Nefopam: Difference between revisions
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{WikiDoc Cardiology Network Infobox}} +, -<references /> +{{reflist|2}}, -{{reflist}} +{{reflist|2}})) |
Kiran Singh (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Drugbox | {{Drugbox | ||
| Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| Watchedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 445783136 | |||
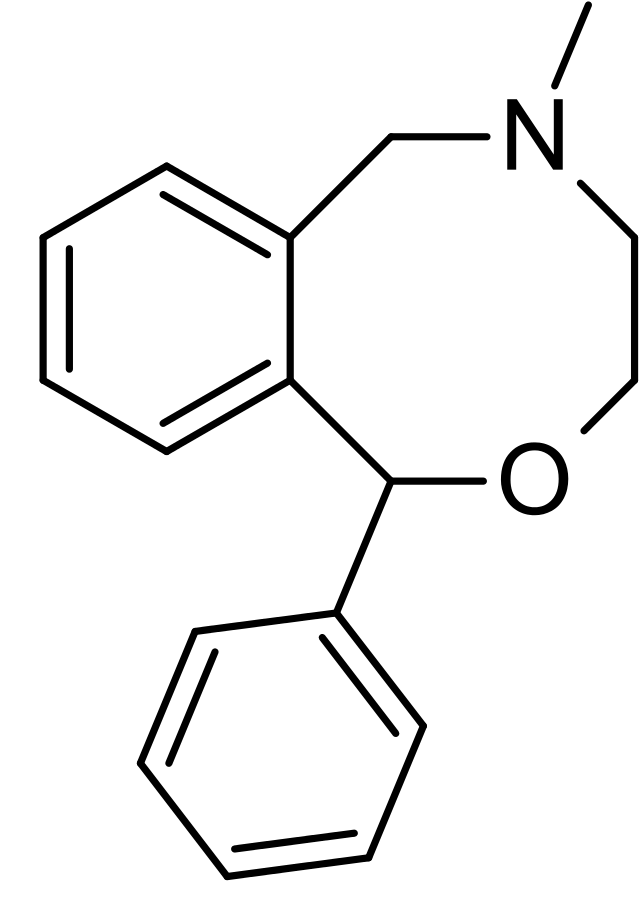
| IUPAC_name = 5-methyl-1-phenyl-1,3,4,6-tetrahydro-2,5-benzoxazocine | | IUPAC_name = 5-methyl-1-phenyl-1,3,4,6-tetrahydro-2,5-benzoxazocine | ||
| image = | | image = Nefopam2DACS.png | ||
| width = 130px | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| tradename = Acupan | |||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|international|nefopam}} | |||
| pregnancy_category = | |||
| legal_AU = S4 | |||
| legal_UK = POM | |||
| routes_of_administration = Oral, Intravenous, Intramuscular | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = | |||
| protein_bound = 73% | |||
| metabolism = Hepatic | |||
| elimination_half-life = 4-6 hours | |||
| excretion = Urine, faeces (6%) | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 13669-70-0 | | CAS_number = 13669-70-0 | ||
| ATC_prefix = N02 | | ATC_prefix = N02 | ||
| ATC_suffix = BG06 | | ATC_suffix = BG06 | ||
| PubChem = 4450 | | PubChem = 4450 | ||
| | | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | ||
| C=17|H=19|N=1|O=1 | | UNII = 4UP8060B7J | ||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = D08258 | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 4295 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| C=17 | H=19 | N=1 | O=1 | |||
| molecular_weight = 253.34 g/mol | | molecular_weight = 253.34 g/mol | ||
| | | smiles = CN1CCOC(C2=CC=CC=C2C1)C3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| InChI = 1/C17H19NO/c1-18-11-12-19-17(14-7-3-2-4-8-14)16-10-6-5-9-15(16)13-18/h2-10,17H,11-13H2,1H3 | |||
| InChIKey = RGPDEAGGEXEMMM-UHFFFAOYAV | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C17H19NO/c1-18-11-12-19-17(14-7-3-2-4-8-14)16-10-6-5-9-15(16)13-18/h2-10,17H,11-13H2,1H3 | |||
| | | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | ||
| | | StdInChIKey = RGPDEAGGEXEMMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
}} | }} | ||
'''Nefopam''' ( | __Notoc__ | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{CMG}} | |||
==Overview== | |||
'''Nefopam''' (brand names: '''Acupan''', '''Silentan''', '''Nefadol''' and '''Ajan''') is a centrally-acting but non-opioid [[analgesic]] [[drug]] of the benzoxazocine [[chemical class]] which was developed by Riker Laboratories in the 1960s.<ref>US Patent 3830803</ref> It is widely used, mainly in [[Europe]]an countries, for the relief of moderate to severe pain as an alternative to [[opioid]] analgesic drugs. Animal studies have shown that nefopam has a potentiating (analgesic-sparing) effect on morphine and other opioids by broadening the antinociceptive action of the opioid and possibly other mechanisms, generally lowering the dose requirements of both when they are used concomitantly.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Girard|first=P|author2=Pansart, Y |author3=Gillardin, JM |title=Nefopam potentiates morphine antinociception in allodynia and hyperalgesia in the rat.|journal=Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior|date=April 2004|volume=77|issue=4|pages=695-703|pmid=15099914|doi=10.1016/j.pbb.2004.01.018}}</ref> | |||
== Use == | |||
