Retinoblastoma differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Ahmed Younes (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
[[Image:Home_logo1.png|right|250px|link=https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Retinoblastoma]] | [[Image:Home_logo1.png|right|250px|link=https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Retinoblastoma]] | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}}: {{AE}} {{Simrat}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Retinoblastoma must be differentiated from other diseases that cause [[leukocoria]] such as [[congenital]] [[cataract]], persistent fetal vasculature, [[Coats disease]], [[coloboma]] of [[choroid]] or [[optic disc]], [[toxocariasis]], [[astrocytic]] [[hamartoma]], [[retinopathy of prematurity]], [[vitreous hemorrhage]], [[uveitis]], [[retinal dysplasia]], and [[medulloepithelioma]].<ref name="wiki"> Retinoblastoma. Wikipedia(2015) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Retinoblastoma#cite_note-30 Accessed on October 2, 2015</ref> | Retinoblastoma must be differentiated from other diseases that cause [[leukocoria]] such as [[congenital]] [[cataract]], persistent fetal vasculature, [[Coats disease]], [[coloboma]] of [[choroid]] or [[optic disc]], [[toxocariasis]], [[astrocytic]] [[hamartoma]], [[retinopathy of prematurity]], [[vitreous hemorrhage]], [[uveitis]], [[retinal dysplasia]], and [[medulloepithelioma]].