Short bowel syndrome electrocardiogram: Difference between revisions
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
There are no [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] findings associated with short bowel syndrome. In case of [[malnutrition]] and [[Electrolyte disturbance|electrolyte imbalance]], an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] may be helpful. | There are no [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] findings associated with short bowel syndrome. In case of [[malnutrition]] and [[Electrolyte disturbance|electrolyte imbalance]], an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] may be helpful. [[Hypokalemia]] might present with [[Cardiac arrhythmia|arrhythmia]], [[ST segment depression]], low [[T wave]], prominent [[U waves]] and [[QRS complex|QRS]] prolongation. [[Hypocalcemia]] might present with [[QT prolongation|QT interval prolongation]]. [[Hypomagnesemia]] might present with [[QT prolongation|QT interval prolongation]] and [[Ventricle (heart)|ventricular]] and [[Supraventricular tachycardia|supraventricular arrhythmia]]. | ||
==Electrocardiogram== | ==Electrocardiogram== | ||
*There are no [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] findings associated with short bowel syndrome. | *There are no [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] findings associated with short bowel syndrome. | ||
*In case of [[malnutrition]] and [[Electrolyte disturbance|electrolyte imbalance]], an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] may be helpful. | *In case of [[malnutrition]] and [[Electrolyte disturbance|electrolyte imbalance]], an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] may be helpful.<ref name="pmid15261358">{{cite journal |vauthors=Diercks DB, Shumaik GM, Harrigan RA, Brady WJ, Chan TC |title=Electrocardiographic manifestations: electrolyte abnormalities |journal=J Emerg Med |volume=27 |issue=2 |pages=153–60 |year=2004 |pmid=15261358 |doi=10.1016/j.jemermed.2004.04.006 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Findings on an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] suggestive of [[hypokalemia]] in a patient with short bowel syndrome include: | *Findings on an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] suggestive of [[hypokalemia]] in a patient with short bowel syndrome include:<ref name="pmid22745618">{{cite journal |vauthors=Levis JT |title=ECG diagnosis: hypokalemia |journal=Perm J |volume=16 |issue=2 |pages=57 |year=2012 |pmid=22745618 |pmc=3383164 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid22413702">{{cite journal |vauthors=Pepin J, Shields C |title=Advances in diagnosis and management of hypokalemic and hyperkalemic emergencies |journal=Emerg Med Pract |volume=14 |issue=2 |pages=1–17; quiz 17–8 |year=2012 |pmid=22413702 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid21660912">{{cite journal |vauthors=El-Sherif N, Turitto G |title=Electrolyte disorders and arrhythmogenesis |journal=Cardiol J |volume=18 |issue=3 |pages=233–45 |year=2011 |pmid=21660912 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
**[[ST segment depression]] | **[[ST segment depression]] | ||
**Low [[T wave]] | **Low [[T wave]] | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
**Increase in the amplitude and duration of the [[P-wave]] | **Increase in the amplitude and duration of the [[P-wave]] | ||
**[[Cardiac arrhythmias]] and [[AV block]] | **[[Cardiac arrhythmias]] and [[AV block]] | ||
**Ventricular ectopy | **[[Ventricular ectopy]] | ||
[[image:LowKECG.png|thumb|700px|center|An ECG in a person with a potassium level of 1.1 showing the classical ECG changes of ST segment depression, inverted T waves, large U waves, and a slightly prolonged PR interval. By James Heilman, MD - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0<ref name="File:LowKECG.JPG - Wikimedia Commons">{{cite web |url=https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=12210926 |title=File:LowKECG.JPG - Wikimedia Commons |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | |||
<br style="clear:left" /> | <br style="clear:left" /> | ||
* Findings on an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] suggestive of [[hypocalcemia]] in a patient with short bowel syndrome include:<ref name="pmid22439169">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fong J, Khan A |title=Hypocalcemia: updates in diagnosis and management for primary care |journal=Can Fam Physician |volume=58 |issue=2 |pages=158–62 |year=2012 |pmid=22439169 |pmc=3279267 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
* Findings on an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] suggestive of [[hypocalcemia]] in a patient with short bowel syndrome include: | ** Narrow [[QRS complex]] | ||
** | ** [[QT prolongation|Prolongation of the QT interval]] | ||
* Findings on an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] suggestive of [[hypomagnesemia]] in a patient with short bowel syndrome include: | * Findings on an [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] suggestive of [[hypomagnesemia]] in a patient with short bowel syndrome include:<ref name="pmid9549292">{{cite journal |vauthors=Iannello S, Prestipino M, Cavalleri A, Spina S, Belfiore F |title=[Precordial discomfort and ECG changes of repolarization associated with hypomagnesemia in a young women following colectomy for diffuse colonic lipomatosis] |language=Italian |journal=Minerva Cardioangiol |volume=45 |issue=11 |pages=581–6 |year=1997 |pmid=9549292 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
** | **[[QT prolongation|Prolongation of the QT interval]] | ||
**[[Atrioventricular block|AV block]] | |||
**[[Atrial]] ectopy | |||
**[[Supraventricular tachycardia]] | |||
**[[Cardiac ectopy|Ventricular ectopy]] | |||
**[[Torsade de pointes|Torsades de pointes]] | |||
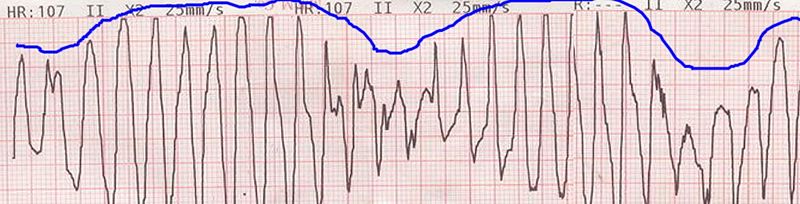
[[image:Tosadesdepointes.jpg|center|thumb|700px|EKG with a tracing to help show the twisting (blue line) pattern of complexes seen in torsade de pointes. Copyleft image obtained courtesy of Dr. C. Michael Gibson, MD.]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
| |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:Surgery]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Radiology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:10, 30 July 2020
|
Short bowel syndrome Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Short bowel syndrome electrocardiogram On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Short bowel syndrome electrocardiogram |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Short bowel syndrome electrocardiogram |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sadaf Sharfaei M.D.[2]
Overview
There are no ECG findings associated with short bowel syndrome. In case of malnutrition and electrolyte imbalance, an ECG may be helpful. Hypokalemia might present with arrhythmia, ST segment depression, low T wave, prominent U waves and QRS prolongation. Hypocalcemia might present with QT interval prolongation. Hypomagnesemia might present with QT interval prolongation and ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmia.