Nefopam has additional action in the prevention of shivering, which may be a side effect of other drugs used in surgery.<ref name="Alfonsi">{{cite journal | author= Alfonsi P, Adam F, Passard A, Guignard B, Sessler DI, Chauvin M | title= Nefopam, a Non-sedative Benzoxazocine Analgesic, Selectively Reduces the Shivering Threshold | journal=Anesthesiology |date=January 2004 | pages=37–43 | volume=100 | issue=1 | pmid=14695722 | doi= 10.1097/00000542-200401000-00010 | pmc= 1283107}}</ref> Nefopam was significantly more effective than [[aspirin]] as an analgesic in one clinical trial,<ref name="Cohen">{{cite journal | author= Cohen A, Hernandez CM | title= Nefopam hydrochloride: new analgesic agent | journal= Journal of International Medical Research | year=1976 | pages=138–43 | volume=4 | issue=2 | pmid=799984}}</ref> although with a greater incidence of side effects such as sweating, dizziness and nausea, especially at higher doses.<ref name="Wang">{{cite journal | author= Wang RI, Waite EM | title= The clinical analgesic efficacy of oral nefopam hydrochloride | journal= Journal of Clinical Pharmacology |date=July 1979 | pages= 395–402 | volume=19 | issue=7 | pmid=479385 | doi=10.1002/j.1552-4604.1979.tb02498.x}}</ref><ref name="Pillians">{{cite journal | author= Pillans PI, Woods DJ | title= Adverse reactions associated with nefopam | journal= New Zealand Medical Journal |date=September 1995 | pages= 382–4 | volume= 108 | issue= 1008 | pmid=7566787}}</ref> Nefopam is around a third to half the potency and slightly less effective as an analgesic compared to [[morphine]],<ref name="Sunshine">{{cite journal | author= Sunshine A, Laska E | |||
| title= Nefopam and morphine in man | journal= Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics |date=November 1975 | pages= 530–4 | volume= 18 | issue= (5 Pt 1) | pmid=1102231}}</ref><ref name="Phillips">{{cite journal | author= Phillips G, Vickers MD | title= Nefopam in postoperative pain | journal= British Journal of Anaesthesia |date=October 1979 | pages= 961–5 | volume=51 | issue=10 | pmid=391253 | doi= 10.1093/bja/51.10.961}}</ref><ref name="Heel">{{cite journal | author= Heel RC, Brogden RN, Pakes GE, Speight TM, Avery GS | title= Nefopam: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy | |||
| journal= Drugs | year=1980 | pages= 249–67 | volume= 19 | issue=4 | pmid=6991238 | doi= 10.2165/00003495-198019040-00001}}</ref> or [[oxycodone]],<ref name="Tigerstedt">{{cite journal | author= Tigerstedt I, Tammisto T, Leander P | title=Comparison of the analgesic dose-effect relationships of nefopam and oxycodone in postoperative pain | journal= Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica |date=December 1979 | pages= 555–60 | volume=23 | issue= 6 | pmid=397711 | doi= 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1979.tb01486.x}}</ref> but tends to produce fewer side effects, does not produce respiratory depression,<ref name="Gasser">{{cite journal | author= Gasser JC, Bellville JW | title= Respiratory effects of nefopam | journal= Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics |date=August 1975 | pages=175–9 | volume=18 | issue=2 | pmid=1097153}}</ref> and has much less [[drug abuse|abuse]] potential, and so is useful either as an alternative to opioids, or as an adjunctive treatment for use alongside opioid(s) or other analgesics.<ref name="Heel">{{cite journal | author= Heel RC, Brogden RN, Pakes GE, Speight TM, Avery GS | title= Nefopam: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy | |||