<ref name="wiki"> Retinoblastoma. Wikipedia(2015) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Retinoblastoma#cite_note-30 Accessed on October 2, 2015</ref> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Disease/Condition}} | ! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Disease/Condition}} | ||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Age of presentation }} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Risk factors }} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Unilateral/bilateral }} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Prominent clinical feature }} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Differentiating Signs/Symptoms }} | ! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Differentiating Signs/Symptoms }} | ||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Differentiating Tests}} | ! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Differentiating Tests}} | ||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Axial length }} | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; width: 200px;" | {{fontcolor|#FFF|Imaging findings }} | |||
|- | |- | ||
| style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |Congenital Cataract | | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #DCDCDC; font-weight: bold" |Congenital Cataract | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 7 May 2019

Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]: Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Simrat Sarai, M.D. [2]
Overview
Retinoblastoma must be differentiated from other diseases that cause leukocoria such as congenital cataract, persistent fetal vasculature, Coats disease, coloboma of choroid or optic disc, toxocariasis, astrocytic hamartoma, retinopathy of prematurity, vitreous hemorrhage, uveitis, retinal dysplasia, and medulloepithelioma.[1]
Differential diagnosis
Retinoblastoma must be differentiated from other diseases that cause leukocoria. The common causes of leukocoria in children include:[1]
- Congenital cataract
- Persistent fetal vasculature
- Coats disease
Less common causes of leukocoria include:
- Coloboma of choroid or optic disc
- Toxocariasis
- Astrocytic hamartoma
- Retinopathy of prematurity (stage 4, 5)
- Vitreous hemorrhage
- Uveitis
- Retinal dysplasia
- Medulloepithelioma
Differentiating features of some common and less common differential diagnosis are:
| Disease/Condition | Age of presentation | Risk factors | Unilateral/bilateral | Prominent clinical feature | Differentiating Signs/Symptoms | Differentiating Tests | Axial length | Imaging findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital Cataract |
