Stomatitis differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
Usama Talib (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Usama Talib (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Every type of stomatitis should be differentiated from various other subtypes and from many other disease that can involve the oral cavity such as [[Agranulocytosis|agranulocystosis]], [[behcet's disease]], [[immunodeficiency]] and [[tumors]] of the oral cavity like [[leukoplakia]] | Every type of stomatitis should be differentiated from various other subtypes and from many other disease that can involve the oral cavity such as [[Agranulocytosis|agranulocystosis]], [[behcet's disease]], [[immunodeficiency]] and [[tumors]] of the oral cavity like [[leukoplakia]].<ref name="Gangrenous stomatitis">{{cite book |last1=Mandell |firs1t=Gerald |last2=Gouglas |first2=Gordon |last3=Bennett |first3=John |date= |title=Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases |location= Harvard Medical School |publisher=WILEY MEDICAL |page=383 |isbn=0-471-87643-7}}</ref><ref name="pmid10597357">{{cite journal| author=Scully C| title=A review of common mucocutaneous disorders affecting the mouth and lips. | journal=Ann Acad Med Singapore | year= 1999 | volume= 28 | issue= 5 | pages= 704-7 | pmid=10597357 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10597357 }} </ref> | ||
==Differential diagnosis== | ==Differential diagnosis== | ||
Revision as of 19:12, 29 March 2017
|
Stomatitis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Stomatitis differential diagnosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Stomatitis differential diagnosis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Stomatitis differential diagnosis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sara Mehrsefat, M.D. [2], Usama Talib, BSc, MD [3]
Overview
Every type of stomatitis should be differentiated from various other subtypes and from many other disease that can involve the oral cavity such as agranulocystosis, behcet's disease, immunodeficiency and tumors of the oral cavity like leukoplakia.[1][2]
Differential diagnosis
Stomatitis must be differentiated from its different kinds and from various other diseases that can mimic stomatitis or have accompanying features involving other organs:[1][2]
- Tumors of the tongue
- Autoimmune diseases[7]
- Agranulocytosis
- Fordyce's spots
- Drug induced
- Burning mouth syndrome
- Syphilis
- Coxsackie virus accompanies involvement of the hands and the mouth
- HIV
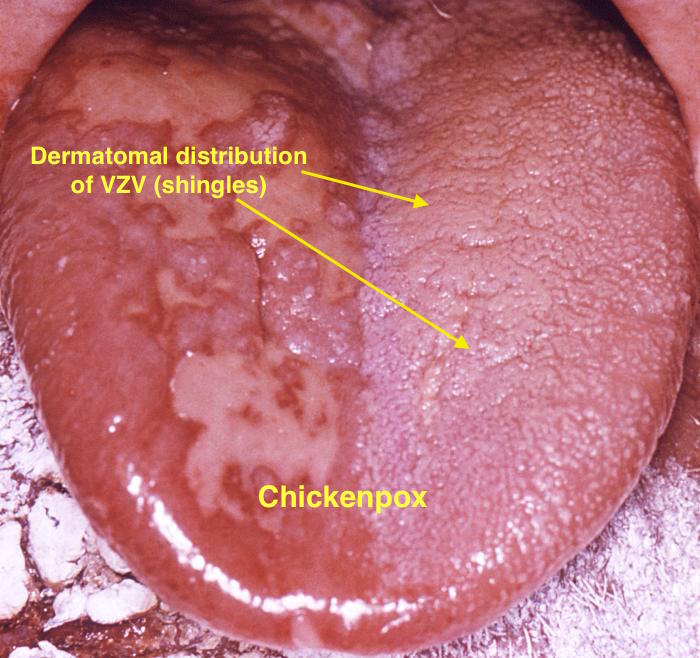
- VZV or Chicken pox
| Disease | Presentation | Risk Factors | Diagnosis | Affected Organ Systems | Important features | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diseases predominantly affecting the oral cavity | ||||||