Electrocardiogram
- There are no ECG findings associated with short bowel syndrome.
- In case of malnutrition and electrolyte imbalance, an ECG may be helpful.[1]
- Findings on an ECG suggestive of hypokalemia in a patient with short bowel syndrome include:[2][3][4]
- ST segment depression
- Low T wave
- Prominent U waves
- Prolongation of the QRS duration
- Increase in the amplitude and duration of the P-wave
- Cardiac arrhythmias and AV block
- Ventricular ectopy
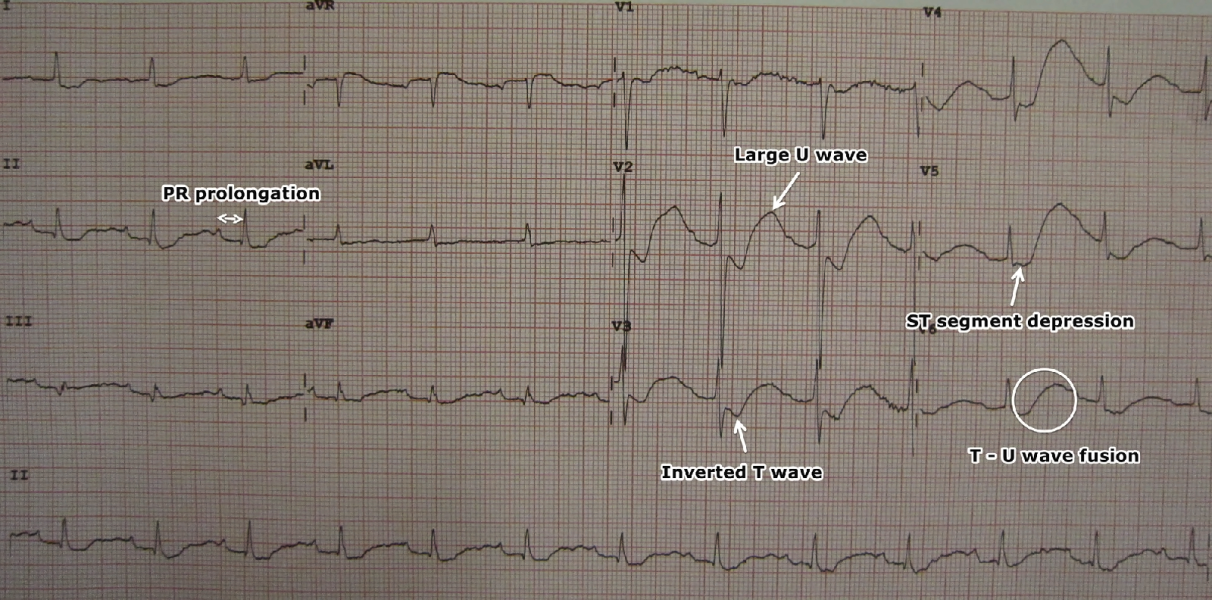
- Findings on an ECG suggestive of hypocalcemia in a patient with short bowel syndrome include:[6]
- Findings on an ECG suggestive of hypomagnesemia in a patient with short bowel syndrome include:[7]
References
- ↑ Diercks DB, Shumaik GM, Harrigan RA, Brady WJ, Chan TC (2004). "Electrocardiographic manifestations: electrolyte abnormalities". J Emerg Med. 27 (2): 153–60. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2004.04.006. PMID 15261358.
- ↑ Levis JT (2012). "ECG diagnosis: hypokalemia". Perm J. 16 (2): 57. PMC 3383164. PMID 22745618.
- ↑ Pepin J, Shields C (2012). "Advances in diagnosis and management of hypokalemic and hyperkalemic emergencies". Emerg Med Pract. 14 (2): 1–17, quiz 17–8. PMID 22413702.
- ↑ El-Sherif N, Turitto G (2011). "Electrolyte disorders and arrhythmogenesis". Cardiol J. 18 (3): 233–45. PMID 21660912.
- ↑ "File:LowKECG.JPG - Wikimedia Commons". External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Fong J, Khan A (2012). "Hypocalcemia: updates in diagnosis and management for primary care". Can Fam Physician. 58 (2): 158–62. PMC 3279267. PMID 22439169.
- ↑ Iannello S, Prestipino M, Cavalleri A, Spina S, Belfiore F (1997). "[Precordial discomfort and ECG changes of repolarization associated with hypomagnesemia in a young women following colectomy for diffuse colonic lipomatosis]". Minerva Cardioangiol (in Italian). 45 (11): 581–6. PMID 9549292.