| journal= Drugs | year=1980 | pages= 249–67 | volume= 19 | issue=4 | pmid=6991238 | doi= 10.2165/00003495-198019040-00001}}</ref><ref name="Kapfer">{{cite journal | author= Kapfer B, Alfonsi P, Guignard B, Sessler DI, Chauvin M | title= Nefopam and Ketamine Comparably Enhance Postoperative Analgesia | journal= Anesthesia and Analgesia |date=January 2005 | pages= 169–74 | volume=100 | issue=1 | pmid=15616073 | doi= 10.1213/01.ANE.0000138037.19757.ED | pmc= 1283103}}</ref> Nefopam is also used to combat severe hiccups.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Bilotta|first=F|author2=Rosa, G|title=Nefopam for severe hiccups.|journal=The New England Journal of Medicine|date=December 2000|volume=343|issue=26|pages=1973-4|pmid=11186682|doi=10.1056/nejm200012283432619}}</ref> | |||
==Side effects== | |||
Common side effects include nausea, nervousness, dry mouth, light-headedness and [[urinary retention]].<ref name = MS>{{cite web|title=Data Sheet ACUPAN™ Nefopam hydrochloride 30 mg tablets 20 mg intramuscular injection|work=Medsafe New Zealand|publisher=iNova Pharmaceuticals (New Zealand) Limited|date=3 September 2007|url=http://www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/datasheet/a/acupantabinj.pdf|format=PDF|accessdate=10 March 2014}}</ref> Less common side effects include vomiting, blurred vision, drowsiness, sweating, insomnia, headache, confusion, hallucinations, tachycardia, aggravation of angina and rarely a temporary and benign pink discolouration of the skin or [[erythema multiforme]].<ref name = MS/> | |||
===Contraindications=== | |||
It is contraindicated in people with convulsive disorders, those that have received treatment with irreversible [[monoamine oxidase inhibitors]] such as [[phenelzine]], [[tranylcypromine]] or [[isocarboxazid]] within the past 30 days and those with [[myocardial infarction]] pain, mostly due to a lack of safety data in these conditions.<ref name = MS/> | |||
=== Interactions === | |||
It has additive anticholinergic and sympathomimetic effects with other agents with these properties.<ref name = MS/> Its use should be avoided in people receiving some types of antidepressants ([[tricyclic antidepressants]] or [[monoamine oxidase inhibitors]]) as there is the potential for [[serotonin syndrome]] or [[hypertensive crises]] to result.<ref name = MS/> | |||
== | === Recreational use and overdose === | ||
Recreational use of nefopam and death from overdose have both been reported,<ref>{{cite journal|last=Bismuth|first=C|author2=Fournier, PE |author3=Bavoux, E |author4=Husson, O |author5= Lafon, D |title=[Chronic abuse of the analgesic nefopam (Acupan)].|journal=Journal de Toxicologie Clinique et Experimentale|date=September 1987|volume=7|issue=5|pages=343-6|pmid=3448182|language=French}}</ref> although these events are less common with nefopam than with opioid analgesic drugs.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Tracqui|first=A|author2=Berthelon, L |author3=Ludes, B |title=Fatal overdosage with nefopam (Acupan).|journal=Journal of Analytical Toxicology|date=May 2002|volume=26|issue=4|pages=239-43|doi=10.1093/jat/26.4.239|pmid=12054367|format=PDF|url=http://jat.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/4/239.full.pdf}}</ref> Overdose usually manifests with convulsions, hallucinations, tachycardia and hyperdynamic circulation.<ref name = MS/> Treatment is usually supportive, managing cardiovascular complications with [[beta-blockers]] and limiting absorption with activated charcoal.<ref name = MS/> | |||
== Pharmacology == | |||
The mechanism of action of nefopam is not well understood, although inhibition of [[serotonin]], [[dopamine]] and [[noradrenaline]] [[reuptake]] is thought to be involved in its analgesic effects,<ref name="Esposito">{{cite journal | author= Esposito, E; Romandini, S; Merlo-Pich, E; Mennini, T; Samanin, R | title= Evidence of the involvement of dopamine in the analgesic effect of nefopam | journal= European Journal of Pharmacology | date= September 9, 1986 | pages=157–64 | volume=128 | issue=3 | pmid=3098570 | doi= 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90762-4}}</ref><ref name="Marazziti">{{cite journal | author= Marazziti, D; Rotondo, A; Ambrogi, F; Cassano, GB | title= Analgesia by nefopam: does it act through serotonin? | journal= Drugs under Experimental and Clinical Research | year= 1991 | pages=259–61 | volume=17 | issue=5 | pmid=1756689}}</ref><ref name="Fuller">{{cite journal | author= Fuller RW, Snoddy HD | title= Evaluation of nefopam as a monoamine uptake inhibitor in vivo in mice | journal= Neuropharmacology |date=October 1993 | pages=995–9 | volume=32 | issue=10 | pmid= 7507578| accessdate= | doi= 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90064-A }}</ref> and there may be other modes of action such as through [[histamine H3 receptor]]s<ref name="Girard">{{cite journal | author= Girard, P; Pansart, Y; Coppé, MC; Verniers, D; Gillardin, JM | title= Role of the histamine system in nefopam-induced antinociception in mice | journal= European Journal of Pharmacology | date= October 25, 2004 | pages= 63–9 | volume=503 | issue=1–3 | pmid=15496297 | doi= 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.09.030}}</ref> and glutamate.<ref name="Verleye">{{cite journal | author= Verleye, M; André, N; Heulard, I; Gillardin, JM | title= Nefopam blocks voltage-sensitive sodium channels and modulates glutamatergic transmission in rodents | journal= Brain Research | date= July 9, 2004 | pages= 249–55 | volume= 1013 | issue=2 | pmid=15193535 | doi= 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.035}}</ref> Recently, like its analogue [[orphenadrine]] which also has analgesic effects, nefopam has been found to act as a [[voltage-gated sodium channel]] [[sodium channel blocker|blocker]], and this may in part or fully mediate its [[antinociceptive]] effects.<ref name="pmid15193535">{{cite journal | author = Verleye, M; André, N; Heulard, I; Gillardin, JM | title = Nefopam blocks voltage-sensitive sodium channels and modulates glutamatergic transmission in rodents | journal = Brain Research | volume = 1013 | issue = 2 | pages = 249–55 |date=July 2004 | pmid = 15193535 | doi = 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.035 | url = http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0006899304006444}}</ref> | |||
The mechanism of action of nefopam is not well understood, although inhibition of [[serotonin]], [[dopamine]] and [[noradrenaline]] [[reuptake]] is thought to be involved in its analgesic effects,<ref name="Esposito">{{cite journal | author= Esposito E, | |||
== | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align: right;" | ||
|+ K<sub>i</sub> values (Human)<ref>{{cite journal|last=Gregori-Puigjané|first=E.|author2=Setola, V |author3=Hert, J |author4=Crews, BA |author5=Irwin, JJ |author6=Lounkine, E |author7=Marnett, L |author8=Roth, BL |author9= Shoichet, BK |title=Identifying mechanism-of-action targets for drugs and probes|journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|date=18 June 2012|volume=109|issue=28|pages=11178–11183|doi=10.1073/pnas.1204524109|pmid=22711801|url=http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2012/06/12/1204524109.full.pdf|format=PDF}}</ref> | |||
! scope="col" | Receptor || K<sub>i</sub> (nM) | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | [[5-HT2A|5-HT<sub>2A</sub>]] | |||
| 1685 | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | [[5-HT2B|5-HT<sub>2B</sub>]] | |||
| 329.5 | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | [[5-HT2C|5-HT<sub>2C</sub>]] | |||
| 56 | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | [[Dopamine_transporter|DAT]] | |||
| 531 | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | [[Norepinephrine_transporter|NET]] | |||
| 33 | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | [[Serotonin_transporter|SERT]] | |||
| 29 | |||
|} | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Orphenadrine]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
{{ | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{Analgesics}} | {{Analgesics}} | ||
{{Histaminergics}} | |||
{{Monoaminergics}} | |||
{{Sodium channel blockers}} | |||
[[Category:Analgesics]] | [[Category:Analgesics]] | ||
[[Category:Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors]] | |||
[[Category:Drugs with unknown mechanisms of action]] | |||
Revision as of 18:01, 8 April 2015
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Acupan |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, Intravenous, Intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 73% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 4-6 hours |
| Excretion | Urine, faeces (6%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H19NO |
| Molar mass | 253.34 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Nefopam |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Nefopam |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Nefopam at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Nefopam at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Nefopam
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Nefopam Risk calculators and risk factors for Nefopam
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Nefopam |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Nefopam (brand names: Acupan, Silentan, Nefadol and Ajan) is a centrally-acting but non-opioid analgesic drug of the benzoxazocine chemical class which was developed by Riker Laboratories in the 1960s.[1] It is widely used, mainly in European countries, for the relief of moderate to severe pain as an alternative to opioid analgesic drugs. Animal studies have shown that nefopam has a potentiating (analgesic-sparing) effect on morphine and other opioids by broadening the antinociceptive action of the opioid and possibly other mechanisms, generally lowering the dose requirements of both when they are used concomitantly.[2]
Use
Nefopam has additional action in the prevention of shivering, which may be a side effect of other drugs used in surgery.[3] Nefopam was significantly more effective than aspirin as an analgesic in one clinical trial,[4] although with a greater incidence of side effects such as sweating, dizziness and nausea, especially at higher doses.[5][6] Nefopam is around a third to half the potency and slightly less effective as an analgesic compared to morphine,[7][8][9] or oxycodone,[10] but tends to produce fewer side effects, does not produce respiratory depression,[11] and has much less abuse potential, and so is useful either as an alternative to opioids, or as an adjunctive treatment for use alongside opioid(s) or other analgesics.[9][12] Nefopam is also used to combat severe hiccups.[13]
Side effects
Common side effects include nausea, nervousness, dry mouth, light-headedness and urinary retention.[14] Less common side effects include vomiting, blurred vision, drowsiness, sweating, insomnia, headache, confusion, hallucinations, tachycardia, aggravation of angina and rarely a temporary and benign pink discolouration of the skin or erythema multiforme.[14]
Contraindications
It is contraindicated in people with convulsive disorders, those that have received treatment with irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors such as phenelzine, tranylcypromine or isocarboxazid within the past 30 days and those with myocardial infarction pain, mostly due to a lack of safety data in these conditions.[14]
