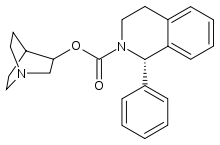
Solifenacin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| [[Regulation of therapeutic goods |Template:Engvar data]] |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 45 to 68 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (69.2%) and fecal (22.5%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H26N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 362.465 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Solifenacin |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Solifenacin Most cited articles on Solifenacin |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Solifenacin |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Solifenacin at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Solifenacin at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Solifenacin
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Solifenacin Discussion groups on Solifenacin Patient Handouts on Solifenacin Directions to Hospitals Treating Solifenacin Risk calculators and risk factors for Solifenacin
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Solifenacin |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
Solifenacin (rINN), marketed as solifenacin succinate under the trade name Vesicare, is a urinary antispasmodic of the anticholinergic class. It is used in the treatment of overactive bladder with or without urge incontinence.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Solifenacin is a competitive muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. The binding of acetylcholine to these receptors, particularly the M3 receptor subtype, plays a critical role in the contraction of smooth muscle. By preventing the binding of acetylcholine to these receptors, solifenacin reduces smooth muscle tone in the bladder, allowing the bladder to retain larger volumes of urine and reducing the number of micturition, urgency and incontinence episodes. Thanks to a long elimination half life, once-a-day dose can offer 24 hour control of the urinary bladder smooth muscle tone.
Contraindications
Solifenacin should not be taken by people with a history of previous hypersensitivity to it, urinary retention, gastric retention, uncontrolled or poorly controlled closed-angle glaucoma, or severe liver disease (Child-Pugh class C). It is also contraindicated in long QT syndrome, as solifenacin,like tolterodine and darifenacin, binds to HERG channels and may prolong the QT interval.
Interactions
Solifenacin is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4. When administered concomitantly with drugs that inhibit CYP3A4, such as ketoconazole, the metabolism of solifenacin is impaired, leading to an increase in its concentration in the body and a reduction in its excretion. The manufacturer recommends that the dosage of solifenacin not exceed 5 mg a day if it is taken with a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor.
As stated above, solifenacin may also prolong the QT interval. Therefore, it should not be administered concomitantly with drugs which also have this effect, such as moxifloxacin or pimozide.
Side effects
The most common side effects of solifenacin are dry mouth, blurred vision, and constipation. As all anticholinergics, solifenacin may rarely cause heat prostration due to decreased perspiration.
Pharmacoeconomics
In a study of cost-effectiveness analysis, the average medical cost per overactive bladder patient with successful treatment is reported to be lowest for 5 mg solifenacin ($6863 per annum) among anticholinergic drugs to treat overactive bladder in the united states (Pharmacotherapy 2006, 26 1694-1702).