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aditya Ganti M.B.B.S. [2]
Synonyms and keywords: Strongyloides infection, Hyperinfection syndrome, Intestinal strongyloidiasis, Infection by strongylus.
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Strongyloidiasis from other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | X-ray | CT scan| Ultrasound | Other Imaging findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies