Minoxidil (oral): Difference between revisions
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
* Allergic | * Allergic | ||
:* [[Rash]]es have been reported, including rare reports of bullous eruptions, and Stevens-Johnson | :* [[Rash]]es have been reported, including rare reports of bullous eruptions, and [[Stevens-Johnson syndrome]]. | ||
* Hematologic | |||
:* [[Thrombocytopenia]] and [[leukopenia]] (WBC <3000/mm<sup>3</sup>) have rarely been reported. | |||
* Gastrointestinal | |||
:* [[Nausea]] and/or [[vomiting]] has been reported. In clinical trials the incidence of [[nausea]] and [[vomiting]] associated with the underlying disease has shown a decrease from pretrial levels. | |||
* Miscellaneous | |||
:* Breast tenderness developed in less than 1% of patients. | |||
* Altered Laboratory Findings | |||
:* [[ECG]] changes: | |||
::* Changes in direction and magnitude of the ECG T-waves occur in approximately 60% of patients treated with minoxidil. In rare instances a large negative amplitude of the [[T wave]] may encroach upon the S-T segment, but the S-T segment is not independently altered. These changes usually disappear with continuance of treatment and revert to the pretreatment state if minoxidil is discontinued. No symptoms have been associated with these changes, nor have there been alterations in blood cell counts or in plasma enzyme concentrations that would suggest myocardial damage. Long-term treatment of patients manifesting such changes has provided no evidence of deteriorating cardiac function. At present the changes appear to be nonspecific and without identifiable clinical significance. | |||
:* Effects of hemodilution | |||
::* [[Hematocrit]], [[hemoglobin]], and [[erythrocyte]] count usually fall about 7% initially and then recover to pretreatment levels. | |||
* Other | |||
:* [[Alkaline phosphatase]] increased varyingly without other evidence of liver or bone abnormality. | |||
:* Serum [[creatinine]] increased an average of 6% and [[BUN]] slightly more, but later declined to pretreatment levels. | |||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | <!--Drug Interactions--> | ||
| Line 186: | Line 203: | ||
|drugInteractions= | |drugInteractions= | ||
* Guanethidine | * [[Guanethidine]] | ||
:* Although minoxidil does not itself cause orthostatic hypotension, its administration to patients already receiving guanethidine can result in profound orthostatic effects. If at all possible, guanethidine should be discontinued well before minoxidil is begun. Where this is not possible, minoxidil therapy should be started in the hospital and the patient should remain institutionalized until severe orthostatic effects are no longer present or the patient has learned to avoid activities that provoke them. | :* Although minoxidil does not itself cause [[orthostatic hypotension]], its administration to patients already receiving [[guanethidine]] can result in profound orthostatic effects. If at all possible, [[guanethidine]] should be discontinued well before minoxidil is begun. Where this is not possible, minoxidil therapy should be started in the hospital and the patient should remain institutionalized until severe orthostatic effects are no longer present or the patient has learned to avoid activities that provoke them. | ||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | <!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
Revision as of 21:13, 3 July 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNINGS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Minoxidil tablets contain the powerful antihypertensive agent, minoxidil, which may produce serious adverse effects. It can cause pericardial effusion, occasionally progressing to tamponade, and angina pectoris may be exacerbated. Minoxidil should be reserved for hypertensive patients who do not respond adequately to maximum therapeutic doses of a diuretic and two other antihypertensive agents.