Interactions
It has additive anticholinergic and sympathomimetic effects with other agents with these properties.[14] Its use should be avoided in people receiving some types of antidepressants (tricyclic antidepressants or monoamine oxidase inhibitors) as there is the potential for serotonin syndrome or hypertensive crises to result.[14]
Recreational use and overdose
Recreational use of nefopam and death from overdose have both been reported,[15] although these events are less common with nefopam than with opioid analgesic drugs.[16] Overdose usually manifests with convulsions, hallucinations, tachycardia and hyperdynamic circulation.[14] Treatment is usually supportive, managing cardiovascular complications with beta-blockers and limiting absorption with activated charcoal.[14]
Pharmacology
The mechanism of action of nefopam is not well understood, although inhibition of serotonin, dopamine and noradrenaline reuptake is thought to be involved in its analgesic effects,[17][18][19] and there may be other modes of action such as through histamine H3 receptors[20] and glutamate.[21] Recently, like its analogue orphenadrine which also has analgesic effects, nefopam has been found to act as a voltage-gated sodium channel blocker, and this may in part or fully mediate its antinociceptive effects.[22]
| Receptor | Ki (nM) |
|---|---|
| 5-HT2A | 1685 |
| 5-HT2B | 329.5 |
| 5-HT2C | 56 |
| DAT | 531 |
| NET | 33 |
| SERT | 29 |
See also
References
- ↑ US Patent 3830803
- ↑ Girard, P; Pansart, Y; Gillardin, JM (April 2004). "Nefopam potentiates morphine antinociception in allodynia and hyperalgesia in the rat". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 77 (4): 695–703. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2004.01.018. PMID 15099914.
- ↑ Alfonsi P, Adam F, Passard A, Guignard B, Sessler DI, Chauvin M (January 2004). "Nefopam, a Non-sedative Benzoxazocine Analgesic, Selectively Reduces the Shivering Threshold". Anesthesiology. 100 (1): 37&ndash, 43. doi:10.1097/00000542-200401000-00010. PMC 1283107. PMID 14695722.
- ↑ Cohen A, Hernandez CM (1976). "Nefopam hydrochloride: new analgesic agent". Journal of International Medical Research. 4 (2): 138&ndash, 43. PMID 799984.
- ↑ Wang RI, Waite EM (July 1979). "The clinical analgesic efficacy of oral nefopam hydrochloride". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 19 (7): 395&ndash, 402. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1979.tb02498.x. PMID 479385.
- ↑ Pillans PI, Woods DJ (September 1995). "Adverse reactions associated with nefopam". New Zealand Medical Journal. 108 (1008): 382&ndash, 4. PMID 7566787.
- ↑ Sunshine A, Laska E (November 1975). "Nefopam and morphine in man". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 18 ((5 Pt 1)): 530&ndash, 4. PMID 1102231.
- ↑ Phillips G, Vickers MD (October 1979). "Nefopam in postoperative pain". British Journal of Anaesthesia. 51 (10): 961&ndash, 5. doi:10.1093/bja/51.10.961. PMID 391253.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Heel RC, Brogden RN, Pakes GE, Speight TM, Avery GS (1980). "Nefopam: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy". Drugs. 19 (4): 249&ndash, 67. doi:10.2165/00003495-198019040-00001. PMID 6991238.
- ↑ Tigerstedt I, Tammisto T, Leander P (December 1979). "Comparison of the analgesic dose-effect relationships of nefopam and oxycodone in postoperative pain". Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 23 (6): 555&ndash, 60. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.1979.tb01486.x. PMID 397711.