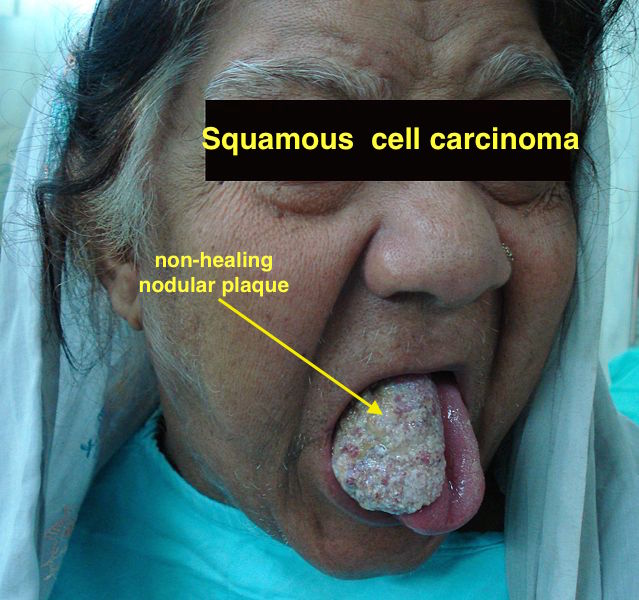
| Squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
| |||
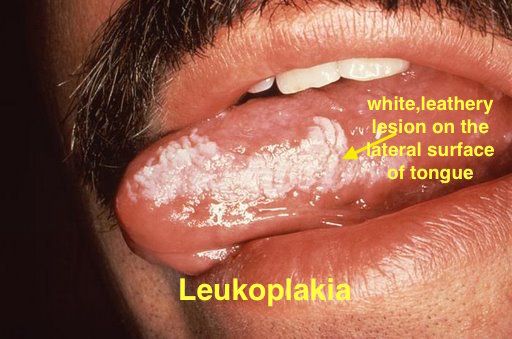
| Leukoplakia |
|
|
|
| ||
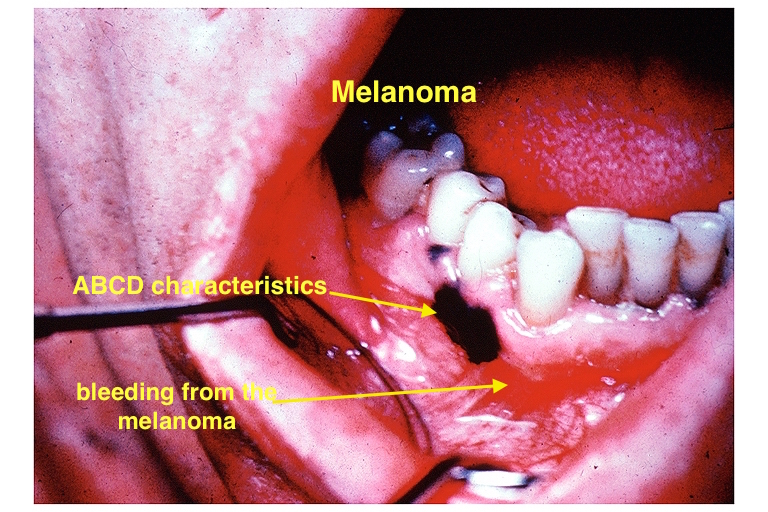
| Melanoma |
|
|
|
|
| |
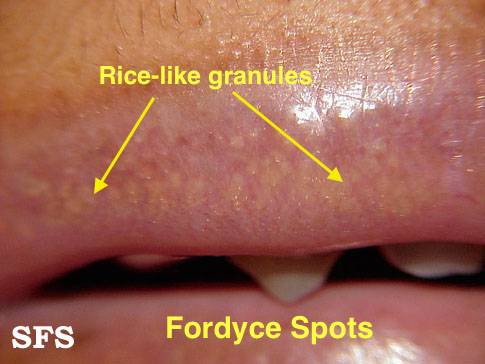
| Fordyce spots |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Burning mouth syndrome |
|
|
||||
| Torus palatinus |
|
|
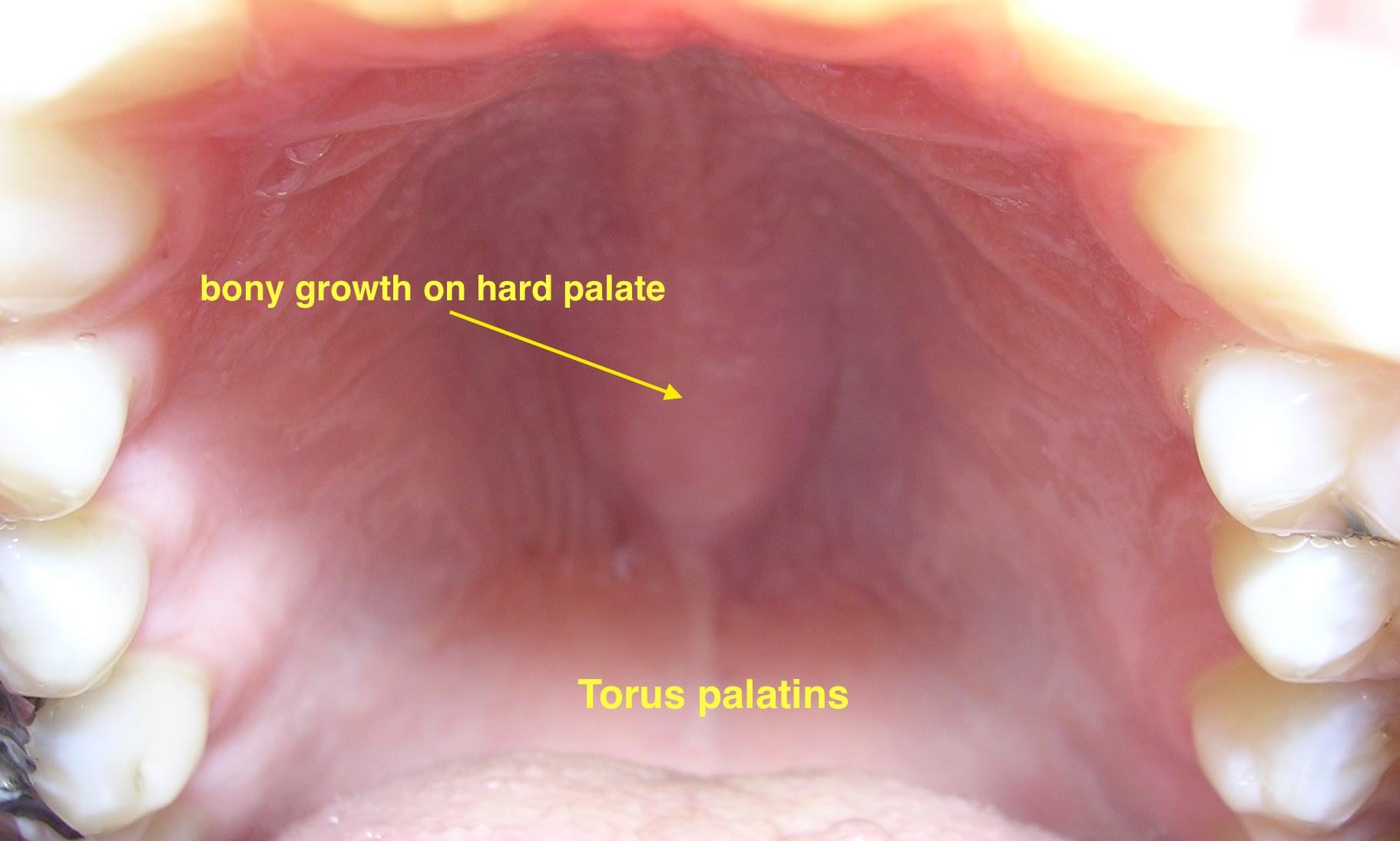
| |||
| Diseases involving oral cavity and other organ systems | ||||||
| Behcet's disease |
|
|
|
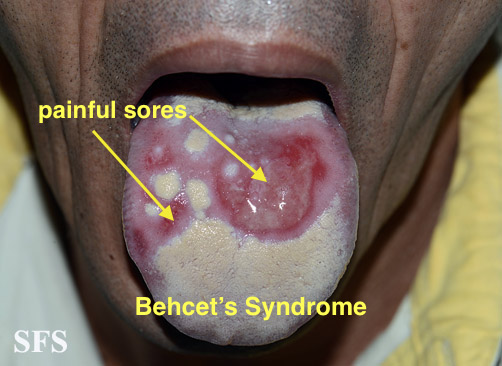
| ||
| Crohn's disease |
|
|
|
|
||
| Agranulocytosis |
|
|
||||
| Syphilis[11] |
|
|
|
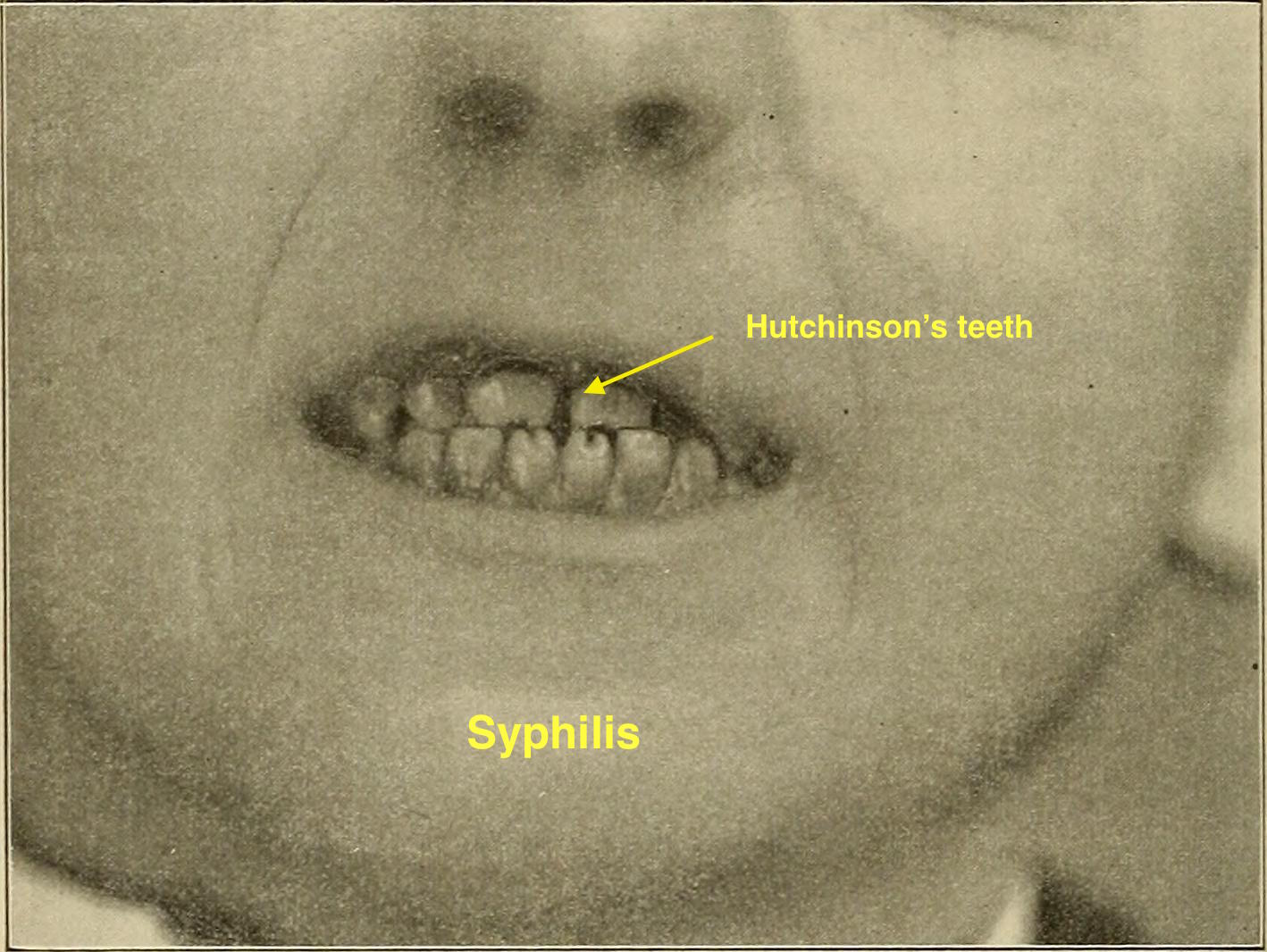
| ||
| Coxsackie virus |
|
|
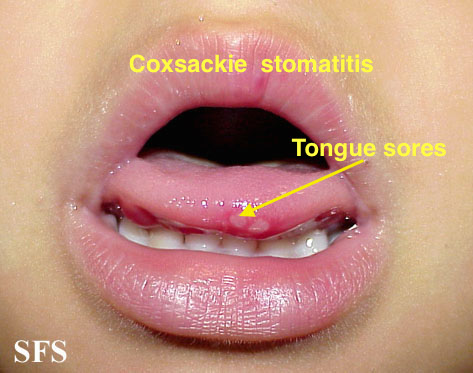
| |||
| Chicken pox |
|
|
|
|
| |
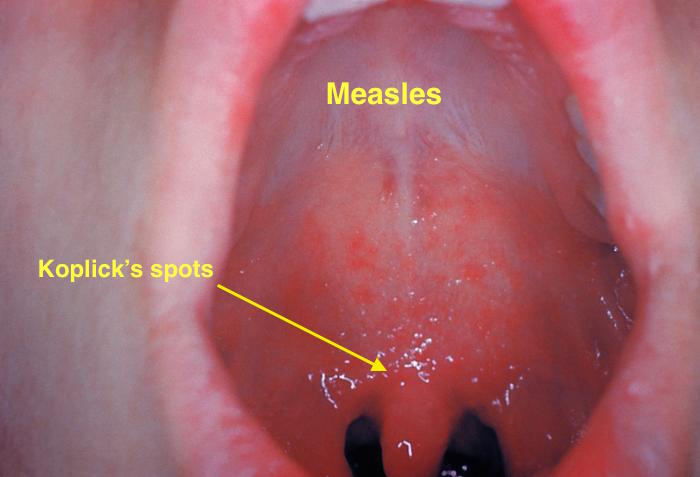
| Measles |
|
|
|
|
| |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mandell; Gouglas, Gordon; Bennett, John. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. Harvard Medical School: WILEY MEDICAL. p. 383. ISBN 0-471-87643-7. Unknown parameter
|firs1t=ignored (help) - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Scully C (1999). "A review of common mucocutaneous disorders affecting the mouth and lips". Ann Acad Med Singapore. 28 (5): 704–7. PMID 10597357.
- ↑ R. Morgan, J. Tsang, N. Harrington & L. Fook (2001). "Survey of hospital doctors' attitudes and knowledge of oral conditions in older patients". Postgraduate medical journal. 77 (908): 392–394. PMID 11375454. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ D. Grady, J. Greene, T. E. Daniels, V. L. Ernster, P. B. Robertson, W. Hauck, D. Greenspan, J. Greenspan & S. Jr Silverman (1990). "Oral mucosal lesions found in smokeless tobacco users". Journal of the American Dental Association (1939). 121 (1): 117–123. PMID 2370378. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ P. DeMatos, D. S. Tyler & H. F. Seigler (1998). "Malignant melanoma of the mucous membranes: a review of 119 cases". Annals of surgical oncology. 5 (8): 733–742. PMID 9869521. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Barry Ladizinski & Kachiu C. Lee (2014). "A nodular protuberance on the hard palate". JAMA. 311 (15): 1558–1559. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.271. PMID 24737369. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Magliocca KR, Fitzpatrick SG (2017) Autoimmune Disease Manifestations in the Oral Cavity. Surg Pathol Clin 10 (1):57-88. DOI:10.1016/j.path.2016.11.001 PMID: 28153136
- ↑ Dalghous AM, Freysdottir J, Fortune F (2006). "Expression of cytokines, chemokines, and chemokine receptors in oral ulcers of patients with Behcet's disease (BD) and recurrent aphthous stomatitis is Th1-associated, although Th2-association is also observed in patients with BD". Scand J Rheumatol. 35 (6): 472–5. PMID 17343257.
- ↑ Ann M. Gillenwater, Nadarajah Vigneswaran, Hanadi Fatani, Pierre Saintigny & Adel K. El-Naggar (2013). "Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL): a review of an elusive pathologic entity!". Advances in anatomic pathology. 20 (6): 416–423. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e3182a92df1. PMID 24113312. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Andrès E, Zimmer J, Affenberger S, Federici L, Alt M, Maloisel F. (2006). "Idiosyncratic drug-induced agranulocytosis: Update of an old disorder". Eur J Intern Med. 17 (8): 529–35. Text "pmid 17142169" ignored (help)
- ↑ title="By Internet Archive Book Images [No restrictions], via Wikimedia Commons" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AA_manual_of_syphilis_and_the_venereal_diseases%2C_(1900)_(14595882378).jpg"
- ↑ Feikin DR, Lezotte DC, Hamman RF, Salmon DA, Chen RT, Hoffman RE (2000). "Individual and community risks of measles and pertussis associated with personal exemptions to immunization". JAMA. 284 (24): 3145–50. PMID 11135778.
- ↑ Ratnam S, West R, Gadag V, Williams B, Oates E (1996). "Immunity against measles in school-aged children: implications for measles revaccination strategies". Can J Public Health. 87 (6): 407–10. PMID 9009400.