|
Overview
Minoxidil (oral) is a vasodilator that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of hypertension that is symptomatic or associated with target organ damage and is not manageable with maximum therapeutic doses of diuretic plus two other antihypertensive drugs. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include hypotension, hirsutism, hypertrichosis, fluid retention, and hypernatremia.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Refractory Hypertension Associated with End Organ Damage
- Dosing Information
- Initial Dosage
- 5 mg/day PO as single dose or 2 divided doses; adjust in 100% increments as required
- Maintenance Dosage
- 10-40 mg/day ORALLY daily in 1-2 divided doses; maximum 100 mg/day
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Minoxidil (oral) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Minoxidil (oral) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Refractory Hypertension Associated with End Organ Damage
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
- Initial Dosage
- 0.2 mg/kg/day PO in a single dose or as 2 divided doses; adjust as required up to 50 mg/day
- Maintenance Dosage
- 0.25-1 mg/kg/day PO in a single dose or as 2 divided daily doses; maximum 50 mg/day
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Minoxidil (oral) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Minoxidil (oral) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Minoxidil tablets are contraindicated in pheochromocytoma, because it may stimulate secretion of catecholamines from the tumor through its antihypertensive action.
- Minoxidil tablets are contraindicated in those patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of the components of the preparation.
Warnings
|
WARNINGS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
* Minoxidil tablets contain the powerful antihypertensive agent, minoxidil, which may produce serious adverse effects. It can cause pericardial effusion, occasionally progressing to tamponade, and angina pectoris may be exacerbated. Minoxidil should be reserved for hypertensive patients who do not respond adequately to maximum therapeutic doses of a diuretic and two other antihypertensive agents.
|
Salt and Water Retention
- Congestive Heart Failure — concomitant use of an adequate diuretic is required — Minoxidil tablets must usually be administered concomitantly with a diuretic adequate to prevent fluid retention and possible congestive heart failure; a high ceiling (loop) diuretic is almost always required. Body weight should be monitored closely. If minoxidil is used without a diuretic, retention of several hundred milliequivalents of salt and corresponding volumes of water can occur within a few days, leading to increased plasma and interstitial fluid volume and local or generalized edema. diuretic treatment alone, or in combination with restricted salt intake, will usually minimize fluid retention, although reversible edema did develop in approximately 10% of nondialysis patients so treated. Ascites has also been reported. diuretic effectiveness was limited mostly by disease-related impaired renal function. The condition of patients with pre-existing congestive heart failure occasionally deteriorated in association with fluid retention although because of the fall in blood pressure (reduction of afterload), more than twice as many improved than worsened. Rarely, refractory fluid retention may require discontinuation of minoxidil. Provided that the patient is under close medical supervision, it may be possible to resolve refractory salt retention by discontinuing minoxidil for 1 or 2 days and then resuming treatment in conjunction with vigorous diuretic therapy.
Concomitant Treatment to Prevent Tachycardia is Usually Required
- Minoxidil increases the heart rate. Angina may worsen or appear for the first time during minoxidil treatment, probably because of the increased oxygen demands associated with increased heart rate and cardiac output. The increase in rate and the occurrence of angina generally can be prevented by the concomitant administration of a beta-adrenergic blocking drug or other sympathetic nervous system suppressant. The ability of beta-adrenergic blocking agents to minimize papillary muscle lesions in animals is further reason to utilize such an agent concomitantly. Round-the-clock effectiveness of the sympathetic suppressant should be ensured.
Pericarditis, Pericardial Effusion and Tamponade
- There have been reports of pericarditis occurring in association with the use of minoxidil. The relationship of this association to renal status is uncertain. Pericardial effusion, occasionally with tamponade, has been observed in about 3% of treated patients not on dialysis, especially those with inadequate or compromised renal function. Although in many cases, the pericardial effusion was associated with a connective tissue disease, the uremic syndrome, congestive heart failure, or marked fluid retention, there have been instances in which these potential causes of effusion were not present. Patients should be observed closely for any suggestion of a pericardial disorder, and echocardiographic studies should be carried out if suspicion arises. More vigorous diuretic therapy, dialysis, pericardiocentesis, or surgery may be required. If the effusion persists, withdrawal of minoxidil should be considered in light of other means of controlling the hypertension and the patient's clinical status.