|
| ||||||
| Coats disease (exudative retinitis or retinal telangiectasis) |
|
| ||||||
| Persistent fetal vasculature (formerly known as persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous) |
|
| ||||||
| Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) |
|
| ||||||
| Ocular toxocariasis |
|
|
| Disease | Prominent clinical feature | Radiological findings |
|---|---|---|
| Ocular cysticercosis |
|
|
| Retinal detachment |
|
|
| Hyperthyroid Ophthalmopathy |
|
|
| Retinoblastoma |
|
|
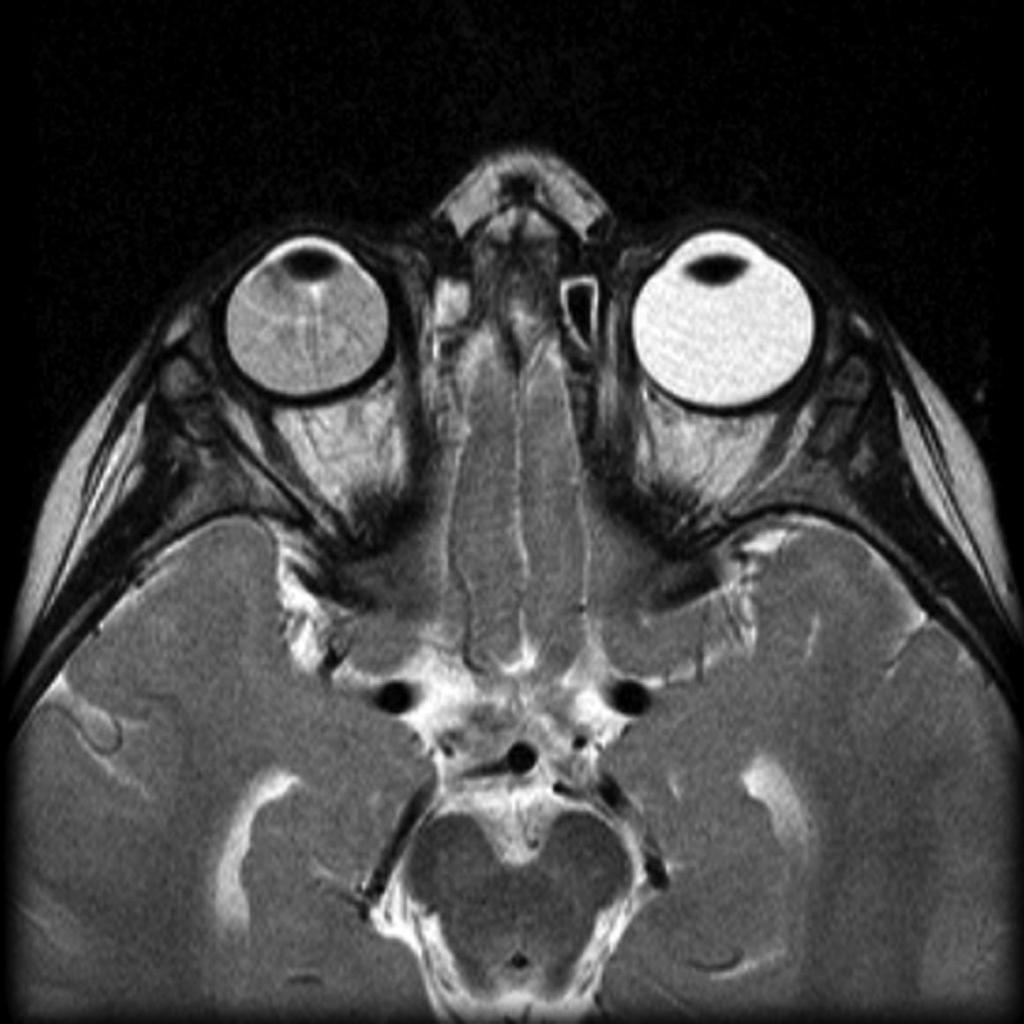 |
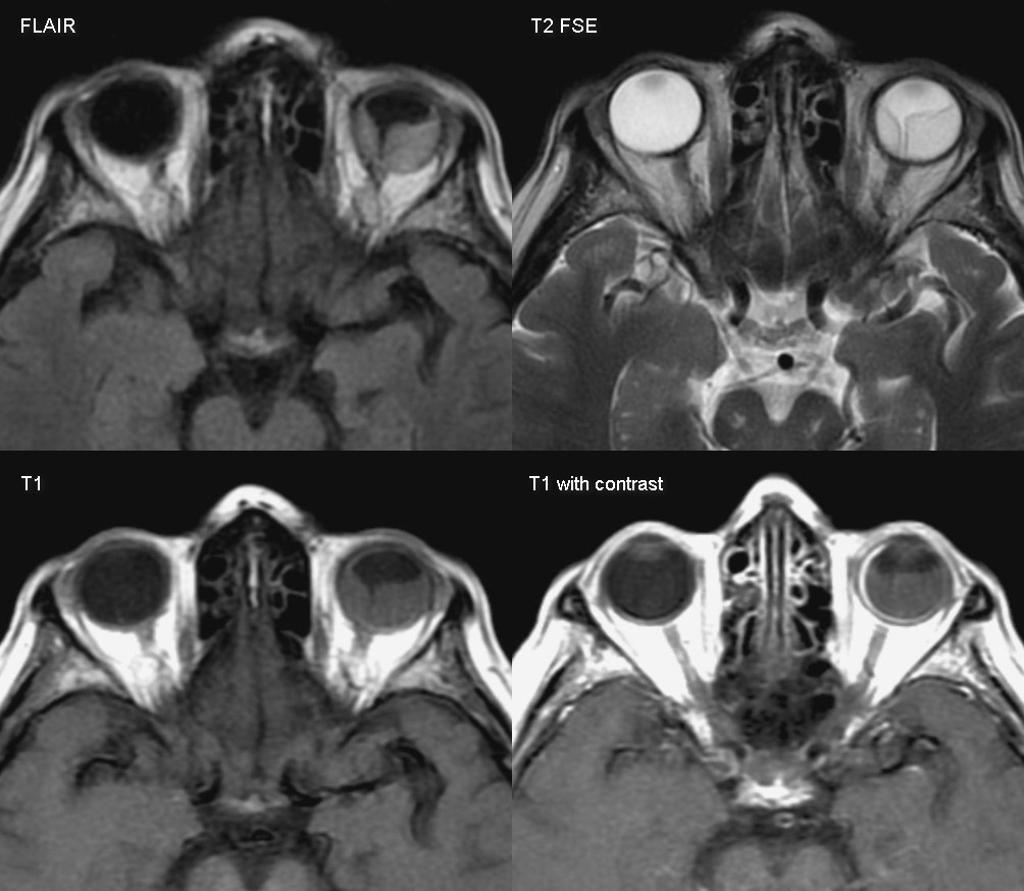 |
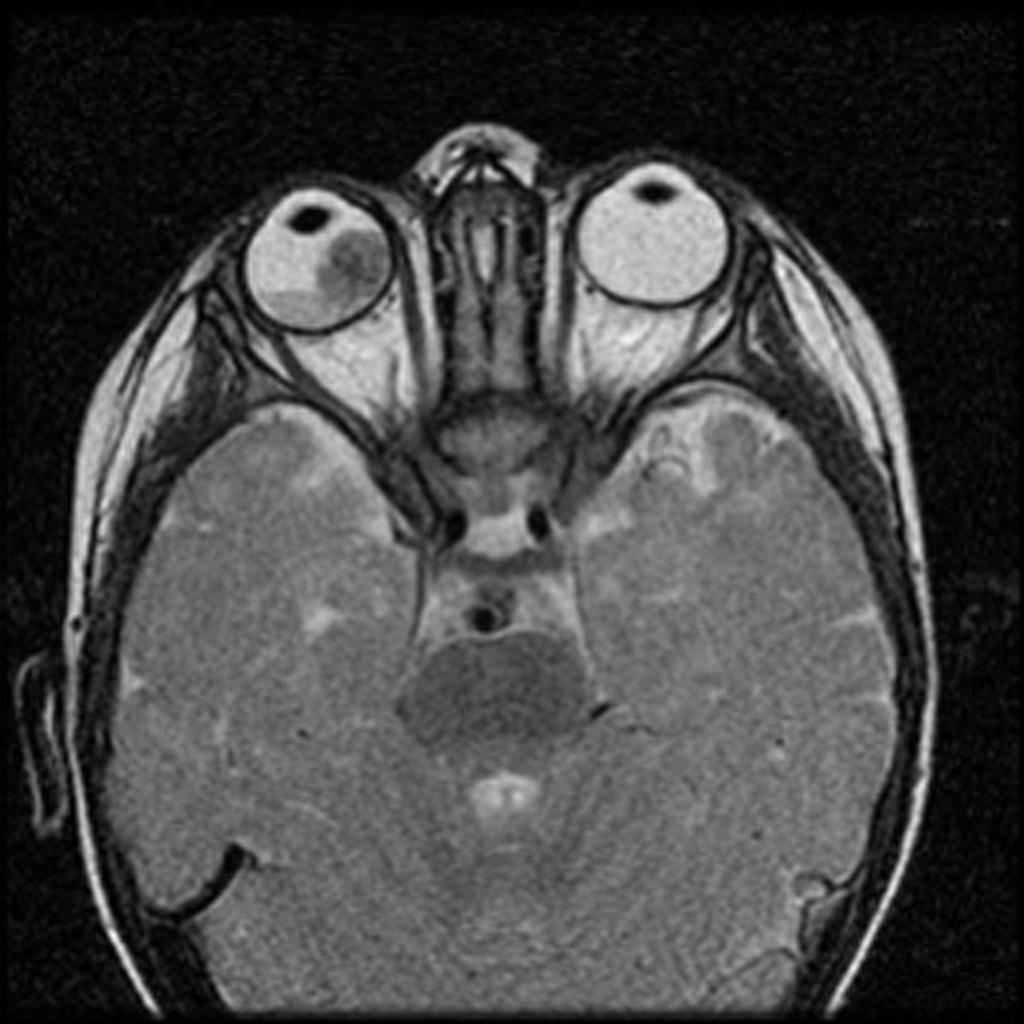 |
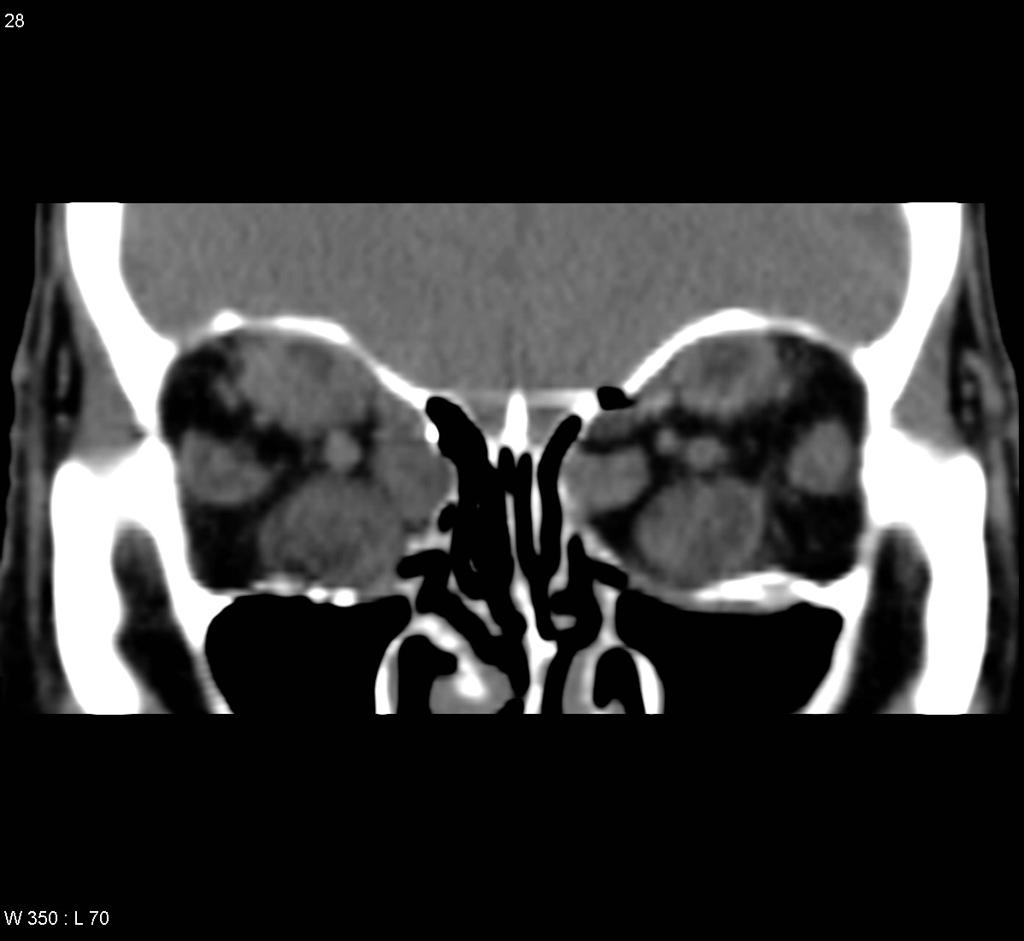 |
|---|
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Retinoblastoma. Wikipedia(2015) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Retinoblastoma#cite_note-30 Accessed on October 2, 2015
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "How to Diagnose and Manage Coats' Disease".
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Management of retinal detachment: a guide for non-ophthalmologists".
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Thyroid Ophthalmopathy - EyeWiki".
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "c.ymcdn.com".