- ↑ Gasser JC, Bellville JW (August 1975). "Respiratory effects of nefopam". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 18 (2): 175&ndash, 9. PMID 1097153.
- ↑ Kapfer B, Alfonsi P, Guignard B, Sessler DI, Chauvin M (January 2005). "Nefopam and Ketamine Comparably Enhance Postoperative Analgesia". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 100 (1): 169&ndash, 74. doi:10.1213/01.ANE.0000138037.19757.ED. PMC 1283103. PMID 15616073.
- ↑ Bilotta, F; Rosa, G (December 2000). "Nefopam for severe hiccups". The New England Journal of Medicine. 343 (26): 1973–4. doi:10.1056/nejm200012283432619. PMID 11186682.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 "Data Sheet ACUPAN™ Nefopam hydrochloride 30 mg tablets 20 mg intramuscular injection" (PDF). Medsafe New Zealand. iNova Pharmaceuticals (New Zealand) Limited. 3 September 2007. Retrieved 10 March 2014.
- ↑ Bismuth, C; Fournier, PE; Bavoux, E; Husson, O; Lafon, D (September 1987). "[Chronic abuse of the analgesic nefopam (Acupan)]". Journal de Toxicologie Clinique et Experimentale (in French). 7 (5): 343–6. PMID 3448182.
- ↑ Tracqui, A; Berthelon, L; Ludes, B (May 2002). "Fatal overdosage with nefopam (Acupan)" (PDF). Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 26 (4): 239–43. doi:10.1093/jat/26.4.239. PMID 12054367.
- ↑ Esposito, E; Romandini, S; Merlo-Pich, E; Mennini, T; Samanin, R (September 9, 1986). "Evidence of the involvement of dopamine in the analgesic effect of nefopam". European Journal of Pharmacology. 128 (3): 157&ndash, 64. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(86)90762-4. PMID 3098570.
- ↑ Marazziti, D; Rotondo, A; Ambrogi, F; Cassano, GB (1991). "Analgesia by nefopam: does it act through serotonin?". Drugs under Experimental and Clinical Research. 17 (5): 259&ndash, 61. PMID 1756689.
- ↑ Fuller RW, Snoddy HD (October 1993). "Evaluation of nefopam as a monoamine uptake inhibitor in vivo in mice". Neuropharmacology. 32 (10): 995&ndash, 9. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(93)90064-A. PMID 7507578.
- ↑ Girard, P; Pansart, Y; Coppé, MC; Verniers, D; Gillardin, JM (October 25, 2004). "Role of the histamine system in nefopam-induced antinociception in mice". European Journal of Pharmacology. 503 (1–3): 63&ndash, 9. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.09.030. PMID 15496297.
- ↑ Verleye, M; André, N; Heulard, I; Gillardin, JM (July 9, 2004). "Nefopam blocks voltage-sensitive sodium channels and modulates glutamatergic transmission in rodents". Brain Research. 1013 (2): 249&ndash, 55. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.035. PMID 15193535.
- ↑ Verleye, M; André, N; Heulard, I; Gillardin, JM (July 2004). "Nefopam blocks voltage-sensitive sodium channels and modulates glutamatergic transmission in rodents". Brain Research. 1013 (2): 249–55. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.035. PMID 15193535.
- ↑ Gregori-Puigjané, E.; Setola, V; Hert, J; Crews, BA; Irwin, JJ; Lounkine, E; Marnett, L; Roth, BL; Shoichet, BK (18 June 2012). "Identifying mechanism-of-action targets for drugs and probes" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 109 (28): 11178–11183. doi:10.1073/pnas.1204524109. PMID 22711801.
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- CS1 maint: Unrecognized language
- Template:drugs.com link with non-standard subpage
- Articles with changed ChemSpider identifier
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles with changed InChI identifier
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- Analgesics
- Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors
- Drugs with unknown mechanisms of action