Interaction with Guanethidine
- Although minoxidil does not itself cause orthostatic hypotension, its administration to patients already receiving guanethidine can result in profound orthostatic effects. If at all possible, guanethidine should be discontinued well before minoxidil is begun. Where this is not possible, minoxidil therapy should be started in the hospital and the patient should remain institutionalized until severe orthostatic effects are no longer present or the patient has learned to avoid activities that provoke them.
Hazard of Rapid Control of Blood Pressure
- In patients with very severe blood pressure elevation, too rapid control of blood pressure, especially with intravenous agents, can precipitate syncope, cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial infarction and ischemia of special sense organs with resulting decrease or loss of vision or hearing. Patients with compromised circulation or cryoglobulinemia may also suffer ischemic episodes of the affected organs. Although such events have not been unequivocally associated with minoxidil use, total experience is limited at present.
- Any patient with malignant hypertension should have initial treatment with minoxidil carried out in a hospital setting, both to assure that blood pressure is falling and to assure that it is not falling more rapidly than intended.
Precautions
General Precautions
- Monitor fluid and electrolyte balance and body weight.
- Observe patients for signs and symptoms of pericardial effusion.
- Use after myocardial infarction
- Minoxidil tablets have not been used in patients who have had a myocardial infarction within the preceding month.
- It is possible that a reduction of arterial pressure with minoxidil might further limit blood flow to the myocardium, although this might be compensated by decreased oxygen demand because of lower blood pressure.
- Possible hypersensitivity to minoxidil, manifested as a skin rash, has been seen in less than 1% of patients; whether the drug should be discontinued when this occurs depends on treatment alternatives.
- Renal failure or dialysis patients may require smaller doses of minoxidil and should have close medical supervision to prevent exacerbation of renal failure or precipitation of cardiac failure.
Laboratory Tests
- Those laboratory tests which are abnormal at the time of initiation of minoxidil therapy, such as urinalysis, renal function tests, EKG, chest x-ray, echocardiogram, etc., should be repeated at intervals to ascertain whether improvement or deterioration is occurring under minoxidil therapy. Initially, such tests should be performed frequently, e.g., 1 to 3 month intervals; later as stabilization occurs, at intervals of 6 to 12 months.
Unapproved Use
- Use of minoxidil tablets, in any formulation, to promote hair growth is not an approved indication.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Minoxidil (oral) in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
- Salt and Water Retention
- Temporary edema developed in 7% of patients who were not edematous at the start of therapy.
- Dermatologic
- Hypertrichosis (elongation, thickening, and enhanced pigmentation of fine body hair)) is seen in about 80% of patients taking minoxidil tablets. This develops within 3 to 6 weeks after starting therapy. It is usually first noticed on the temples, between the eyebrows, between the hairline and the eyebrows, or in the side-burn area of the upper lateral cheek, later extending to the back, arms, legs, and scalp. Upon discontinuation of minoxidil, new hair growth stops, but 1 to 6 months may be required for restoration to pretreatment appearance. No endocrine abnormalities have been found to explain the abnormal hair growth; thus, it is hypertrichosis without virilism. Hair growth is especially disturbing to children and women and such patients should be thoroughly informed about this effect before therapy with minoxidil is begun.
- Allergic
- Rashes have been reported, including rare reports of bullous eruptions, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- Hematologic
- Thrombocytopenia and leukopenia (WBC <3000/mm3) have rarely been reported.
- Gastrointestinal
- Miscellaneous
- Breast tenderness developed in less than 1% of patients.
- Altered Laboratory Findings
- ECG changes:
- Changes in direction and magnitude of the ECG T-waves occur in approximately 60% of patients treated with minoxidil. In rare instances a large negative amplitude of the T wave may encroach upon the S-T segment, but the S-T segment is not independently altered. These changes usually disappear with continuance of treatment and revert to the pretreatment state if minoxidil is discontinued. No symptoms have been associated with these changes, nor have there been alterations in blood cell counts or in plasma enzyme concentrations that would suggest myocardial damage. Long-term treatment of patients manifesting such changes has provided no evidence of deteriorating cardiac function. At present the changes appear to be nonspecific and without identifiable clinical significance.
- Effects of hemodilution
- Hematocrit, hemoglobin, and erythrocyte count usually fall about 7% initially and then recover to pretreatment levels.
- Other
- Alkaline phosphatase increased varyingly without other evidence of liver or bone abnormality.
- Serum creatinine increased an average of 6% and BUN slightly more, but later declined to pretreatment levels.
Drug Interactions
- Although minoxidil does not itself cause orthostatic hypotension, its administration to patients already receiving guanethidine can result in profound orthostatic effects. If at all possible, guanethidine should be discontinued well before minoxidil is begun. Where this is not possible, minoxidil therapy should be started in the hospital and the patient should remain institutionalized until severe orthostatic effects are no longer present or the patient has learned to avoid activities that provoke them.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Minoxidil (oral) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Minoxidil (oral) during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Minoxidil (oral) with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Minoxidil (oral) with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Minoxidil (oral) with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Minoxidil (oral) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Minoxidil (oral) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Minoxidil (oral) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Minoxidil (oral) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Minoxidil (oral) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Minoxidil (oral) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Oral
Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Minoxidil (oral) in the drug label.
Condition1
Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Minoxidil (oral) in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
Description
Management
Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Minoxidil (oral) in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Minoxidil (oral) Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Minoxidil (oral) Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
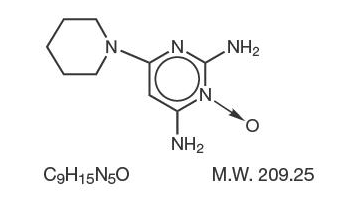
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Minoxidil (oral) in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Minoxidil (oral) in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Minoxidil (oral) in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Minoxidil (oral) in the drug label.
Condition1
Description
How Supplied
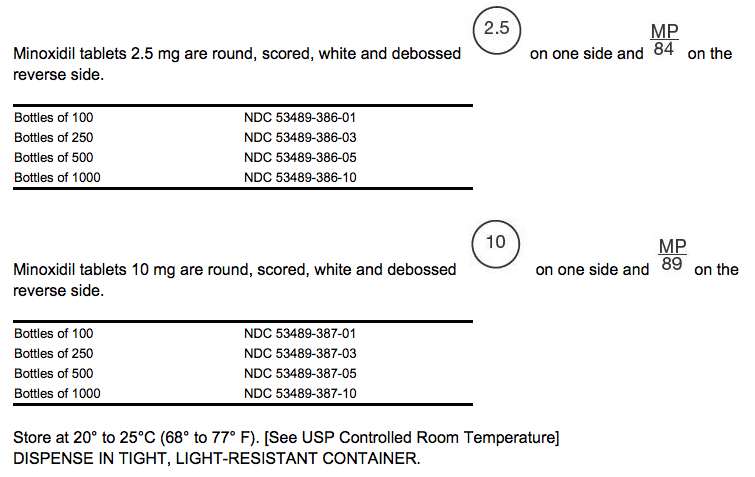
Storage
There is limited information regarding Minoxidil (oral) Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Minoxidil (oral) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Minoxidil (oral) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- The patient should be fully aware of the importance of continuing all of his antihypertensive medications and of the nature of symptoms that would suggest fluid overload. The patient brochure below has been prepared and is included with each minoxidil package.

Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Minoxidil (oral) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.[1]
Brand Names
- Loniten®
Look-Alike Drug Names
- Loniten® — Lipitor®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "MINOXIDIL tablet [American Health Packaging]". line feed character in
|title=at position 18 (help) - ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Minoxidil (oral) |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Minoxidil (oral) |Label Name=Minoxidil04.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Minoxidil (oral) |Label Name=Minoxidil05.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Minoxidil (oral) |Label Name=Minoxidil06.png
}}